stomach
Dr. Ali JafferGI surgeon
DAdvSurg (GI), C.A.B.S, M.B.Ch.B
Site its lie obliquely in the lf hypochondrium ,epigastric and umbilical regions
Shape; j shapeSize ;it mean capacity 2 liters in adult
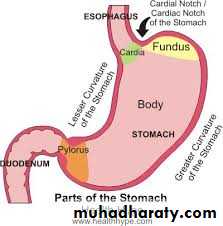
Cardiac orfice;
its more fixed part, position, it lie behind 7th costal cartilage ,1 inch from median plainRelations ant .lf lobe of liver
Post. Diaphragm
Pyloric orifice
less fixed end
Site trans pyloric plane L1
Its connect with duodenum
Anterior quadrate lobe of liver
Posterior neck of pancreas
Borders of stomach
Lesser curvature; It give attachment to the lesser omentum
Greater curviture ; It give attachment to 3 ligaments from above down word;
1- gastrophrenic ligament from fundus2-gastrosplenic ligament from uper part of greater curvature to the spleen.
3-Greater omentum ; From lower part of greater curvature Its related to the rt and lf gastro .epiploic vessels.
Parts of the stomach
Fudus;
Body;
Pyloric region which consist of
*pyloric antrum
* pyloric canal
* sphincter.
Relation of stomach
1-Fundus; diaphragm which separate from the pericardium and heart2-Ant. Sup. surface ; related to diaphragm ,lf costal margin , lf lobe of liver ,ant. abdominal wall
3-post.inf.surface; related to the stomach bed
Lf side stractuers ; Spleen, lf crus of diaphragm, lf suprarenal gland, lf kidney, .Transverse stracture; Splenic artery, body of pancreas , transverse mesocolon, transverse colon
Pyloric end related anterior to the quadrate lobe of liver
Posteriorly related to neck of pancreas and lesser sac Post. Relation of stomach bar area related to the lf crus of diaphragm.Ligaments of stomach
1- lesser omentum;2- greater omentum
3- gastrosplenic ligament(ferom upper 1/3 of greater curvature
4- gastrophenic ligament;(from fundus to the diaphragm)
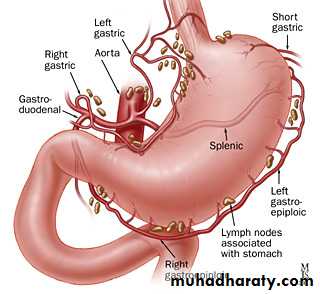
Blood supply
Arterial blood supply
1- lf gastric art.2-rt gastric art.branch from hepatic art.lower lesser curvature
3-lf gastro epiploic art. Along greater curv.(splenic)
4- rt gastro epiplo.art –gastrodud.art---hepatic art.
5- short gastric arts.– splenic art.to the fundus through gastrosplenic art.
Venous drainage;
To the portal vein
Lf &rt gastric vein to the portal vein
Lf gastro epiplo. and short gastric vein to splenic vein
Rt gastro epiplo.to the sup mesenteric vein
Lymphatic drainage
All lymph daring to the coeliac l,n through
Supragastric l.n,infragastic l,n and pancreaticosplenic l.n
Nerve supply
Sympathatic fibers;arise from spinal cord segments from T6 to T10 Runs along or via gastric & gastroepiploic arteriesParasympathatic fiber From vagus
Ant. gastric nerve continuation of lf vagus supply ant. surface of stomach down to the pylorusPost. gastric nerve continuation of RT vagus
Supply posto gastric juice t surface of stomach except the pylorus .it give branch to cealiac plexus
Small intestine
Position: in the infra colic compartment of the greater sac occupying the central & lower parts of the abdomen.
Relations: it is surrounded by the curve of the large intestine & covered anteriorly by the greater omentum & the ant. abdominal wall.
Beginning: at the pyloroduodenal junction.
Termination: at the ileocaecal junction where it joints the caecum.
Length & Parts: it is 6 meters (20feet) long & is formed by 3 parts.
Parts
1. Duodenum: the first 10 inches & fixed to the post. Abdominal wall.2. Jejunum: follows the duodenum. It is 8 feet long and forms the proximal 2/5 of the small intestine.
3. Ileum: next to the jejunum. It is 12 feet long and forms the distal 3/5 of the small intestine. It ends by joining the caecum at the ileocaecal
Duodenum
It is the shortest, widest & the most fixed part of the small intestine.Site: in the epigastric & umbilical regions, above the level of the umbilicus. It is applied to the post. abd.wall against the upper 3 lumbar vertebrae.
Shape: C-shaped loop surrounding the head of pancreas.
Begins: at the pyloric end of the stomach ½ inch to the right of the median plane.
Ends: at the duodenojejunal flexure 1 inch to the left of the median plane.
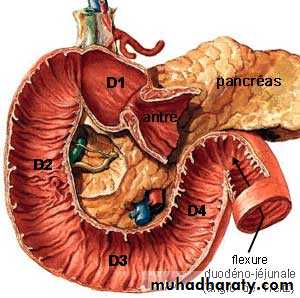
Parts of the duodenum
1st Part (superior) 2 inches long & lies opposite the 1st L. vertebra.2nd part (descending) 3 inches long & extends from L1 to L3 vertebra.
3rd Part (horizontal) 4 inches & lies at the level of L3 vertebra.
4th Part (ascending) 1 inch & ascends from the level of L3 to L2.
Peritoneal relations:
The duodenum is mostly retroperitoneal and fixed to the post.abd.wall except the following 2 mobile parts:1. The proximal 1 inch which is suspended by : a. lesser omentum: aboveb. greater omentum: below
2. The distal end which is attached to the right crus of the diaphragm by a fibro muscular band called the suspensory muscle of
First Part of Duodenum
- Begins: as a continuation of the pylorus, ½ inch to the Rt. Of the median plane at the level of L1 (transpyloric plane).- Course: it passes upwards, backwards & to the Rt. undercover of the quadrate lope of the liver.
