HISTOLOGY OF
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
Dr. Hammed N. Mousa
Associate Professor
Department of pathology.
Contents
• Oesophagus
• Stomach
• Small Intestine
• Large Intestine
Histology of the Digestive System
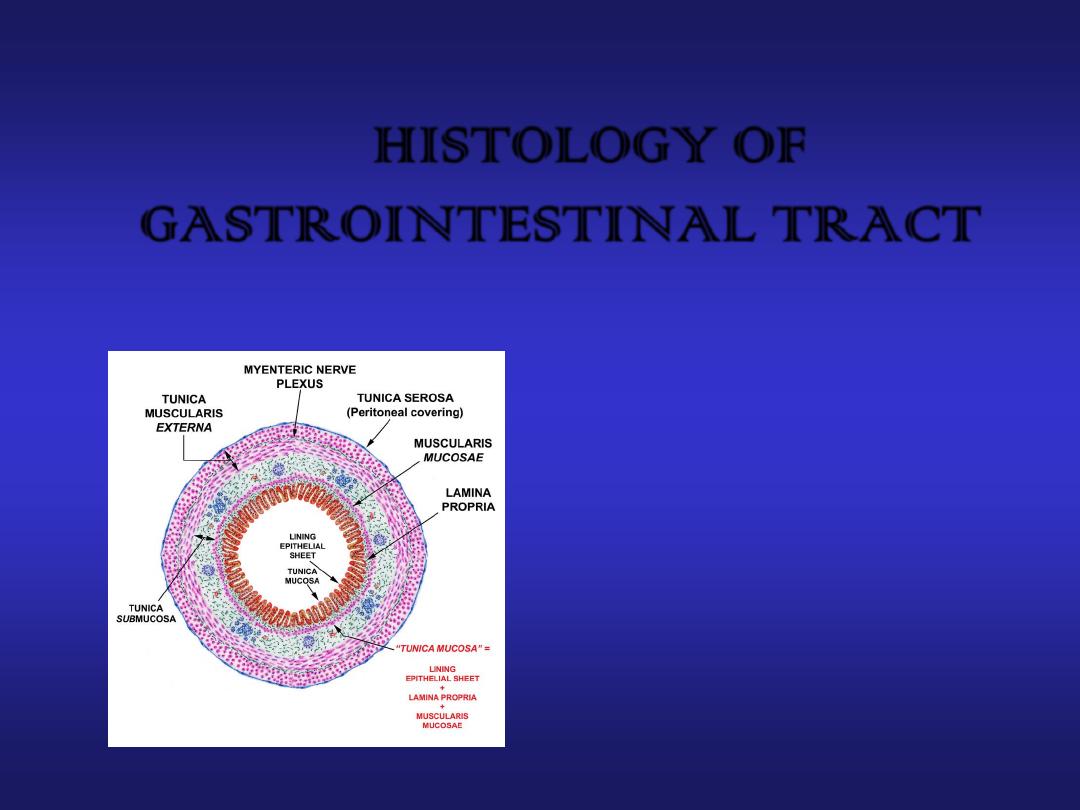
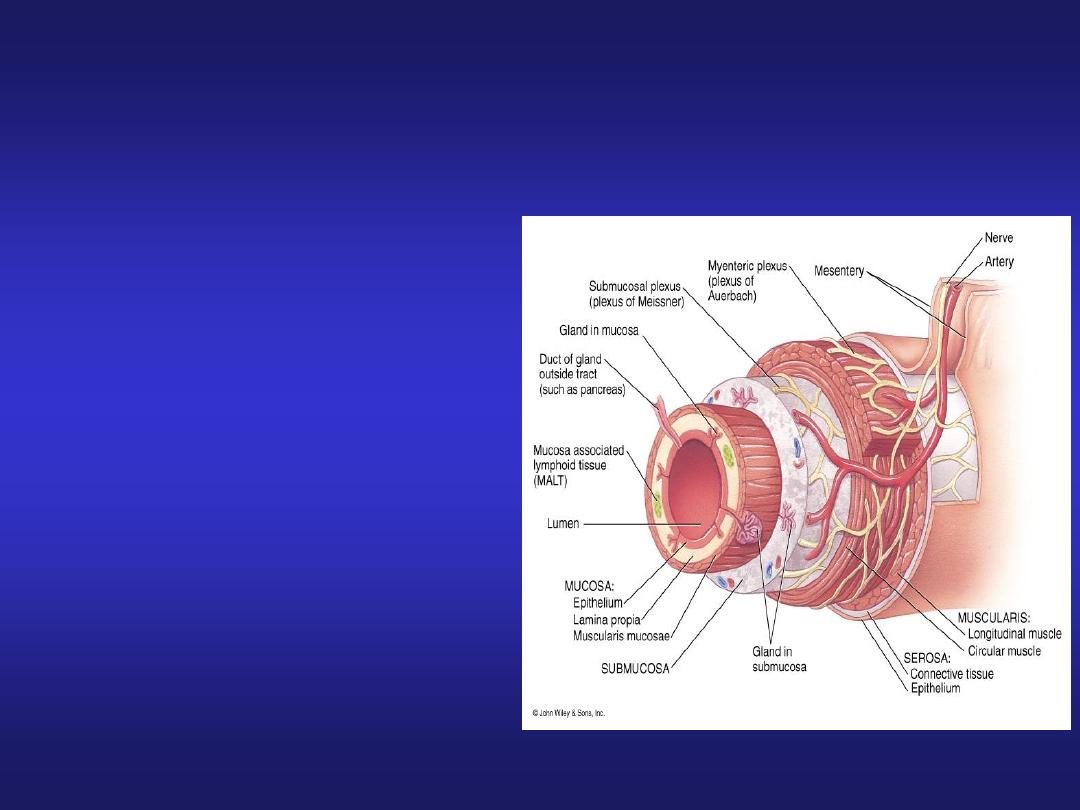
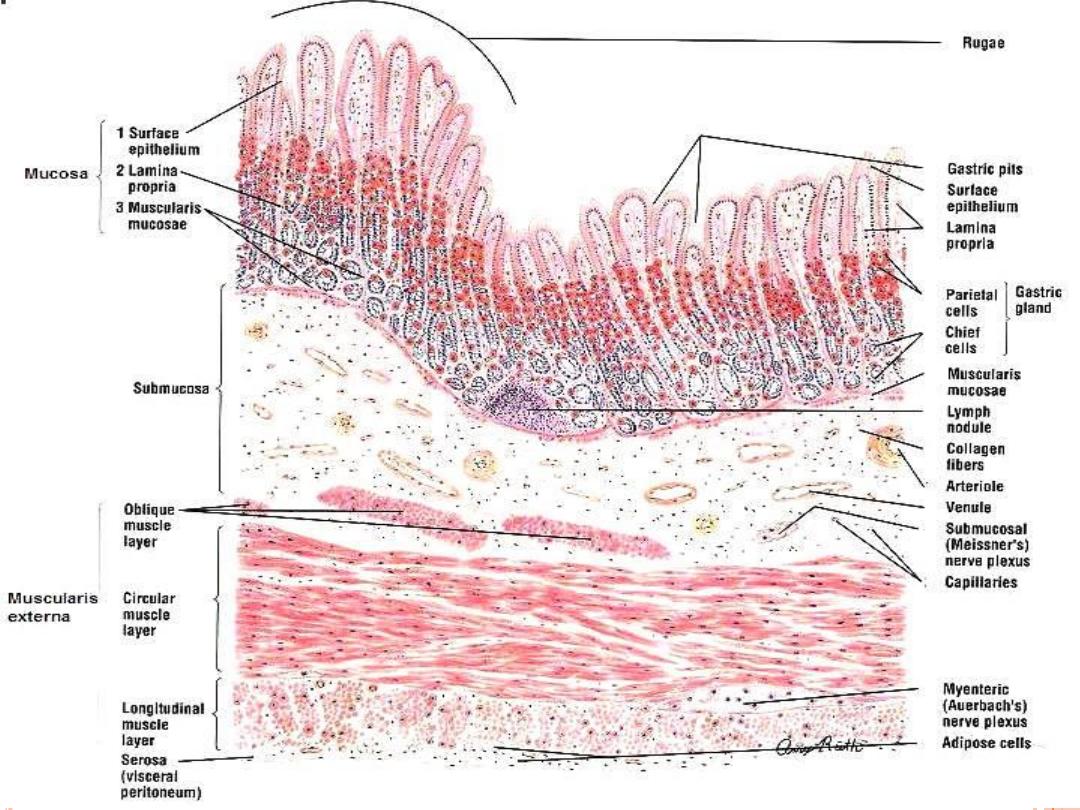
Basic Histological Layers:
1.
Mucosa:
a. Epithelium
b. Lamina Propria
c. Muscularis Mucosae
2.
Submucosa:
Submucosal plexus
“Plexus of Meissner”
3.
Muscularis:
Myenteric plexus
“Plexus of Auerbach
4.
