
Is genetic disorder in globin chain production
Thalassemia Syndrome
Either
alpha thalas
. ,
B-thal
. ,
Sickle thalass
. .
B-thal.
Resulting from deletion or mutation , while
alpha thal
. Resulting mainly from deletion .
Homozygous B-thal ( B-thal major or cooleys anemia
)
:---
C\f :-----
1-
progressive anemia with profound weakness &
cardiac decompensation during the second 6- month of
life if not treat (
most infant & children have cardiac
decompensation of Hb of 4gm/dl or less ..
2-
hepato splenomegaly ( spleen may become so
enlarge causing discomfort & even hypersplenism
which defined by increased requirement of packed
R.B.C. of more than 240 cc/kg/ year .
3-
generally fatigue , poor appetite & lethargy are late
finding of sever anemia in an infant or child .
4-
late finding of disease developed:---
a-
bronze skin ( greenish brown complexion
as result
from combination of pallor , jaundice and hemosiderosis .
b-
repeated blood transfusion resulting iron
overload
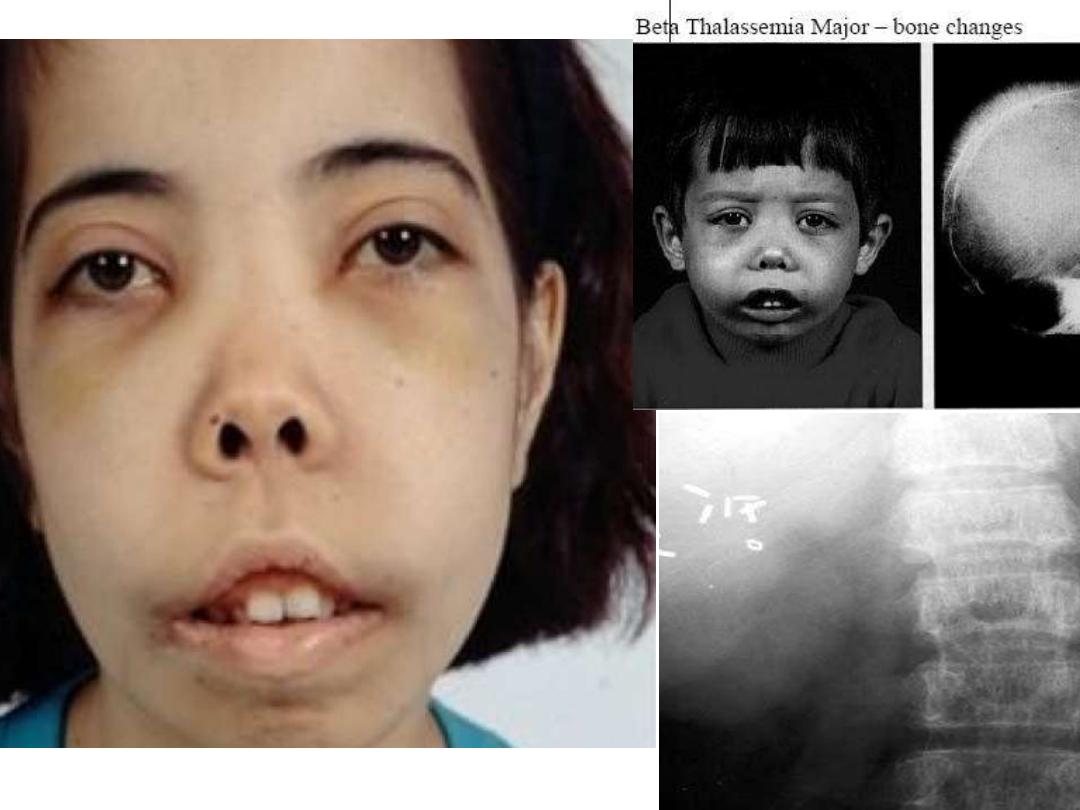
Thalassemic pictures
•
.

Effect of excess production of free globin chain ( B-thal. )
pathophysiology in
over head
•
Lab Finding :---
•
1
- anemia :- decrease Hb & elevation of retic count ( of less than
8%) with normal WBC, elevation of unconjugate bilirubin .
