Cell biologyFor the first stage
By:D. Faten Naeem Abbas
Lecture 8
Cell cycle and division• Cell cycle of eukaryotic cells
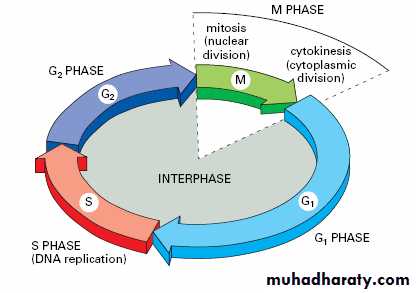
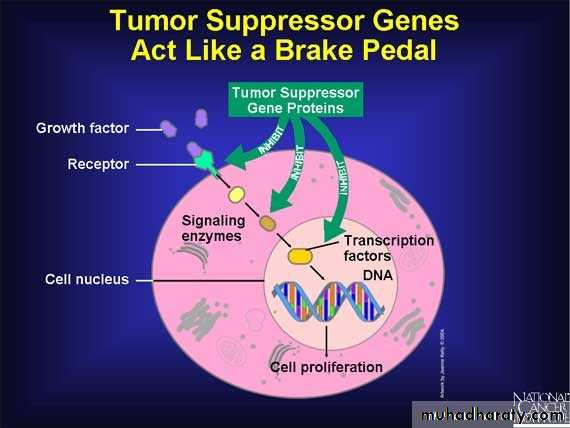
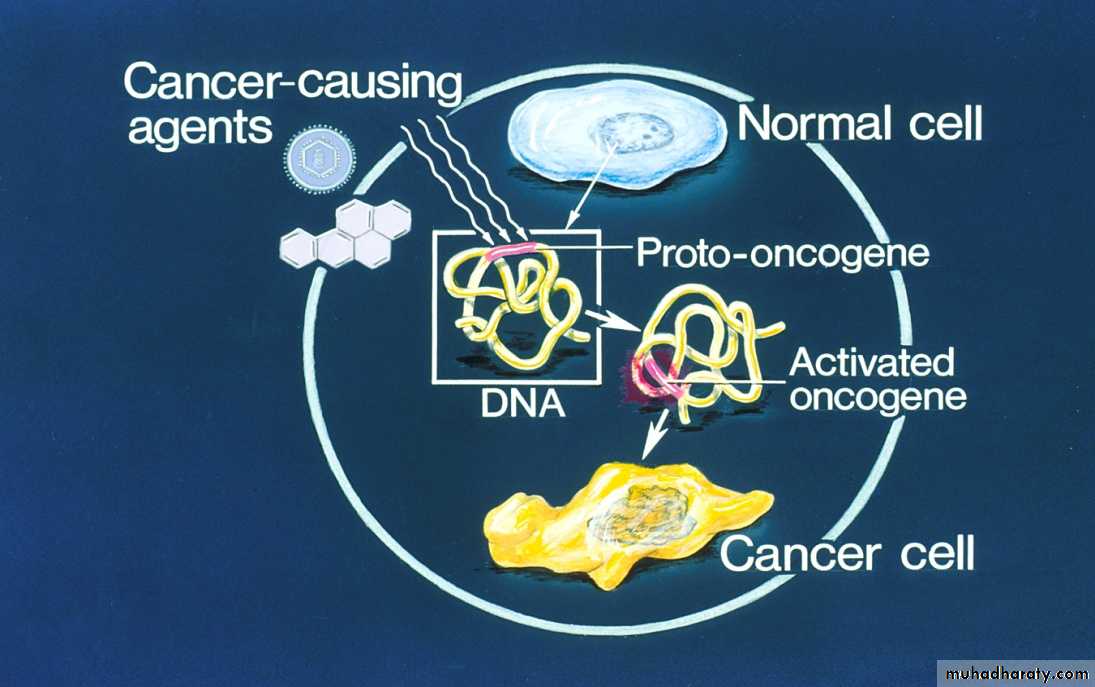
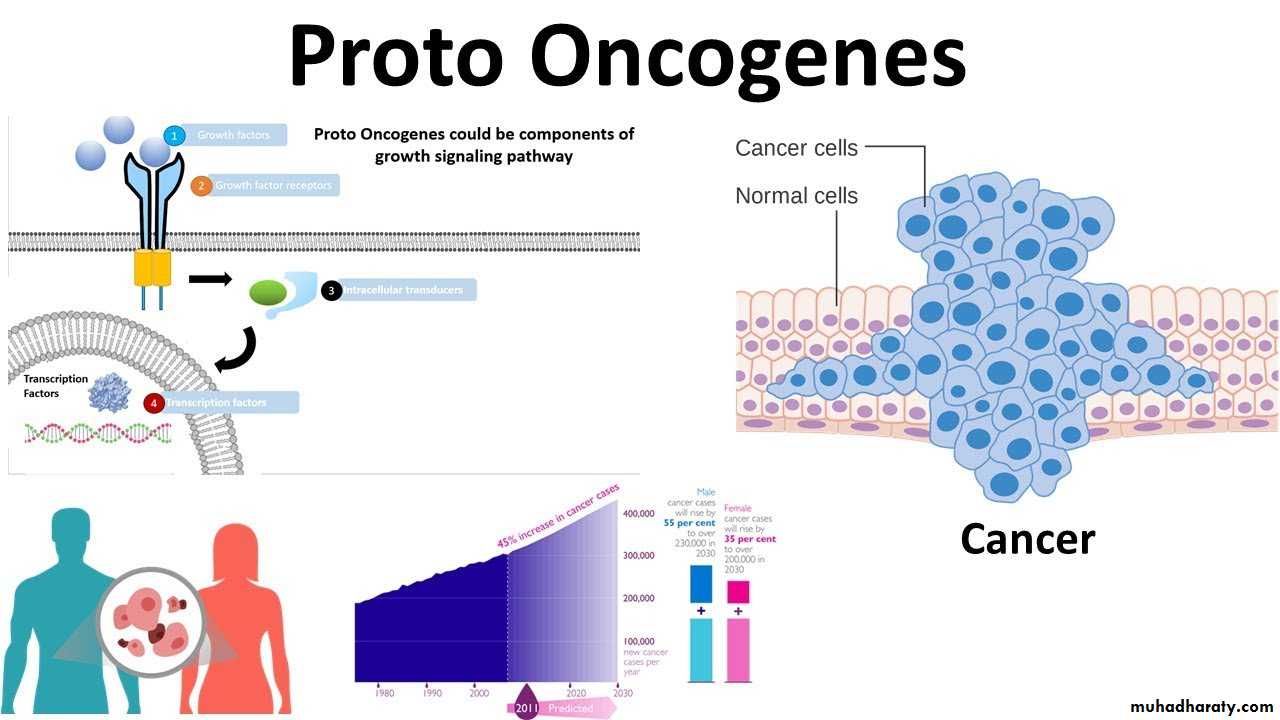
The cell cycle consists of two main phases, which are interphase and M-phase (mitosis phase). The individual phases of the cell cycle proceed after each otherThe process (growth or division) is regulated by a complex of regulatory proteins, which are coded by tumor 1) Suppressor genes (they have a control function) and 2) Proto oncogenes (stimulating division). A failure of their normal function can cause deregulation of the cell cycle and a consecutive malignant transformation of the cell, meaning a change to a cancer cell.
