The major vessels of head and neck
Sub Clavian arteryOrigin; lf subclavian from the arch of aorta behind the lf center of manubrium enter the neck behind lf st. clvicular joint.
Rt ; from the innominate artery behind rt st.clav.joint
Termination ; outer border of 1st rib becoming axillary art.
Scalenus ant muscle descend in front of the art divided it to 3 parts
1st part ; medial to m
2nd part behind the m3rd part lateral to the m.
Relation of 1st part
Ant.
3 super facial str.* Skin *superficial fascia *deep fascia
3m; sternomastoid * sternohyoid * sternothyroid(MHT)
3N..vagus * cardiac branch of vagus * ansa subclavia
3 vessels ; *common corotid art * I.J.V* vertebral vein
Other 3 stracture * lf phrenic n * lf innominate vein * thoracic duct.Post relation ; apex of the lung * cervical pleura * suprapleural membrane.
Relations of 2nd part
Ant.* skin ,suprefascia,deep fascia
* sternomastoid
*subclavian vein,(seperated from the artery by scalenus ant. M)
Scalenus ant. &rt phrenic n on it
Post relation ;
Same as 1st part
Relations of 3rd part
Ant relation; * skin ,superfascial fascia & deep fascia
* clavicle ,subclavius m,
Post relation ; 1st rib and lower trunk of brachial plexus
Branches of subclavian artery
1st part give 3 branches
1- vertebral art.
2- thyrocervical trunk
3- internal mammary art.
2nd part ; give one br. Costocervical trunk.
3rd part ; no branch
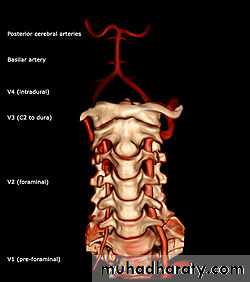
Vertebral artery
Origin ;1st part of subclavian art.Its course divided to 4 parts
1st part; from its origin to trans. process of c6.
2nd part ; ascend in foramina transversaria of the upper 6 c.v
3rd part ; lie in sub occipital triangle
4th part enter the cranial cavity through f.magnum
Termination ; end at the lower border of pons by joining its fellow of opposite side to form basilar art.
Branches of vertebral artery;
A- in the neck;
1-spinal branches—enter the intervertebral foramina to supply spinal cord
2- muscular branch; supply deep m. of the neck
B- branches in the cranial cavity ;
1- ant & post spinal arteries
2- medullary branches
3- post. inf. cereballar art
Internal mammary(thoracic )artery
Origin ; from the lower surface of1st part of subclavian art.Termination ;opposite to the 6th intercostal space by dividing into 2 terminal ;musculophrenic & superior epigastric art.
Branches;
1-pericardiophrenic art.
2- pair of ant.intercostal art.in each of the upper 6 intercostal spaces
3- perforating arteries which supply skin and breast
4- superior epigastric enter the rectus sheath
Thyrocervical trunk
its very short trunk arise from the 1st part of subclavain art. It divided immediately into 3 branches;A-inf thyroid art ; branches;
1- ascending cervical art
2- muscular br.
3- inf. Laryngeal art. Accompanies recurrent laryng.n to supply the larynx
4- pharyngeal br. Supply pharynx
5- esophageal & tracheal branch.
6- terminal glandular br. To the thyroid gland
.
B- suprascapular artery
It enter the post triangle of the neck
C- transverse cervical art. It divided at the ant. Border of levetor scapulae into 2 br. superfascial and deep
Superfascial supply trapezius m
Deep pass deep to the levetor scapulae
4- costocervical trunk.
Arise from the 2nd part of subclavian art.It end in front of neck of first rib by dividing into;
A- sup.intercostal art.
B-Deep cervical art.it reach sub occipital triangle where it anastomoses with descending br. of occipital art.
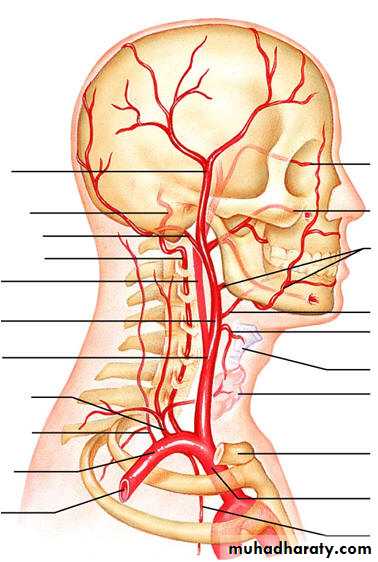
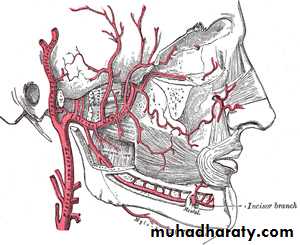
Common corotid artery (CCA)
Origin; lf CCA from aortic arch and enter the neck behind lf sternoclavicular joint.RtCCA its one of 2 terminal br.of inominat art. Enter the neck behind rt sternoclavicular art.
