
Streptococcus species
Streptococci r G+ve , spherical, that arranged
as pairs or chains during growth, some are
saprophytic as normal flora of body, others are
pathogenic to humans and cause different
diseases.

Scientific classification
• Kingdom : Eubacteria
• Tribe: Actinobacteri
• Phylum : Firmicutes
• Class : Bacilli
• Order : Lactobacillales
• Family: Streptococcaceae
• Genus: Streptococcus
• Species : S.pyogenes, S.pneumonia, etc
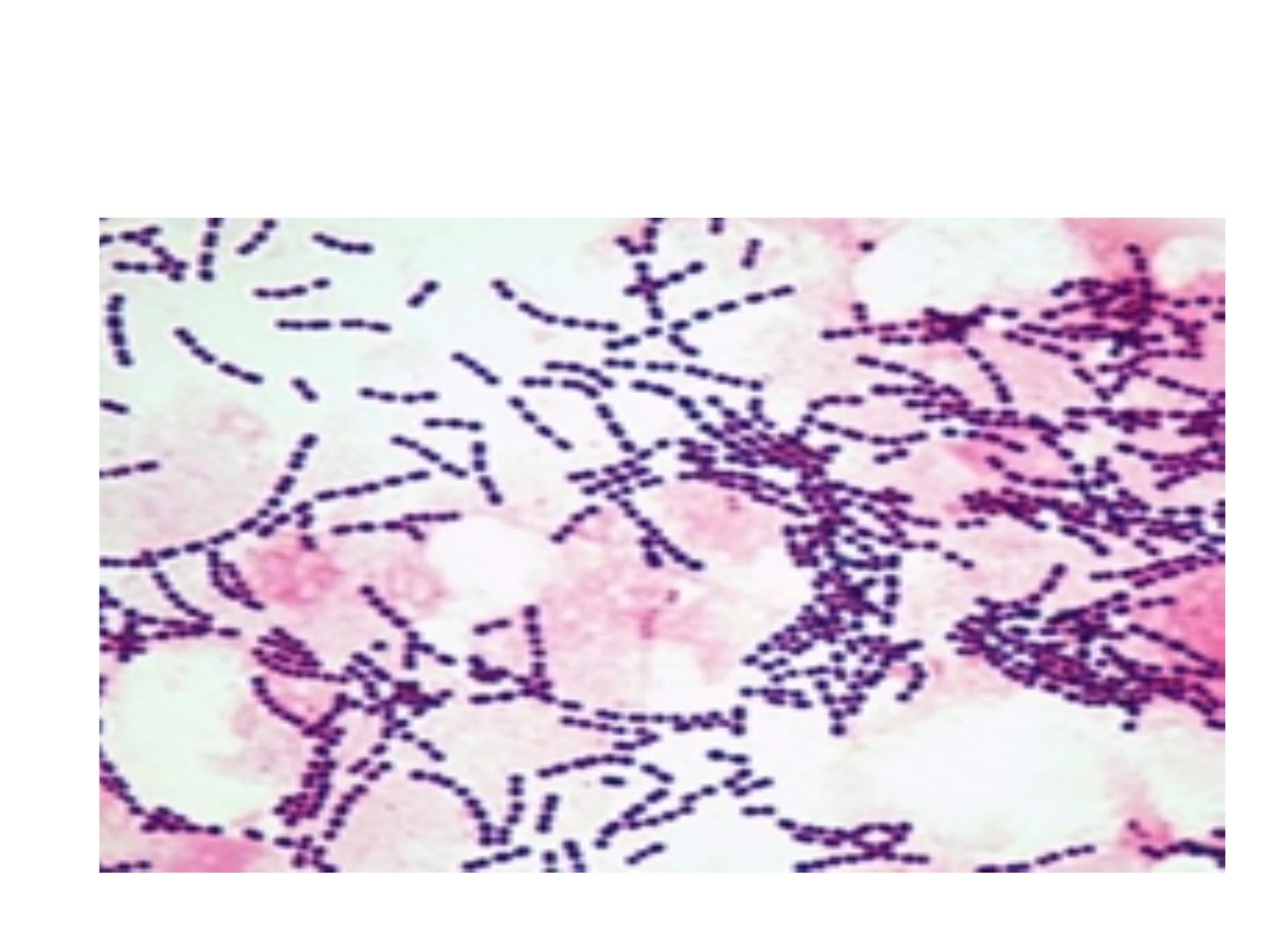
Streptococcus spp
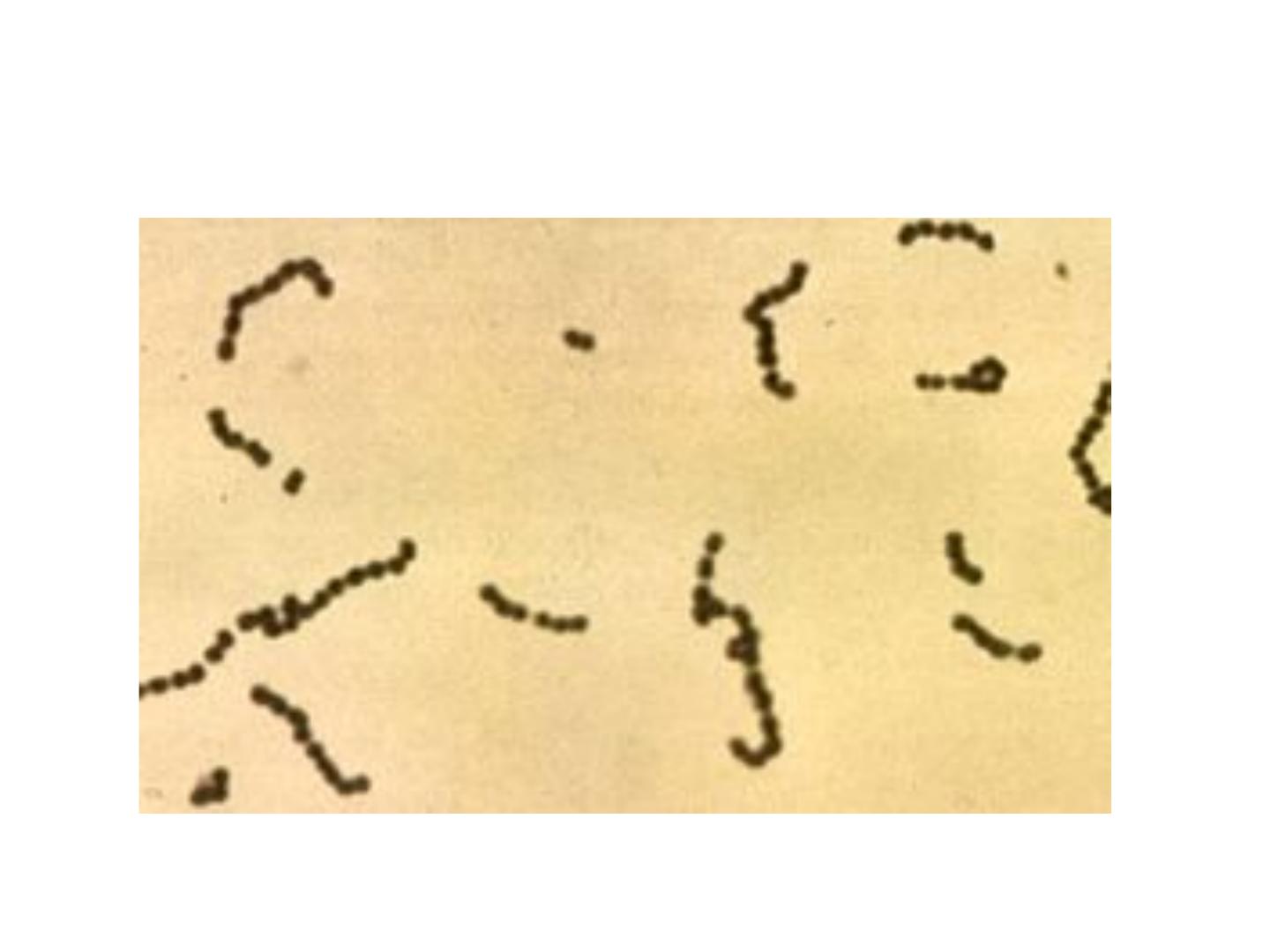
Streptococcus appears as chain

Streptococci
• Stre r heterogeneous group and no one system
suffices classify.
• System use to classification depend on colony
growth characteristic, type of hemolysis, antigenic
composition of group specific cell-wall substances,
biochemical reactions and antigenic composition
of the capsular polysaccharide (like Stre.
pneumonia), finally molecular genetics also used
for study Streptococci.