2-
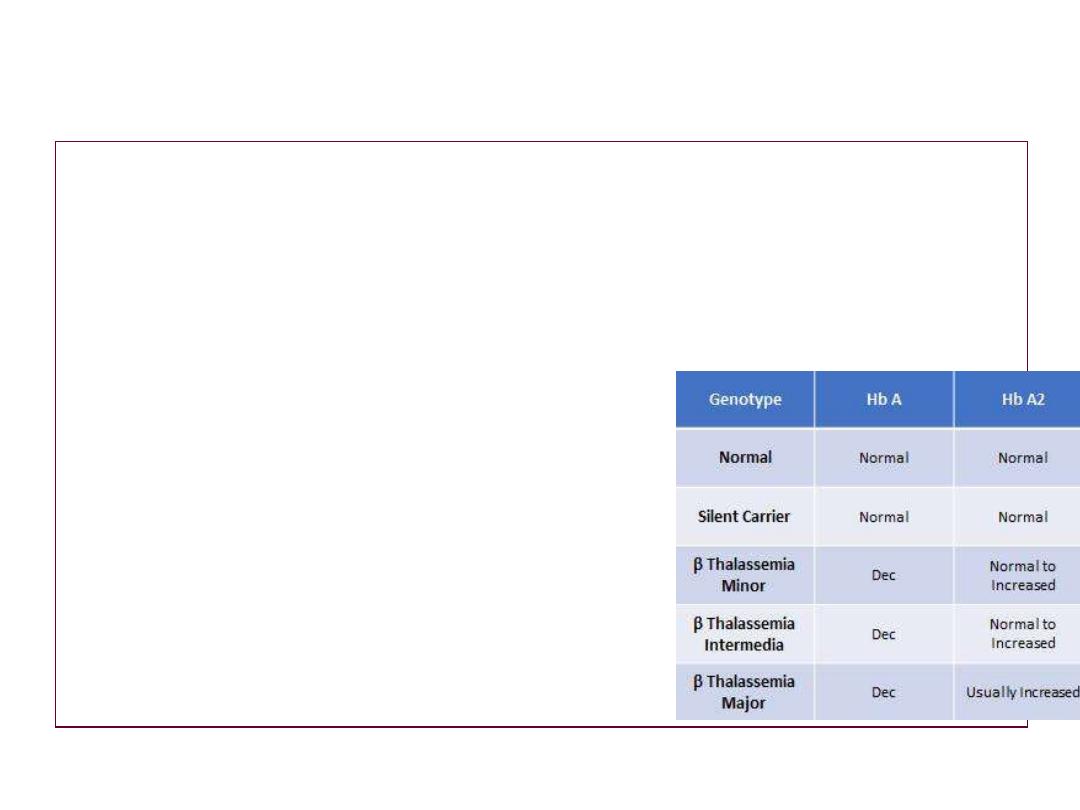
Hb-electropheresis is diagnostic
( Hb F may reached 98% & A2 2% .