• Multiplication (division) of the cell belongs to its primary functions. Cell division is a part of subsequent processes, known as cell cycle.
• In multicellular organisms it is not only the way how to increase number of cells, but include also the structural and functional specialization of cells – via differentiation. If particular cell will continue in cell cycle toward its division, depends on many factors (extracellular and intracellular), stimulating or inhibiting.
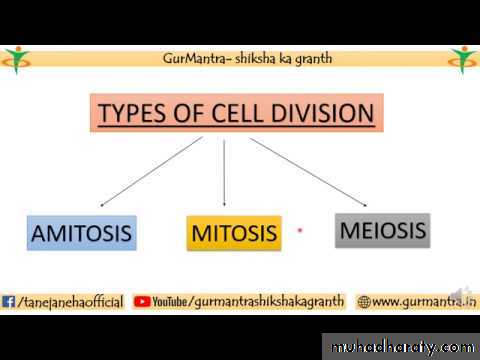
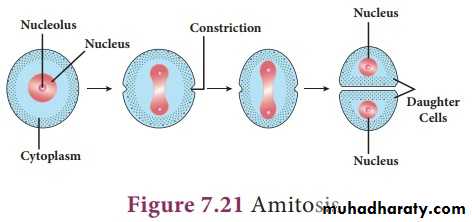
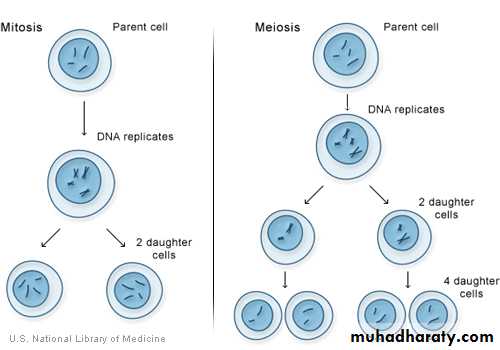
• In regard to way of division and its result, we recognize generally three types of cell division (amitosis, mitosis and meiosis).