Classification of strep
• Strepto are classified according to oxygen
requirements into
• 1- Aerobic: classified into 3 groups
• A- alpha – hemolytic Streptococci like S.
viridans, and S. pneumoniae
• B- beta- hemolytic St as S pyogen
• C- Non-hemolytic S. such as S faecalis
(enterococcus)

Classification of Stre
• 2- Anaerobic : it is called Peptostreptococcus
which is normaly present in vagina, intestinal
tract and upper respiratory tract. It may cause
puerperal sepsis, UTI and abscesses.

Culture
• Poor culture on ordinary media, so it need
nutritive requirements like blood and 10% of
Co2.
• Most pathogenic grow best at 37 C˚(especially
hemolysis)
• Group D (enterococci) grow well at 15 C˚ -45
C˚ and can grow in high Nacl concentration
(6.5%).
• Most Strep r facultative anaerobic

Antigenic structure
• Hemolytic stre can be devided into serologic group
(A-H,K-U), certain groups can be subdevided into
types, antigenic substances are
• 1-group specific cell w antigen: which is cho, it is
lancefield groups(A-H,K-U). Its function
antigenic and colonizing agent
• 2-M- protein: is a major virulence
factor(antiphagocytic factor) of group A, it’s a hair
like projections of streptococcal cell wall, when M
protein is present the Stre are virulence

Antigenic structures
• 3- T-substance: antigenic and colonizing agent
• 4- R-protein: antigenic and colonizing agent
• 5-Nucleoprotein: antigenic

Strep viridans
• It is considered as normal flora (commensal)
bacteria of the mouth and throat,
• It can pass the blood especially after teeth
extraction or tonsillectomy and this dangerous
in people with congenitally deformed or
rheumatic heart valves. Organism tend to settle
on such areas of abnormal endocardium cause
Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis(SBE)
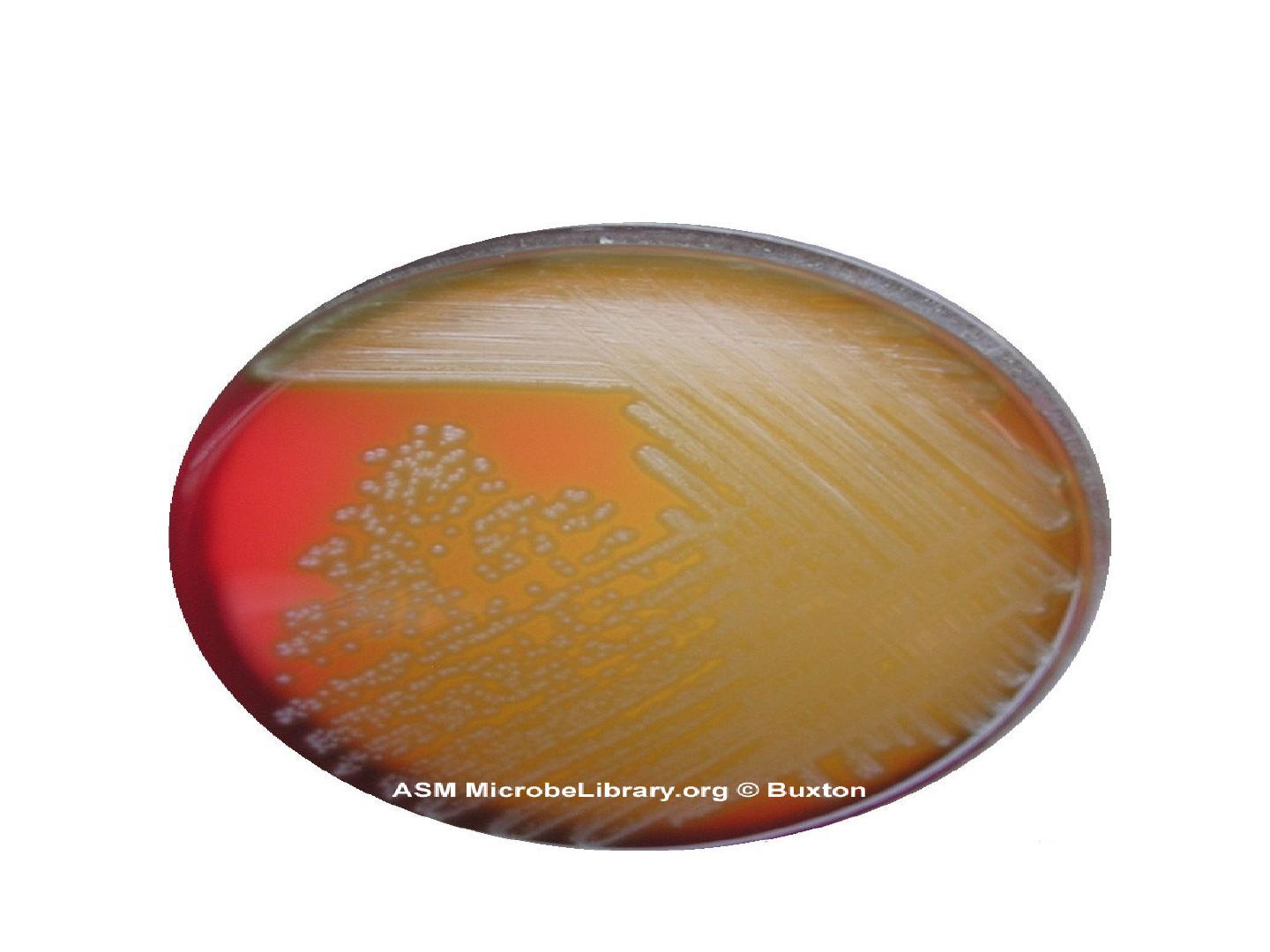

Strepto.vridinas on blood agar

Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis
It is a disease clinically manifested by fever,
anaemia, weakness, heart murmur, enlarged
spleen and renal lesions.
The clinical course is gradual and the disease is
fatal in untreated cases

Laboratory Diagnosis
1- blood culture: from febrile attack patient take
5-10 ml of blood and diluted by 50-100 ml of
nutrient broth. Incubated at 37 C˚ for at least
24 hrs and then examined by
A- subculture on plate of blood agar and
examined the colonies, which are surrounded
by greenish pigmentation.
B- smear is done from suspected colonies &
stained by Grams stain.