Course;it ascend to the neck inside corotid sheath with IJV & vagus
Through its COURSE overlapped by sternomastoid m
Termination; it end at the upper border of thyroid cartilage (disc between c3,c4) by dividing to internal and external C.ARelations of CCA;
Ant (superfascial ) relations;
1- 3 superfascial layer ; skin,superfascial,deep fascial
2- 3 sterno m. *sternohyoid * sternothyroid * sternomastoid
3- 3 thyroid structure; * the lateral lobe of thyroid gland * middle thyroid vein * superior thyroid vein4- superior belly of hyoid & the loop of ansa cervicalis.
Post; (deep ) relations;
Transverse process of lower 4 cervical vertebra2- vertebral muscle longus colli & longus capitus
3- sympathetic chain embeded in post.wall of rectus sheath
4- vertebral art.
5- inf.thyroid artery
6- thoracic duct
Medial relations; *trachea & oesophagus with RLN in between
* larynx and pharynx
Lateral relation; *the IJV * the vagus N
COROTID BODY;
Its oval structure about ½ cm on the post aspect of bifurcation of CCA it contain chemoreceptor sensitive to the PH ,receive sensory from glossopharyngeal nerve.
Carotid sinus
It’s a dilatation in the upper end of CCA and beginning of ICA it contain baroreceptor sensitive to the changes in BP its supply by glossopharyngeal n.Internal carotid artery (ICA)
Beginning; its one of terminal branch of CCA at the level ofupper border of thyroid cartilage ( disc between c3&c4).Termination; in the cranial cavity ,lat to the optic chiasma by dividing to the ant cerebral and middle cerebral art.
Course ; its divided to 4 parts;
1- cervical part ; ascend inside carotid sheath in the neck2- intrapetrous part; in carotid canal inside petrous part of temporal bone
3- intracavernous part ; inside the cavernous sinus
4- intracraneal part; the terminal part of the artery inside the cranial cavity.
Cervical part of ICA
Course ;it ascend vertically up word with in carotid sheath to reach carotid canal at the base of skull.Relations ; anteriolateral ( superfascial)
*skin * s.fascia * deep fascia
*Sternomastoid m
*Hypoglossal nerve
*ECA lie superfascial to the ICA above the level of digastric m but separated from it by these stractures;
1- styloid process
2- apart of the parotid gland
3- pharangeal br. Of vagus nerve
4- glassopharangeal n
Post relations ;
IJV & cranial nerves 9.10.11. lie post to the upper part of the A ( at the base of skull)Laterally; vagus nerve posteriolat.
IJV lat.to the ICA.in the carotid sheath.
Medially ; wall of pharynx
Branches; no branches in the neck
Intrapetrous part of ICA
COURSE ;it reach the cranial cavity via the upper end of foramin lacerum.
Relations ; ICA lies infront of the middle & internal ear cavities
Branches ; caroticotympaic br.to the middle air cavity
Intracavernous part of ICA
At the upper end of f.lacerum it pierces the post.wall of the cavernous sinus.Relations ; medialy body of sphenoid and pitutary gland
Lateraly; abdoscent nerve (inside the cavity of sinus)
Occulomotor ,trochlear,ophthalmic &maxillary n (imbeded in the lat.wall
Ant,sup ;optic n.
Branches; 1- sup & inf hypophyseal arteries to the pitutary gland
2- meningeal brs to the meninges of ant cranial fossa.INTRACRANEAL PART;
Brs in the brain
1- ophthalmic art
2-Ant chorid art
3-Post.comincating art, 4- ant cerebral a .5-middle cerebral art.
EXTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY
ORIGIN;its one of terminal branches of CCA at the upper border of thyroid cartilage (disc between c3&c4)
Termination it end behind the neck of mandible (inside parotid gland) by dividing into maxillary and superfascial temporal artery.
