
NEOATAL JAUNDICE (NNJ):
NNJ is the most common clinical condition in the
neonatal period, it affects 60% of term and 80% of
premature neonates.
It is clinically visible when total serum bilirubin
(TSB) exceeds 5mg/dl. The yellow color results from
accumulation of unconjugated (with indirect Van
Den Bergh reaction) lipid-soluble bilirubin pigment
in the skin. If presents in abnormally high level; this
fraction can cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) and
becomes neurotoxic.
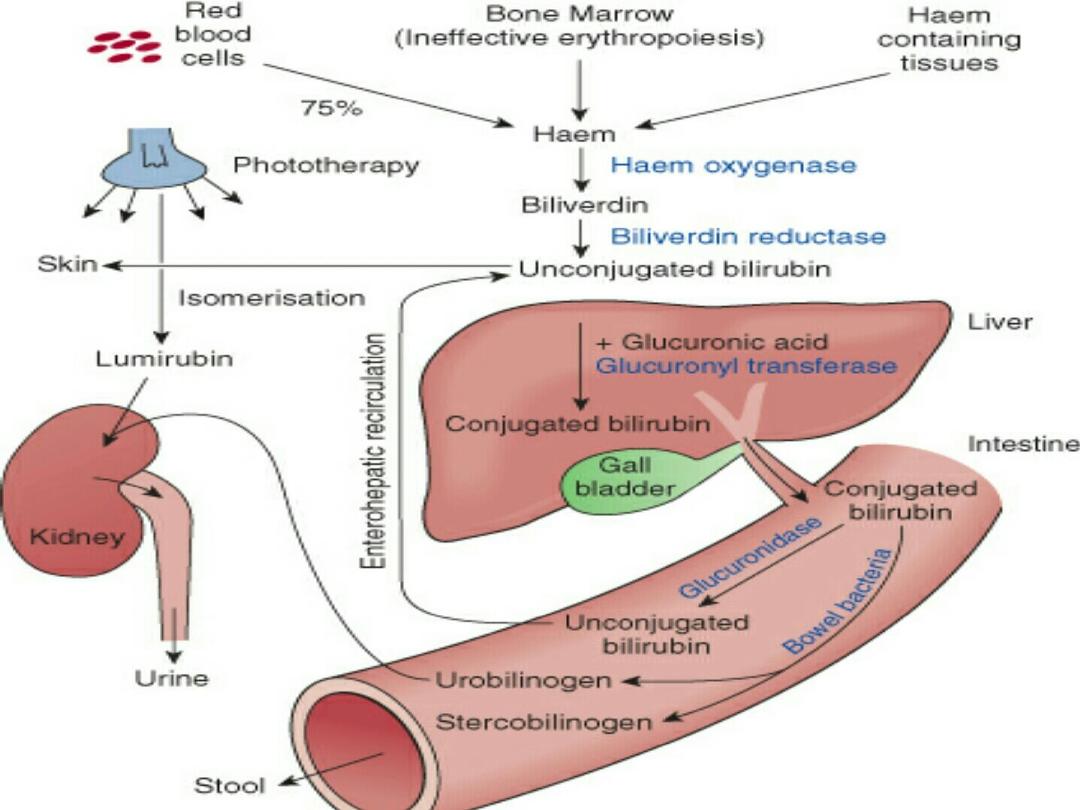

BILIRUBIN METABOLISM:
• It is derived from breakdown of heme-containing
proteins in the R.E.S. (75% comes from
hemoglobin and 25% comes from heme-
containing substances (e.g. myoglobin,
cytochrome). Bilirubin exists in circulation in two
forms: albumin-bound(which is carried to the
liver & enter the liver via specific receptors),and
free bilirubin.

In the liver; the enzyme glucuronyl transferase
conjugate bilirubin to glucuronic acid, so it becomes
water-soluble(with direct Van Den Bergh reaction),
& it can be excreted through the gut, but in the
intestine it may be deconjugated by beta-
glucoronidase and reabsorbed in the liver
(Enterohepatic circulation). This fraction of
bilirubin(direct or conjugated) is not neurotoxic
(because it does not cross the B.B.B.) but abnormal
levels indicate serious underlying liver or systemic
illnesses.