Laboratory diagnosis
Stre. Pneumoniae is also give colonies
surrounded by greenish pigmentation and it
looks like viridans morphologically. Therefore
can be differentiate between them by the
following
Differences St viri Str pneu
Bile solubility insolub soluble
Inuline fer not ferme fermented
Res to optochin res not resistant

Differences
Differences S viridans St pneumonia
Pathogenicity no path fatal septicaemia
to mouse
Quellung reaction negative positive

Species of viridans strep
S. mitis, S. mutans, S. salivarius and S. sanguis
Treatment of St viridans prolonged course of beta
lactam drugs(penicillin and cefalosporin)

Beta haemolytic Streptococci
Streptococcus pyogenes: its important one that
causes several medical conditions and found by
lancefield that Beta haemolytic strep
Can be claasified into many groups from (A-U),
According to cell antigen (specific cho antigen)
called C-antigen, the most pathogenic one is
group A which is called S pyogen
These above groups subdivided into more than 80
types according to M-protein
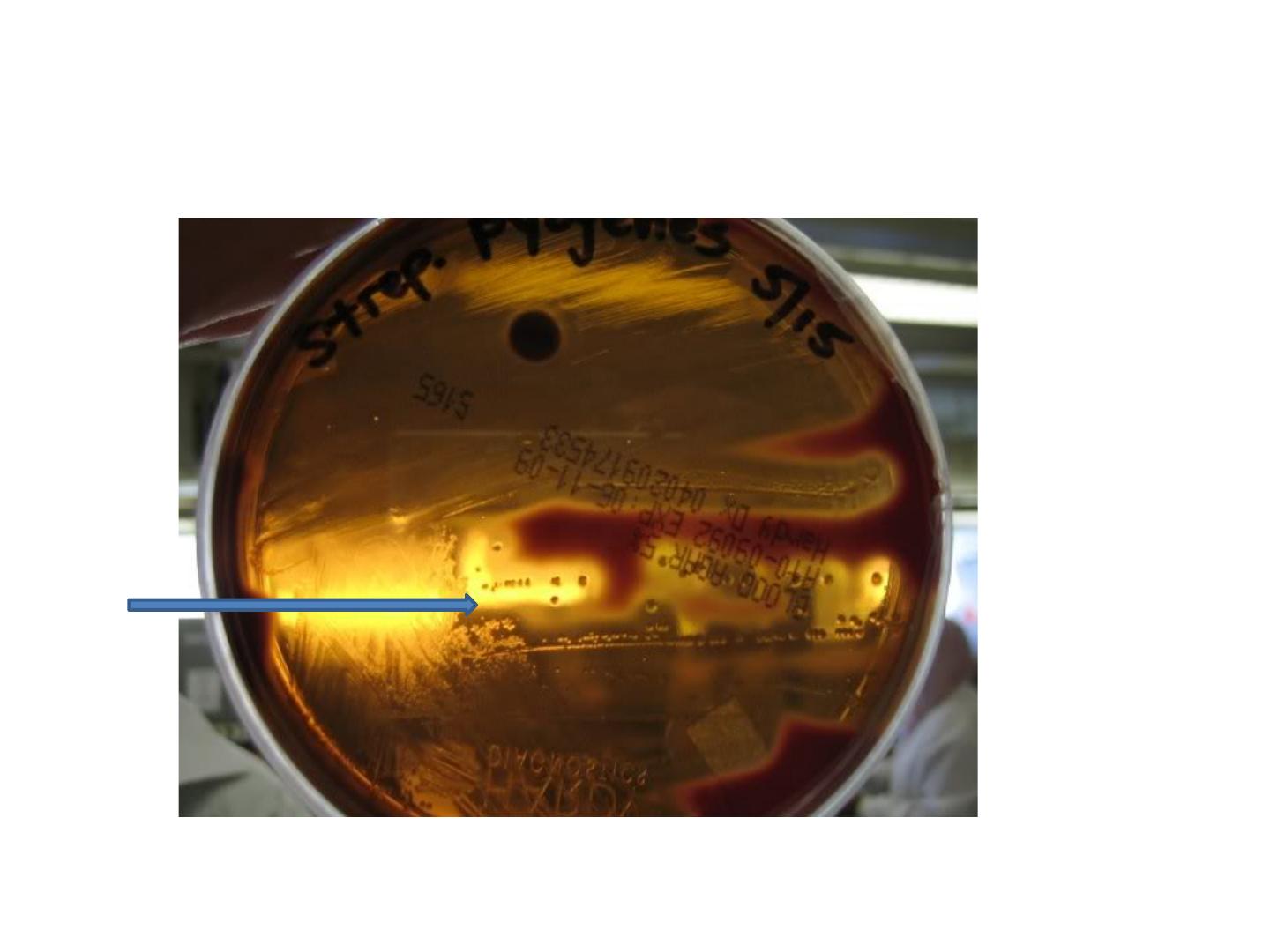
Beta hemolytic Streptococci
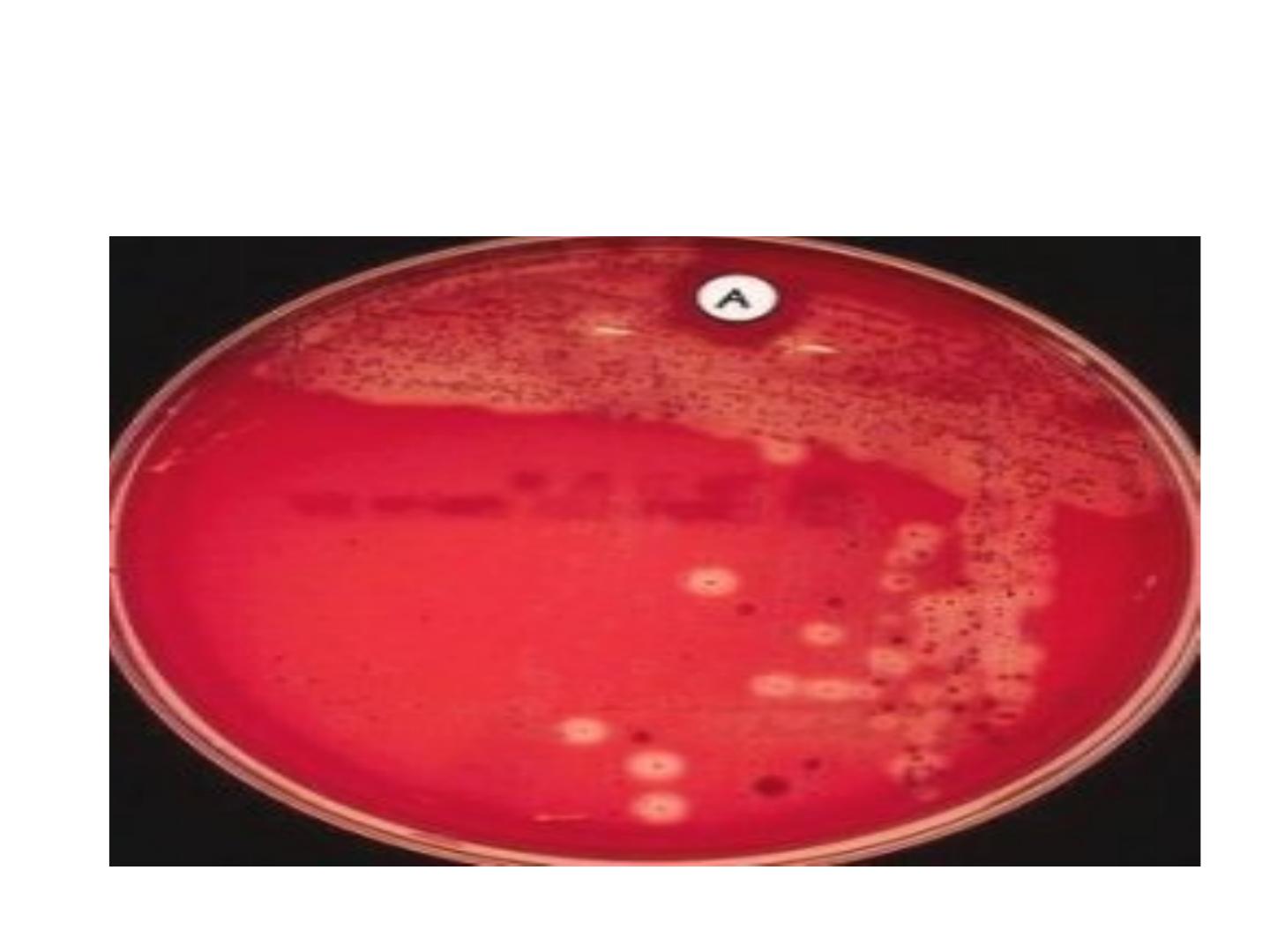
Beta hemolytic Streptococci

Products of Strep.pyogenes
1- haemolysins: there r two Stroptolysin O,
Streptolysin S
2-hyaluronidase : spreading factor
3- streptokinase: (fibrinolysin) which tranforms
plasminogen into plasmin that digests fibrin
into other proteins. It can be used for treatment
of coronary artery and venous thrombosis if
given I.V.