•
3-
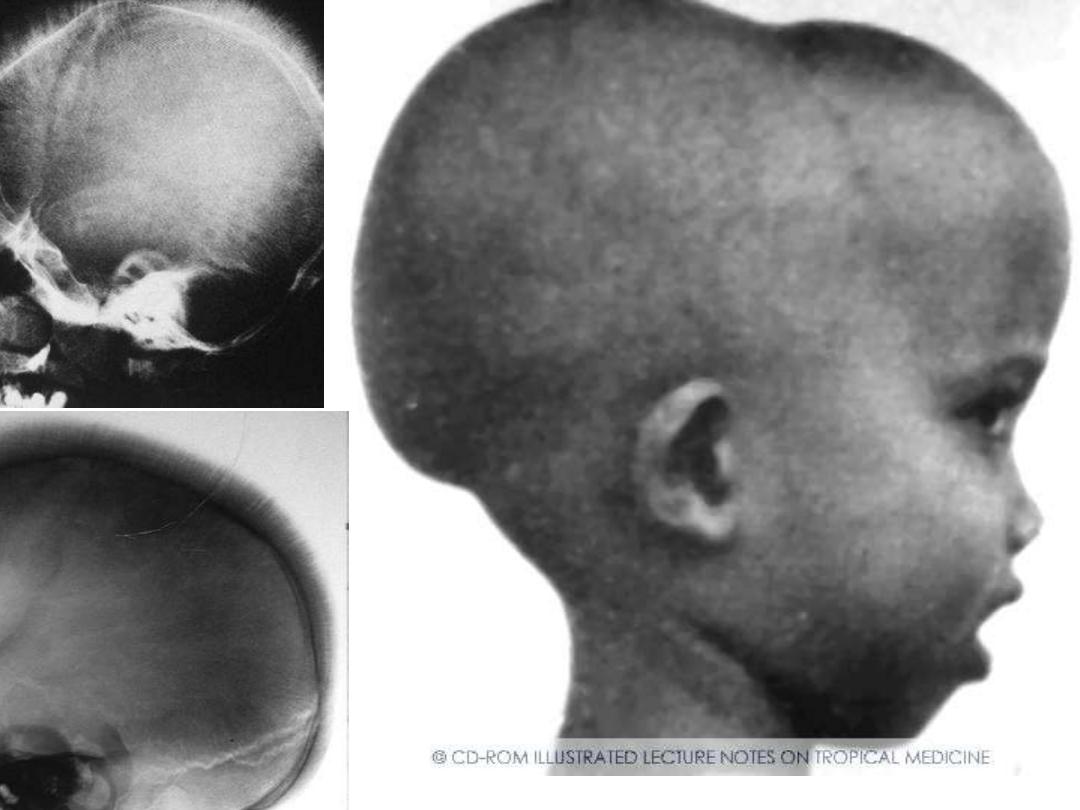
if no treatment well resulting B.M. expansion .
•
X-Ray finding as Hair on end appearance .
•
4-
with frequent blood transfusion lead to increase iron in body
which measure by S. ferritin .
•
DD :----
A-
other causes of hypochromic microcytic anemia ( IDA ,lead & copper
poisoning & pyredoxine deficiency.
B-
anemia with increase retic count
( thalass. Intermedia , SCA,HbC ,HbS ,
HbE & auto immune hemolytic anemia ).
C-
anemia with low retic count .( aplastic anemia
as black fan diamond
syndrome & fanconi anemia )
D-
cong. Spherocytosis .
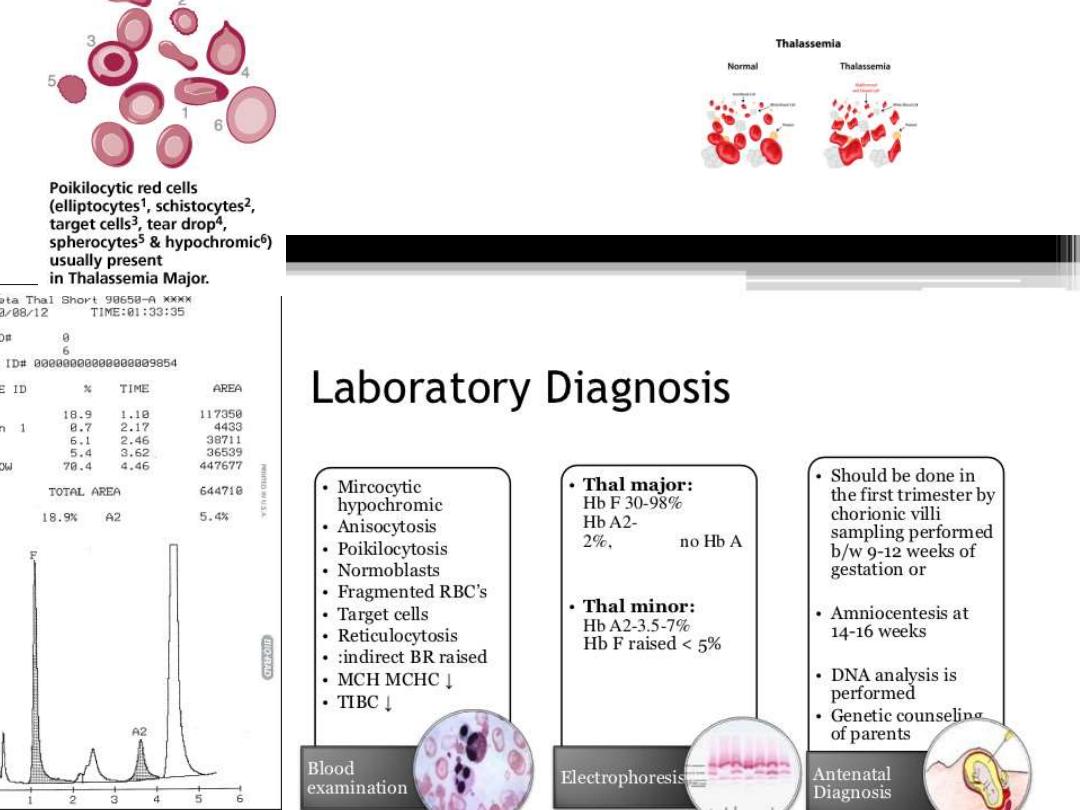
Lab finding in thalassemia
.