ETIOLOGY
OF NNJ:
1. Increased load e.g. by hemolysis, polycythemia.
2. Hypoproteinemia: which reduces bilirubin
binding.
3. Displacement of bilirubin from combination sites
by drugs, acidosis.
4. Damaged or reduced activity of transferase enz.
(e.g.prematurity,hypoxia,hypothyroidism,infection)
5. Exaggerated enterohepatic circulation
e.g. ileus, constipation, hypothyroidism.

RISK FACTORS FOR NNJ :
1. L.B.W. and prematurity.
2. Male sex.
3. Polycythemia or extravasated blood
e.g. cephalhematoma (which
provides more Hb for breakdown).
4. Hemolytic disorders.
5. Sepsis.

CLINICAL FEATURES OF NNJ :
• NNJ usually starts on the face and proceeds
caudally. Division of the body into zones can
be used for rough estimation of TSB level :
Face: 5mg/dl, Chest: 10, Abdomen: 15, Soles:
20mg/dl., but this estimation will change few
hours after putting the baby under
phototherapy.

INDICATIONS OF INVESTIGATIONS:
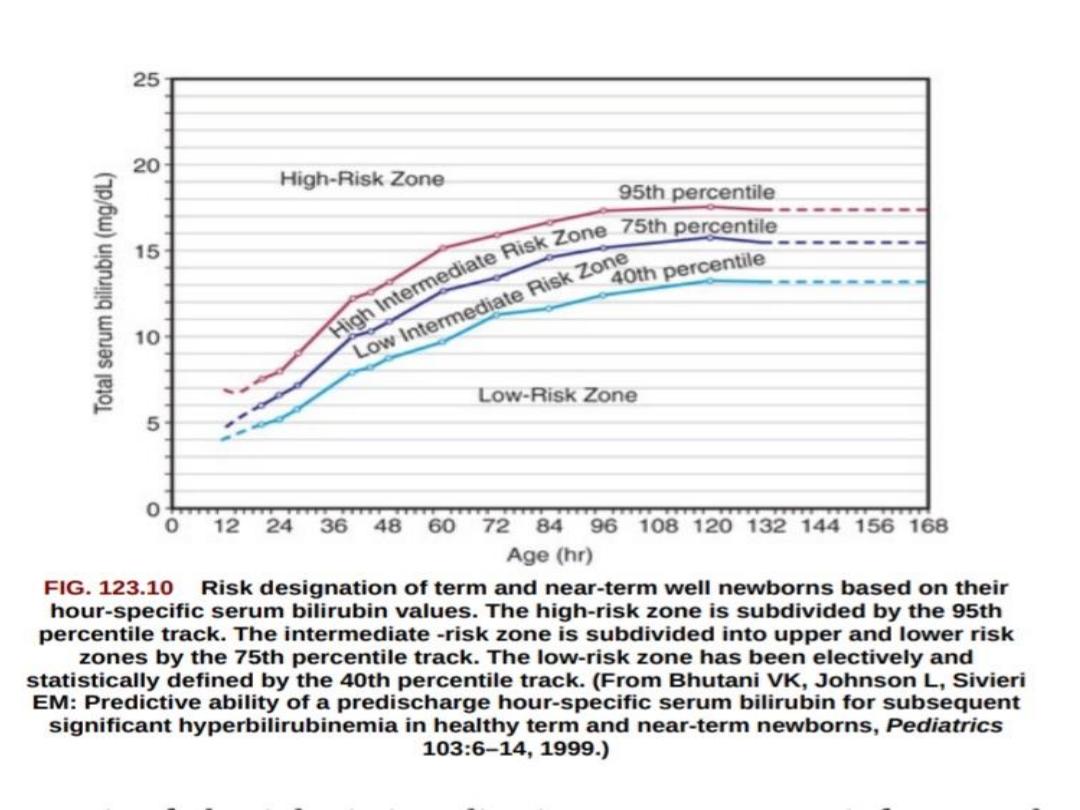
1. If N.N.J. appears on the first 24-36 hours.
2. Rise of TSB > 5mg/dl/24 hours.
3. TSB > 12mg/dl in term infants and > 10mg/dl in
preterm infants.
4. Jaundice persisting more than 10-14 days.
5. Direct hyperbilirubinemia (defined as direct bilirubin
level more than 1.5mg/dl or more than 10% from total
bilirubin level)
which is always abnormal
.

