بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Plasma membrane
The structure and function of cells are critically dependent on membranes, which not only separate the interior of the cell from its environment but also define the internal compartment of eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles .
Generally, a plasma membrane protects a cells by acting as a barrier between its living contents and the surrounding environment. It regulates what goes being unique to the organisms.
In multicellular organisms, cell junctions requiring specialized features of the plasma membrane connect cell together in specific ways and pass on information to neighboring cells so that the activities of tissues and organs are coordinated.
At the turn of century, investigators noted that lipid soluble molecules entered cells more rapidly than water soluble molecules this promoted then to suggest that lipids are a component of the plasma membrane.
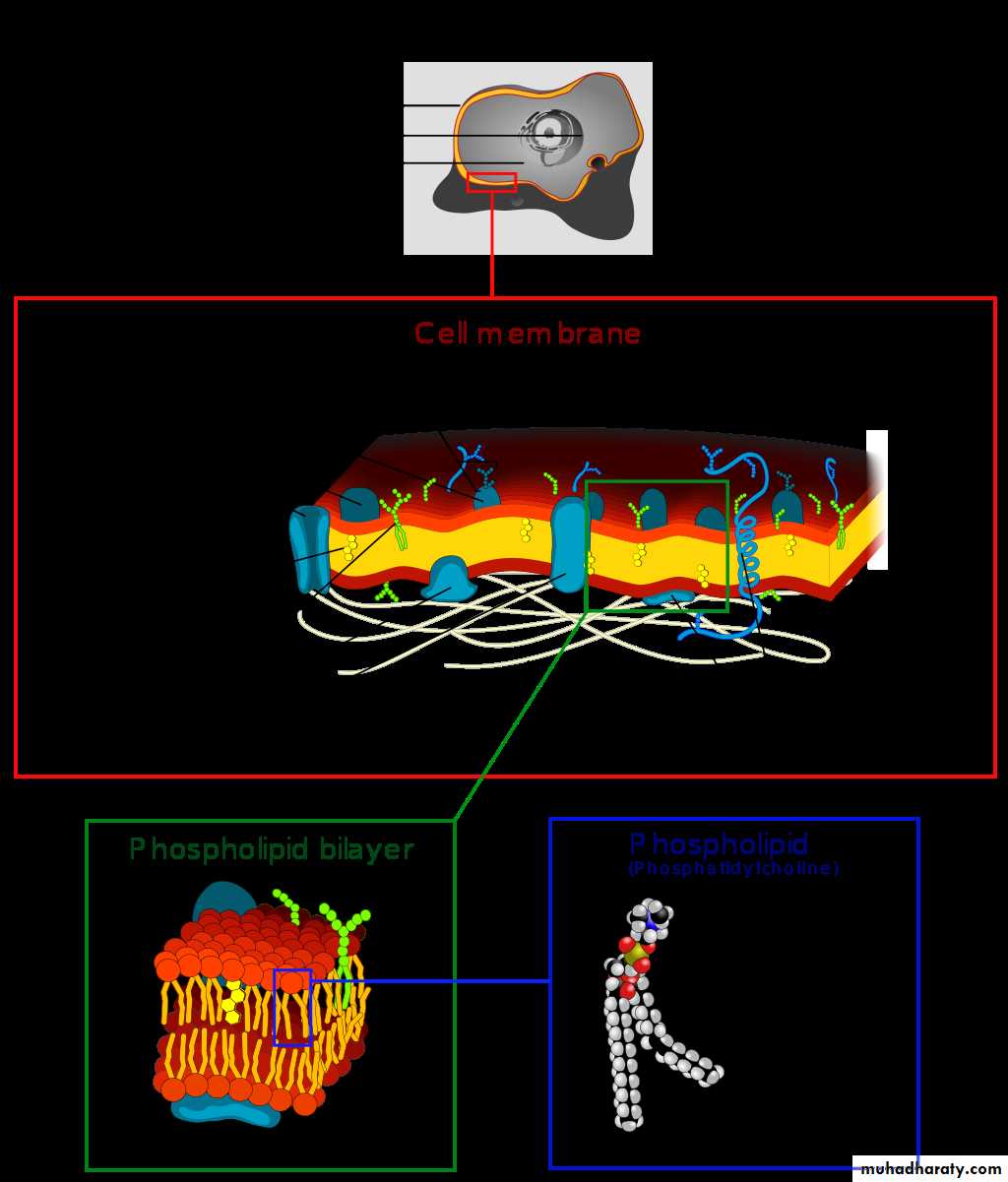
The formation of biological membrane is based on the properties of lipid and all cell membrane share a common structural organization:
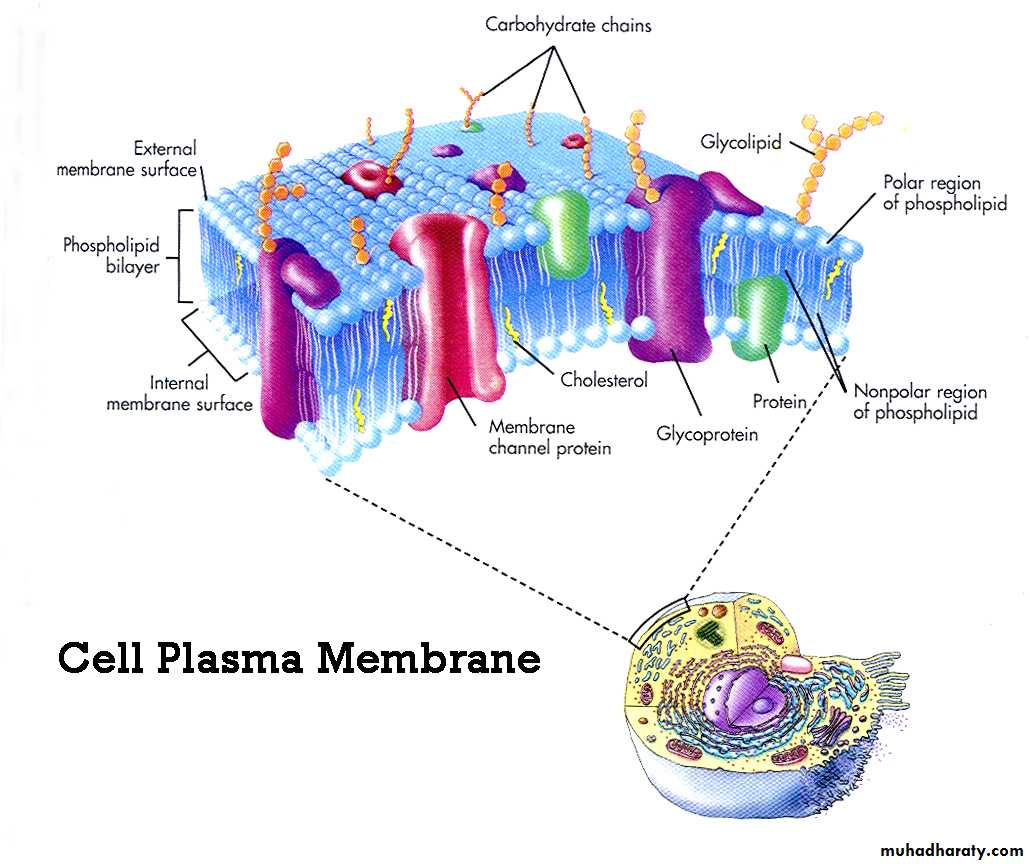
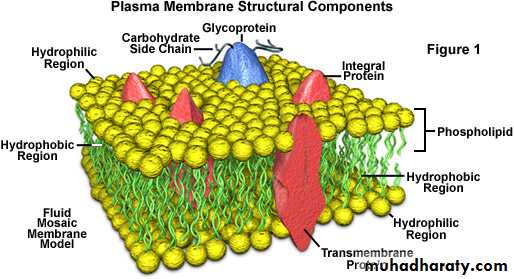
Bilayer of phospholipids with associated proteins.