- Ends: close to the neck of the gall bladder by curving downwards to become the 2nd part.
Peritoneal connection:
- Its 1st inch is completely covered by peritoneum & and gives attachment to the lesser omentum above & greater omentum below.- Its 2nd inch is covered by peritoneum only infront & above.
2nd Part of Duodenum
(A) Anteriorly
1. Rt. Lobe of liver 2. Transverse Colon3. Coils of jejunum(B) Posteriorly
1. The hilum of Rt. Kidney & adjoining part of ant. Surface.2. Rt. Renal vessels 3. Rt. Psoas major muscle
(C) Laterally
1. Fat infront of the right kidney
2. Rt. Colic flexure 3. ascending colon
(D) Medially:
1. Head of pencreas
2. Ampulla of vater (hepato-pancreatic ampulla) opens in the posteromedial aspect of 2nd part of duodenum just below its middle.
3. Sup. & Inf. Pancreatico-duodenal vessels in the groove between head of pancreas & 2nd part of duodenum
3rd Part of Duodenum
Length: it is the longest part (4 inches long).Course: it passes horizontally form Rt. To Lt. at the level of L3 vertebra.
Peritoneum: it is covered by peritoneum anteriorly and inferiorly.
A. Superiorly: head of pancreas B. Inferiorly: Coils of jejunumC. Anteriorly:1. Coils of jejunum 2. Root of mesentery 3. Sup. Mesenteric vessels
D. Posteriorly (from right to left):
1. Rt. Psoas major m. (separated from duodenum by the Rt. Ureter).
2. Inferior vena cava (separated from duodenum by the Rt. Gonadal vessels)
3. Abdominal aorta (separated from duodenum by the inf. Mesenteric artery).
4th part of Duodenum
Relations of the 4th part ..
(a) Anterolaterally: Coils of Jejunum.
(b) Medially (to the Rt.): 1. uncinate process of pancreas2. abdominal aorta
3. vertebral column
(c) Posteriorly:
1. med. Border of lt. psoas major M.
2. Lt. renal vessels
3. Lt. sympathetic chain
Suspensory muscle of duodenum
(Lig. Of Treitz)- It is a fibromuscular band which suspends the duodenojejunal flexure.
- It arises from the Rt. Crus of diaphragm close to the esophagus.
- It descends behind the pancreas to be attached to post aspect of the duodenojejunal flexure & the 3rd & the 4th parts of duodenum.
- It contains striated & smooth muscle fibers & also elastic fibers.
Arterial supply of duodenum :
1. sup. pancreatico duodenal a. (branch of gastroduodenal a.)2. inf. pancreatico duodenal a. (branch of sup. Mesenteric a.)
3. Branches from hepatic, Rt. Gastric, Rt. Gastroepiploic & supraduodenal arteries.
Venous drainage : into splenic, sup. Mesenteric & portal veins.
Lymphatic drainage : into pyloric, sup. Mesenteric & hepatic lymph nodes.
Nerve supply : sympathetic nerves from T9 & T10 and parasymp. Nerves from vagi pass through the coeliac plexus & accompany the arteries to duodenumDifferences between Jejnum & Ileum
1. Length jej 2.5 , ileum 3.52. Site umblical region
3. Lumen jej wider4. Wall thicker , thick mucosa and muscle
5. Circular folds of mucosa are numorous6. The juj.arteries anastemosis together forming 2 arcades (simple art.arcades) while ilium forming 3,4 or even 5 arcades.
7.Peyres patches (aggregation of lymphoid follicles in sub mucosa)abscent in juj.
Mesentery of Small Intestine
Definition: it is a peritoneal fold enclosing the free part of the small (jejunum & ileum) & connecting it to the post. Abdominal wall.
Shape: fan-shaped fold having broad free border & narrow attached border:
(a) Free border: is 6 meters (20feets) long & encloses the jejunum & ileum.(b) Attached border: (Root of mesentery): 6 inches long & 6 inches away from the free
The root crosses 6 structures on the post. Abd. wall. (2 parts of duodenum, 2 large vessels & 2 muscles) :
1. The 3rd part of duod. 2. the 4th part of duod.
3. Abdominal aorta 4. Inferior vena cava
5. Rt. Psoas major m. 6. Rt. Iliacus m.
Contents of the mesentery:
• Coils of jejunum & ileum in the free margin of the mesentery.2. Superior mesenteric artery & its branches:
It gives 12-16 jejunal & ileal branches.
3. Sup. Mesenteric V. & its tributaries:
- Runs in the root of mesentery on the Rt. Side of the sup. Mesenteric artery.- Receives tributaries corresponding to the branches of the sup. Mesenteric a.
It ends by joining Splenic vein to form portal vein.
4. Lymphatics & 3 raws of mesenteric L.Ns.
(a) Small lymph nodes near the intestine in the free border.
(b) Medium-sized L.Ns in the middle of the mesentery
(c) Large L.Ns: lie along the sup. Mesenteric vessels,
5. Dense plexuses of autonomic nerve fibers around the arteries.
6. Extraperitoneal fatty tissueIleocaecal valve
It is the valve which guards the opening of the ileum into the caecumSite & surface anatomy: it lies in Rt. Iliac fossa at the point of junction between Rt. Lat. Vertical plane & the intertubercular plane.
Structure: it has 2 lips (upper&lower) & 2 frenula (Rt&Lt)
Function: it regulates the passage of ileal contents into the cecum & prevents reflux from cecum to ileum.
Mechanism: it closes actively by symp. Stimulation & passively by distention of cecum.
large intestine
It begins from iliocecal valve in the rt iliac fossa and end at anal orfice .Differences between large and small intestineLarge intestine ch. By
1- appendices epiploicae small peritoneal sac filled with fat scattered over the surface of large bowel except caecum ,appendix and rectum2- taenia coli longitudinal muscle fiber absent in appendix and rectum
3- saculation ( hustration),it occur because length of tania coli is shorter than the true length of large intestin.