PHYSIOLOGIC JAUNDICE:
It is due to:
1. Increased destruction of RBCs (short life span).
2. Decreased uptake of bilirubin by the liver.
3. Decreased ability of the liver to conjugate
bilirubin.
4. Increased enterohepatic circulation.

CHARACTERISTICS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL
JAUNDICE:
1. It does not rise more than 12.9 ,very rarely 15mg/dl.
2. It appears on the 3
rd
- 4
th
day of life.
3. It rarely increases by more than 5mg/dl/day.
4. It disappears by one week in full term infants and by
two weeks in preterm infants.
5. Healthy
baby
.

PATHOLOGIC JAUNDICE:
1. If it occurs in the first 24 hours of life.
2. If T.S.B. level rises 0.5mg /dl/hour or 5mg /dl/day.
3. If T.S.B. level exceeds 15mg/dl in term infants or
10mg/dl in preterm infants.
4. If there is evidence of acute hemolysis or
an underlying illness.
5. If it is direct hyperbilirubinemia.

CLINICAL
TYPES
OF
NNJ:
a. EARLY JAUNDICE:
which lasts<10 days.
b. PROLONGED JAUNDICE:
>10 days in term and >14 days in preterm
babies.

COMMON CAUSES OF EARLY NNJ:
• 1.Hemolytic disease of the newborn (mostly due
to feto-maternal blood group incompatibilities,
other causes include intrauterine infection, RBC
membrane defect e.g.spherocytosis, RBC enzyme
defect e.g.G6PD deficiency).
2.Crigler-Najjar syndrome (due to A.R. deficiency
of glucuronyl transferase).
3.Breast feeding jaundice (due to decreased milk
intake and dehydration. Rx: encourage breast
feeding, especially at night).

BLOOD
GROUP
INCOMPATIBILITY:
a.Rh incompatibility:
It occurs when RBCs of Rh+ve fetus pass through the
placenta of Rh-ve mother, so antibodies are formed in
the mother & pass through the placenta to the fetus &
cause hemolysis (pallor, H.S.M.).
The 1
st
. baby is not affected unless preceded by
sensitization due to previous abortion or
amniocentesis.
TSB can rise to dangerous levels with high retic count &
strong +ve Coombs test.

Not all Rh-ve mothers produce hemolysis
in their babies because:
1. The baby may be Rh-ve.
2. Not all mothers produce enough antibodies.
3. The mother might have been immunized by anti- D
immunoglobulin.
4. Feto-maternal transfusion occurs only in 50% of
pregnancies.
5. Small family.
6. When the mother and baby are also ABO incompatible.

-Hemolysis in utero causes severe anemia & edema
( HYDROPS FETALIS )
which is treated by
intrauterine blood transfusion.
-The aim of treatment is to correct anemia and to
prevent neurotoxicity.
-After birth; if cord blood sample shows:
TSB of >5mg/dl, Hb of <10g/dl, retic count of >15%,
or +ve Coombs test: early blood exchange
transfusion is indicated.

b. ABO INCOMPATIBILITY:
• - The mother is O and the baby is A or B.
• - IgG antibodies are responsible.
• - Coombs test is –ve.
• - blood film shows microspherocytes.
c.MINOR (SUBGROUP) INCOMPATIBILITIES:
C,E,Kell,Duffy.

PROLONGED
JAUNDICE
:
-Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
-Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.

UNCONJUGATED HYPERBILIRUBINEMIA:
1. Breast milk jaundice:
Betaglucuronidase in breast milk causes
deconjugation of bilirubin diglucoronide in the
intestine. TSB
is 10-30mg/dl, healthy baby, kernicterus is
rare, Rx: stop breast feeding for 48 hr. only.
2. Congenital hypothyroidism.
3. Intestinal stasis or ileus.
4. Sepsis.
5. Galactossemia, Cystic fibrosis.