Products of Strep. pyogenes
4- Erythrogenic toxin: responsible for the
characteristic erythema of scarlet fever and it
causeses vasodilation of peripheral small blood
vesseles.
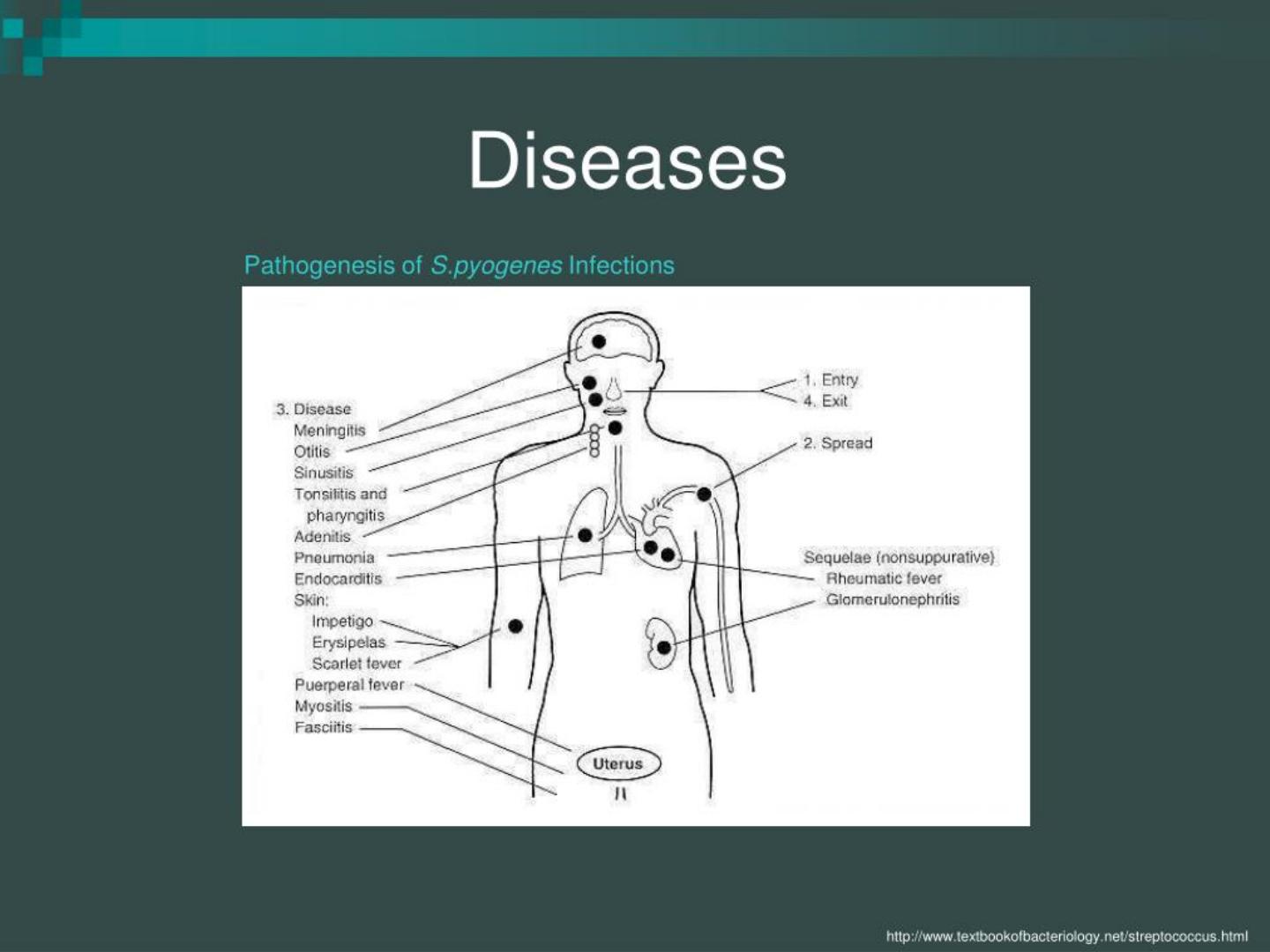

Diseases caused by group A
Scarlet fever:
Way of infection: droplet infection.
Clinical picture: fever, sore-throat, and erythematous
skin rash. The disease occurs usually in children.
Diagnosis : 1- schultz-charlton reaction: I.D.
injection of antierythrogenic toxin (prepared in
animal or from convalescent serum) in one of the
erythematous areas will lead to fading and
disappearance of the rash within 6-12 hrs in
positive cases. This is a neutrilization test in vivo.
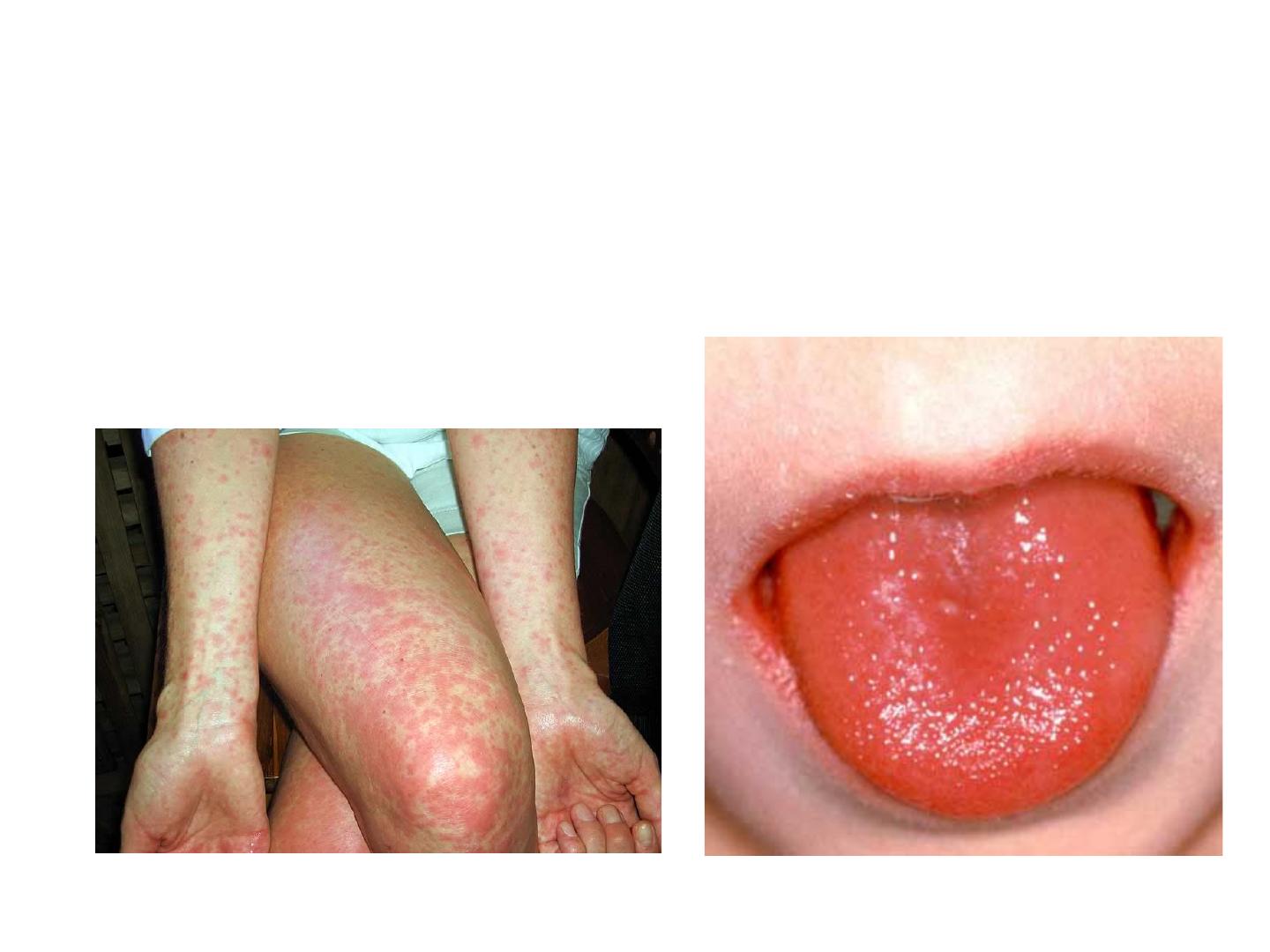