4-diameter.
5- site
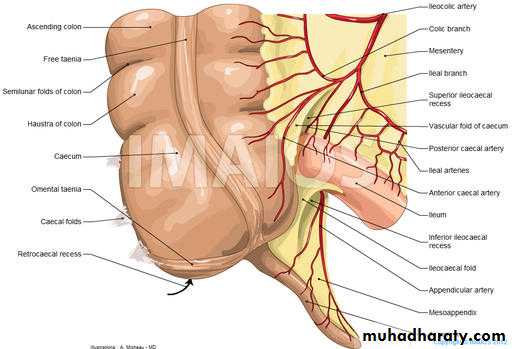
Caecum
Site in rt iliac fossa above the lateral half of inguainal ligament.Surface anatomy atriangular area in rt iliac fossa bounded by
Above- intertubercular plain
below -Lateral ½ of inguinal ligament
Medialy – rt lateral vertical plan
Shape blind pouch 3 inch in length
Comminication
Above – medially –ilium
Posteriomedial– appendix
Peritoneal covering completely cover
Relation
Anterior– ant .abd,wall, lower part of greater omentum..coil of small intestin
Posterior-- 2 muscles rt psoas major,,rt iliacus
2 nerve rt cut, n, of thigh,rt femoral n
2 vessels rt ext.iliac vessels& rt gonadal (test or ovarian)
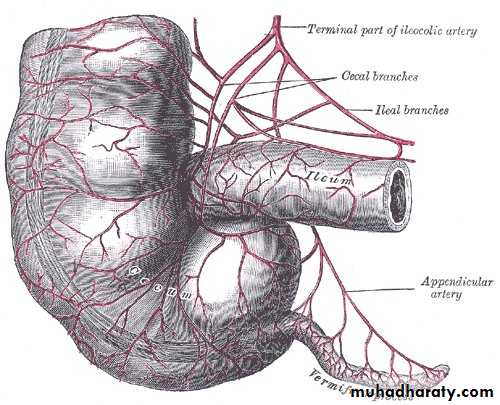
Appendix
Site –rt iliac fossa, attach to post. medial aspect of caecum 1 inch below iliocaecal valveSize ½ -9 inch average 4 inch it’s the narrowest part of GIT
Shape worm like tube
appendixPertonial covering completely cover
Contains of mesoappendix
1- app,vessels 2-lymphatic and l.n
3- autonomic nerve fiber 4- extrapertoneal fatty tissue.
Position of appendix;
Retrocaecal 65%
Pelvic 31%
Preilial 1.5%
Post ilial 0.5%
Subcaecal
Blood supply;
Appendicular artery branch from iliocolic artery.
Appendicular veinhich drain to the sup. mesent,vein.
Lymphatic drainage; 1-to the append. Ln 2-To the l.n along iliocolic art. 3-L.n along sup.mesentric artery
Nerve supply ;sympathetic from T10 segment via sup mesenteric plexus
Parasympathetic via vagus nerve
Ascending colon
site RT lumber regionBegning ;from caecum to the RTcolic flexure.
Taenia coli ; 1ant&2 post..
Pertonium ant.and sides only
Relation;
Anteriorly and laterally;
Ant. Abd. wall, rt border of greater omentum,, coil of ilium
Medially coils of ilium
Posteriorly; from above down word
Lower part of rt kidney
Origin of transverses abdomens
Quadrates lumborus muscle
Iliohypogastric and ilio inguinal nerve
Iliac crest and ilio lumber ligament
Iliacus muscle
Lateral cutnous nerve of the thigh
Blood supply right colic and ascending branch of iliocolic artery
Transverse colon
Size 18-20 inchesTaenia coli –2 ant .&1 post.
Pertonium; it completely covered with peritoneum except the rt 2 inch wher it adherent to the 2nd part of dued. and head of pancreas
It has transverse mesocolon
Relation of transverse colon
Anterior sup. from rt to lf
Rt lobe of liver..gall bladder..great curvature of stomach…greater omentum.
Posterior from rt to lf
2nd part of duodenum, head of pancreas,Dj flexure &coil of jejunum .
Inferiorly…coil of small intestine
Blood supply; middle colic and ascending branches of upper lf colic art.
Colic flexuresRight colic flexure
Position L2 ,
Shape a blunt forming right angle
Attachment to the diaphragm no
Relation ant sup..rt lobe of liver,, post.inf.. Rt kidney medially 2nd part of duodenum
Blood supply; RT olic art.
Left colic flexure
LF L1
Lf sharp forming acute angle
yes through phrencocolic ligament.
ant.sup spleen and tail of pancreas
Post inf lf kid. and diaphragm
Medialy lf kidney
lf colic art.
Descending colon
Site; in the lf lumber and lf iliac region ,start from lf colic flexure to the lf border of pelvic brim where it become pelvic colon(sigmoid)
Size 10-12 inch double length of ascending colon but narrow lumen.
Taenia coli; one ant .and 2 post, same ascending.
Peritonium cover in front and sides same ascending.
Relation; anterior and laterally ;
Ant. Abdominal wall
Lf border of greater omentium
Coil of small intestine
Medial relation;
coil of small intestine
Posterior relation;
It descend on the fallowing strictures;
Diaphragm,Lower lat part of the lf kidney, Origin of lf trans. abdominus m, Lf quadretous lumborous m. and structures infront of it {a-subcostal n &vessels, b-iliohypogastric n, c- ilioinguinal n.}, Lf iliacus muscle & stracture related to it {A- lat. cutanous n . Of thigh B-femoral n.}, Lf psoase major m & structure related to it {A-lf gonodal v.B- lf genetofemoral n.C- lf external iliac artery}
Blood supply; left colic artery
Pelvic (sigmoid )colon
Site ;lf iliac fossa ,in pelvic cavityShape; s shape
Size ; 16 inches
Begins; infront of ext.iliac artery at the lf border of pelvic prim ,2 inch above the inguinal ligament.as a continuation of descending colon.