Serosa
Histology of the Mucosa
Organ
Epithelium
Mouth
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous
Pharynx
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous
Esophagus
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous
Stomach
Simple Columnar
Small Intestine
Simple Columnar
Large Intestine
Simple Columnar
Anus
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous
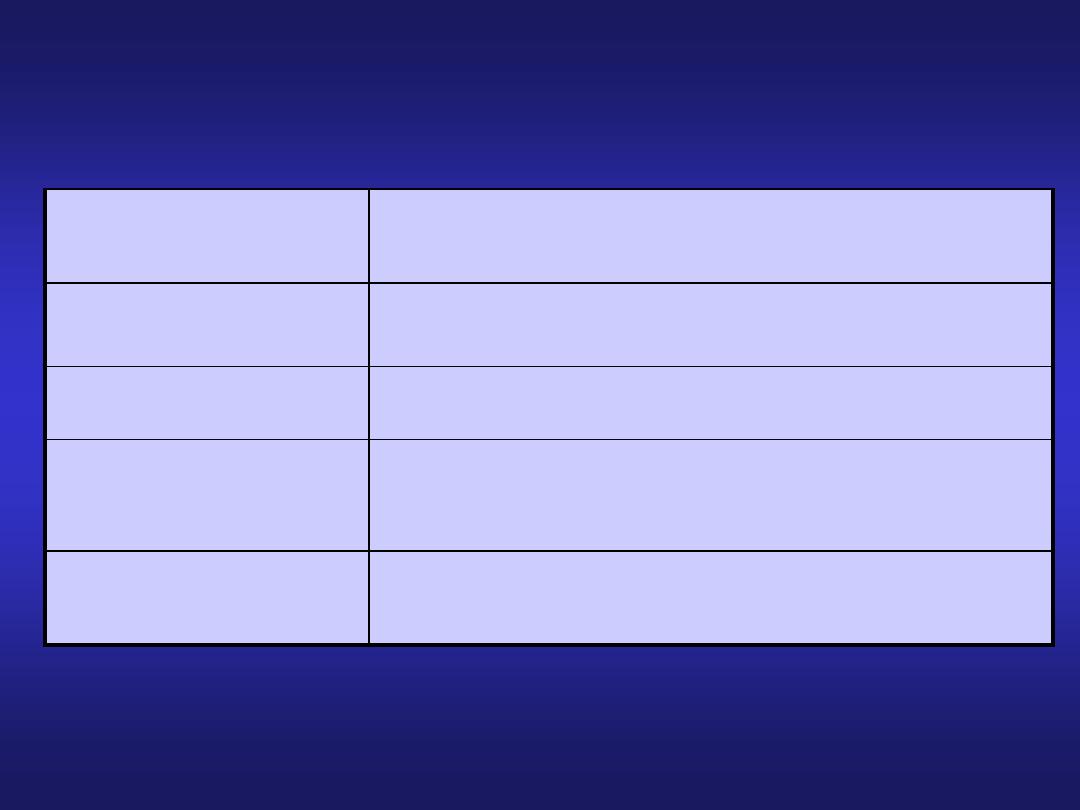
Histology of the Mucosa
Organ
Folds of the epithelium
Esophagus
none
Stomach
L: Rugae, S: gastric pits
Small Intestine
L: Plicae circulares, Villi S: Crypts
of Lieberkuhn, microvilli
Large Intestine
L: Haustra S: Intestinal glands
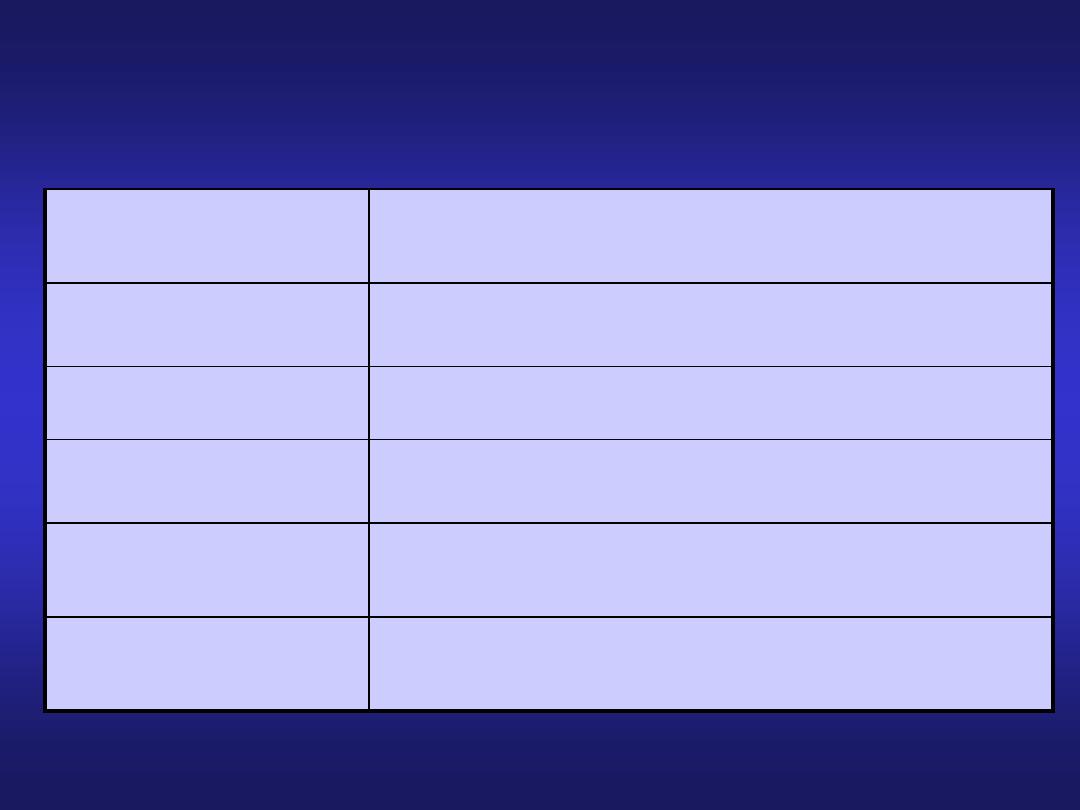
Histology of the Submucosa
Organ
Specialized structures