CONJUGATED HYPERBILIRUBINEMIA:
1. Infections (intrauterine inf. or neonatal sepsis).
2. Metabolic e.g. galactosemia.
3. Cystic fibrosis.
4. Biliary atresia.
5. Choledochal cyst.
6. Hypothyroidism.
7. Idiopathic neonatal hepatitis.
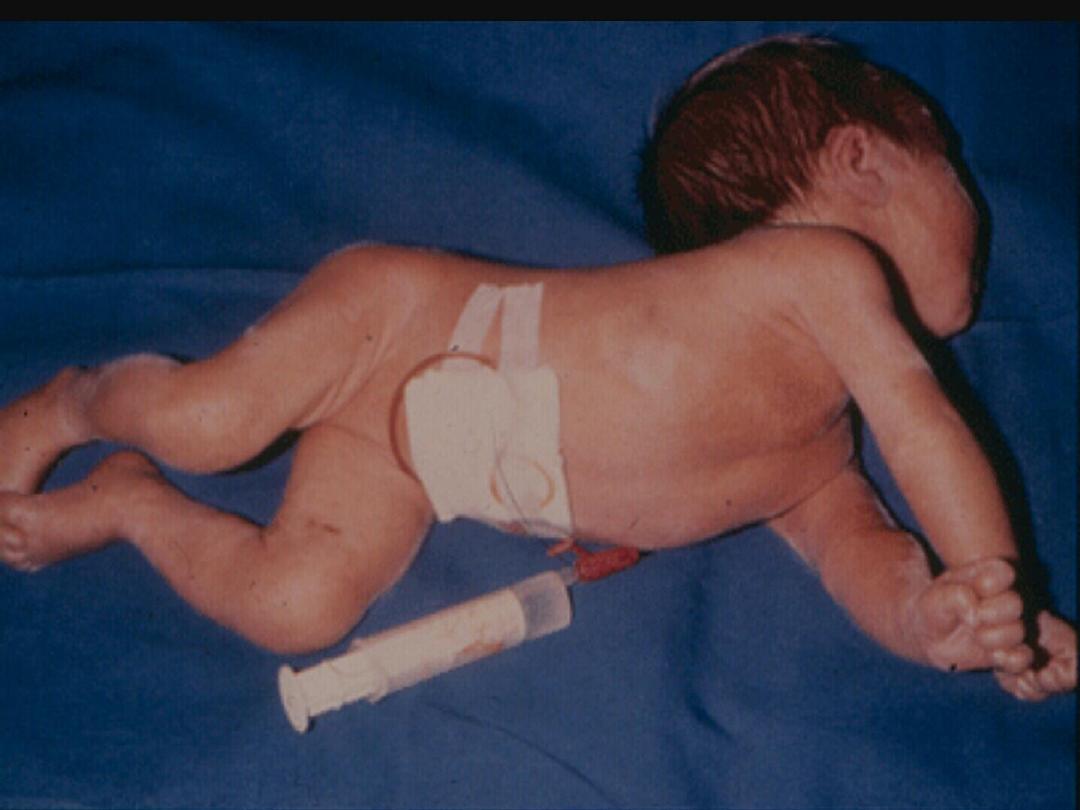
BILIRUBIN
ENCEPHALOPATHY
:
-Acute:
seen in the first weeks after birth , as poor
feeding, hypotonia, high pitched cry & opisthotonus.
-Chronic:
seen after first year of life, as athetosis,
deafness, mental handicap, and dental dysplasia.