It enter the parotid gland which lying as the deepest structure inside the gland.
Branches of ECA
.superior thyroid artery, lingual art, fascial art .those arise from the ant.aspect.Occipital art & post auricular art. those from post aspect
Ascending pharyngeal art. From medial aspect
Maxillary & superfascial temporal art. Those terminal bra.
Sup.thyroidal art
Origin from ant surface of ECA below the greater horn of hyoid bone.Branches
* infrahyoid art. * sternomastoid br *to cricothyroid br * sup. laryngeal art runs with the internal laryngeal n * terminal glandular br.
Fascial art.
Origin from ant. Aspect of ECA above tip of greater horn of hyoid bone.Branches in the neck
1- tonsillar br. 2- sub mental art. 3- glandular br(to sub mandibular salivary gland) 4-ascending palatine to the soft palat -
Superfascial temporal art
Origin; inside the parotid gland ( deep to the neck of mandible)Branches; 1- glandular to the parotid
2- transverse facial art.
3- zygomatico orbital art
4- ant.auricular art
4- middle temporal art.
Terminal brs frontal and parietal br
Veins of the neck
1- ant.jugular vein; it begins near the hyoid bone by union of small veins and end by joining the EJV.
RT & LF CONNECTED BY jugular arch.
2- ext.j.vein; begins below the angle of mandible by union of 2 veins .
3-Internal jugular vein
Begning; in the jugular foramin as a continuation of the sigmoid venous sinus
Termination; behind the medial end of the clavicle by joining the subclavain vein to form innominate vein.
It has 2 bulb (dilatation) sup one in upper end
Inf.one one cm above the clavicle above which 2 valves.Rt IJV larger than lf
Surface anatomy ; it lie along vertical line drown from the lobule of ear to the medial end of the clavicle.
Tributaries of IJV
1-inf petrosal sinus2- pharyngeal vein
3- lingual v
4- common fascial v
5- sup.thyroid v
6- middle thyroid v
Subclavian vein
Begning ; at the outer border of 1st rib as a continuation of axillary vein
Termination ; behind the medial end of the clavicle by joining theIJV to form innominate v.
Tributaries;
Only one the ext.jugular vein
Nerves of head &neck
Its include1- cranial nerves
2- cervical nerves
3- cervical sympathetic chain
4- para sympathethetic ganglion and nerves
Cranial nerves
12 pairs arise inside the cranial cavity from the brain and brain stem .1st olfactory
2nd optic n
3rd oculomotor n
4th trochlear n
6th obducent n
7th facial n
7th facial n
8th vestibulo cochlear n
9- glassopharyngeal n
10th vagus
11th accessory n
12th hypoglossal n
Olfactory n its sensory n
Trigeminal n.It’s the thickest cranial n.
Its mixed sensory receive sensation from ant.1/2 of the scalp,face,orbit, nasal cavity & oral cavity.
Motor supply 4 m.of mastication & 4 other stracture.
Trigeminal ganglion
Its sensory ganglionSite in middle cranial fossa
Branches; 1-ophthalmic n ( the smallest)
2- maxillary n (medium size)
3-mandibular n (largest)
Fascial nerve
Type ; mixedOrigin ; it emerges from the anterolateral aspect of the brain stem at the lower border of pons.
Intracranial part ;course of n;
Leave the cranial cavity by entering the internal auditory meatus. then it pass downwards in the post wall of middle ear to reach the stylomastoid foramen
Extra cranial part;
It leave through stylomastoid foramen it form motor fiber only.
Then curve around lateral side of base of styloid process
It enter post medial surface of parotid gland(lying superficial to ECA & retromandibular n)
It end in the gland by dividing to 5 terminal brs.
Branches of facial n
1-Temporal,2-zygomztic,
3-buccal,
4-marginal br &cervical br,
5-?
Vestibulo cochlear nerve
Sensory n, formed of 2 part1- cochlear part carrying hearing impulses
2- vestibular part carry equilibrium impulse
It enter the internal audatory meatus with fascial n
Glasso pharangeal nerve
Type; mixed;Origin post lateral sulcus of medulla
It leave the cranial cavity through middle compartment of jugular foramen
Terminarion; by dividing into terminal brs supplying mucous mem. Of pharynx tonsil and post 1/3 of tongue
VAGUS NERVE
TYPE mixed contain parasympathetic motor and sensory
Origin; post medial of sulcus of medulla
It leave cranial cavity through middle compartment of jugular foramen
Vagus descend vertically inside the carotid sheath
At the root of neck the vagus n. crosses infront of 1st
part of subclavian art. To enter the thorax.