Esophagus
Submucosal mucous glands
Stomach
None
Duodenum
Brunner’s glands
Ileum
Peyer’s Patches
Large Intestine
None
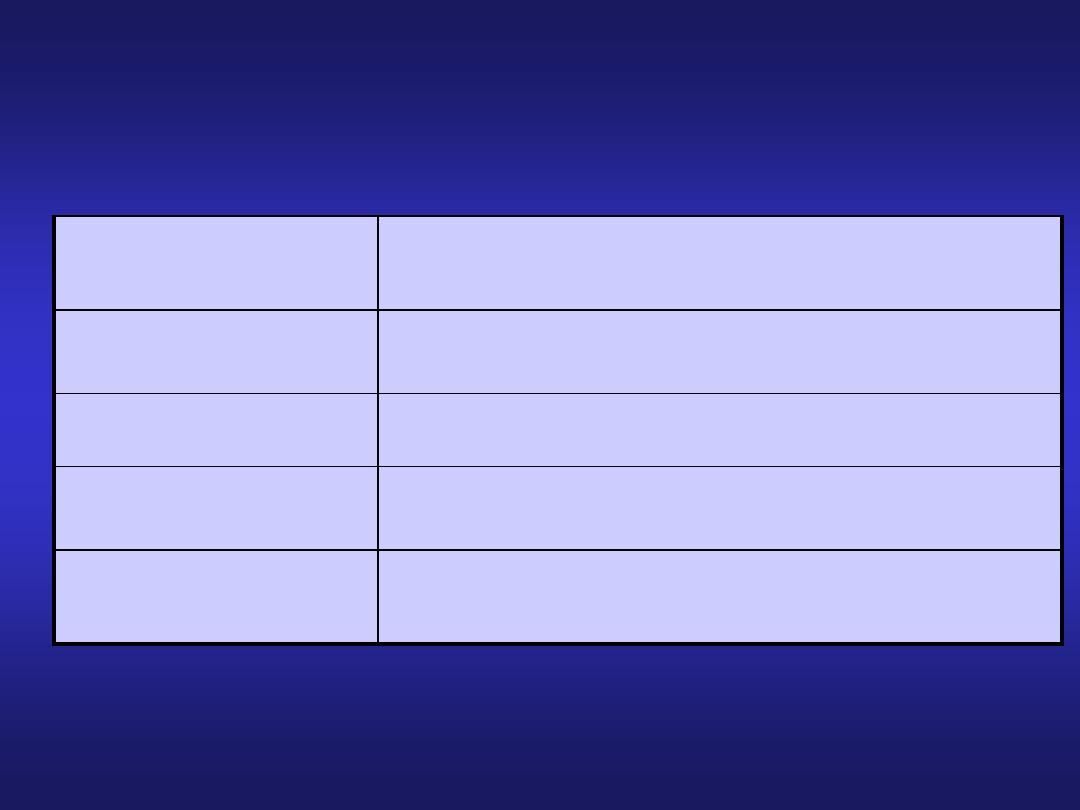
Histology of the Muscularis
Organ
Smooth muscle layers
Esophagus
2, circular and longitudinal
Stomach
3, oblique, circular, and longitudinal
Small Intestine
2, circular and longitudinal
Large Intestine
2, circular and longitudinal
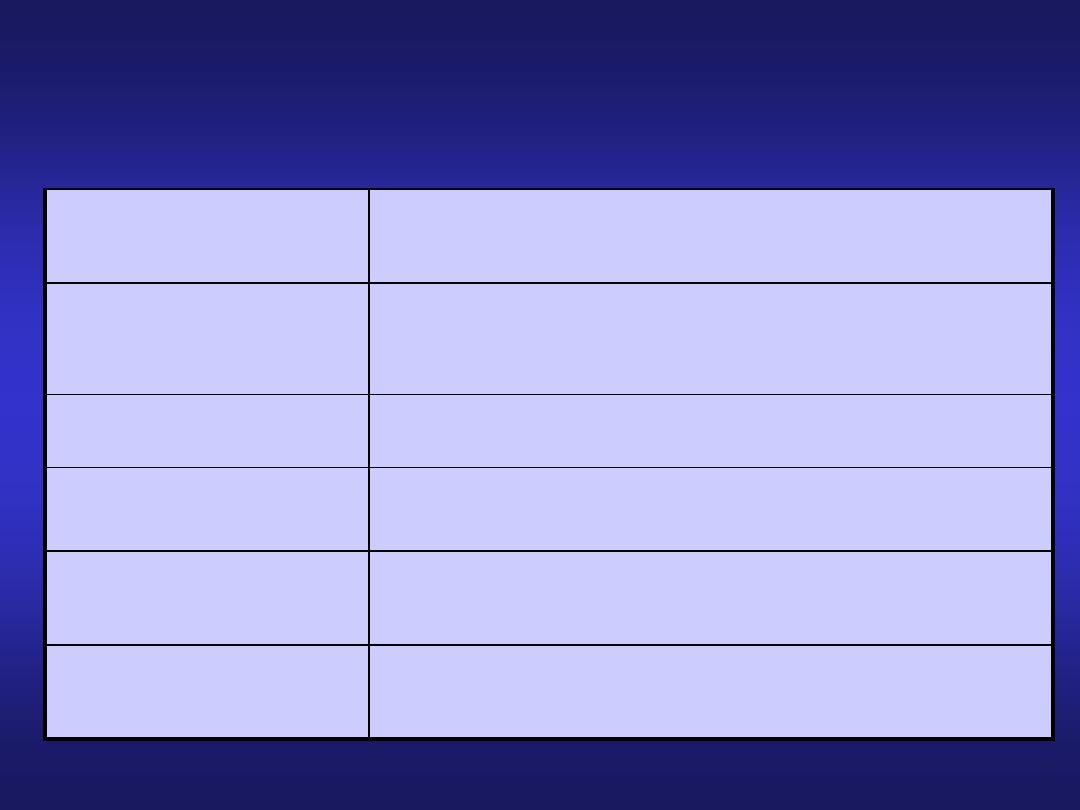
Histology of the Serosa
Organ
Serosa
Esophagus
Adventitia due to the fact that the
esophagus is not in a cavity
Stomach
Visceral Peritoneum
Small Intestine
Visceral Peritoneum
Large Intestine
Visceral Peritoneum
Anus
Adventitia
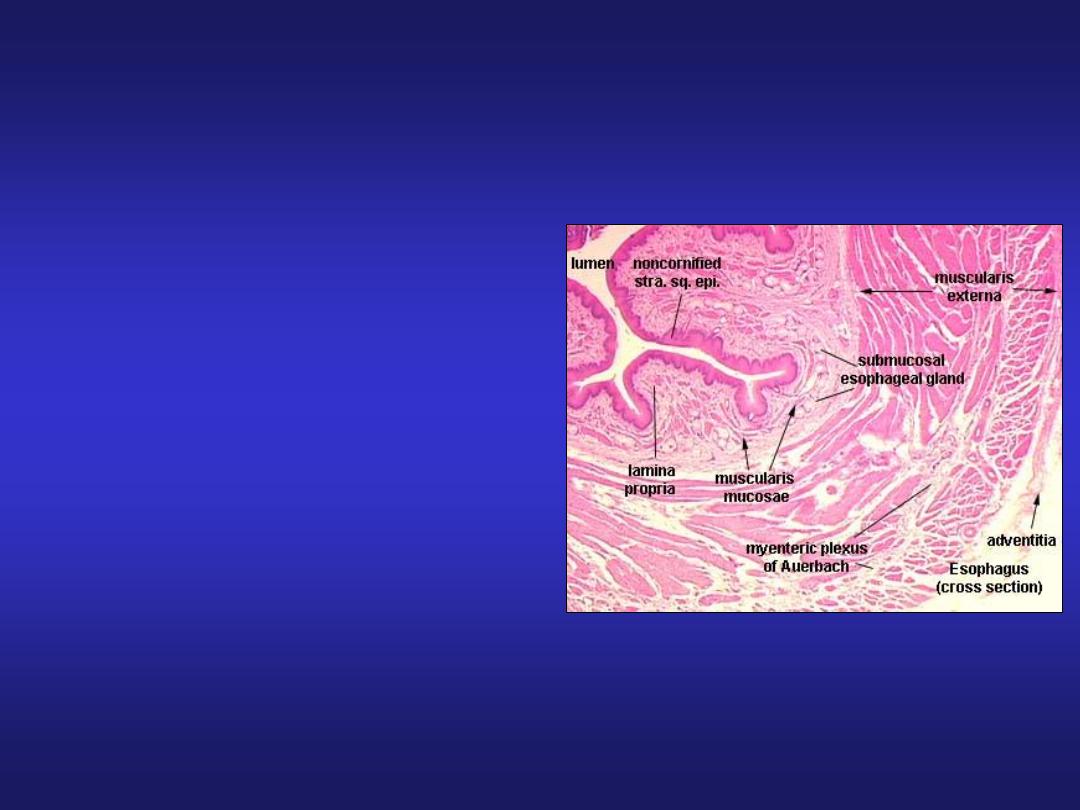
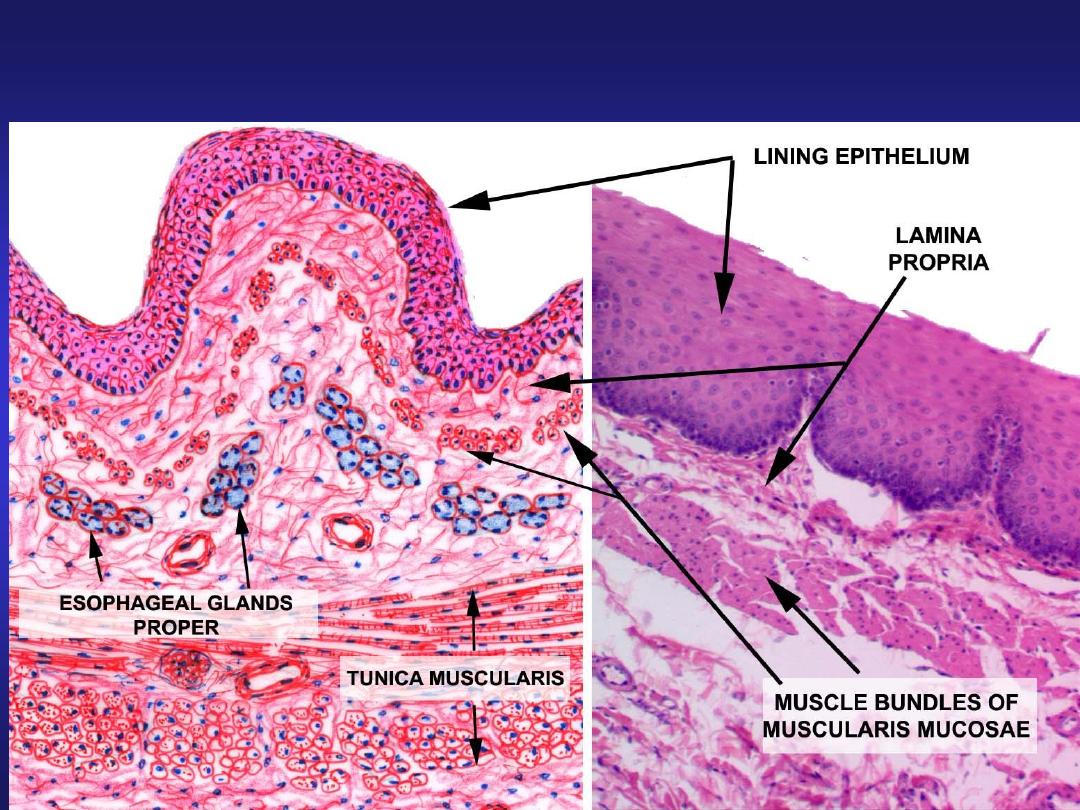
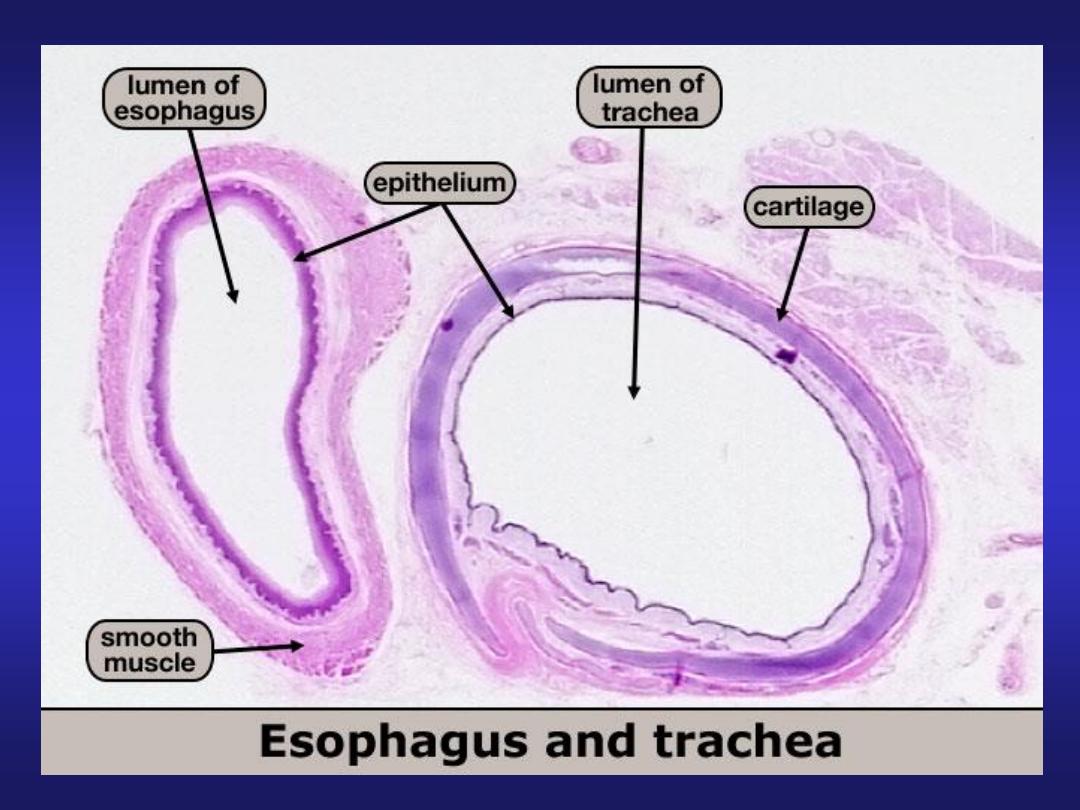