End ;opposite the 3rd sacral piece by becoming rectum
Relations
Sup.and to the rt;
Coil of ilium
Inferior;
According to the sex
In female uterus
In male urinary bladder in both male and female
Postreiorly;
Sacrum and structure infront of it;(piriformis and sacral plexus)
Lf ureter
Lf internal iliac vessels
Blood supply; lower lf iliac (sigmoid arteries)
Pertonial covering; completely covering
Has mesentry cold pelvic mesocolon connecting it to the post.abdominal wall.
Pelvic mesocolon
Its peritoneal fold attaching the pelvic colon to the upper part of the post. wall of pelvis. Shape; inverted v shape
Attachment;
A- lat. Limb attach to the med. side of lf ext. iliacB- medial limb attach to the front of sacrum till the 3rd sacral piece
C-The apex ; attach infront of the lf ureter.
Content of pelvic mesocolon;
1- segmoid colon in free margin2- sigmoid artery;(lower lf colic)
3-sup.rectal v.
4- sympathetic fibers
5- extraperitonial fatty tissue
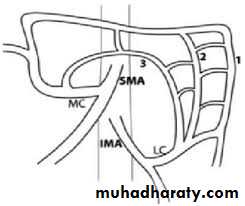
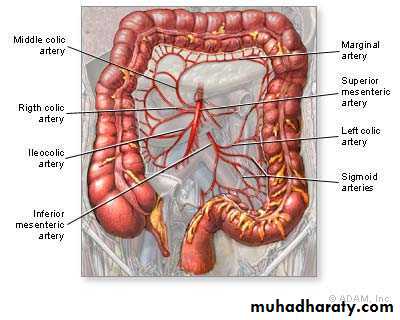
Blood supply of the colon
Caecum, ascending ……. Right colic arteryTransverse colon proximal 2/3 ……. Middle colic artey
Distal 1/3……….. Left colic artery
Descending colon……. Left colic artery
Sigmoid colon……. Sigmoidal branches.
Marginal artery ;its an arterial arcade lying along the concavity of colon . Its formed by anastemosis of iliocolic, middle colic, upper and lower lf colic a.
Lymphatic drainge of colon
Pass through 4 groups of l.n1- epicolic l.n on wall of colon
2- paracolic along inf. Border
3- intermediate l.n along the colic arteries
4- terminal l.n along the trunk of sup & inf mesenteric a. which continuous with para oartic l.n
Vesseles of post.abdominal wall
Abdominal aortaBeginning; diaphragmatic opening at lower border of T12 as a continuation of descending thoracic aorta.
Course; descend infront of upper 4 lumber vertebra.
Termination; lower border of L4 BY dividing to rt & lf common iliac art.
Relations
Anterior; from above downward;
1- coeliac trunk
2- body of pancreas and 3 structures behind to it *splenic v * lf renal v* origin of sup. Mesenteric art
3- 3rd part of duod. & origin of inf. mes. art.
4-upper part of root of mesentery
5-paraital peritoneum separating it from coil of small intestine.
Posteriorly
1- upper 4 lumber vertebra & intervertebral disc
2-ant.longitudinal ligament
3- 3rd and 4th lumber veins
Rt ; cisterna chyli & thorasic duct ,lower part of RT azygous vein , RT coeliac ganglion , crus of diaphragm & IVC
Lf --- lf crus of diaphragm ,lf coeliac ganglia, lf sympathetic chain, body of pancreas, inf. mesenteric v.
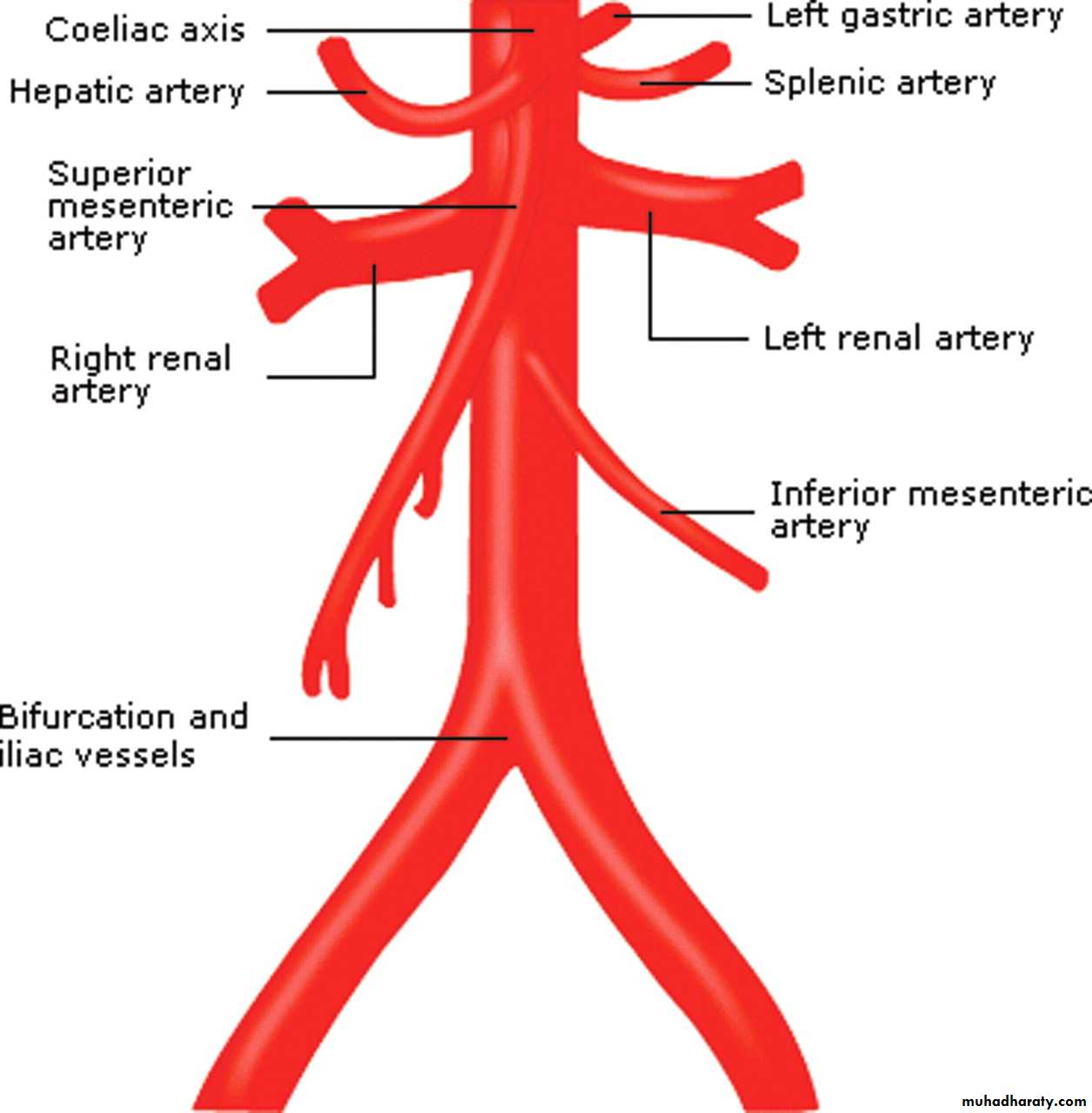
BRANCHEAS OF A.A
Single branches
1- coeliac trunk upper of L1
2- sup. Mesenteric A lower of L1
3- inf . Mesenteric A. L3
4- median sacral art. From back of aorta as a continuation of A.
Paired branches
1-Rt & lf inferior phrenic A . ; upper L12- rt&lf middle supra renal A. lowerL1
