22 October 2012
1بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَنِ الرَّحِيمِ
EmberyologyLec.1
الدكتورة
منى زهير عبد الكريم
MB.ChB.MSc
The development of a new individual begins by the union of 2 cells :
One from the male known as sperm.One from the female known as ovum.
About 280 days after fertilization a new individual is born divided into 3 stages:
Zygot : 2 week (all cells look like each other).
Emberyonic stages : 3-8 week (tissues & organs are formed).
Fetal stage : 9- 40 week (body grows in weight & length).
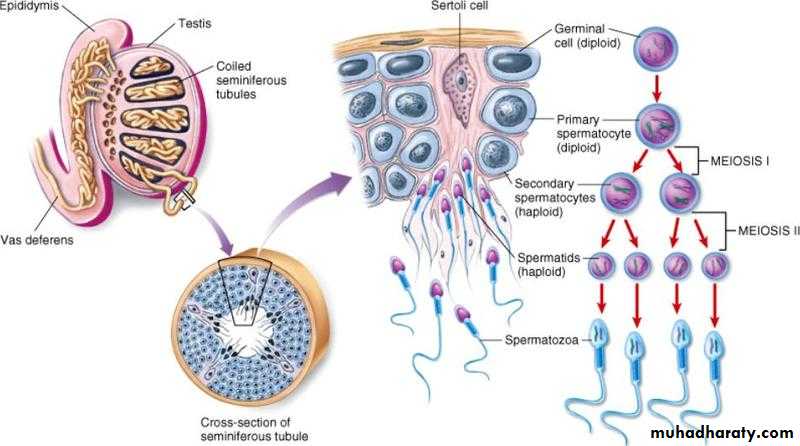
Gametogenesis
Formation of sperm & mature ovum both contain haploid number of chromosome include:Spermatogenesis
Oogenesis
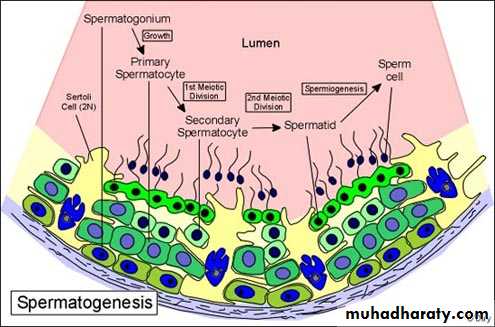
Spermatogenesis: 2 steps
1.Spermatocytogenesis to get spermatids.2.Spermiogenesis: modification of spermatids to get sperms.
SpermatogenesisSpermatogonia Type A & B spermatogonia
Type A - stem cell
Type B – proginator cells primary spermatocyte 2 secondary spermatocyte
4 sprematids each with haploid number of chromosomes (23 chromosomes)
Seminal fluid:
Volume - 3-5 ccContent - 100 million sperms genetically of 2 types one carries X- chromosomes & other carries Y- chromosomes.
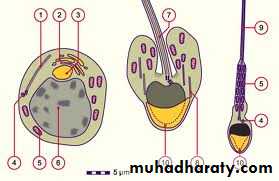
Spermiogenesis
nucleus - head of the spermGolgi - head cap of acrosome
Mitochondria - sheath around the middle piece to supply energy for the sperm
Centrioles:
Proximal – axial filament
distal - terminal ring
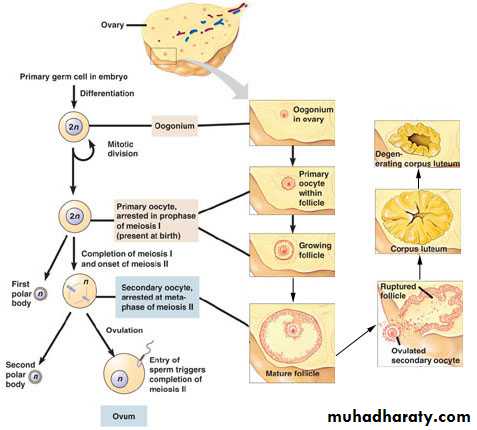
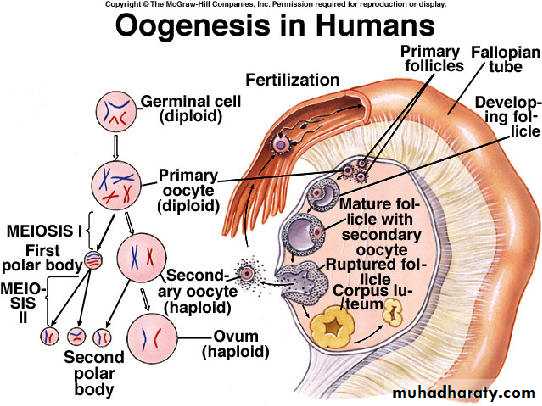
Oogenesis
cyclic changes take place every lunar ( 28 days) under influence of FSH & LH hormones from anterior pitutary gland include 3 steps:Formation of graffian follicle
Ovulation
Formation of Corpus luteum
Formation of graffian follicle (follicular stage):
Primary oocyte secondary oocyte + first polar body mature ovum tow polar bodies.primordial follicle primary follicle secondary follicle tertiary follicle mature graffian follicle
Ovulation
Rupture of mature graffian follicle + discharge of the mature ovum.