Oesophagus
• Mucosa: Stratified squamous
non - keratinized epithelium
• Submucosa: contains
Meissner’s plexus and
oesophageal glands
• Muscularis externa:
Upper one-third: skeletal fibres
Middle one-third: mixed fibres
Lower one-third: smooth fibres
• Adventitia: loose connective
tissue
Oesophagus
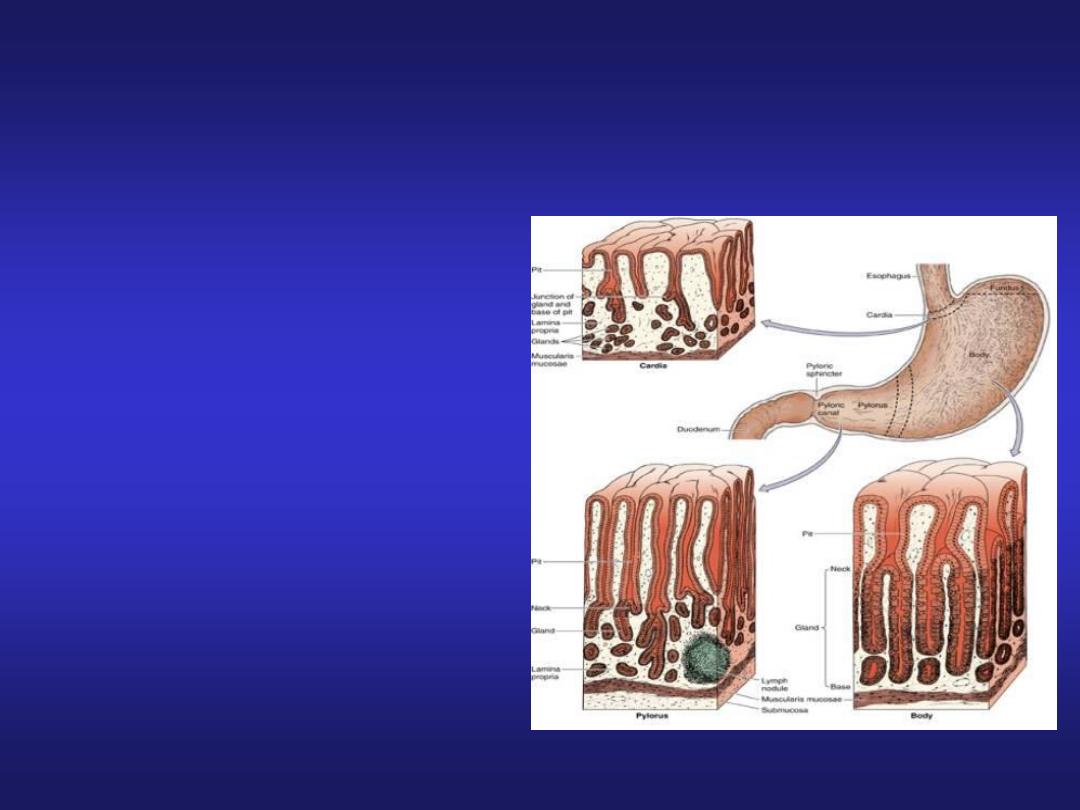
Stomach
• Mucosa:simple columnar
epithelium and presence of
gastric pits.
• Stomach is divided into
three histological regions on
the basis of nature of glands:
Cardiac region
Fundic region (fundus &
body)
Pyloric region
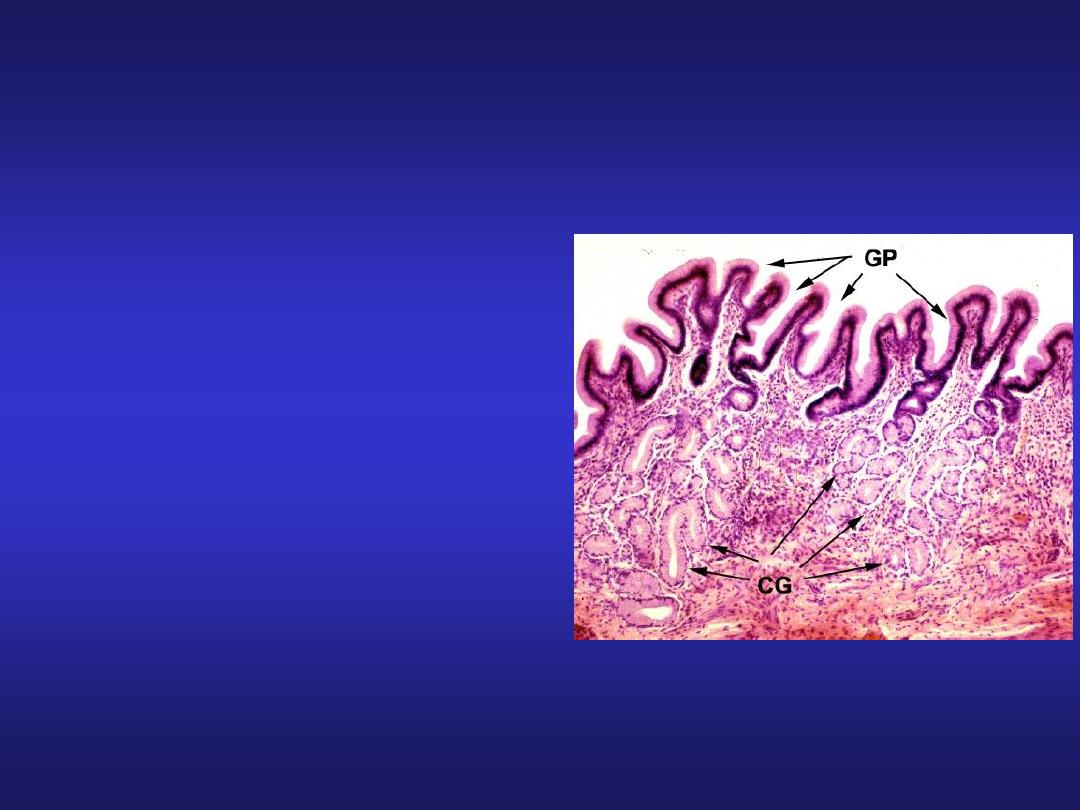
Stomach (Cardiac Region)
• Mucosa: simple columnar
with oval nuclei, mucous
secreting cardiac glands in
lamina propria.
• Submucosa: connective
tissue.