3- rt&lf renal art. L2
4- rt& lf gonodal art. L3
5- rt& lf common iliac A. lower L4.
+ 4 pairs of lumber arteries from back of A. from l1 to l4
MEDIAN SACRAL ART
It arise from the back aorta, just above its bifurcation. descend in front of L4&L5.It enter the pelvis in front of sacral promontory.
Branches;
1- 5th pair of lumber arteries
2- twigs to the sacral canal
3- twigs to the rectum
Inf.phrenic arteries rt&lf
Arise from side of aa at level of L1 upper border
Ascend upward to diaphragm
Rt A pass behind ivc
Lf pass behind the oesophagus
Each artery give sup.suprarenal art.
Middle suprarenal art rt&lf
Arise;from the side of AA at lower border of L1. then go to supplying the suprarenal glandsRenal arteries rt &lf;
Origin; side of AA at L2 levelReach kidney infront of renal pelvis and ureter
Rt one is longer and pass behind ivc, rt renal vein& head of pancreas
Lf one shorter pass behind the lf renal vein &and body of pancreas
Branches;
1- inf suprarenal art,
2- terminal branches 5
3- ureteric branches to the upper end of ureter
Gonodal arteries
They are testicular or ovarian art. they arise from anterio lateral aspect of AA. At level of L3.TERMINATION;
Testicular a. reach deep ing. ring then superfascial ing. ring pass through ing. canal as a constitution of spermatic cord to reach the testis.
Ovarian art. it cross the ext. ilic vessels to enter the suspensory lig. of ovary to reach the broad ligament then reach the ovary via mesoovarium.
Lumber arteries
4 pairs arise from back of AA.
They supply ; muscles of post abdominal wall,Muscles of lat. abdominal wall and Spinal cord
5th paird arise from median sacral a.
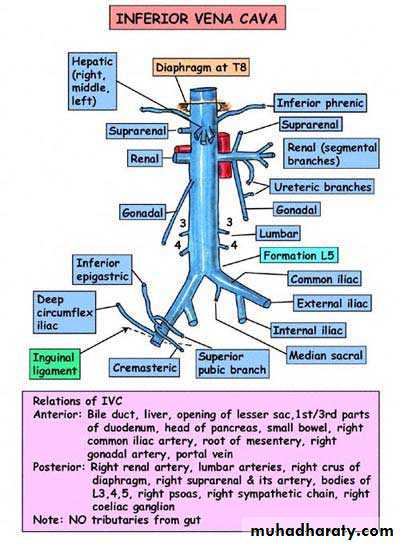
Inferior vena cava
Beginning;in front body of vertebra L5 (AORTA L4) by union rt&lf common iliac v.
Course ascend up rt to the aorta and pierce diaphragm at level of t8
Termination; open to the lower part of rt atrium .
Relations
Anterioly;
Below the duodenum;
1- RT common iliac art.
2- root of mesentery and sup. mesentric vessels
3- RT gonodal vessel
At the duodenum
1- 3rd part of duod.
2-head of pancreas and cbd
3- 1st part of duodenum.
Above the duodenum
1-The epiploic foramen ; which separate the ivc from the margin of lesser omentum and its contents( portal v, hepatic art. &cbd)
2-Post.surface of rt lobe of liver
Post relation;
A- the lower part of ivc is related to1- bodies of lower 3 l. vertbra
2-Rt psoas major m
3-Rt sympathetic chain
Upper part of ivc is related to ;
1- RT crus of diaphragm but separated from it by ;
a- RT coeliac ganglion
B- 3 arteries;
*RT inf phrenic art
*RT middle supra renal art
*RT renal art.
Rt side relation to ivc;
* rt lobe of the liver(in the upper part)
*medial border of rt kidney( in middle part)
*rt ureter ( in the lower part)
Lf side related to
*caudate of the liver( in upper part)
*RT crus of diaphragm (in middle part)
*abdominal aorta( in the lower part)
Tributaries of ivc
1- 2 common iliac v.