Factors:
Hormons – LH from anterior pituitary gland.
Increase intrafollicular fluid pressure.
Weakness of the wall due to ischaemia.
Contraction of smooth muscle fibers.
Once the ovum is sheded the 1st meiotic division is compeleted and immediately the seconary oocyte enter the 2nd meiotic division which is not compeleted until fertilization take place to get a single mature ovum + 3polar bodies.
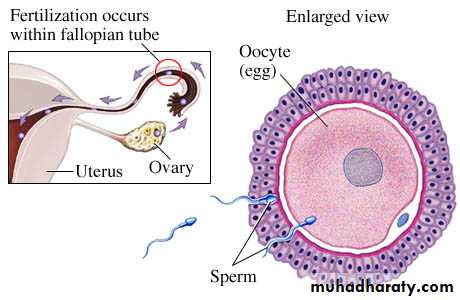
Fertilization
Fusion of sperm with ovum.Site : ampulla of uterine tube.
Events:
head of one sperm pass through corona radiata and zona pellucida with the aid of proteolytic enzymes secreted from the acrosomal cap.
The head (male pronucleus) fuses with nucleus of ovum (female pronucleus) to form zygot with diploid number of chromosomes
M,b
Results of fertilizationRestoration complet “diploid”number of chromosomes.
Determination of sex of the new organism.
Initiation of cleavage.
Formation of zygot.
Luteal phase (formation of corpus luteum)
The wall of ruptured graffian follicle collapses and become folded.Granulosa cells granulosa lutein cells (large, polygonal, pale, 80% of parenchyma)
Theca interna theca lutein cells
(small, peripheral , dark, 20% of parenchyma).
Vascular connective tissue core.
Function: secrete progesterone which responsible for the secretory (post- ovulatory) phase in the endometrium of the uterus to prepare it for implantation.
Fate :
If ovum is not fertilized degeneration
Corpus albicans after 14 days from the date of ovulation
Fate :
If ovum is fertilized corpus luteum persist and increase in size + increase production of progesterone which:
Essential for maintainance of pregnancy.
Increase growth and secretion of endometrial glands which provide nutrition for emberyo until placenta is functioning.
This is called corpus luteum of pregnancy persist till 4th month and then regress and secretion of progesterone become the function of placenta.
c
Cleavage:
Repeated mitotic division of the zygot, rapid, occurs in succession & starts immediately after fertilization.
The human zygot:
24-30 hours – 2 cell stage
40-48 hours – 4 cell stage
16 cell – early morula (look like mulberry) a solid ball still surrounded by zona pellucida
Late morula:
4 days after fertilization32 cell stage
Still solid
Reach uterine cavity and obtain nutrition from endometrial secretion called uterine milk
Start to arrange into inner and outer cell mass but not very clear.
