ACUTE ARTERIAL OCCLUSION(Acute Limb Ischemia )
ByDr.Ahmed Abdul-Ameer Daffar
( Cardio-Thoracic &Vascular Surgeon )
Definition
Sudden cessation of limb perfusion.Etiology
Embolism. The heart is the most common source of distal emboli, which account for more than 90% of peripheral arterial embolic events.AF being the most common source
Myocardial infarction
Left ventricular aneurysm
Cardiomyopathy
Valvular heart disease
Subacute bacterial endocarditis
Aortic aneurysm
Native vessel thrombosis
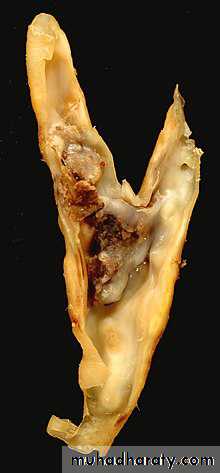
Atherosclerotic plaque rupture
Complication of aneurysm
Reconstruction thrombosis (ex:-thrombosis of a prosthetic conduit)
Trauma
Aortic dissection
• Pathophysiology
The most common cause of acute limb ischemia is embolization and the most common source is the heart and mainly due to AF. The most common site of embolization is the lower limbs. Early intervention may restore limb function and prevent irreversible ischemic changes. Delay of intervention leads to development of irreversible ischemic changes ( gangrene ).
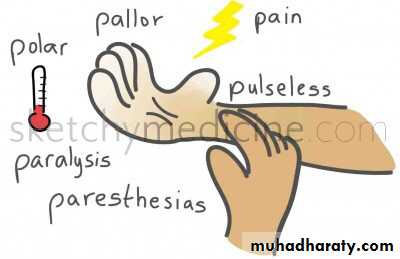
Clinical Manifestations
Acute Limb ischemia manifests with the “six Ps":Pain
Pallor
Paralysis
Paresthesia
Pulselessness
Poikilothermia
The 6 Ps
• Treatment
Anticoagulation with heparin is indicated as soon as possible.IV fluid should be started and a Foley catheter inserted to monitor urine output.
Baseline labs should be obtained including renal & liver function tests, electrolytes, platelet count, ECG, etc….
Analgesia
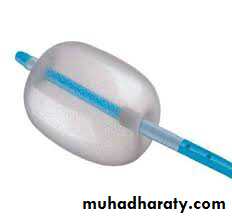
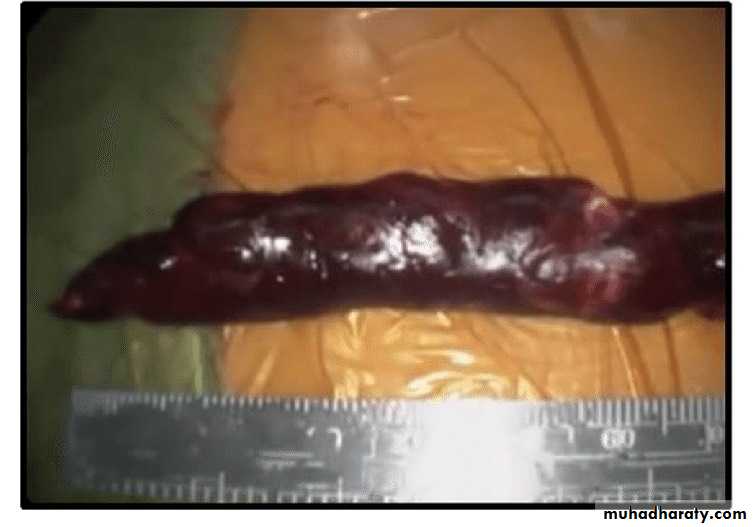
Embolectomy is indicated before irreversible changes appear in the affected limb.
Fogarty Catheter
Embolus
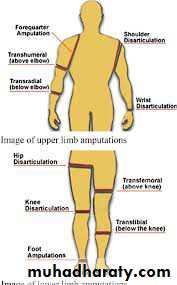
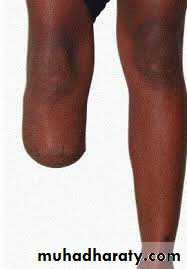
Amputation may be indicated in established gangrene.
Patients with prosthetic limbs
Chronic limb ischemia
ByDr.Ahmed Abdul-Ameer Daffar
( ( Cardio-Thoracic & Vascular Surgeon
Asymptomatic
Intermittent claudicationRest pain
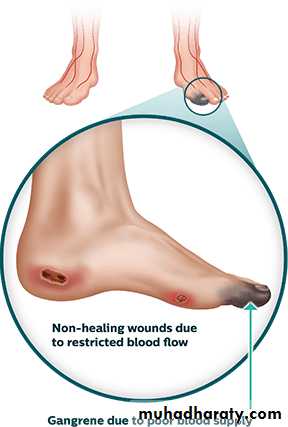
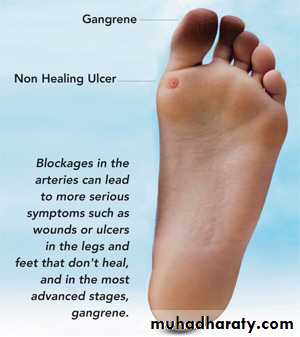
Ischemic ulceration
The end stage of vascular insufficiency is frank tissue infarction or gangrene.
Clinical evaluation
Features of chronic ischemia
Absent distal pulseMuscle atrophy
Brittle nails
Hair loss
Etc…
Physical Examination
Reduced ABIColor duplex scanning
Traditional angiography
CTA
MRA
Investigations
Conservative measures
Control of Hypertension, hyperlipidemia and D.M.Smoking abstinence
Graduated exercise program
Control of weight
Pharmacologic agents
Platelet inhibitors such as aspirin
Vasodilating agents such as tolazoline
Hemorrheologic agents such as pentoxifylline
Treatment
Percutaneous Trans-luminal Angioplasty
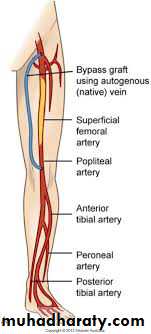
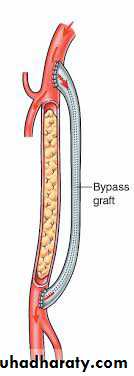
Bypass surgery
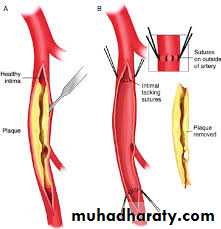
Endarterectomy
Amputation ( last option )