•
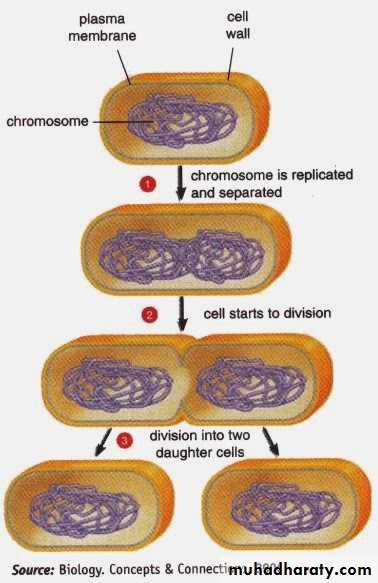
¤ Amitosis (direct division) happens immediately after replication of DNA. In form of “binary fission” is typical in bacterial cells. Multiplication of intracellular organelles (mitochondria and chloroplast) termed as endo-re-duplication or fission.
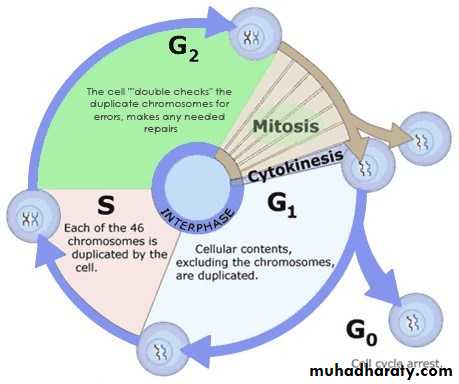
¤ Mitosis is an indirect division, between replication of DNA (S-phase of cell cycle) is intermission (gap) G2 phase of cell cycle. Mitosis is for multicellular organisms as a standard mode of cell division, because it promises genetic identicalness of daughter cells (identical).
¤ Meiosis (reductive division) is an essential precondition to gametes origin – e.g. haploid cells having single chromosome of each type. Fertilization of gametes re-creates the original – specific (diploid) number of chromosomes (According to species of organisms).
1. Mitosis
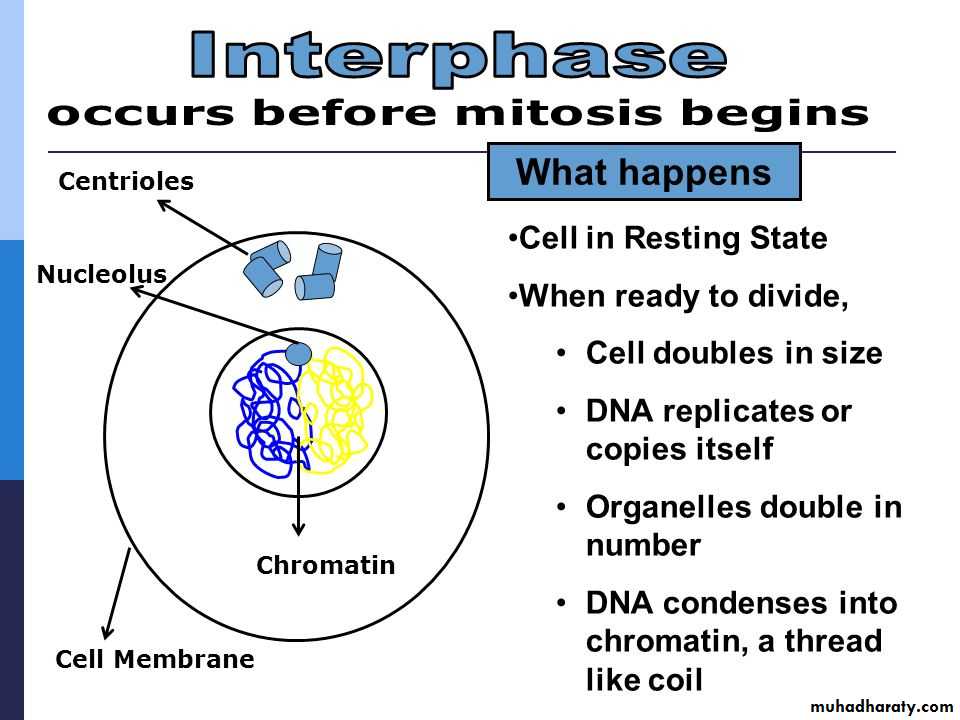
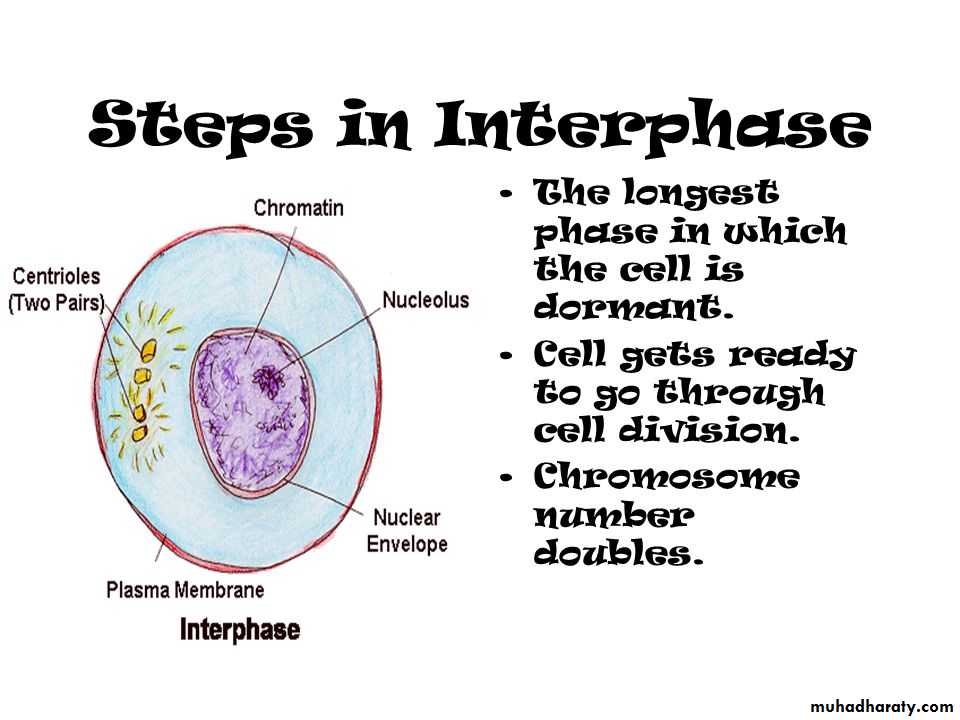
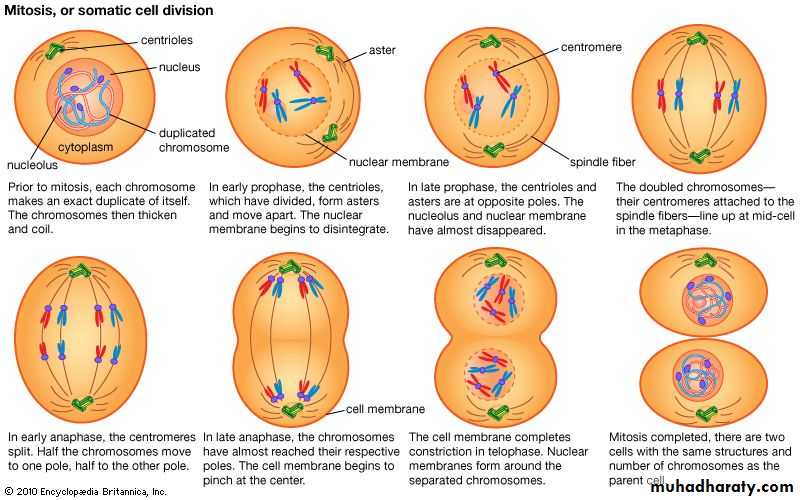
Cell division is a sequence of process within steps by which living organisms are enabled to grow and have ability of reproduction. During cell division through mitosis, genetic material enters replication in a mature cell and is shared in equal way in the two daughter new cells.Before cell begins its division, it enters an interphase state (stage) which is a period taken by the cell to grow. There are important activities that take place during interphase, replication of genetic material and organelles to be ready for cell division are all take place in interphase. Cell division through mitosis the mature cell genome is transported to the new formed daughter cells, and new cells will be similar to the mother cell.
• By the beginning of mitosis, the cell chromosomes enter into a condensation. In most eukaryotic cells, the nuclear membrane separates genetic material (DNA) from thecytoplasm into membrane vesicles. The ribosome dissolves; the chromosomes arranged and align themselves. Microtubules are responsible in pulling apart of the sister chromatids of every chromosome.
The homologous chromosomes (daughter chromosomes) are moved towards opposite sides. The formation of nuclear membrane takes place on separated daughter chromosomes.
• In animal cells, the pinching of cell membrane is done inwards, to create to form two daughter cells.
• In plant cells, the cell wall that is divided is built in between the daughter cells. The parent cell will split in half and produce to two daughter new cells.