•
.

Treatment of thalassemia
•
1- blood transfusion
:--
•
aim of blood transfusion is to promote general health & well being
& avoid the consequences of ineffective erythropoiesis
•
Blood transfusion in a dose of 20cc/kg given within 4-6 hr to
maintain Hb level in normal range that not result in B.M. expansion
i.e pre transfusion is more than 9.5gm/dl
–10.5 gm/ dl is good
.
•
2- treatment of iron overload :---
•
iron overload is measured by 1- s- ferritin
•
2- liver biopsy supplemented by
ferritometry.
•
3- T2 weighted MRI imaging .
•
Hemosiderosis is prevented by using chalating tharapy (
desferioxamine to form desferal
–iron complex which excreted by
urine & stool & inhance its excretion by vit C

Indication of desferal therapy :-
1-
if s. ferritin of more than 1000 nano gram/ dl
2-
if s. ferritin is not available , we depend on no. of blood transf. 10
—20 time or
3
—5 year from onset of blood transfusion .
Desferal givenby special pump ( S.C.) IN a dose 20-50 mg |kg \day
•
And S .T.
increase dose to 100 mg \ kg if
:---
•
1
-cardiomyopathy .
2-
if s. ferritin of more than 2500 nanogram\dl .
•
S .E
.:-- ototoxicity , retinal change , bone dysplasia with truncal shortening .
•
Oral iron chelator ( defriprone
) :-- is not effective as desferal but more effective in
removing cardiac iron .
S .E
MAY associated with neutropenia , arthritis , hepatic fibrosis .
---
-
also now :
used oral desferasirox (
Exjade
) which better for compliance , optimum dose is well
defined as maintanance dose between 30--< 40 mg/kg/day ( starting dose at
20mg/kg/day and increased dose 5
—10 mg/kg every 3-6 month depend on S.ferritin
and safety of drug .
•
3-splenectomy :- indicated in following
:--
•
1- hypersplenism 2- thal. Intermedia with falling steady state of height .
•
Before splenectomy ;-- pts should receive pneumo coccal & meningococcal vaccine
.& then kept on prophylaxis pencilin therapy .
•
4-
B. M transplantation to cure pts
.( hemapoitic stem cell transplant which most
success if pt of less than 15year of age , not excess of iron store or hepatomegally .