2- 2pair of lumber veins ( 3rd &4th)
3- 2 renal v (rt&lf)
4- 2 rt side v. (rt suprarenal & rt gonodal)
5- 2 inf phrenic v.
6- 2 hepatic veins
Renal veins
2 large vein open to the ivcRt – short and lies behind 2nd part of duod.
Lf vein-- longer in 3 times, pass infront of aorta and behind body of pancreas ,splenic vein
It receive 2 tributaries
1- lf gonodal vein ( LF VARICOCELE MORE COMMON)
2- lf supra renal vein
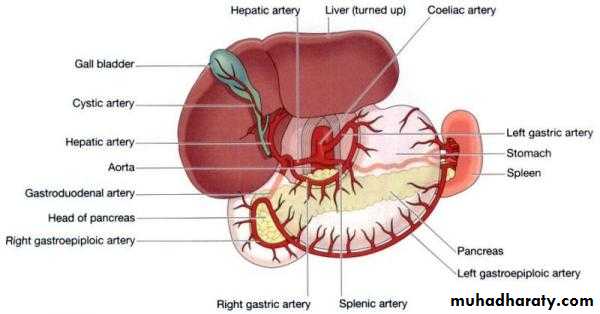
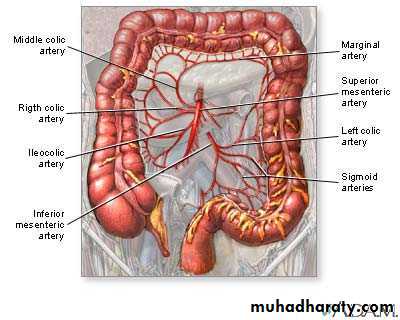
BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE GUT
1- CAELIAC TRUNKOrigin; From abdominal oarta at the level of upper border of L1
Branches ;
1- lf gastric artery anastomoses with rt gastric artery in the middle of lesser curvature.
Branches;
a- esophageal br.
b- gastric branches to the surfaces of the stomach.
2- Splenic artery
Largest branches of coeliac art.
Course and relations;
It runs along the sup. border of pancreases.
Divided into 5-6 terminal
Branches;
1- pancreatic bra.—to the body and tail of pancreas.
2- short gastric arts. 5-7 small branches supply fundus of stomach runs along the gastosplenic ligament
3- lf gastroepiploic art.,runs along the upper 1/3 of greater curvature ,end by anastomosing with rt gastro epiploic art.
4- terminal splenic branches 5-6 to the spleen
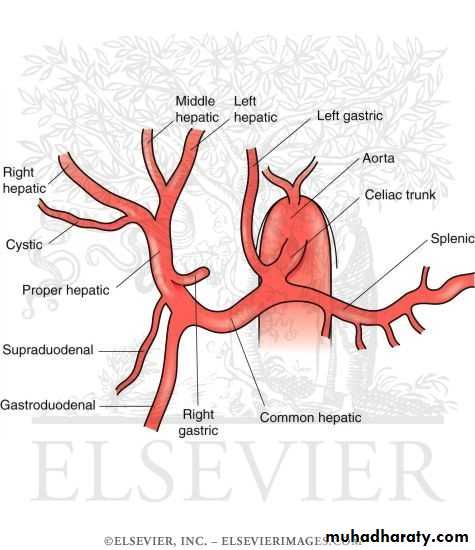
3-Hepatic artery
Branches;a- gastroduod.art.behind 1st part of duod.it gives
i- rt gastro epiploic a.
ii-sup pancreatico duod.a.
b-rt gastric art.it end by anastemosis with lf gastric art.
c-supraduod.art.small supply upper part of duod.
d-rt terminal hepatic art
e-lf terminal hepatic art.
f- cystic art.it arise from rt terminal hepatic art.pass behind cystic duct and common hepatic duct
2-Sup.mesentric art
Origin front of abd.aorta at lower border of L1
Course and relation ;it arise behind the body of pancreas between splenic vein and lf renal vein
Sup mesentric vein lie on its rt side
Branches;
1-inf.pancreatico art. lower 1l2 of duod. part of the head of pancreas
2-juj.and ilial branches— except terminal part of ilium
3-iliocolic art. Start from terminal part of ilium
4-rt colic art.
5-Middle colic
3- inferior mesenteric artery
Branches ;1- sup.lf colic artery pass to the lf behind pertonium of post abd.wall
Divided to ascending branch and descending branch.
It supply lf 1/3 of trans.colon and upper part of descending colon.
2-inf.lf colic(segmoid ) art.2-3 bra.
They supply lower part of descending colon + sigmoid colon
They anastomose with descending branch of sup. Lf colic art. and with the sup rectal art.
3- sup. rectal art. continuation of inf. mes.art.