• Muscle layer: inner
circular, outer longitudinal.
• Serosa: simple squamous
epithelium.
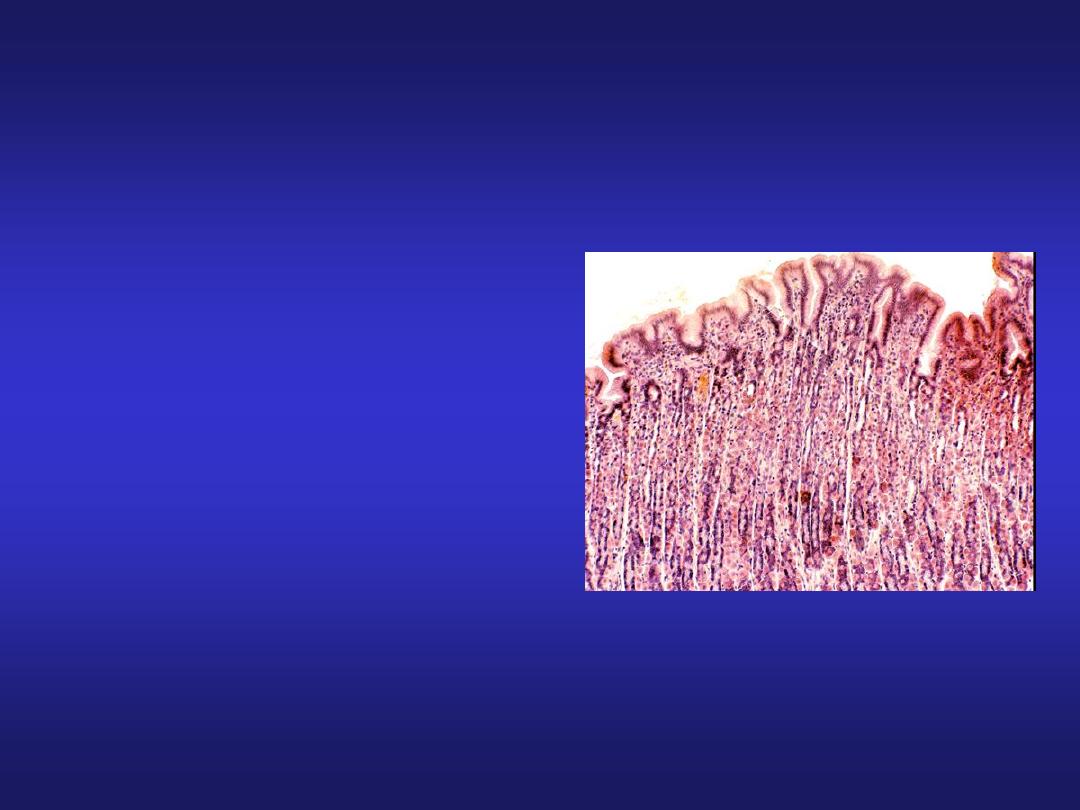
Stomach (Fundic Region)
• Mucosa: simple columnar
with oval nuclei, presence
of gastric glands in lamina
propria.
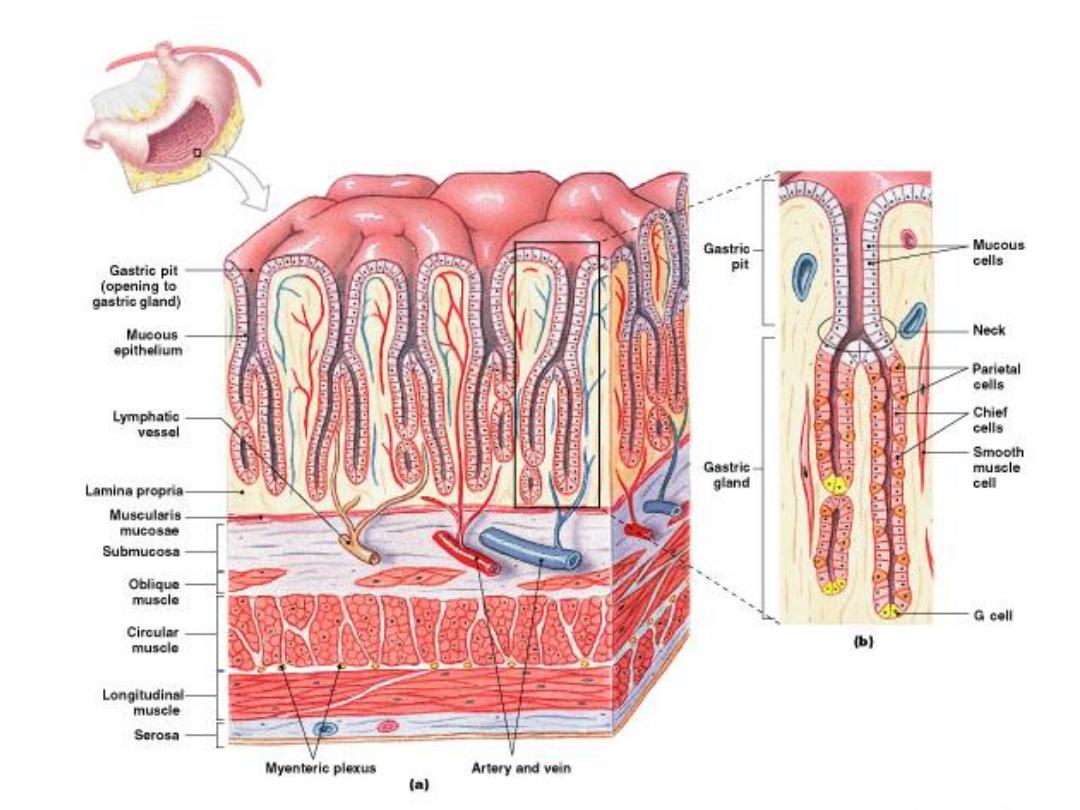
Figure 24–13
The Stomach Lining
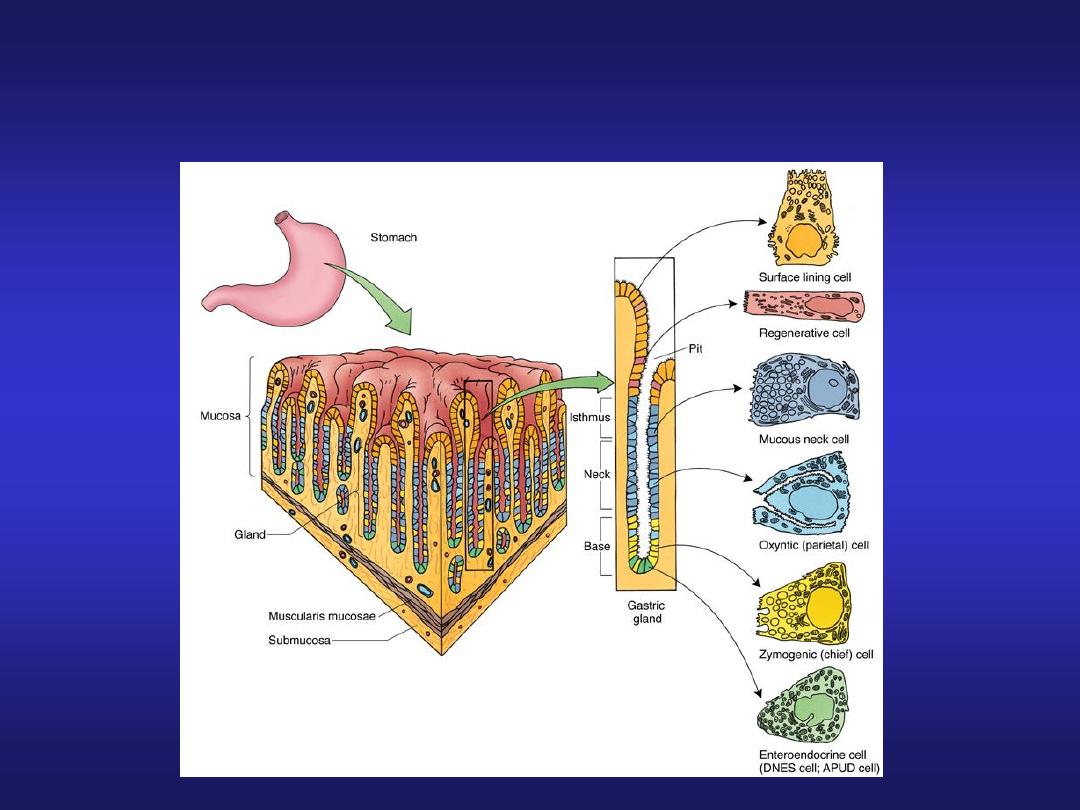
Gastric Glands
• Found in
fundus
and
body
of stomach, extend deep
into underlying lamina
propria
• Secrete gastric juice,
mucus, and gastrin
• Each gastric pit
communicates with several
gastric glands
• Two types of secretory cells
in gastric glands secrete
gastric juice:
– parietal cells
– chief cells
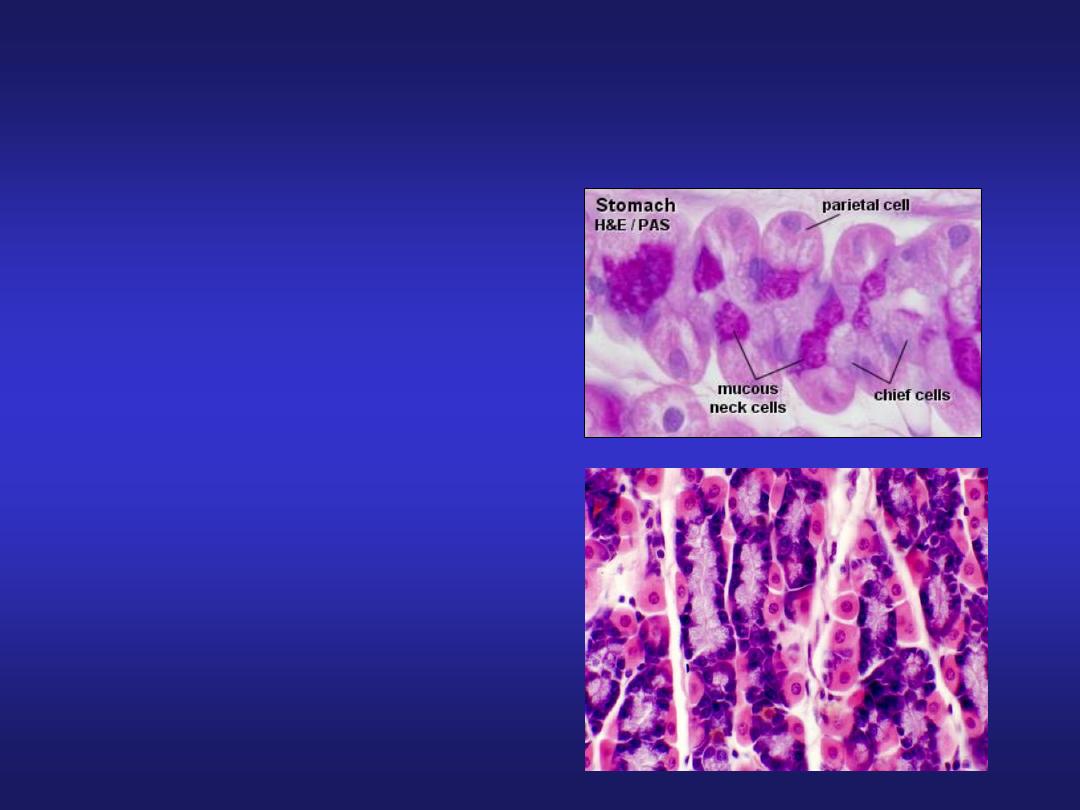