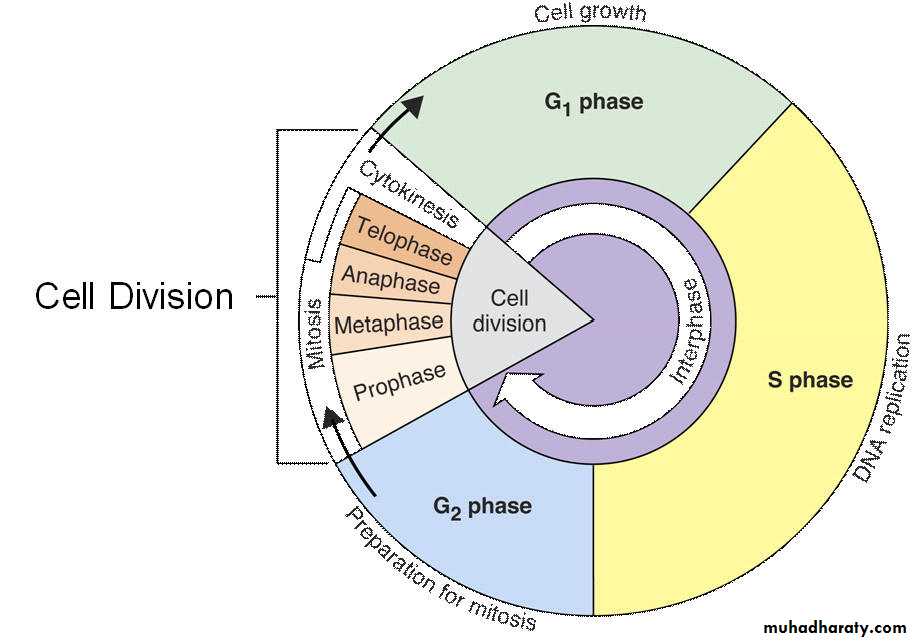
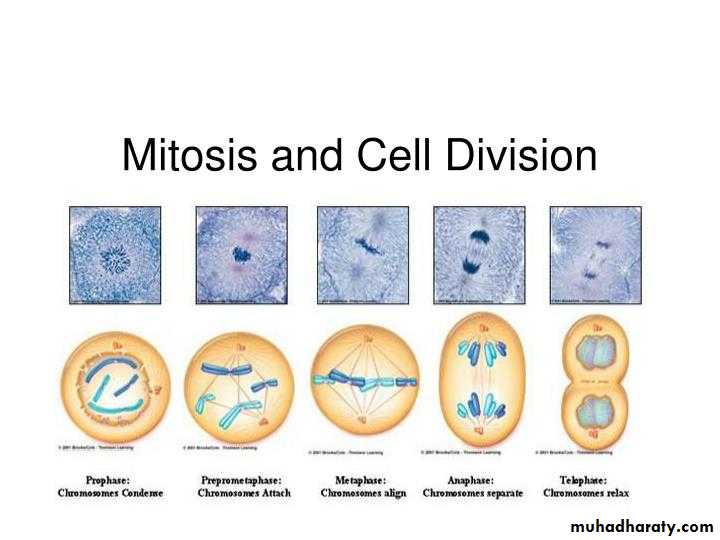
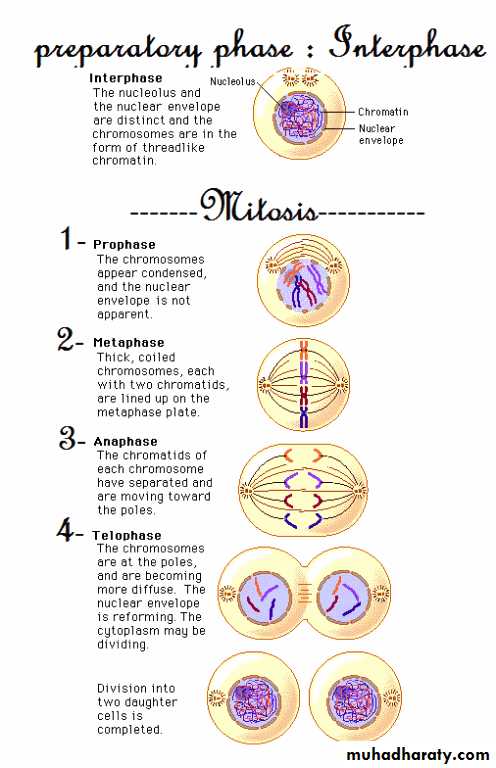
Phases of mitosis
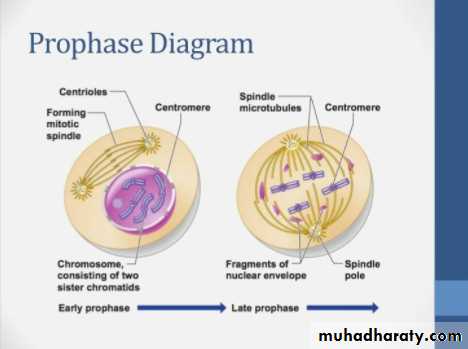
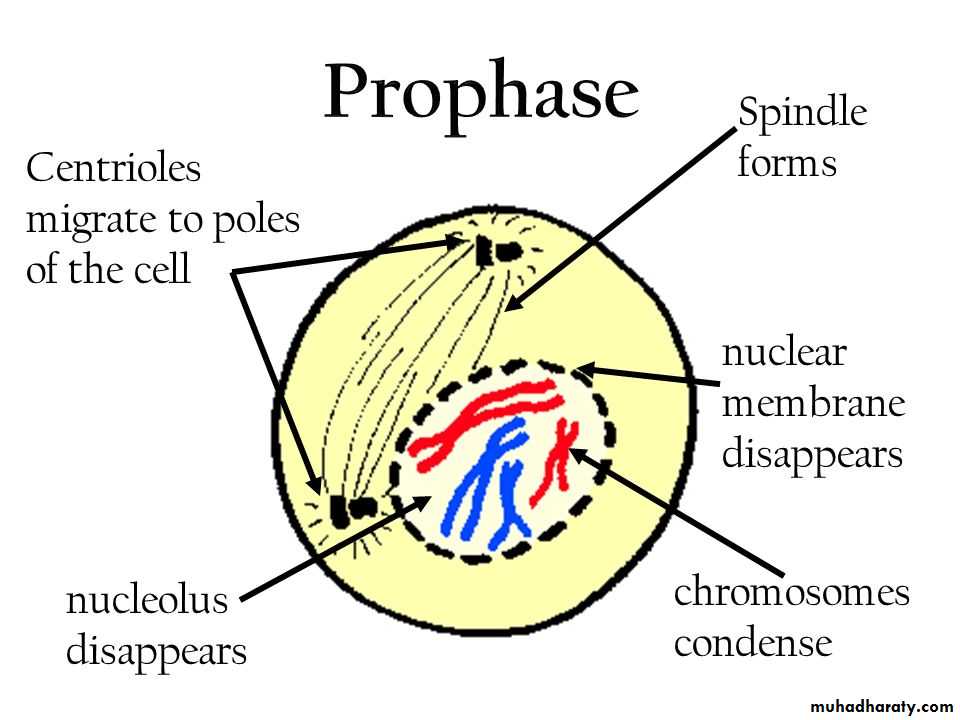
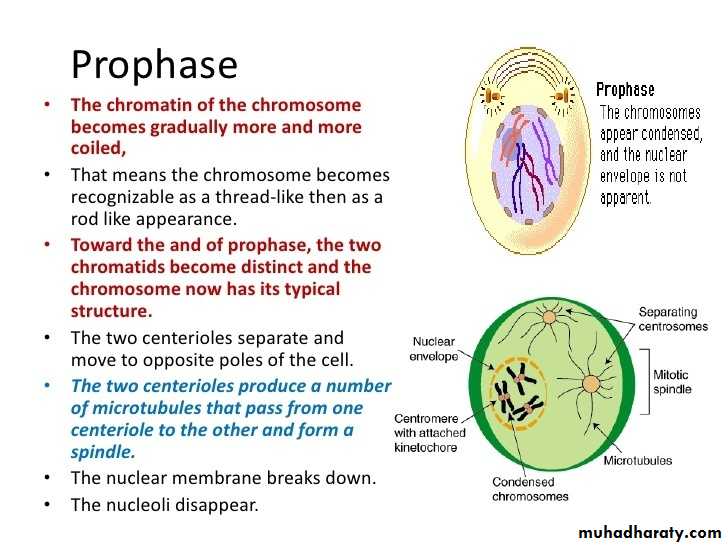
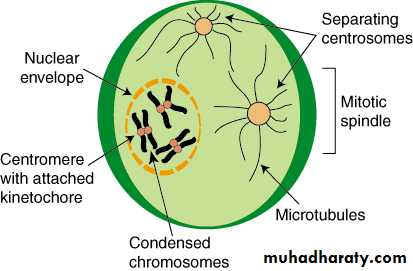
ProphaseIn first stage of prophase, the cell organelles prepare for cell division and chromosomes begin condensation for facilitating its migration to poles when cell dividing. Formation of mitotic spindles takes place by this step of mitosis. Between two centromeres mitotic spindles are formed out microtubules. These spindles are responsible in organizing chromosomes when a cell dividing through mitosis.