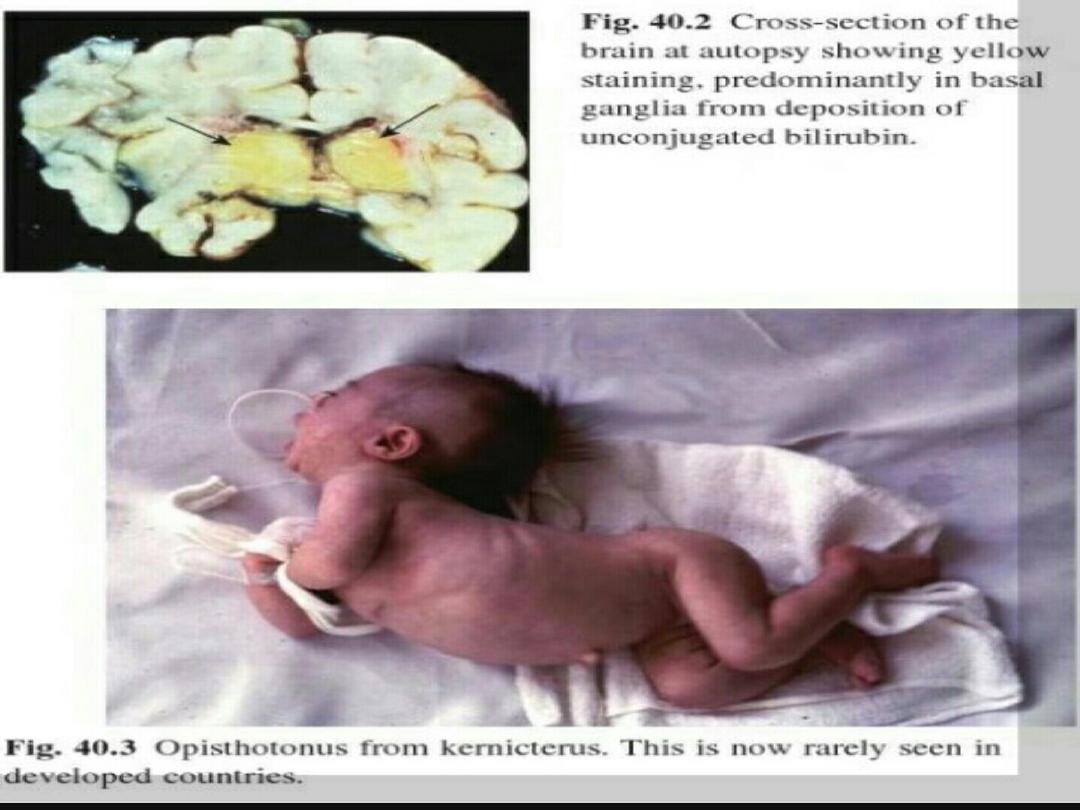
KERNICTERUS :
• Is a pathological term which means yellowish
staining of brain (especially basal ganglia,
brain stem, hippocampus, & cerebellum) and
spinal cord, due to
deposition of indirect
(unconjugated) bilirubin
, resulting in
neuronal injury, necrosis, & neuronal loss.