Membrane lipids:
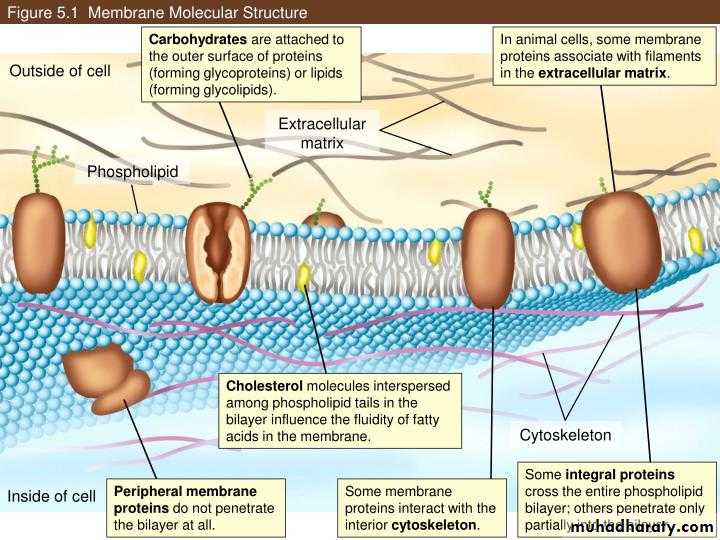
Lipids constitute approximately 50% of the mass of most cell membrane, although this amount differs depending on the type of membrane .The fundamental building blocks of all cell membranes are phospholipids, which are amphipathic molecules consisting of two hydrophobic fatty acid chains linked to phosphate containing hydrophilic head group.
There are two other types of lipids in the plasma membrane.
1- Glycolipids: have a structure similar to phospholipids except that the hydrophilic head is a diversity of sugars joined to form a straight or branching carbohydrate chain , Glycolipids have a protective functions.
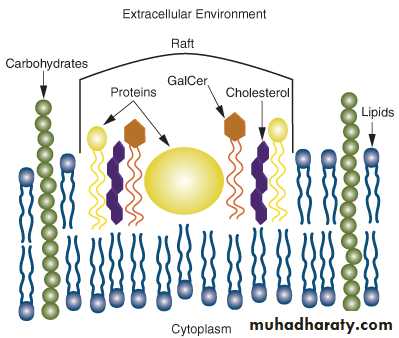
2- Cholesterol: is a lipid that is found in animal plasma membranes, cholesterol reduced the permeability of the membrane to the most biological molecules.
The membranes of many eukaryotic cells contain sterols, which provide strength to the then fluid structure. Recall that Mycoplasma, a group of bacteria lacking a cell wall, also have sterols in their membranes. The sterol found in animal cell membranes is cholesterol, whereas fungal membranes contain ergosterol. This difference is exploited by antifungal medications that act by interfering with ergosterol synthesis or function.
Membrane proteins:
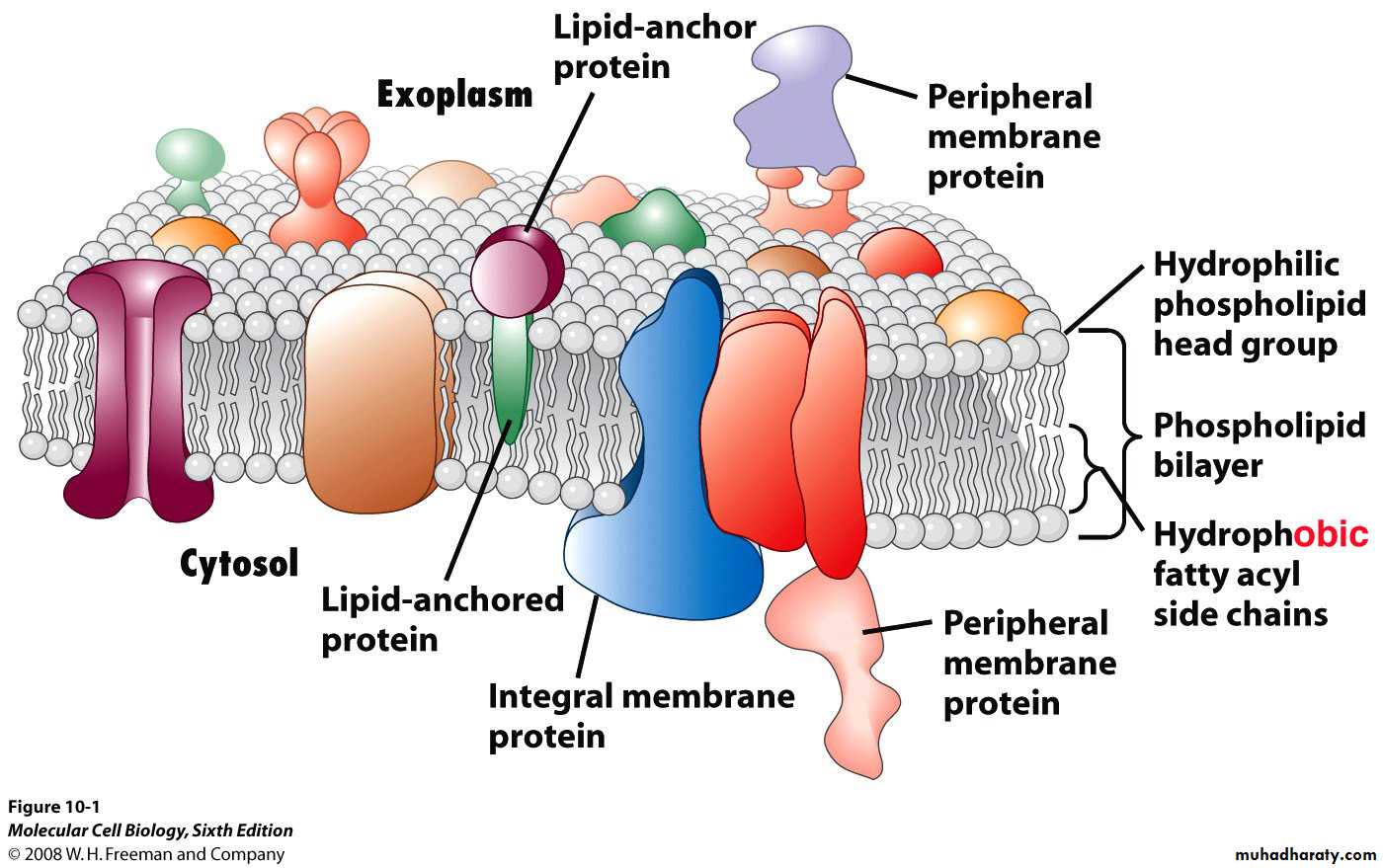
Proteins are the other major structure of cell membrane, constituting 25 - 75% of the mass various membrane of the cell. While phospholipids provide the basic structural organization of membrane. These protein are divided into two general classes, based on the nature of their association with the membrane:*Integral membrane protein: are embedded directly within the lipid Bilayer .