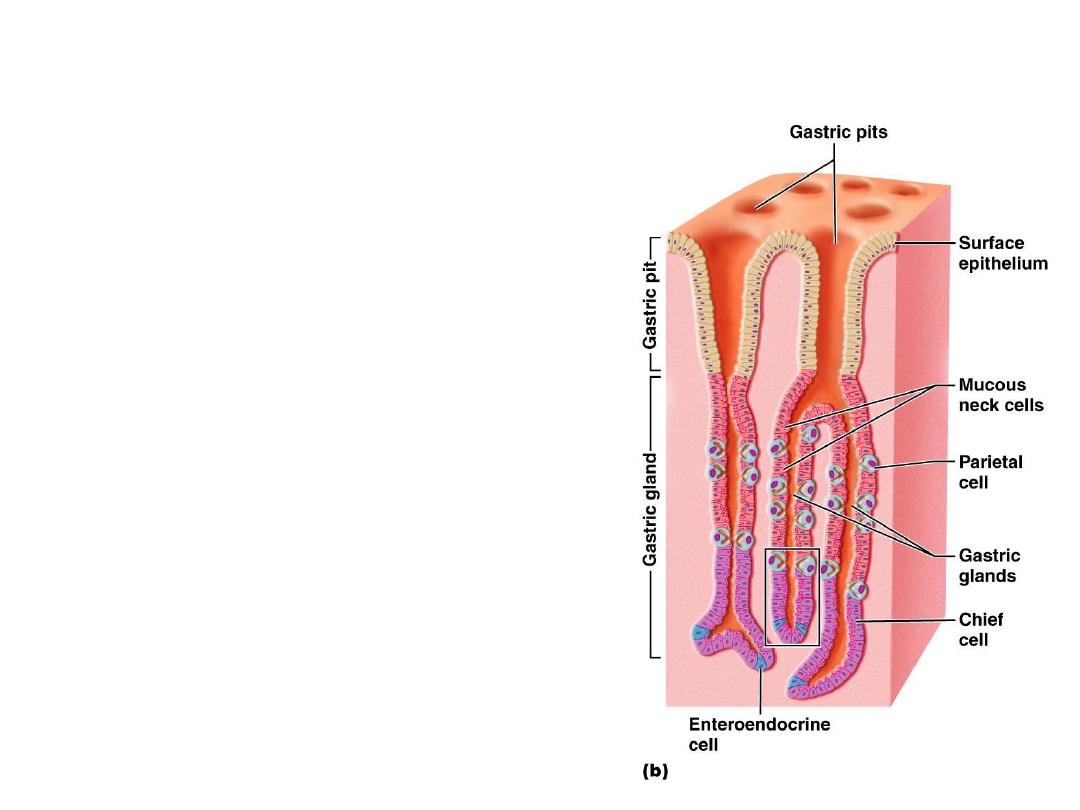
Stomach (Fundic Region)
Cells of fundic region:
• Mucous neck cells
• Parietal (oxyntic) cells
• Chief (peptic/zymogen) cells
• Enteroendocrine cells
• Undifferentiated cells
Cells of fundic region
Cells of fundic region
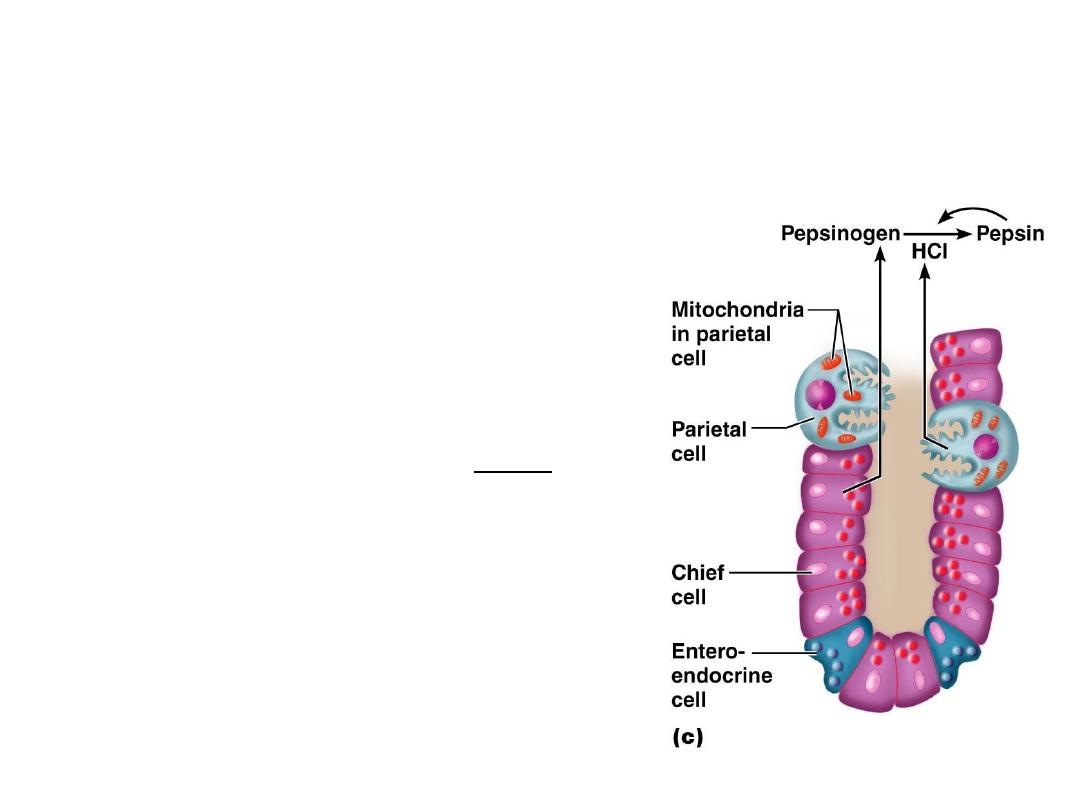
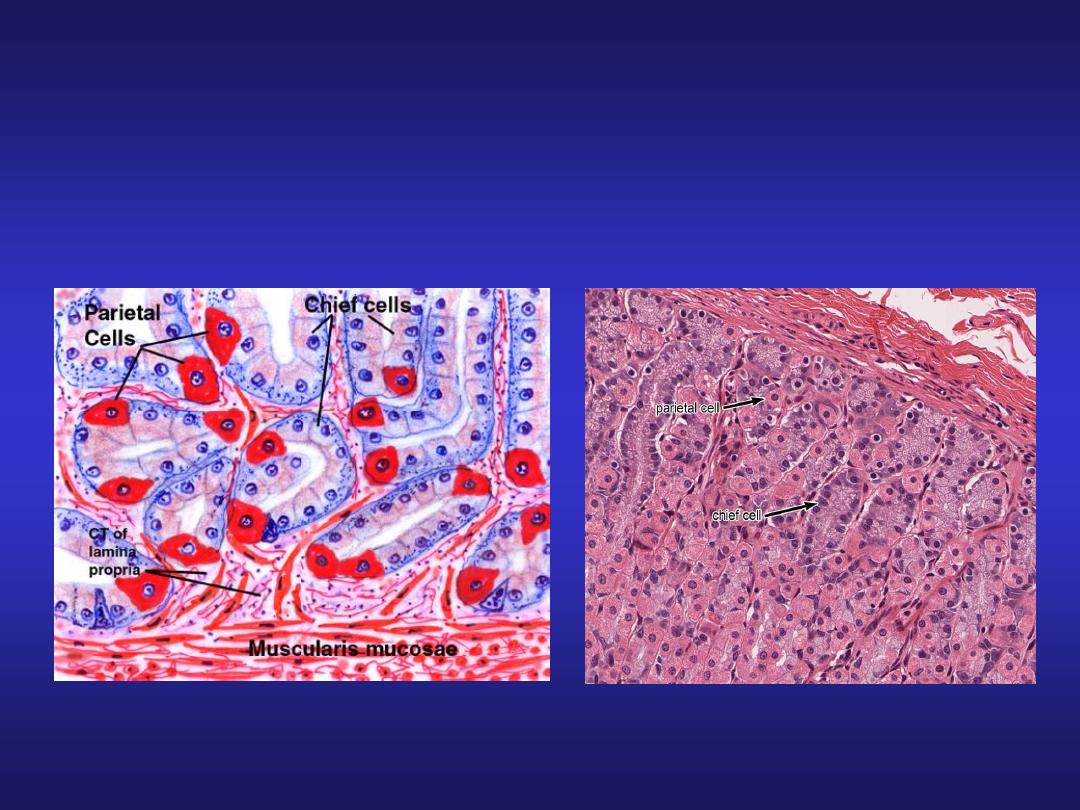
Gastric Gland cells of Fundus and
Body
• Parietal Cells
– Mostly in proximal portions of
glands
– Secrete
intrinsic factor
and
hydrochloric acid
(
HCl)
• Chief Cells
– Most abundant near base of
gastric gland:
– Secrete
pepsinogen
(inactive
proenzyme)
– Pepsinogen is converted by
HCl in the gastric lumen to
pepsin