Risk factors for bilirubin encephalopathy:
1. Severe hyperbilirubinemia.
2. Prematurity.
3.Sepsis.
4. Asphyxia.
5. Acidosis
.
6. Hypoglycemia.
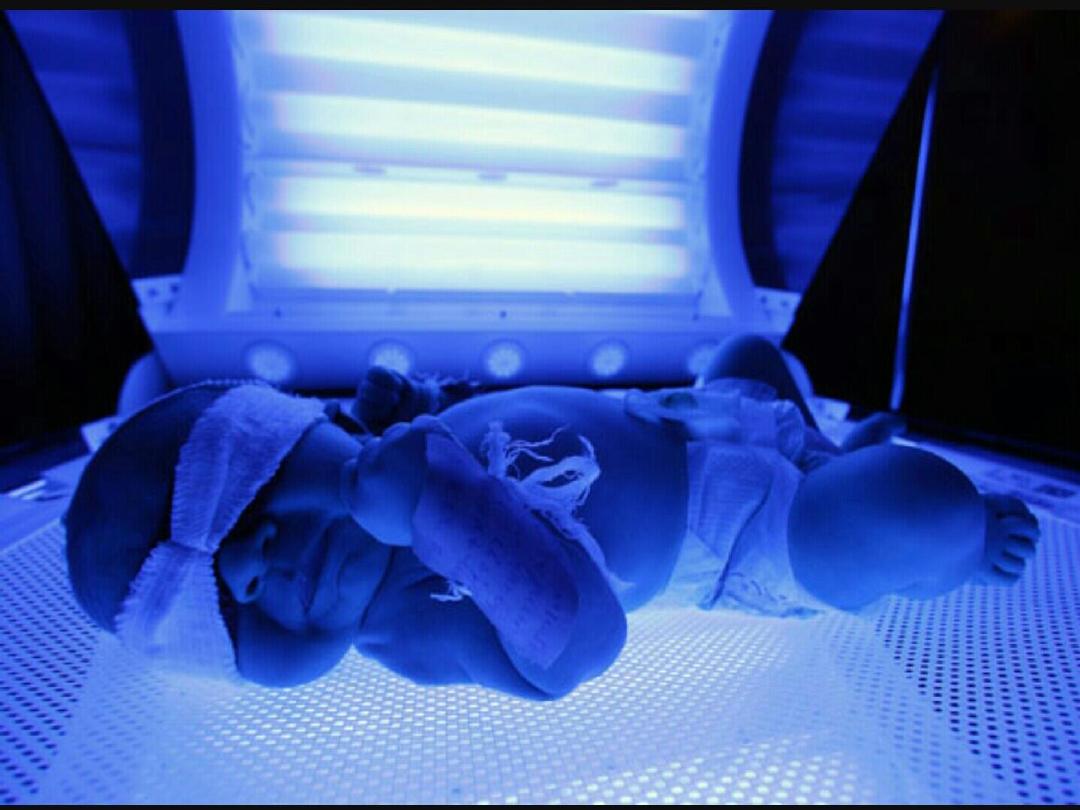
TREATMENT OF NNJ:
The aim of Rx is to prevent neuronal damage by
unconjugated bilirubin, either by phototherapy or by
doing blood exchange transfusion (B.E.T.) .
Also treat underlying causes e.g. sepsis, acidosis,…
PHOTOTHERAPY:
Bilirubin absorbs light in the blue range(wave length
420-470nm) which converts unconjugated bilirubin
into non-toxic conjugated bilirubin (by photo-
isomerization).
Phtotherapy decreases bilirubin level by
2.5-3 mg/dl/day.
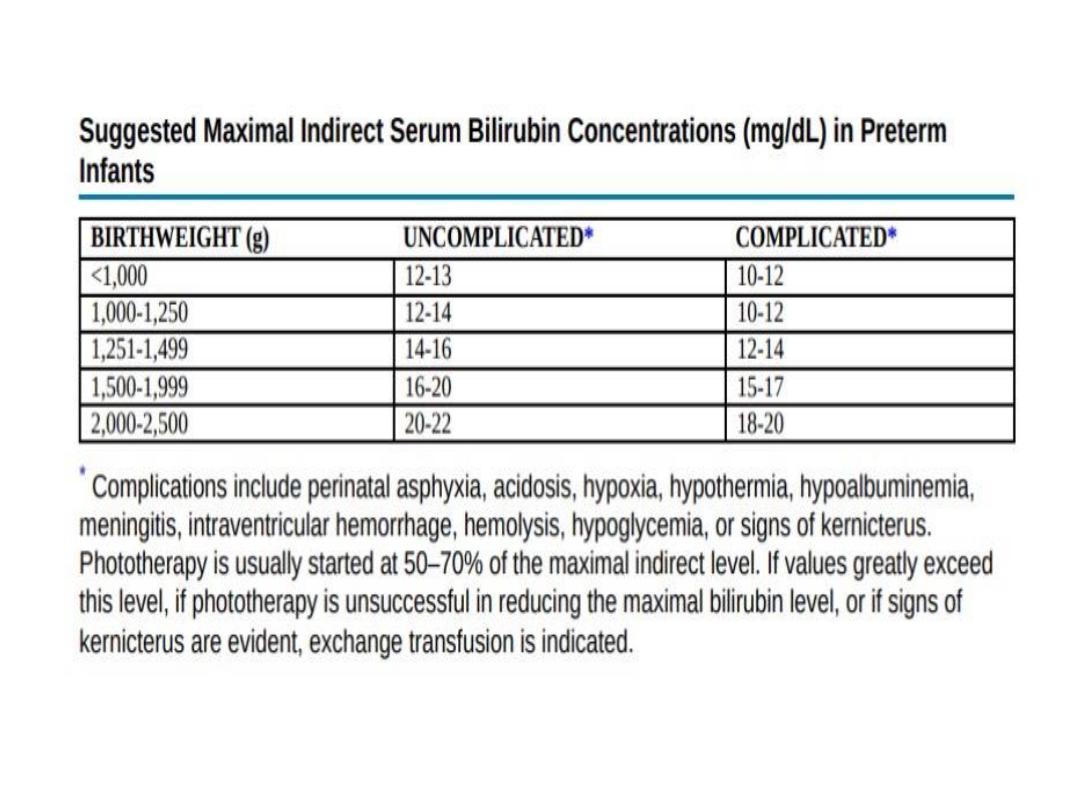

EFFICACY
OF
PHOTOTHERAPY DEPENDS ON:
1. The light energy emitted.
2. The distance between the light & the baby
(average 60 cm.).
3. Amount of skin exposed, so turn the baby
frequently.
4. Rate of hemolysis.
5. Hydration.