Streptococcus pyogenes
• 2-throt swabs inoculated on b .a. but this not
conclusive, because St py. My be present in the
throat of normal carriers.
• Susceptibility to scarlet fever:
• This done by the dick test : 0.1 ml of standard
erythrogenic toxin is injected I. d. in one
forearm (test) and 0.1 ml of heated toxin
(inactive) in the other forearm(control)

Results
• 1- dick positive : erythematous rash in the test forearm
and no reaction in the control one this mean susceptible.
• 2- dick negative: no reaction in both forearms this mean
immuned.
• 3- pseudo positive and pseudo negative appear in
hypersensitive persons in which reactions appear in both
forearms . It may be more sever in the test than the
control pseudo positive or more severe in the control
than test pseudo negative. Pse + means susceptible , pse
–ve means immuned.

Puerperal sepsis
• Clinical picture: fever following labour or
septic abortion accompanied with foul-
smelling uterine discharges.
• Ways of infection:
• 1- endogenous : from the patient here -self
either from her throat or the commensal
anaerobic strep in the vagina.
• 2- exogenous: from droplets coming from the
medical staff or instruments or gloves

Diagnosis
• 1- A uterine swab is taken and inoculated on blood
agar to show the beta haemolytic colonies. Film
stained by grams stain.
• 2- Blood culture: the disease always accompanied
by bacteremia therefore blood culture is of value
• not only st.pyo. Is responsible for puerperal sepsis.
Other orgs may be the cause as St.aureus, St
epidermidis, E. coli, Stre. faecalis and
Closteridium welchii.

Acute follicular tonsillitis
• Clinical picture: fever, sore-throat with white
spots or membrane on the tonsils. The
differential diagnosis may rest between
streptococcal infection, diphtheria, vincents
angina(combination of spirochaetes and
fusiform bacilli) and monilia (fungal infection)
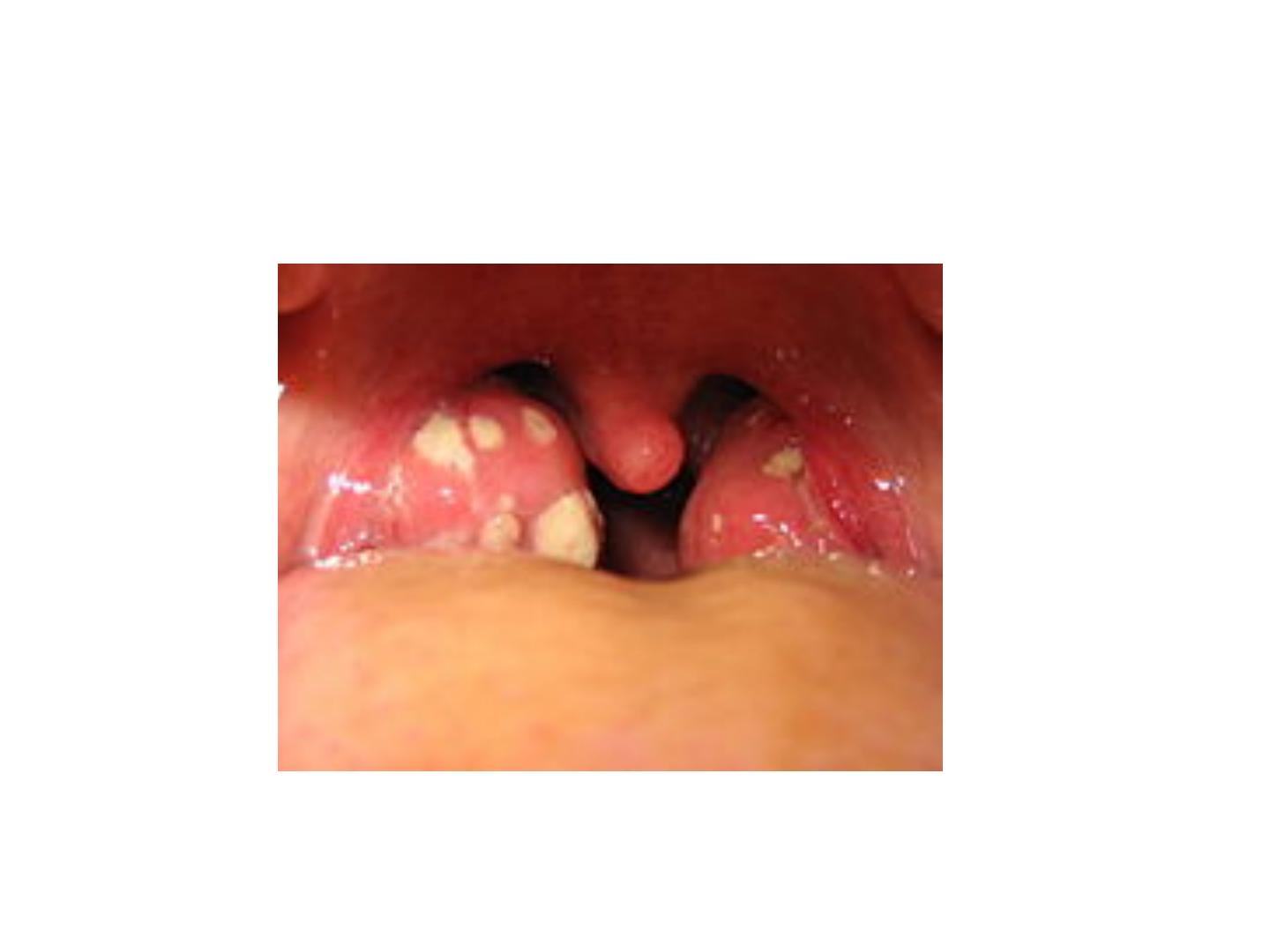

Diagnosis of acute follicular tonsillitis
• 1- throat swab is taken and then inoculated on a
plate of b. a.
• Treatment: broad spectrum antimicrobial agents
like beta lactam drugs