Anastemosis between SMA and IMA
Sup.pancreaticoduod.(coeliac)anastemose with inf.pancreaticduod.art(sup.mes.aert)
Middle colic art.(sup.mese.art) with sup.lf colic art.(inf.mes.art
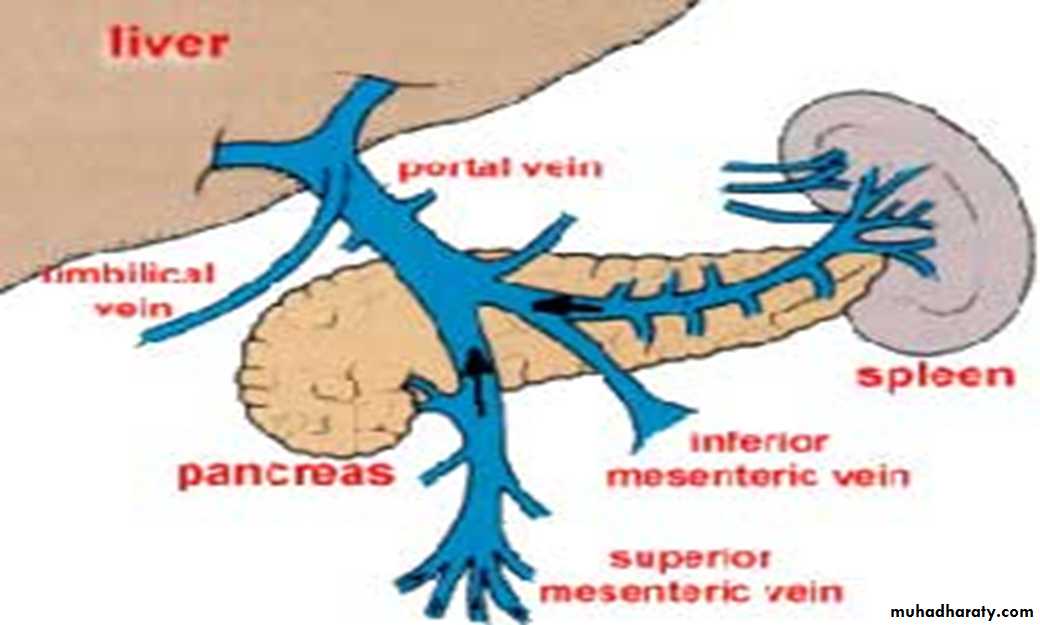
Portal vein
Origin; form behind neck of pancreas at level of L2 by union of 2 veins –splenic and sup.mesentric veinLength about 8 cm
Tributaries of portal veinA- 2 main tributries *splenic & sup mes.vein
B- 2 vein from stomach lf gastric & rt gastric veinC- vein drain in to the terminal branch
i.Cystic vein to the rt terminal bran.
ii.Para umbl vein from ant,abdominal wall
to the lf terminal branch.
2 lig.attach to the lf branch of portal vein
1-ligmantum teres (oblitration of umbl,vein2- lig,venosum; oblitration ductus veinosum of the feotus
which reach to the ivc
Portal circulation
Its venous drainge of GIT spleent pancreas GB to the live.It differ from systemic circulation by
1- draining vein portal---IVC
2- organ drained GIT (except liver)---remining part of body + liver
3- begning network of capillaries in submucosa of elimentary trac ----capillaries in the wall of draind abdomin and pelvic organ
4- termination sinusidal cappiliraies in liver ----sys.inthe rt atrium
5- quality of blood de O BLOOD with product of GIT digestion no detoxification ----deO blood but detoxificat in the liver
Site of portosystemic anastemosis
At lower end of oesophagus; lf gastric with azugous vein tributaris ( oesoph.varices)2-at anal canal ; sup.rectal with middle and inf rectal veins (internal piles)
3- around umblicus ; paraumblical vein ( portal) with epigastric veins of ant abdominal vein (caput medusae)
4- vein of ritzius ; sup .mes.vein ( portal) +IVC(systemic)
5- on post abdominal wall colic veins(portal) with renal and lumber veins
6- at the bar area of the liver --between twigs from the vein of the liver with phrenic vein of diaphragm
The diaphragm
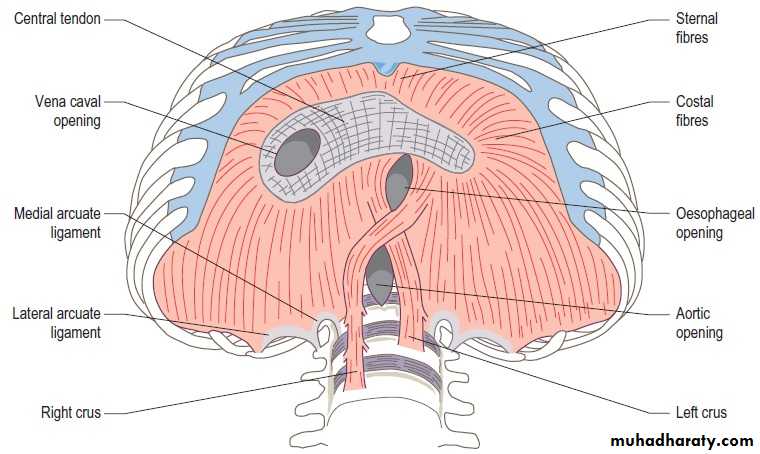
Origin of diaphragm;
Periphral part of diaphragm. origin divided to 3 parts;
sternal origin ;from back of xiphoid process
Costal origin; from inner surface of lower 6 ribs and there costal cartilage.
Vertebral origin; by 2 muscular band called rt&lf crura and 5 tendinous arches called arcute ligaments(one median,2 medial,2 lateral)
Rt crus arise from front of upper 3 L.V
Lf crus arise from front of upper 2 L.V
Median arcute lig. it’s a tendinous arch
connecting 2 crura in front of aorta.
Medial arcute ligs. connecting the RT
crus with tip of trans. process of L1
Lat.arcute lig s connecting
t. process of l1 with the last rib
Insertion of diaphragm
All fiber converge to be insertedto central tendon
Nerve fiber;
Motor ; rt&lf phrenic nerves
Sensory ; phrenic sensory to the central part
Lower 6 thoracic nerve are sensory to the peripheral part.
Arterial supply;
1- phrenic branches of thoracic and abdominal aorta.2-precardiophrenic and musculo phrenic branch of internal mammary art.
3- lower 3 post. intercostal arteries.
Action
1- it’s a major muscle of insp. On contraction it descend leading to increase in the vertical diameter of the thorax thus air is sucked2- increase intra abdominal pressure useful in vomiting .labour, micturition
3- rt crus has a sphincter action on the lower end of esophagus.
4- it help in venous return of blood to the heart by
A- increase intra abdo.pre. b- decrease intra thoracic pre. C- widening the IVC opening.
Major foramina of the diaphragm
V.C OPENING OESOPHAGEAL OP. AO.OPT8 t10 T12
Minor foramina of the diaphragm
1- sup .epigastric art.
2- musculo phrenic art. pass between 7th and 8thrib
3- lower 5 intercostal n
4- lf phrenic n
5- the greater and lasser splanchic ns.