During prophase, cells do not only create structures, but it enters in breaking down some structures. Ribosomes are created by nucleolus which always resides in cell nucleus. The nucleolus will disappear quickly as a cell ready for division. In later prophase, or prometaphase, the breaking of nuclear membrane take place at this stage and found as a second stage of prophase. As nuclear membrane breaks, chromosomes get of nucleus to cytoplasm. Between centrosomes, there are mitotic spindles and these spindles take their expansion and begin capturing chromosomes.
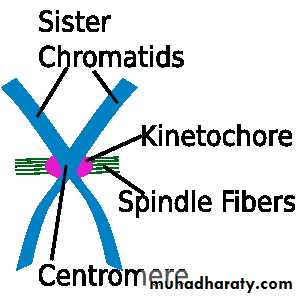
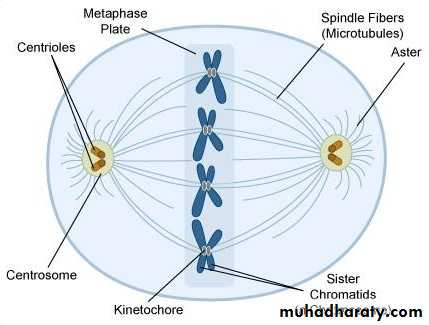
• After condensation of chromosomes, chromosomes get compacted. In mitotic spindles, microtubules are found and capture chromosomes and bind them kinetochore. The kinetochore is a structure located on the centromere of the sister chromatids, the region where the chromatids are the most tightly form their bonding and connection.
•
• MetaphaseThe beginning of metaphase, already started with bonding of mitotic spindles and chromosomes. And here they are found on line in the middle of the cell. At this stage, chromosomes have ability to divide. Each chromosome has two kinetochores and facilitate anchoring of chromosomes and microtubules. These are necessary for a cell to divide in proper manner.
After chromosomes organization, the mature cell enters the process known as spindle checkpoint. Where spindles verify if chromatids are organized in proper way for cell division.
Misalignments of chromatids can late cell division and in case cell division takes place with this problem of improperly attachment of chromatids, future problems in individual health.
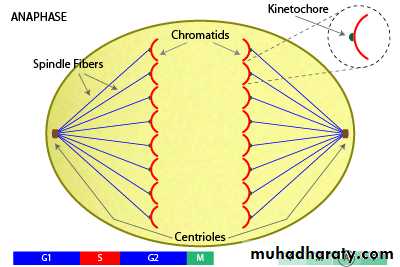
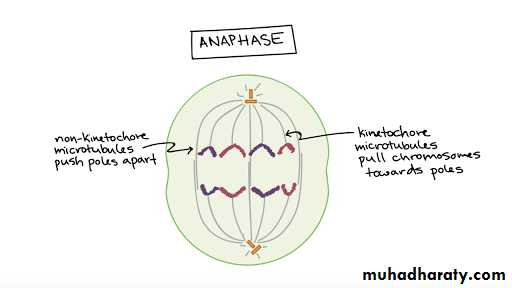
• AnaphaseChromatids have already aligned in central part of the cell, in anaphase, the centrosomes begin pulling on chromatids. During this phase, sister chromatids are pulled by means spindles and leave central part to poles. They create daughter chromosomes separately. The microtubules, at this stage begin elongating and facilitate a cell to divide in two daughter cells.
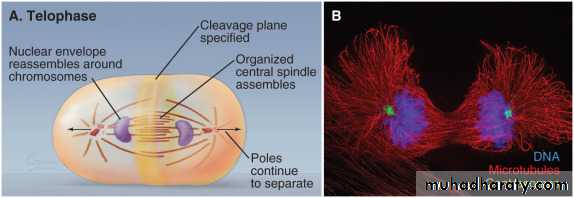
• TelophaseTelophase is the last and final step of a cell to divide. When a cell finished dividing in two daughter cells, the formed cells enters the process of living independently and begins establishing new cell structure. Breaking down of mitotic spindles occurs at this stage and these spindles return back in the initial state in its constituents. Chromosomes get unwound and get their form like strings or chains. Nuclei are formed in both new cells already produced and formation of nuclear membrane renew on formed nucleoli.