Erysipelas
• It is a condition characterized by creeping
inflammation with vesicular sharply
demarcated margin and browny oedema.
• Way of infection: contamination of wound by
Strep. pyogenes.
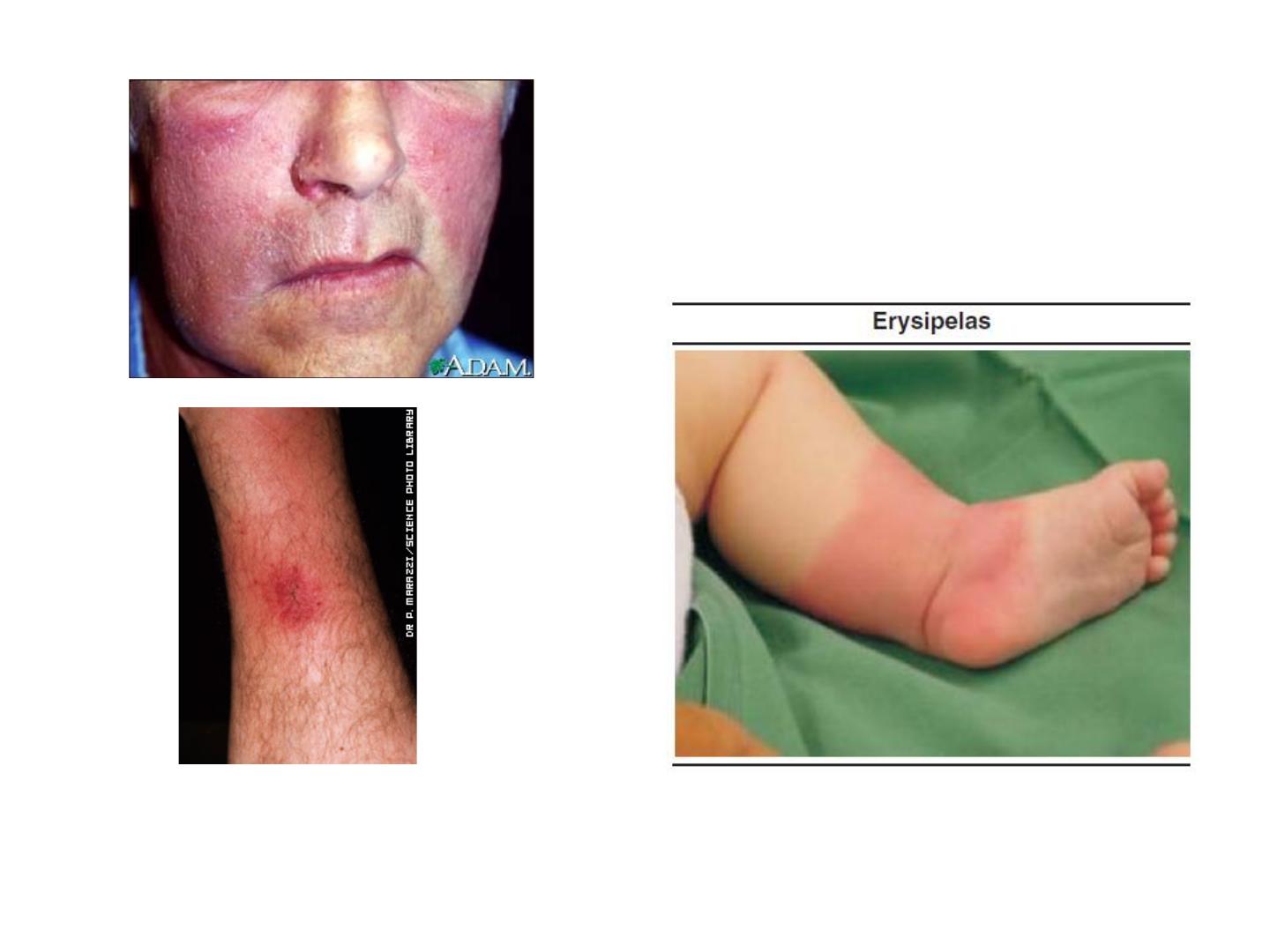

Diagnosis
• The vesicular contents is inoculated on blood
agar and examined as before. Blood culture can
be used.
• Treatment of case is penicillin

Impetigo
• Clinical picture: it is a local infection of the
superficial layers of the skin especially in a
small children, leads to the development of
superficial blisters which break readily and
spread by continuity. The infected area is
covered with honey-coloured crusts

Impetigo

Diagnosis :
• Swabs is taken from the lesion and inoculated
on blood agar plate at 37 C˚ for 24 hrs
• Treatment: beta lactam drugs with local skin
ointment

Acute endocartitis
• It is associated with streptopccocal infection
when occurs bacteremia , beta streptococci may
settle on heart valves producing the case

Poststreptococcal diseases
• Following an acute group A strep infection,
there is a latent period of 1-4 wks , after which
nephritis or rheumatic fever occasionally .
These conditions occur due to hypersensitivity
response. Nephritis is commonly preceded by
infection of the skin, while the rheumatic fever
by infection of the respiratory tract.