(active proteolytic
enzyme)
• Enteroendocrine cells.
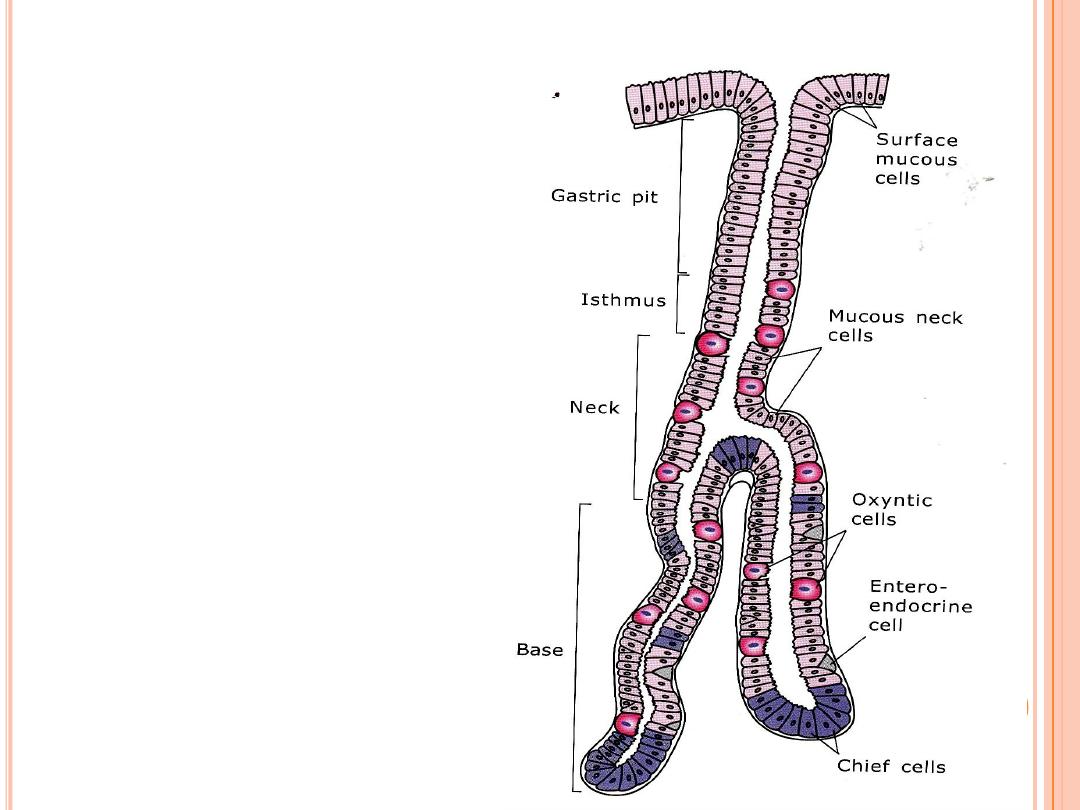
Enteroendocrine and
APUD cells:
- Located in the basal
portion of gastric glands
- Secretes serotonin,
histamine and gastrin.
These are endocrine cells
which release their
products into the blood
vessels.
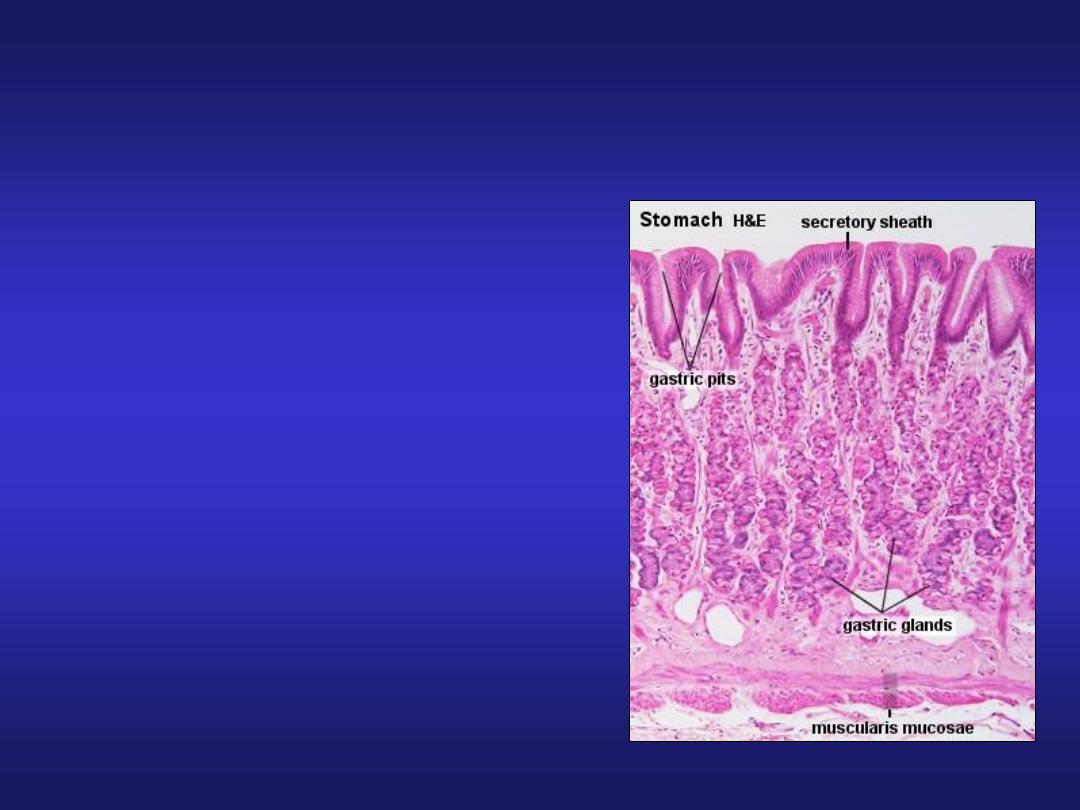
Stomach (Fundic Region)
• Submucosa: contains blood
vessels, lymphatics and
Meissner’s plexus.
• Muscularis Externa: an inner
oblique (absent in pylorus),
middle circular and outer
longitudinal layer.
• Serosa: consist of surface layer
of flattened mesothelial cells
resting on a thin layer of loose
connective tissue with blood
vessels and lymphatics.