COMPLICATIONS OF PHOTOTHERAPY:
1. Equipment failure.
2. Dehydration.
3. Loose stool.
4. Skin rash.
5. Bronze baby syndrome.
6. Eye damage.
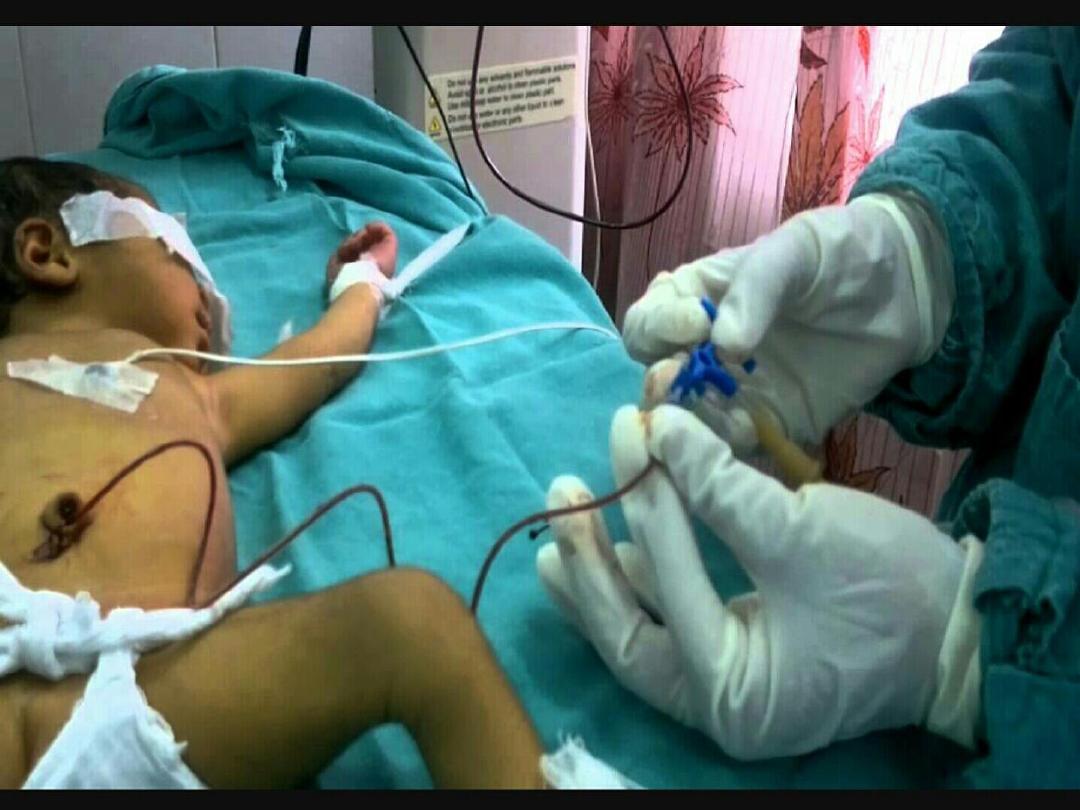
BLOOD EXCHANGE TRANSFUSION:
-
B.E.T. is done when kernicterus is present or imminent
.
-A double volume exchange replaces 85% of the infant
RBCs and reduces pre-exchange bilirubin level to 50%.
-Volume of blood needed/ml= 85x2xbody weight.
-The time needed is about 1.5 - 2 hours.
-There is no strict rule for indications of B.E.T.
;
a healthy term infant may need BET if TSB exceeds
25mg/dl, whereas kernicterus may occur in a sick
premature at a significantly lower TSB level.

COMPLICATIONS
OF B.E.T. :
1. EARLY COMPLICATIONS:
Acidosis, Hypoglycemia, Bradycardia,
Hypocalcemia, Apnea, Infection, Hypothermia.
2. LATE COMPLICATIONS:
-Portal vein thrombosis and portal hypertension.
-Late onset anemia.
-Graft versus host disease.
-Inspissated bile syndrome.
