Ketone Bodies Metabolism
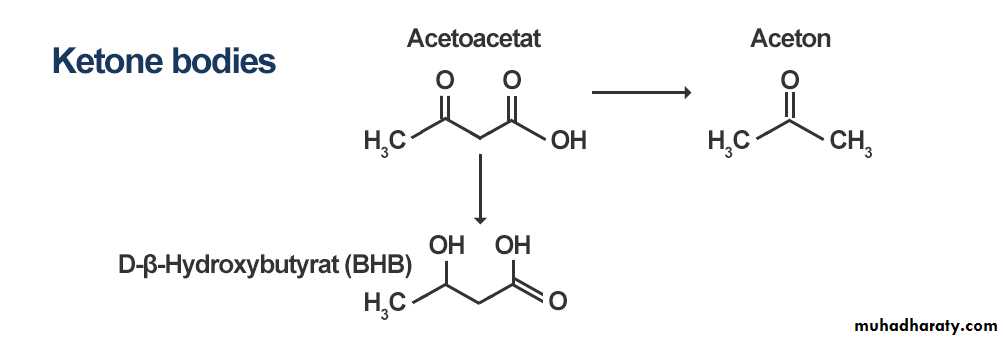
Under certain metabolic conditions associated with high rate of fatty acid oxidation ,the liver produce a considerable quantities of acetoacetate and β-hydroxy butyrate which pass by diffusion from the liver to the blood. Acetoacetate undergo spontaneous decarboxylation to acetone. These three compounds [acetoacetate (acetoacetic acid)+ β hydroxy butyrate+ acetone] are collectively called ketone bodies.
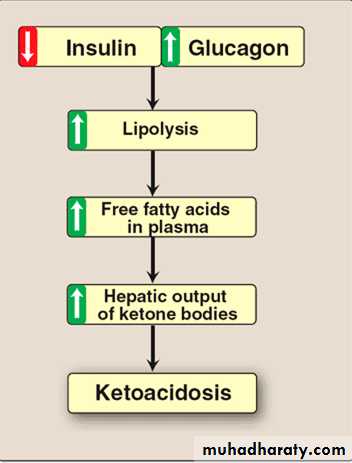
When the liver is flooded with fatty acids mobilize from adipose tissue (ex: in uncontrolled diabetes) the resulting elevated acetyl CoA stimulate pyruvate carboxylase (increase in gluconeogenesis) so oxaloacetate will be directed to gluconeogenesis rather than citric acid cycle, therefore; acetyl CoA cannot be utilized efficiently by citric acid cycle so it directed to ketone bodies formation.
KETOGENISIS
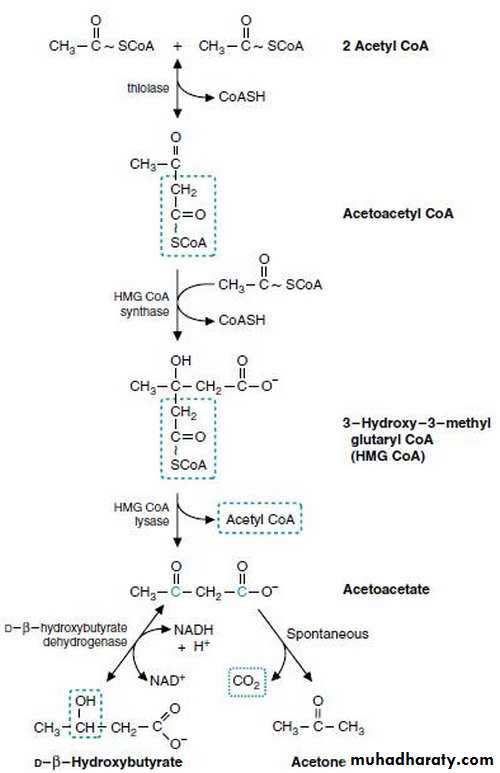
The formation of the ketone bodies is happen in the liver mitochondria. The starting material is acetoacetyl CoA which come from two sources:During the course of β oxidation pathway (the last four carbon atoms)
By condensation of two molecules of acetyl CoA.
In the liver mitochondria the following reaction will occur:
The acetoacetyl CoA will react with acetyl CoA lead to the formation of HMG CoA {beta – or three- hydroxy methyl glutaryl CoA}.This reaction catalyzed by the enzyme HMG CoA synthase. This is the rate limiting step in the formation of the ketone bodies.By the action of the second enzyme HMG CoA Lyase the HMG CoA will be converted to Acetoacetate (the first ketone body).
Acetoacetate can be reduced to β hydroxy butyrate (the second ketone body) by the action of enzyme β hydroxy butyrate dehydrogenase and in reversible reaction. or the acetoacetate can be spontaneously decarboxylated in the blood to Acetone (the third ketone body) which is volatile and nonmetabolized compound and exhaled in the breathing .
β hydroxy butyrate is quantitatively the predominant ketone bodies found in the blood and urine of uncontrolled diabetes (diabetes with ketosis).
Q. Why the β hydroxy butyrate is quantitatively the predominant ketone bodies found in the blood and urine ?
Because the formation of the ketone bodies is the result of increase the rate of β oxidtion that result in increase the production of NADH (more than the NAD) this NADH catalyze the conversion of acetoacetae to β hydroxy butyrate.
