Odontogenic infections
2019-2020Treatment of periapical abscess
Drainage :1-through the root canal pathway or cortical trephination.
2- incision and drainage in the vestibule
( labial , buccal, lingual and palatal) with or without drain .
3- extra oral incision and drainage with drain placement ( corrugated drain, or iodoform drain).
4- antibiotics, analgesics, mouth wash.
5- definitive treatment ( extraction, root canal therapy , periapical surgery and then the final restorative procedures).
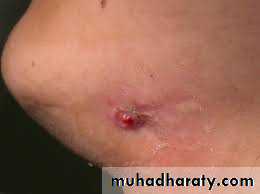
Sinus tract E.O
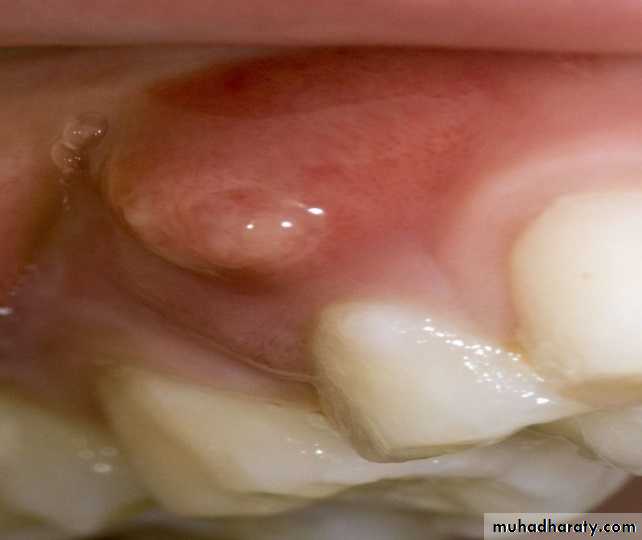
Sinus tract I.O
Sinus tract : is a tract leading from enclosed area of infection to an epithelial surface .
It is usually associated with chronic P.A abscess in general, although in acute exacerbation of chronic abscess is also observed (pheonix abscecss) .
Factors that determine the extent of infection are:
1- microbial virulence, number and toxic factors produced and released by infecting microbes.2- host defense mechanisms. Like medical status, extremes of age.
3- local anatomic factors like the blood supply, muscle attachments, and density or thickness of the bone.
From the site of the initial lesion, inflammation may spread in three ways:
1. By continuity through tissue spaces and planes.
2. By way of the lymphatic system.
3. By way of blood circulation.
Spread of infection Inside Tissues
Anatomical factors influencing the direction of spread with in the tissue
Spread of Pus Inside TissuesThe most common route of spread of inflammation is
by continuity through tissue spaces and planes and usually pus is formed in the cancellous bone, and spreads in various directions by way of the tissues presenting the least resistance.
Whether the pus spreads buccally, palatally or lingually depends mainly on the position of the tooth in the dental arch, the thickness of the bone, and the distance it must travel.
In upper lateral incisor pus may travel
palataly due to palatal orientation of its
root apex .
Spread of Pus Inside Tissues
Purulent inflammation that is associated with apices near the buccal or labial alveolar bone usually spreads buccally, while that associated with apices near the palatal or lingual alveolar bone spreads palatally or lingually respectively.
The important spaces and potential spaces in the vicinity of the jaws are as follows
Potential spacesPotential spaces
Related to the upper jawCanine Fossa Abscess
Anatomic Location. The canine fossa, which is wherethis type of abscess develops, is a small space between
the levator labii superioris and the levator anguli oris muscles.
Canine Fossa Abscess
Treatment. The incision for drainage is performedintraorally at the mucobuccal fold (parallel to the alveolar
bone), in the canine region . A hemostat is then inserted, which is placed at the depth of the purulent accumulation until it comes into contact with bone , while the index finger of the
Non dominant hand palpates the infraorbital margin.
Finally, a rubber drain is placed, which is stabilized with a suture on the mucosa.
SUBMANDIBULAR SPACE
Clinical Presentation. The infection presents as moderate swelling at the submandibular area, which spreads, creating greater edema that is indurated and redness of the overlying skin ,Also the angle of the mandible is obliterated, while pain during palpation and moderate trismus due to involvement of the medial pterygoid muscle are observed as well.
Treatment.
The incision for drainage is performed on the skin, approximately 1.5 cm beneath and parallel to the inferior border of the mandible.During the incision, the course of the facial artery and vein
(the incision should be made posterior to these) and
the respective branch of the facial nerve should betaken into consideration.
A hemostat is inserted into the cavity of the abscess to explore the space and an attempt is made to communicate with the infected
spaces.
Blunt dissection must be performed along the medial surface of the mandibular bone also, because pus is often located in this area as well. After drainage, a rubber drain is placed .