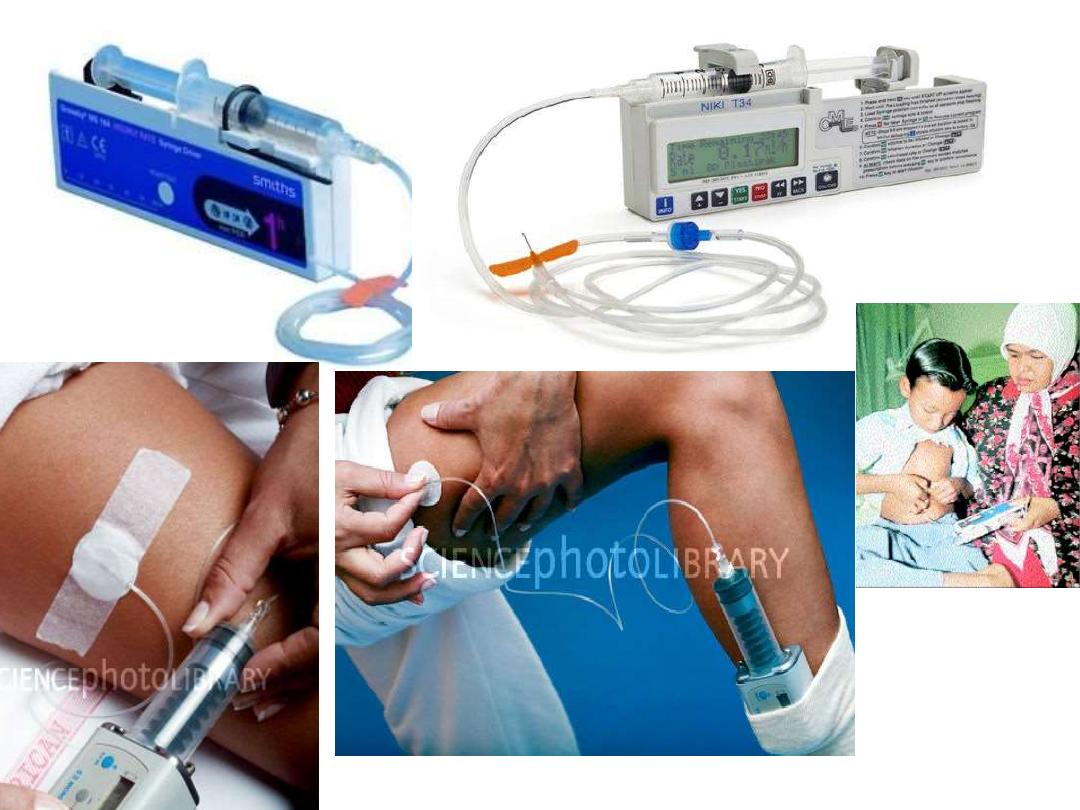
•
major
intermedia
•
A- Clinical presentation :--
•
Age
•
less than 2year
more than 2 year
•
Hb level
less than 7 gm
8-10gm
•
HSM
sever
moderate to sever
•
iron overload
after 10 -20 units of blood
may presented at time of
•
transfusion
diagnosis
•
B-hematologica
l ;--
•
HbF
More than 50%
less than 50%
•
HbA2
less than 4
more than 4
•
C- genetic parents
•
both carrier with high HbA2
one or both atypical
•
carrier of high Hbf
•
B-thal. & borderline A2
•
--5-
Thalass. Intermedia
c
riteria to differentiated between major & intermedia

Alpha thalassemia
•
Depend on gene geletion :---
•
A
-
deletion of one gene called silent trait ( carrier ) :- has no symptoms .
•
B-
deletion of 2 gene called thalass. Trait :--has mild anemia ( Barts Hb is 5-
10
% ) .
•
C-
deletion of 3 gene called Hb-H Dis. :--has marked anemia .
•
is generally asymptomatic with moderate anemia , mild splenomegally ,
occasionally jaundice or gall stone .
•
transfusion is not usually reguired for treatment of anemia .
•
brilliant cresyl blue can stain Hb-H .
•
D
-
deletion of 4 gene ( Hydrops fetalis ) .
•
has 80-90% of Barts Hb with Gower 1 , 2 & portland Hb
•
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
.
•
-6-

Transfusion Reaction
adverse events associated with transfusion include :---
•
1
– non hemolytic febrile reaction .
•
2
– allergic reaction .
•
3
– anaphylactic reaction .
•
4
– auto immune hemolytic anemia .
•
5
– delayed transfusion reaction .
•
Major complication of thalassemia :---
•
A-
excess erythropoisis :---1- bone changes to face .
•
2-bone :- cortical thining & risk of
fracture .
•
3- spinal cord compression .
•
4- LAP especially mediastinum & HSM
•
B-
iron over-load .
•
C-
endocrine failure like short stature , delayed puberty, D.M, hypothyriodism & hypo-
parathyridism ,
•
d-
cardiac complication .
•
e-
hepatic involvoments .
•
f-
chronic hemolysis .
– gall stone .
•
g-
infection
•
•
thank you
•
---7---
