Cell biologyFor the first stage
By:D. Faten Naeem Abbas
Lecture 3
The Protoplasm• Protoplasm is an important living part of cell had been discovered in biology. Many biologists and scientists remembered an initial information about this live material in plant and animal cells, until 1835 as The French scientist (Felix Dujardin) defined this living substance in protozoa and he called it as Sarcodina. In 1846 the German scientist of plants (Von Mohl) used a term“ protoplasm" to describe the live material in the cells.
• In 1861, Max Schultze had confirmed that a protoplasm is an essential material for living things, Thomas Huxley in 1868 confirmed that protoplasm is a physical basis of life, that mean all physical, chemical and physiological properties of protoplasm are identical in all living organisms, therefore protoplasm is the main material in cell and a cell described as protoplasm-mass surrounded by cell membrane and contained a nucleus, this theory called protoplasm theory.
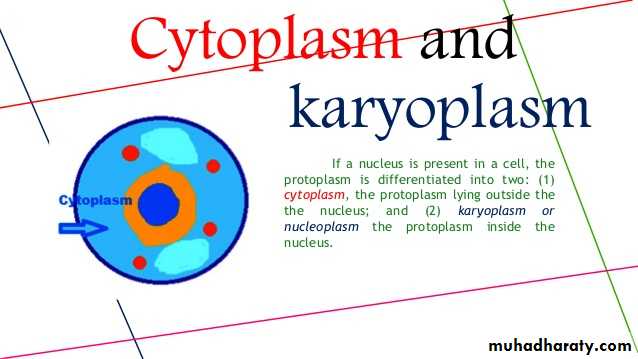
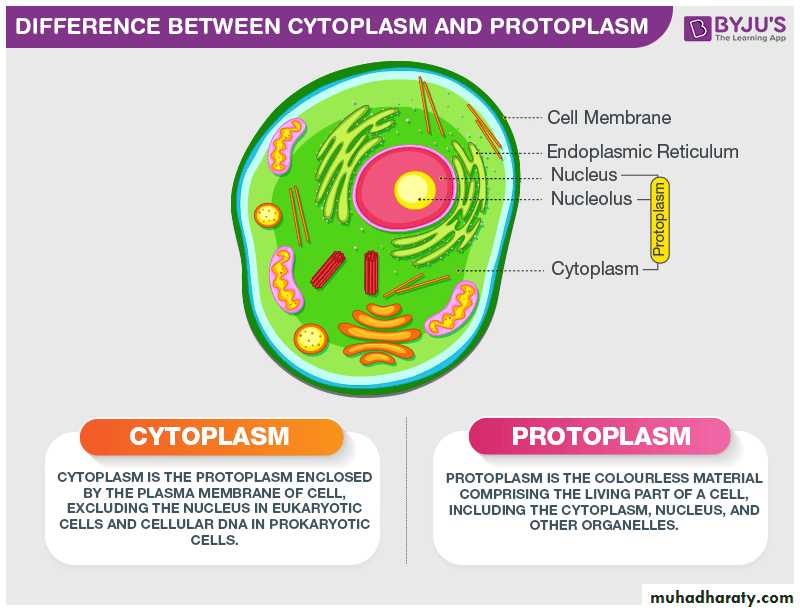
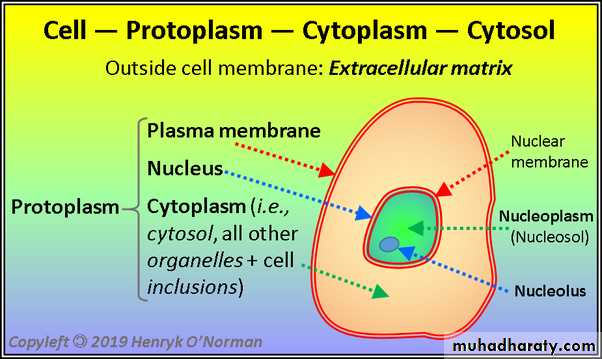
Protoplasm can be divided into two parts according to its location
1-Cytoplasm: is the large part of protoplasm that surrounds the nucleus and enclosed by cytoplasmic membrane.2-Karyoplasm: is the small part which located in the nucleus and enclosed by nuclear membrane and it is called also a nucleoplasm
Physical properties:
Protoplasm in normal conditions is not detectable (colourless) and sometimes appeared like grey coloration, semi- translucent, it's viscosity was similar to that of white part of egg (Albumin), has a density higher than the water density, there are many important materials are presented in protoplasm such as:1-Soluble materials or molecules distributed (dissolved) in water as ions which have a diameter less than 1/1000000 mm.
2-Insoluble solid materials which appeared as suspension which have intermediate diameter.
3-Some distributed materials appeared as adhesion particles with each other, intermediate in diameter.
Nature of protoplasm:
1-Protoplasm may be appeared as sol or gelatinous substance and this property depending on temperature effect & quantity of water.2-protoplasm particles are characterized by their continuous movement under micrograph but this pseudo-movement not transport their particles from site to other but only in same place.
3-It has ability to compose a plasma membrane.
4- According to physical properties, it is highly affected by heating and become solid substance when temperature raised more than 45°c and does not retained to sol condition until to decline the temperature so this will lead to death of living organisms due to increase the density of protoplasm then all metabolic activities will be stopped.
Chemistry of protoplasm:
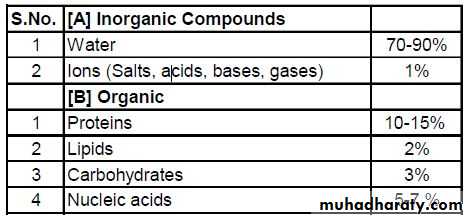
Protoplasm contain the essential molecules such as: Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen. Also, it has Na, K, Ca, P, S, Cl, Fe, Mg within less amount. In addition, very less amount Cu, Zn, I, Br, Mn, Al, Silicon, and Cobalt are included in protoplasm.In human: protoplasm consist of the following molecules like Oxygen 65%, Carbon 18%, Hydrogen 10%, and Nitrogen 3%.
Organic compounds in protoplasm are (main compounds): Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins. Other inorganic compounds which presents in protoplasm are (Salts and Water).