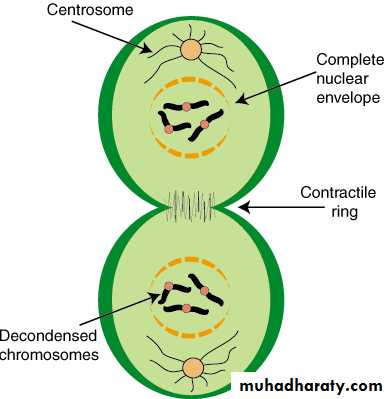
• The complete cell division cannot take place until cytokinesis takes place and finishes
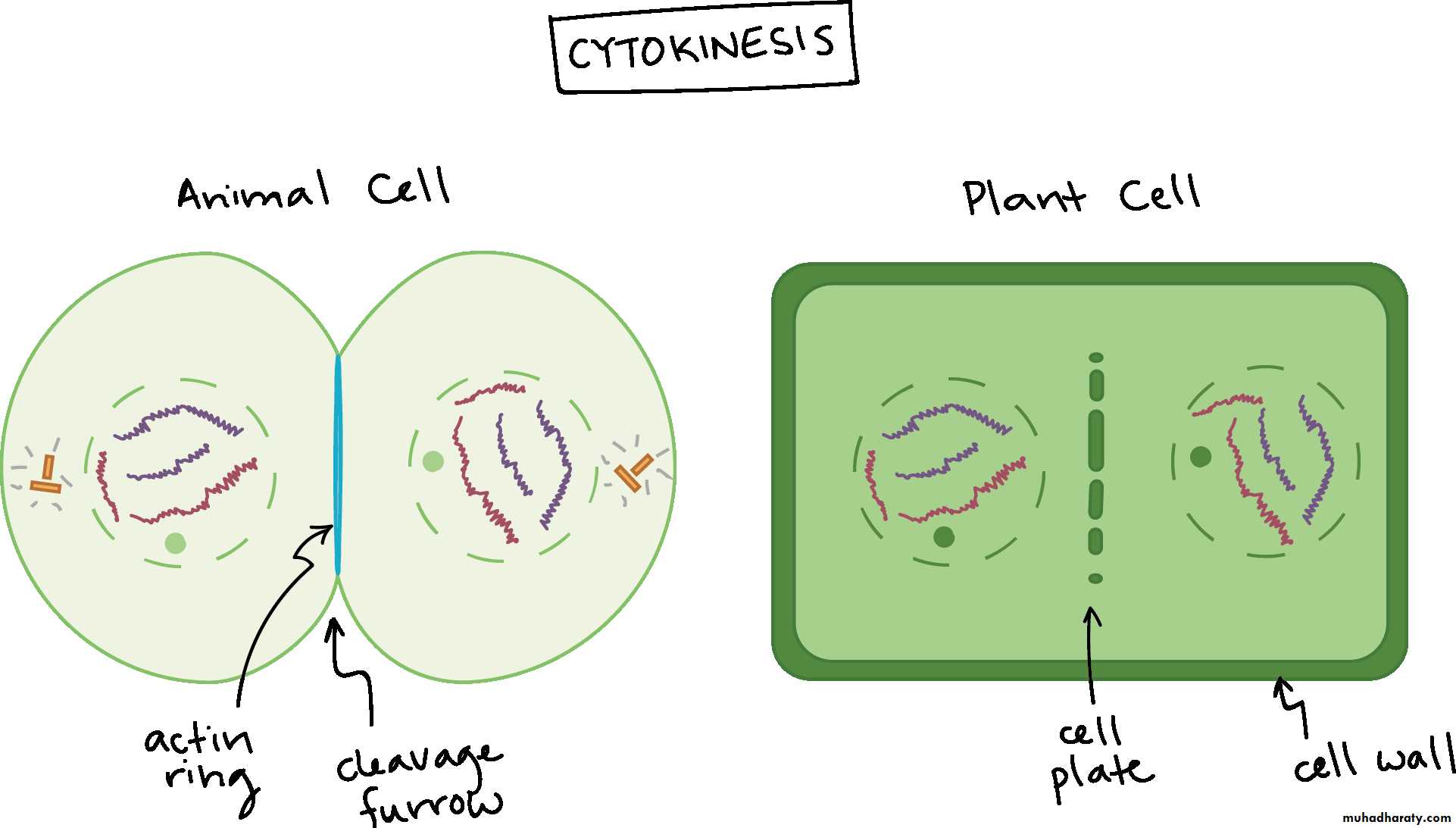
Cytokinesis
• Cytokinesis is the process that assures the division of mature cell into two new daughter cells with the same genome. It occurs in last phases of cell division. During cell division in animals, the cytoplasm is pinched and create cleavage furrow, and this continue up to the end of cytoplasm division.• There is a difference on plant cells, they don’t use the same process of division like that of animal cells, and one factor that makes difference is that their cell wall makes plant cells to be rigid. They easily make their new cell wall in central part of the cell.
• The four phases of mitosis are all integral to cell division and replication. Without mitosis, the cells in your body could not replicate, and life as we know it wouldn’t exist.
Thanks