6- subcostal n & v pass behind lat arcute ligament
7- sympathetic chain pass behind medial arcute ligament.
8- inf. Hemiazygos v pierce the lf crus.
Abdominal lymph nodes
According to their relation to the abdominal aorta they are classified to the1- preaortic l.n which are a- coeliac l.n b- sup&inf. mesentric l.n .
Group a receive lymph from gastric ,hepatic, & pancreatico splenic l,n while group b received lymph from mesentric l.n ,coeliac l.n,pararectal l.n along side of the rectum.
All these l.n send lymph (efferent) through intesinal lymph trunk to the cysterna chyli.
2- rt& lf aortic groups ;(on the rt & lf sides of the abdominal aorta drain lymph from kidney ,ureter ,fallopian tubes ,upper part of body of uterus send lymph( efferent) to the lumber lymph trunk which open to cisterna chyli.
3- retroaortic lymph node (behind abdominal aorta),have no particular area of drainage.
The cisterna chyli
Its aspindle shaped lymph sac about 2 inch long.Site; infront of upper 2 lumber vertebrae between abdominal aorta (to the lf) and azygous vein (to the rt) over laped by the rt crus of diaphragm.
It received intestinal l.trunk &rt&lf lumber l.trunk(which drain the lower limb &all the abdomin except the upper surfice of the liver.
Upper end forming the thoracic duct.
Autonomic plexuses of abdomen
Coeliac plexus
It’s a plexus of autonomic nerve fiberSite ;infront of abdominal aorta & crura of diaphragm around the coeliac trunk.
Plexus end lateraly in a number of nodule called coeliac ganglion.
Coaliac ganglia;
site on each side of coeliac trunk
Size ;is the largest ganglion on the body
Aortic plexus (intermesentric)
Site ; its surround the abdominal aorta between the origin of sup and inf mesenteric art, continue above with coeliac plexus and inf with hypo gastric plexus.
Formed of; 1.Sympathetic fiber ; from coeliac plexus &1st and 2nd lumber splanchnic nerve
2. Parasympathetic fiber; from pelvic splanchnic nerve of both sides(S.2,3,4)
SUP.HYPOGASTRIC PLEXUS
SITE; just below the bifurcation of abdominal aorta infront of L5 it continuous above with the aortic plexus and below divided to rt & lf which join with rt and lf hypo gastric plexus
Formation; 1- sympathetic fiber a- aortic plexus b- 3rd &4th lumber splanchic nerve of both sides
Parasympathatic from pelvic splanchic nerve of both side (S 2,3,4)
INFERIOR HYPOGASTRIC PLEXUS
SITE;there are 2 plexuses rt &lf lying in the extrapertoneal tissue of the pelvis on each side of the rectum and base of urinary bladder (or cervix of uterus)
Formation; formed of
A- sympathetic fiber; from 1- sup.hypogastric plexus 2- the upper 2 sacral sympathetic ganglia.
B- parasympathetic fiber from pelvic splanchic nerve (S2,3,4)
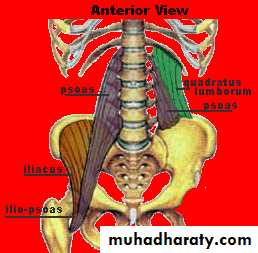
Posterior Abdominal Wall Muscles
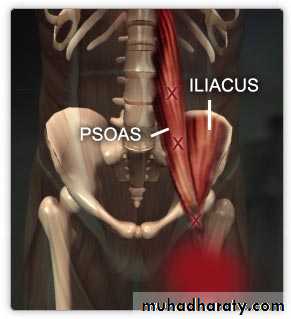
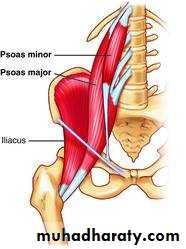
Psoas major muscle
Origin ;1-ant.surface of 5 L.transv.process2-from the 4 tendentious arch
Course; it leave the abdomen behind lateral part of ing. ligament closely relate to the iliacus m.
Insertion; together with iliacus producing ilio psoase tendon inserted to the ant.and med. aspect of lesser trochanter of femur.
Nerve supply; ventral rami of L 1,2,3
action
1- powerful flexion of thigh and rotated
medially
2-flexion of pelvis over the thigh
3-one psoas produce lat. flexion of
v. column toward it side
Psoas minor muscle
It’s a long slender m. lying in front of psoas major m.in60% of people.
Origin ;from side of T12 and L1 v.and the disc in between.
Insertion; by long tendon into the ilio pubic eminence of
hip bone
Nerve supply; branch from L1.nerve.
Action; weak flexor of the trunk
Quadrotus lumborum muscle
Its quadrilateral m lying post lat. To psoas major.
Origin ;ilio lumber lig. and inner lip of iliac crest
Insertion ;TIP of transverse process of upper
4 L.V& medial half of lower border of last rib.
Nerve supply; branch from t12&upper 4 L. nerve.
Action; 1- lat. Flexion of vert..coloumn
2-muscle of inspiration by fixing the last rib
during contraction of diaph.
Nerves of post. abdominal wall
Lumber plexus;Site; in the post part of psoas major m.
Formation; from ant. Rami of upper 4 lumber nerves (L1,2,3,4).EACH OF which divided to ant,and post.divisions.
Branches;
Large branches;
1- femoral n.(post division of L2,3,4
2-obturator nerve (ant. divisions of L2,3,4)
Small branches;
1- iliohypogastric n L1
2- ilioinguainal L1
3- gentofemoral L1,2
4- lat.cutanouse nerve of the thigh(post.division of L2,3).
Lumbar part of sympathetic chain
It enter the abdomen by passing behind medial arcute lig. of diaphragm.
There are 2 chain rt one behind ivc lf one on the lf side of aorta.
It leave the abdomen by passing behind common iliac vessels
Each chain contain 4 ganglia