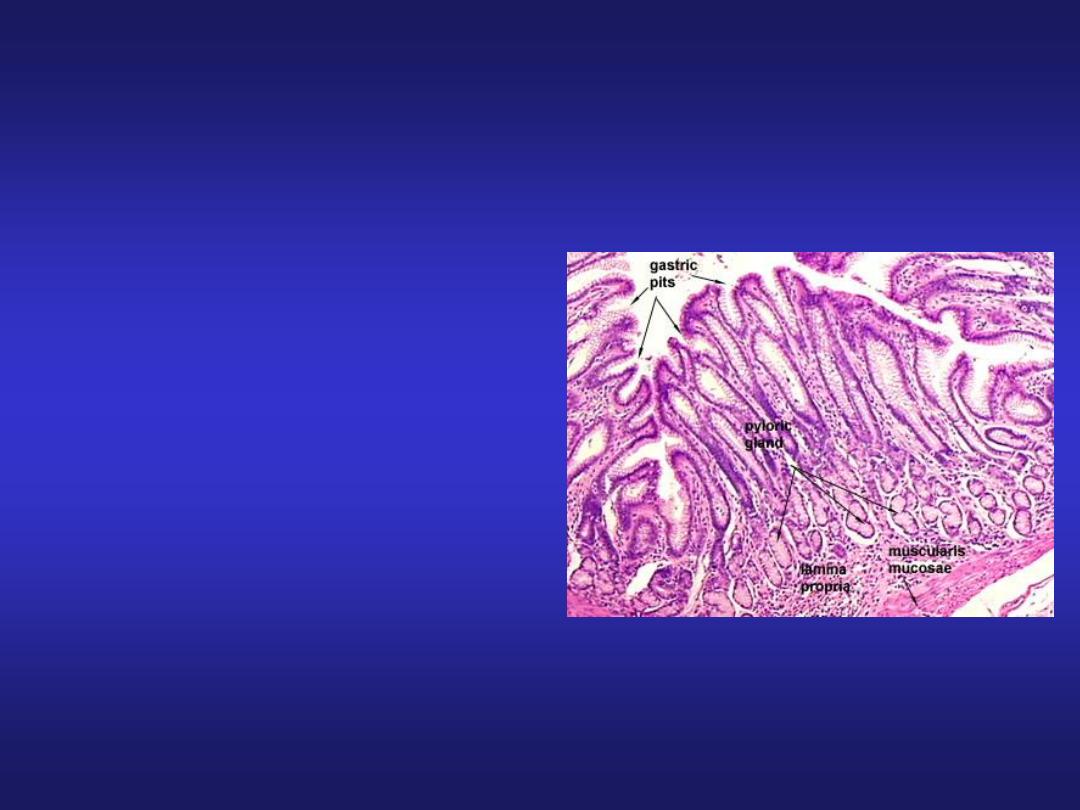
Stomach (Pyloric Region)
• Mucosa: pyloric glands in
lamina propria & deeper
gastric pits extending half
the thickness of mucosa.
• Muscularis Externa: inner
circular (thickened to form
pyloric sphincter) and outer
longitudinal layer.
• Submucosa & Serosa: same
as in fundic part.
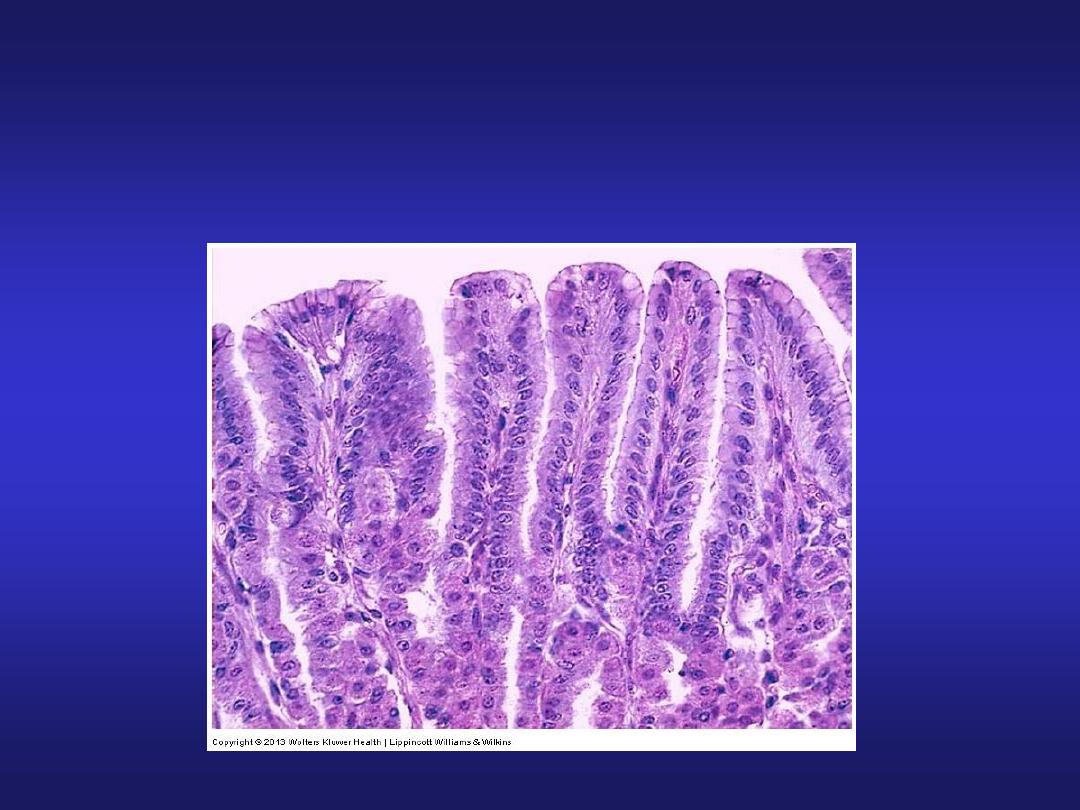
Stomach (Pyloric Region)
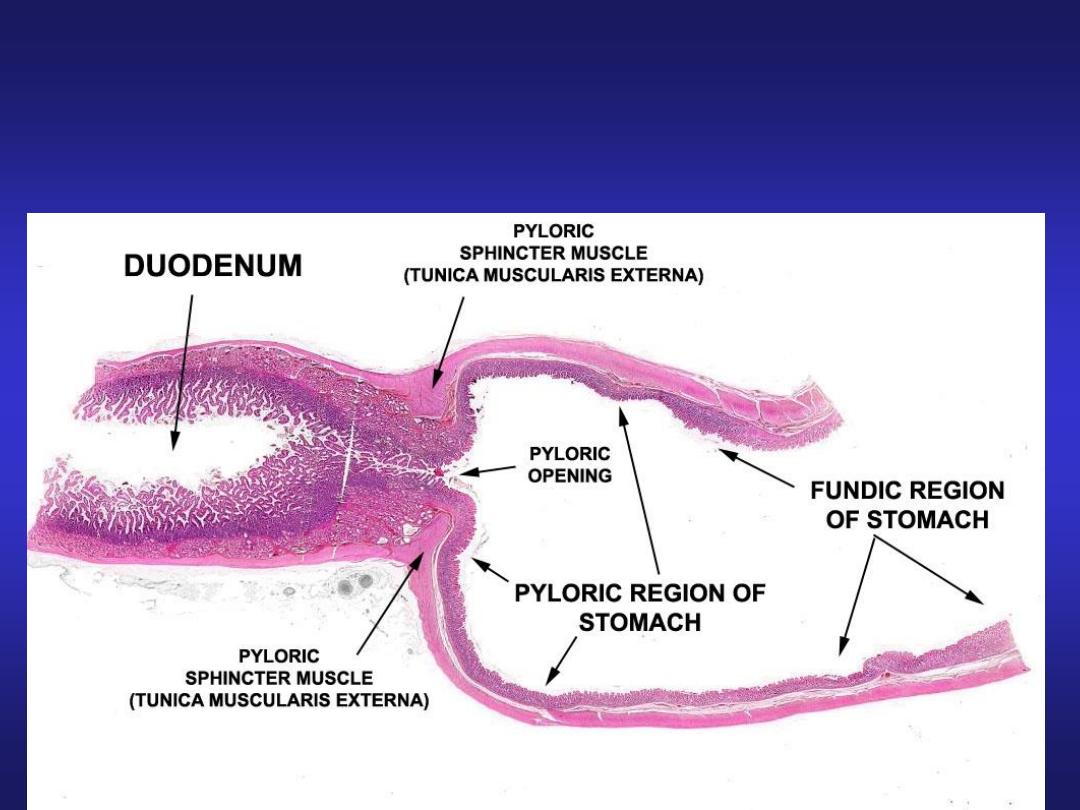
Pyloric Glands

MCQ
Q1. Stratified squamous non-keratinized
epithelium is a feature of:
a. Oesophagus
b. Stomach
c. Appendix
d. Rectum

MCQ
Q2. Deep gastric pits is a feature of:
a. Oesophagus
b. Cardiac part of stomach
c. Fundic part of stomach
d. Pyloric part of stomach