UTILIZATION OF KETON BODIES
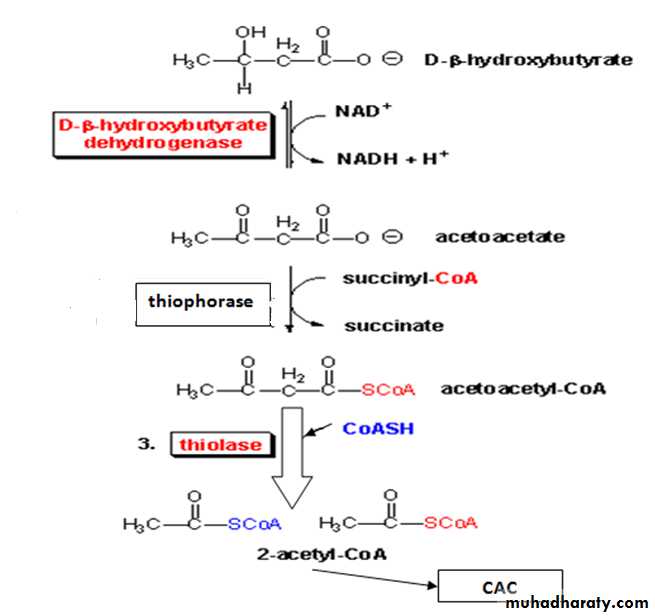
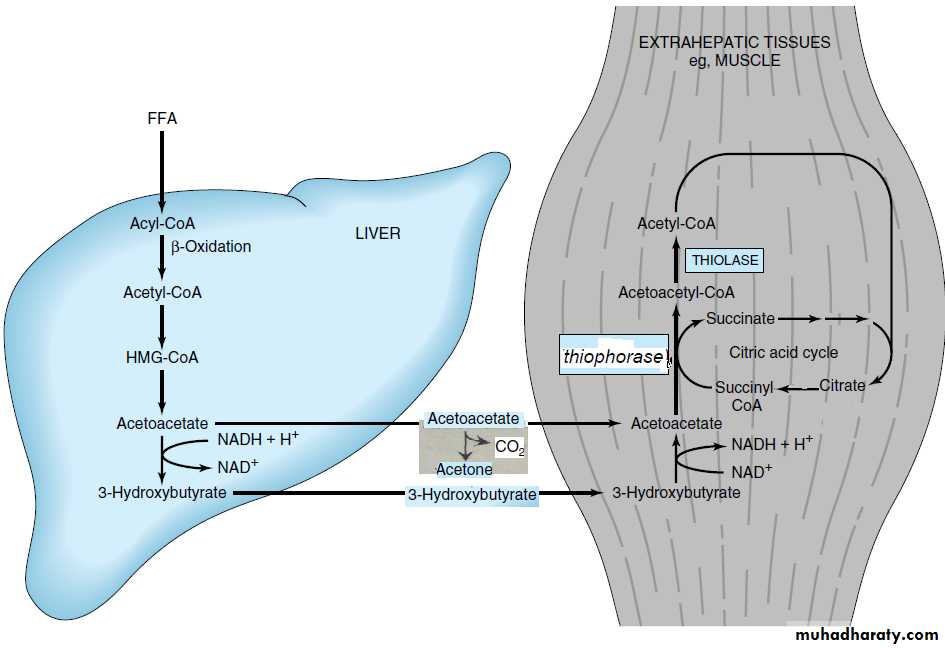
the liver is equipped with an active enzymatic mechanism for the production of ketone bodies but it cannot be metabolized further these ketone bodies ,however these ketone bodies can be used as energy source by skeletal muscles, heart muscles and to limited extent by brain.(that mean the ketone bodies just like the lactate are waste product to the liver but energy source to other organs).
β Hydroxy butyrate will converted back to acetoacetate by the same reversible reaction that catalyzed by β hydroxy butyrate dehydrogenase.
The causes of ketosis mainly :
1-Uncontrolled diabetes (type 1).
2-Starvation.
MECHANISM OF KETOSIS
When the rate of ketone bodies production exceed the rate of utilization, there blood level rises this condition called (ketonemia)and eventually when exceed the renal threshold will excreted in urine and this condition called (ketonuria) which often seen in cases of uncontrolled type 1 diabetes.
In individual with sever ketosis the blood level of ketone bodies may reach 90 mg/dl (n.v less than 3mg/dl) and the urinary ketone bodies may rises up to 5000 mg/24 hour and the smell of acetone may sense in the breathing of the patient.
Increase in blood ketone bodies lead to acidosis because the acetoacetate and the β hydroxybutyrate are acids (as the carboxyl group of acetacetate has Pka value of 3.8 and β hydroxy butyrate 4.8 therefore they loss there hydrogen when circulating in the blood which lower the PH of the blood) also the excretion of glucose and ketone bodies in urine cause to diuresis leading to dehydration {decrease in plasma volume} so increase in hydrogen ion in the blood associated with decrease the plasma volume leading to sever KETOACIDOSIS.