At end of 4th day
Morula allows some fluid to pass through it
single cavity called blastocele
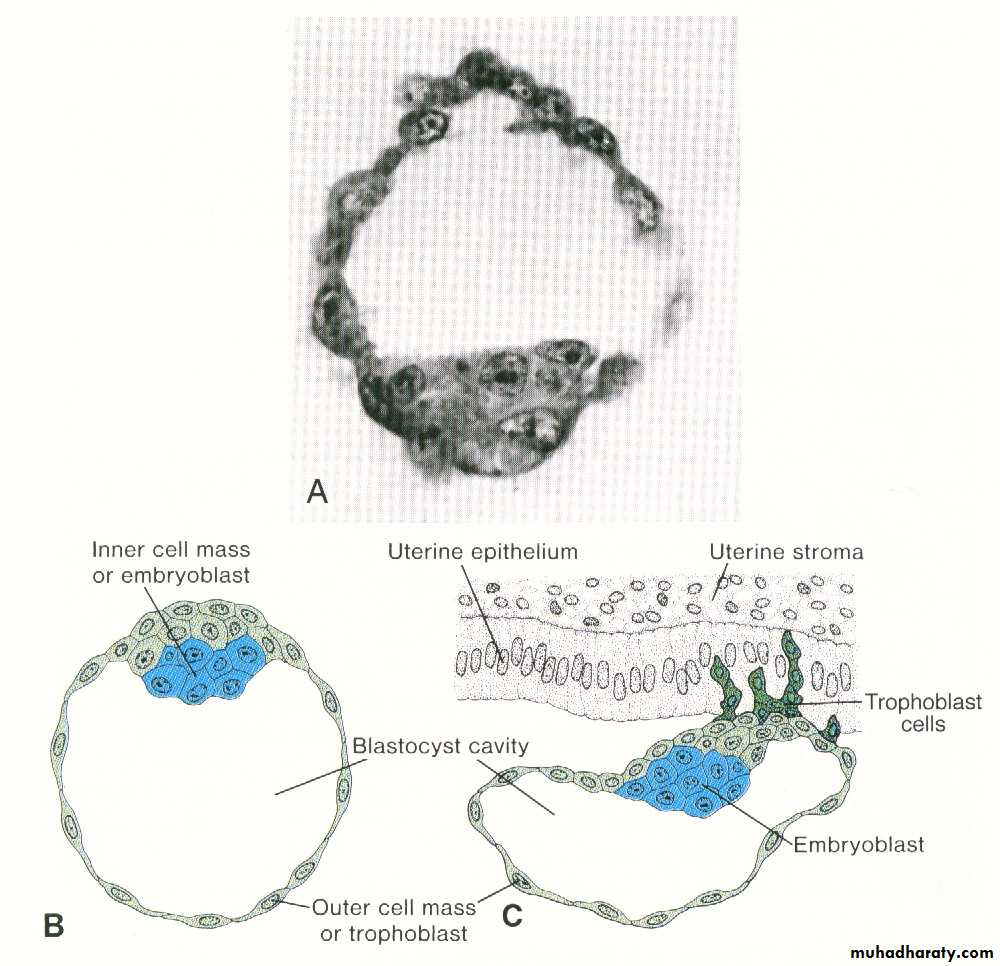
Blastocyst :
Early:64 cell stage
Well diffrentiated inner and outer cell mass
Begin to lose zona pellucida & stick to endometrium on posterior wall of fundus.
Late blastocyst:
6 day after fertilizationNo zona pellucida
Bigger
107 cells :
Inner 8 – emberyonic disc at emberyonic pole
Outer 99 – trophoblast at abemberyonic pole
Implantation
Embedding of blastocyst in the endometrial mucosa usually in the upper posterior wall of fundus start at 6 day and completed at 12 day post fertilizationsteps:
• Late blastocyst lose zona• Stick to endometrium
• Creats tiny opening with the aid of proteolytic enzymes secreted by trophoblast
• Invades the mucosa & burrow itself into the endometrium
• This process take 1 week (6-12) day after fertilization when completed 0pening closed by fibrin coagulum and finally replaced by endothelium similar to endometrial mucosa.
Abnormal implantation sites:
• Intrauterine- placenta praevia implants near the cervix 3 types:• Placenta praevia lateralis: implants just above the internal os of cervix
• centralis: around the internal os &close it
• marginalis: margin of the placenta reaches above the internal os
Abnormal implantation sites:
2. extrauterine (ectopic pregnancy):Tubal pregnancy- ampulla of uterine tube end with abortion
Interstitial pregnancy
Ovarian pregnancy
Intraabdominal – in the peritoneum of abdomen
Pelvic implantation: in rectouterine pouch of Douglas.
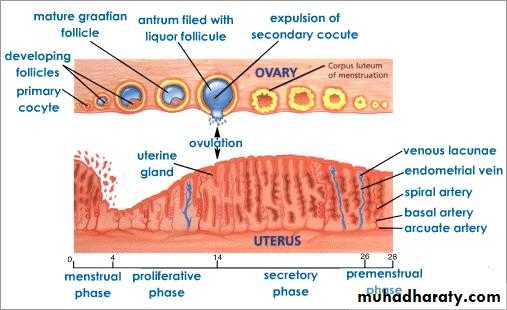
Menstrual cycle
Cyclic changes in the endometrium of the uterus
Occurs every lunar month(28 days) starts from menarche till menopause
Stages:
Menstrual-
30-60 cc of blood is lost due to degeneration of corpus luteum and subsequent lowering of progesterone
Proliferative-
7-10 days after bleeding is stoppedCoincides with the follicular stage of the ovarian cycle due estrogen secreted by the the follicular cells of the growing follicle
Stratum basalis replace the endometrium- 2-3 mm thickness
Uterine glnds & arteries grow
Secretory phase:
Start immediately after ovulationDue effect of progesterone secreted by corpus luteum
Last 10-14 days
Endometrium 5-8 mm thickness ready for implantation
Glands are tortous & secret uterine milk
Arteries are spiral & coiled