It has 2 sensory ganglia a- sup.ganglia ( in the jugular foramen) &inf ganglia just below jugular foramen
Branches of vagus nerve in the neck.
*2 brs.arise from sup ganglion ;1- meningeal br. Sensory to the dura matter of post cranial fossa.
2- auricular br. Sensory to the skin of medial side of auricle ,post wall of external auditory meatus & tympanic membrane.
*2 brs .arise from inf .ganglion;
1- pharyngeal br.(motor) arise from cranial accessory n. it supply the pharyngeal m except the stylopharyngeus m
2- sup. Laryngeal n.(mixed) it divided to 2 branches a- internal laryngeal n. accompanies the sup. Laryngeal art. And supply mucous mem.of upper half of larynx (above vocal cord)
B- external laryngeal n. (motor) passes deep to the sup.thyroid art. To reach the cricothyroid m. supplying it.
*2 cardiac branches sup& inf (parasympathetic)— both joining cardiac plexus
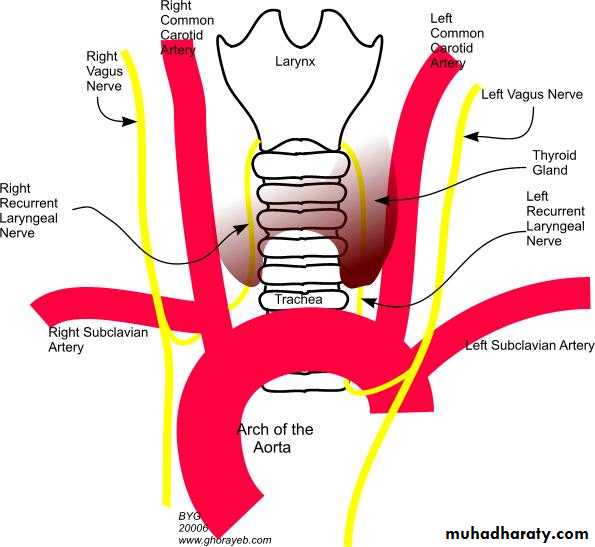
* RLN; (MIXED MOTOR AND SENSORY);
Rt one; it arise from rt vagus at the root of the neck infront of 1st part of subclavian art. then it hook below, then behind the artery .
It ascend along the rt groove between the trachea and esophagus closely related to the medial surface of thyroid gland and inf. Thyroid art.
Lf one; it arise from lf vagus on the lf side of arch of aorta in the thorax then it hook around the ligamentum arteriosum on the lower surface of the aortic arch .
It ascend to the neck along the lf groove between trachea and esophagus closely related to the medial surface of thyroid gland and inf. Thyroid art.
Each RLN enter the larynx behind the cricothyroid joint inside the ligament of burry accompanied by the inf laryngeal art (br,of inf,thyroid art)
BRANCHES OF RLN.
A- MOTOR to all laryngeal m. except cricothyroid m.Also give twigs to the trachea ,esophagus and inf constrictor m. of pharynx.
B- SENSORY; to the mucous membrane of lower ½ of larynx. (below the vocal cord)
11 accessory nerve
Type ; purely motor nerve.Origin ; it arise by 2 roots cranial &spinal
Cranial root ; arise from post sulcus of medulla
Spinal root; arise from the upper 5 or 6 cervical segments of the spinal cord.
* the spinal root ascend through foramen magnum to joint the cranial root inside the cranial cavity.
* the united accessory n leave the cranial cavity through middle compartment of the jugular foramen.
* just below the jugular foramin the 2 root separate from each other
Spinal root pierces the deep surface of ster. mastoid m supplying it
* it cross the post. Triangle of the neck finely pierce the trapezius m and supplying it.Branches of accessory nerve
1- cranial accessory n.;
A- pharyngeal br. (supplying all m. of pharynx except stylopharangeus m and all muscles of palate except tensor palati m.
B- laryngeal br. Supplying the muscles of larynx
2- the spinal accessory n– supplying 2 muscles sternomastoid &trapizious m
Hypoglossal nerve
Type ; purely motor nerve .
It supply all intrinsic &extrinsic muscels of tongue except palatoglossus.
Origin ; from antlateral sulcus of medulla.
* it leaves the cranial cavity through the ant condylar foramen
It descend deep to the styloid process stylohyoid m. and post belly of diagastric m.