Acute glomerulonephritis
• This is develop after 3wks from strep infect,
particularly with m types 2, 4,12, and 49, and
some strains are particularly nephritogenic .
Glomerulonephritis may be initiate by Ag –Ab
complex on the glomerular basement
membrane . The Ag is the streptococcal cell
membrane. In an acute nephritis there is blood
and protein in urine, oedema, high blood
pressure and urea nitrogen retention, serum
complement levels are low
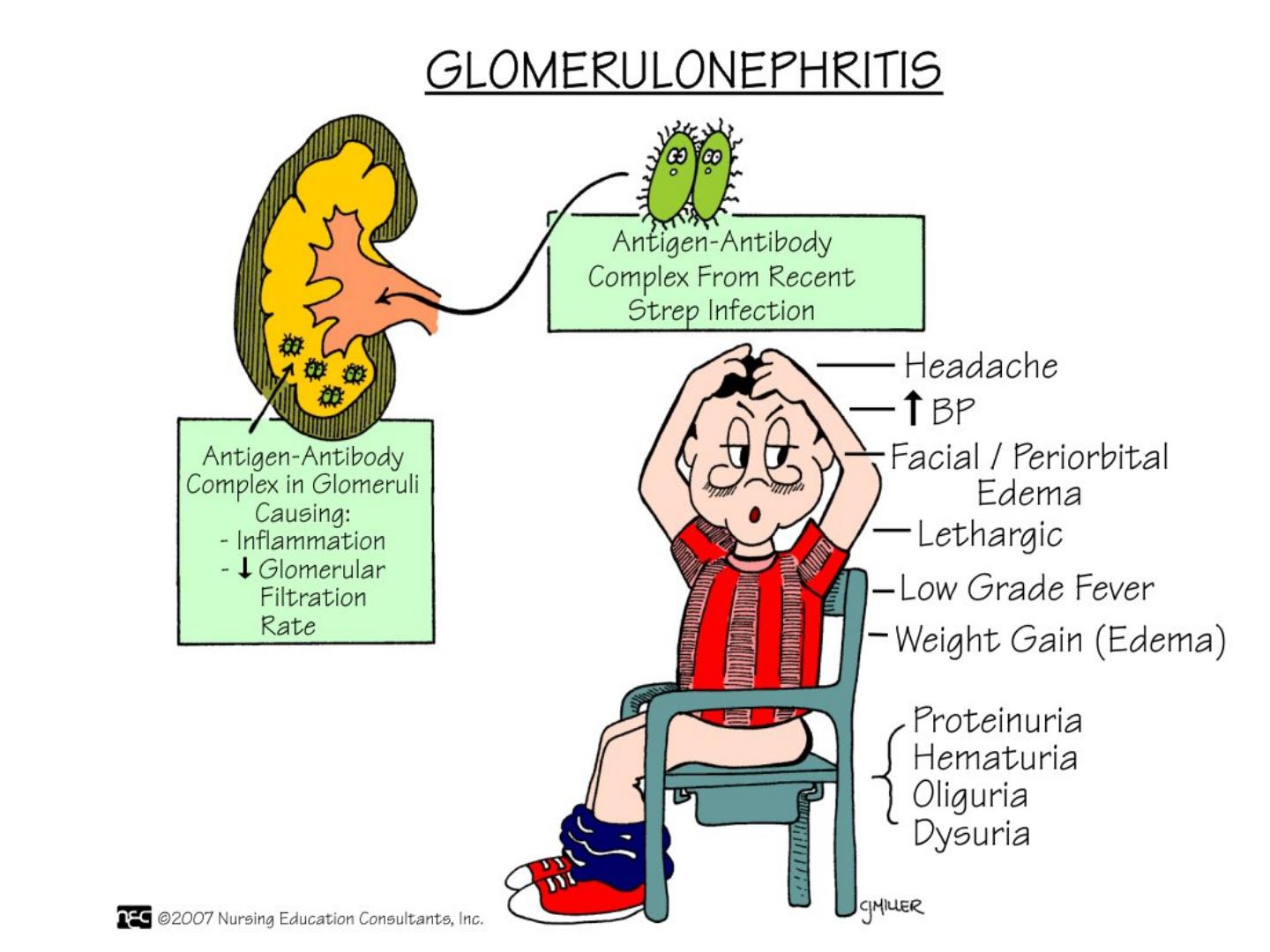
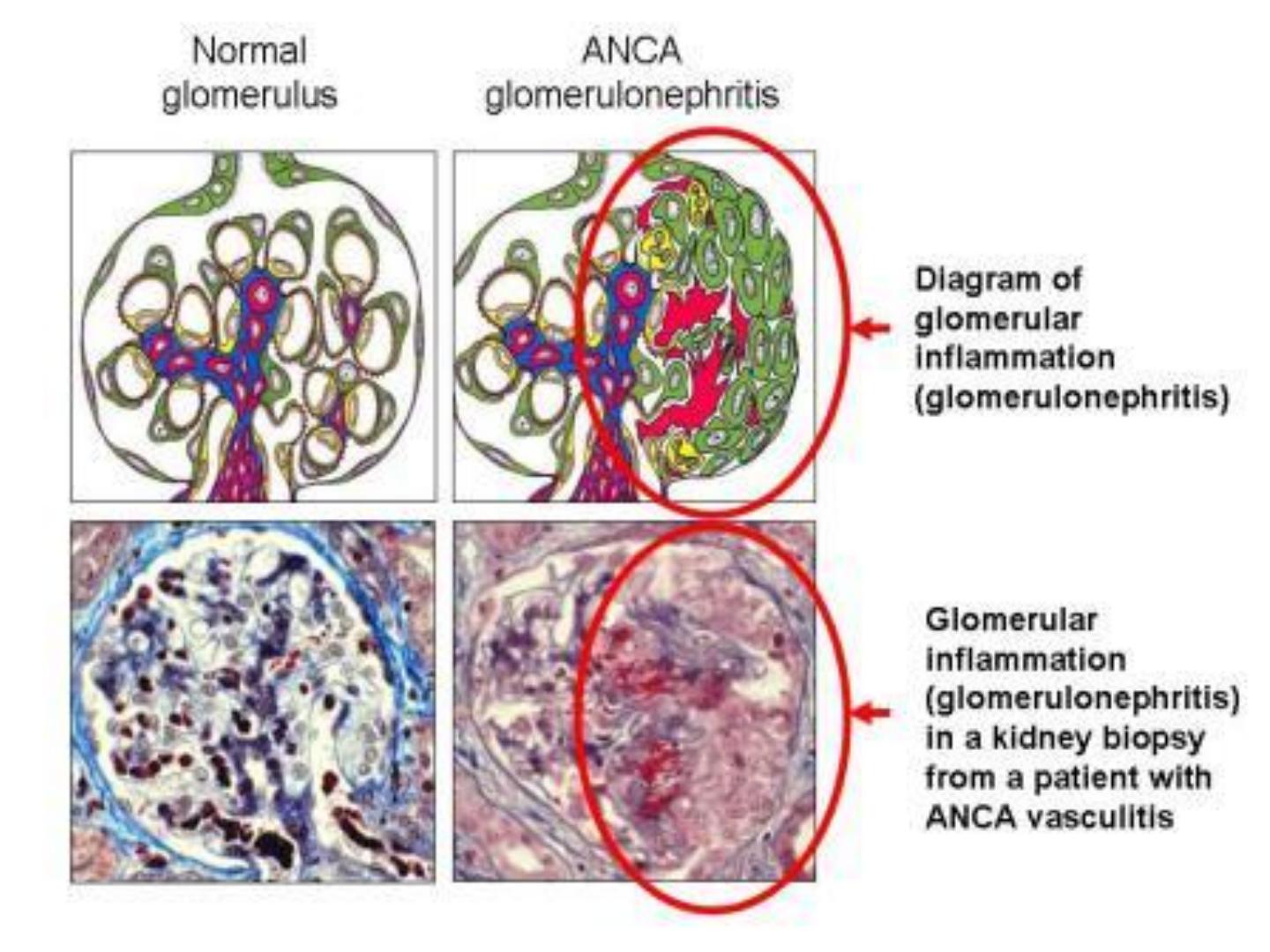

• A few patients die, some develop chronic
glomerulonephritis with kidney failure, the
majority recover completely.

Rheumatic fever
• This is the most serious sequel of haemolytic
streptococci infection because it results in
damage to heart valves and muscle. Certain
strains of group A Stre. Contain cell mem Ag
that cross – react with human heart tissue Ags.
The onset of rheumatic fever is often preceded
by Stre infection 1-4 wks earlier in untreated
cases.