*peripheral membrane proteins: are not inserted into the lipid Bilayer but are a associated with the membrane indirectly, generally by interaction with integral membrane proteins (called transmembrane proteins ) span the lipid Bilayer , with proteins exposed on both sided of the membrane.
The carbohydrate chains of Glycolipids and glycoprotein serve as the finger prints of the cell. The carbohydrate chains of the Glycolipids and glycoproteins form a carbohydrate coat that envelope the outer surface of the plasma membrane
The lipid and protein composition of the inside half differs from the outside half., on the inside some protein serve as links to the cytoskeletal filament and on the outside some serve as links to an extracellular matrix.
Membrane protein diversity:
These are some of the functions performed by proteins found in the plasma membrane :1-channel protein: allows a particular molecules or ion to cross the plasma membrane freely . cystic fibrosis** an inherited disorder , is caused by faulty chloride (Cl-) channel ; a thick mucus collects in airways and in pancreatic and liver ducts .
2-carrier protein: selectively interacts with a specific molecules or ion so that it can cross the plasma membrane . the inability of some person to use energy to sodium – potassium( Na+ , K+ ) transport has been suggested as the caused of their obesity .
3-cell recognition protein: the MHC (major histocompatibility complex). glycoprotien are different for each person , so organ transplant are difficult to achieve. cells with foreign MHC glycoproteins are attacked by blood cell responsible for immunity.
4-receptor protein: is a specific molecules can bind to it. Pygmies are shorts not because they do not produce enough growth hormone, but because their plasma membrane growth hormone receptors are faulty and cannot interact with the growth hormone.
5-enzymatic protein: catalyzes a specific reaction, the membrane protein, Adenylate cyclase , is involved in ATP metabolism .