Branches of hypoglossal n;
1- n.to styloglossus m2- n. to hypoglossus m
3- n. to genoglossus m
4- n. to all intrensic m of tongue;
Palatoglossus not involved.
Cervical plexusLying in the upper part of neck
Forming by ant.rami of c1,2,3,4
Each ventral rami dividing to ascending and descending br,
Lymphatic drainage of the h&n
The lymphatic tissue of the head & neck forms 1/3 of the lymphatic tissue of the whole body.The lymphatic tissue of H&N divided to a- the adenoid tissue b- the lymph nodes;
Adenoid tissue
Its aggregation of lymphoid tissue which guards the entrance of the elementary & respiratory tracts;
Its forms a ring called the lymphatic ring of Waldeyer which includes;
1-superioly ; the nasopharyngeal tonsil at the roof of the post .wall of the nasopharynx
Inferioly; the lingual tonsil on the dorsum of the post 1/3 of the tongue.
Lateraly; the palatine tonsils one on either side of the nasopharangeal isthmus between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds.
Drainge ; efferent lymphatics from the Waldeyer’s ring drain into the upper deep cervical l.n
Lymph nodes of the h&n
The lymph nodes of the head &neck are arranged inA- superfaicial circular group
B- deep circular group
C- vertical chain in between the 2 circular groups
The superfacial and deep circular groups drain into the vertical group which is called deep cervicalL.N lying along side the IJV deep to sternomastoid m.
The superfacial circular l.n of the head
1- occipital l.n along the occipital art. Drain to upper deep cervical l.n2- post auricular l.n along the post auricular v. Drain to upper deep cervical l.n
3- parotid l.n (superfacial &deep) on the surface of parotid and embedded inside it. Drain to superfacial & deep cervical L.N
4- buccal l.n along the facial vessels on the buccinators m & the mandible drain to submandibular L.N.
The superfacial circular l.n of the neck
1- submental l.n in submental triangle drained from tip of the tongue and floor of mouth send to submandibular & lower deep cervical l.n2- submandibular l.n in submandibular area drain most of the face (cheeks, lip, nose) ,floor of the mouth ,side of the tongue send to upper deep cervical & lower deep cervical l.n
3- ant, cervical l.n lie along the ant.j. vein drain ant region of the neck below hyoid bone send to pretrachial l.n & upper deep cervical l.n
4- superficial cervical l.n lie along the ext j.v. on sternomastoid m. drain lobule of ear & ext. auditory meatus + parotid gland send to upper and lower deep cervical l.n.
The deep circular l.n of h&n
1- retropharangeal l.n lie behind the pharynx in front of prevertibral fascia drain nasopharynx, paranasal sinus. eustachain tube. Sent to upper deep cervical L.N
2- paratracheal l.n lie along side the trachea and eosphagus drain trachea,eosophagus,thyroid gland send to the upper & lower cervical L.N
3- infrahyoid l.n, prelaryngeal l.n,pretracheal L.N all drain the larynx to the upper and lower deep cervical L.N
Vertical group of deep cervical L.N
These are the main L.Nin the neck ,they lie alongside the carotid sheath closely related to the IJV and overlaped by sternomastoid m.The vertival chain ofL.N divided to 2 groups;
A- Upper deep cevical l.n lie along upper part of ijv deep to the sternomastoid
B- lower deep cervical l.n lie along the lower part of ijv deep to the sternomastoid m.
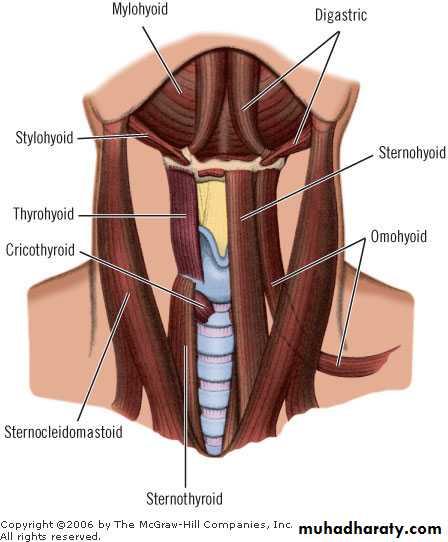
Hyoid bone
Site ; below the tongue and infront of the epiglotisStractures; body ,2 lesser horns ,2 greater horns
Functions; act as a centre for m. acting on tongue, pharynx & larynx.