`

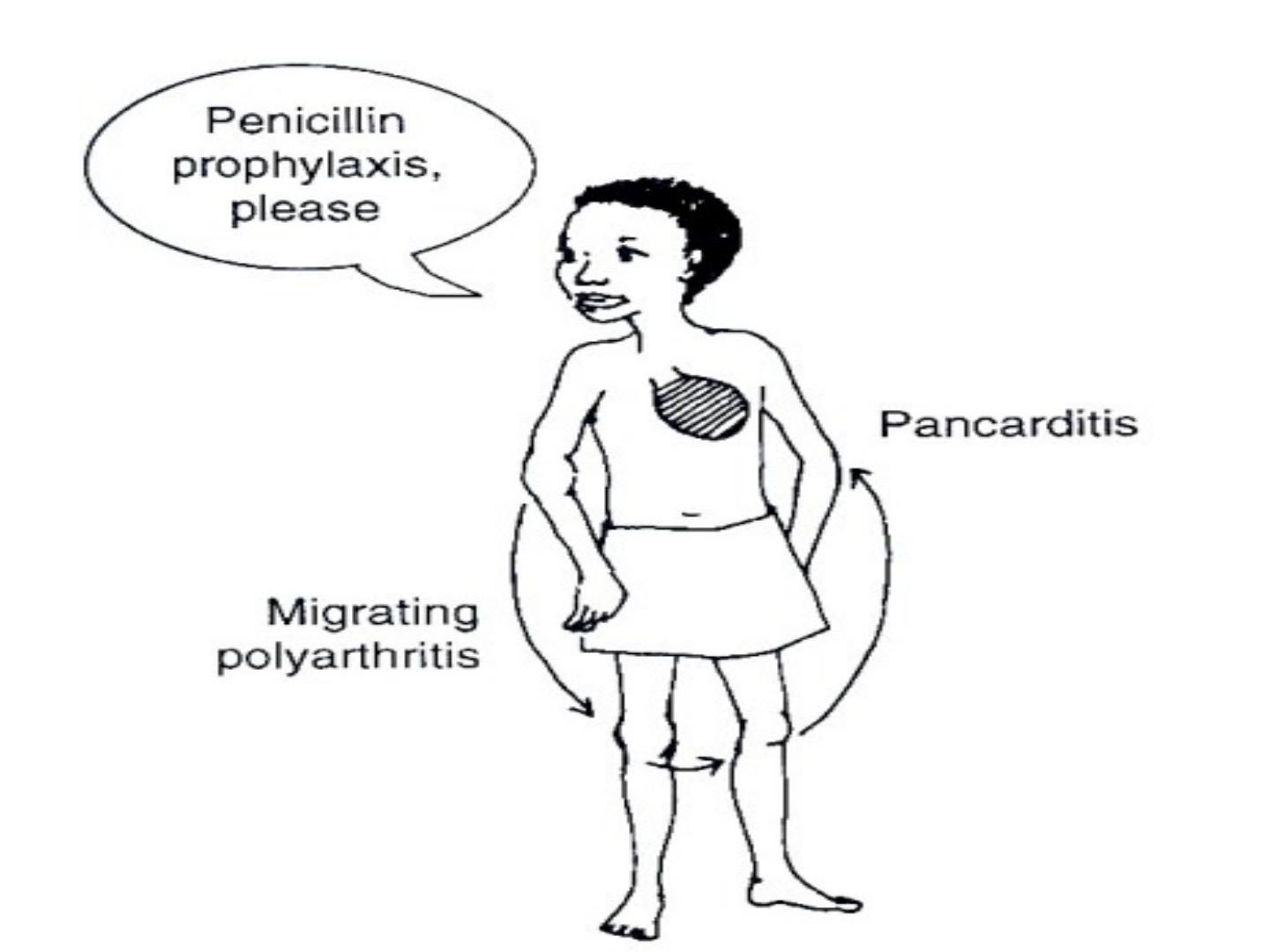
R fever
• Typical symptoms of rh f include fever, malaise,
migratory polyarthritis and evidence of
inflammation of all layers of the heart
(endocardium, myocardium, and pericardium)
i.e. pancarditis.
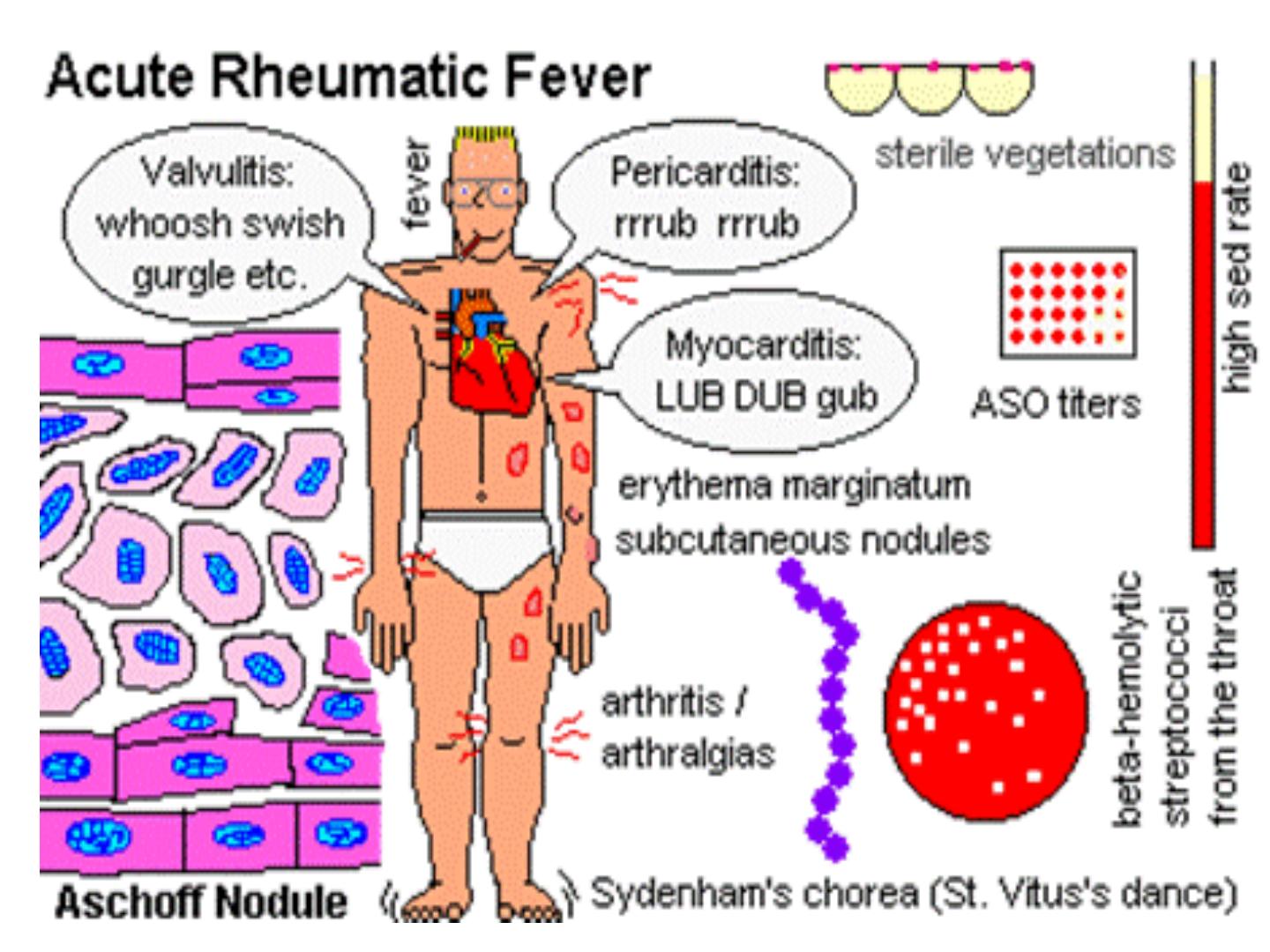

Diagnosis:
• 1- Antistreptolysin O titer (ASOT): patients who
have had a recent infection , with group A
Streptococci develop an antibody response to
streptolysin O. this antibody will combine with
and neutralize streptolysin O in vitro, thereby
inhibiting its haemolytic activity on rbc i.e.
• Streptolysin O toxin + rbc---- haemolysis.
• Streptolysin O toxin+ specific ab at 37 C for 30
min + rbc ----- no haemolysis.
•

Method
• 1- serial dilution of patients serum are tested
against standard amount of streptolysin O
toxin and incubated at 37 C for ½ hr.
• rabbit Rbcs are added to each tube , and re-
incubated for one hr.
• The titer is the last tube showing no
haemolysis which is expressed as reciprocal of
that dilution and the positive case it is usually
above 200 units.

Diagnosis
2- C- reactive protein test:
CRP is an abnormal alpha globulin that appears
rapidly in the serum of patients who have
inflammatory condition and is absent in serum
from normal person. The test has proved useful
in the follow up of patient with rheumatic fever,
so CRP disappears when the inflammation
subsides, reappearing only when the disease
process becomes reactivated.

3- sedimentation rate: it is non –specific because
it is high not only in rheumatic fever but also
in many other diseases. the test has also proved
useful in follow up of the case.

Treatment
1- penicillin as early as possible. Or other beta
lactam drugs
2- anti-inflammatory drugs, like analgesic and
corticosteroid.
3- anticonvulsant medications
4- bed rest

Streptococcus faecalis
Also called enterococcus is always present in
colon. If it leaves its normal habitat (the colon),
it can cause suppurative lesions, UTI,
peritonitis, or puerperal sepsis. It can grow on
ordinary media and also on macConkey’s on
which it gives deep pink colonies.
Enterococcus is quite resistant to many
antimicrobial drugs, therefore antibiotic
sensitivity test must be done before initiation
of treatment.




Other Streptococci of medical
interest
1- Str agalactia: these are beta haemolytic stre
group B they r members of the normal flora of
the female genital tract and an important cause
of neonatal sepsis and meningitis.
2- Peptostreptococcus( many species) these
bacteria grow under anaerobic condition or
microaerophic con and variable produce
haemolysins

