TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
It’s the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease &0 consists of four major defects:Pulmonary stenosis
Ventricular septal defect
Aortic overriding
Right ventricular Hypertrophy
Clinical….features - The severity of obstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract determines the degree of right-to-left shunting, which usually determines the degree of cyanosis and the age of presentation.
- Complications of TOF include polycythemia leading to cerebrovascular thrombosis, hemoptysis secondary to enlarged bronchial arteries, paradoxical embolism ( leading to stroke or end organ failure ), subacute bacterial endocarditis, or brain abscess.
- Squatting is a classical behavioral adaptation of older children with TOF whereby systemic vascular resistance is increased, producing more pulmonary blood flow.
- Hypercyanotic episodes (“tet spells”) are characterized by intense cyanosis that may last minutes to hours, during which time oxygen delivery may be so compromised as to cause loss of consciousness or impairment of myocardial function. Dehydration, viral respiratory infection, and the injudicious administration of medications that lead to peripheral vasodilation all may cause a hypercyanotic episode in a patient who has been previously stable.
Physical Examination
Cyanosis
Ejection systolic murmur heard loudest in the second left intercostal space.
Digital clubbing.
Investigations
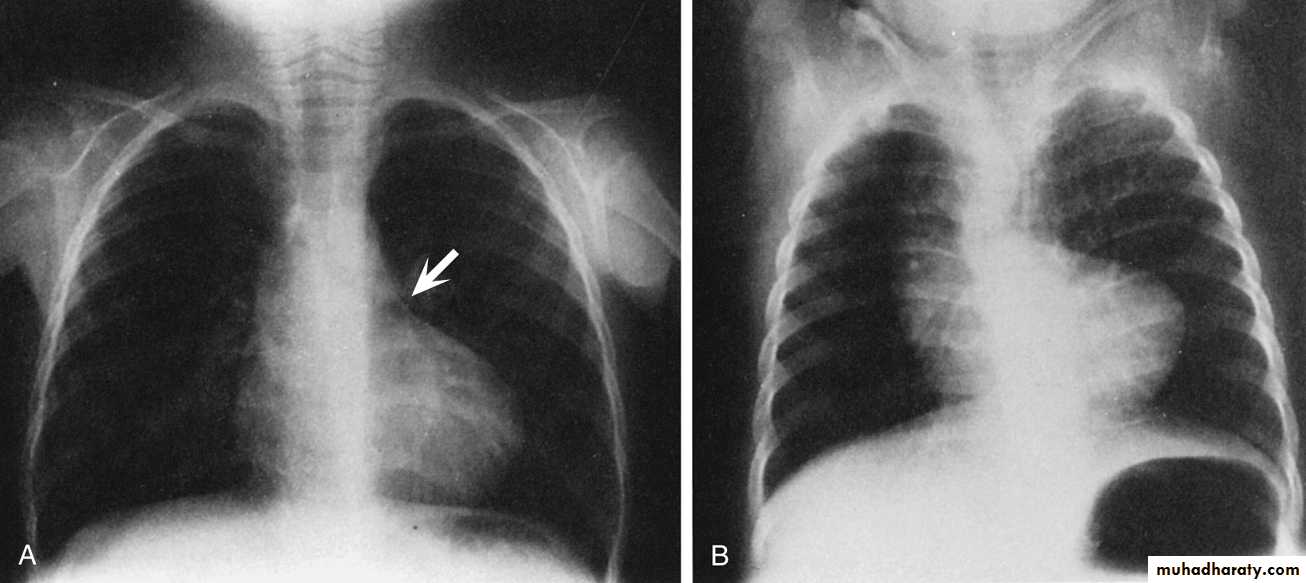
Chest X-Ray
Boot-shaped heart due to RVH + small pulmonary artery.
The lung fields usually appear oligemic
A right aortic arch occurs in approximately 25% of cases.
Chest film of TOF
ElectrocardiogramIt demonstrates right ventricular hypertrophy.
Laboratory Studies
PolycythemiaEchocardiography
It's diagnostic
Cardiac Catheterization
For further evaluationMEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Outpatient ManagementThe goals of medical management are to allow growth and development of the child until surgical repair is undertaken while hypercyanotic episodes or complications arising from the condition are prevented.
The preoperative management includes:
Maintaining these infants in a well-hydrated state.
Adequate feeding regimen.
Every effort should be made to protect these infants from respiratory viruses and dehydration accompanying diarrheal illnesses
Β-Blockers such as propranolol (Inderal) due to their negative chronotropic effects with increased ventricular filling at slower heart rates & relief of RVOT spasm.
Diuretics are contraindicated in cyanotic tetralogy.
Management of Hypercyanotic Episodes
Basic treatment principles include:
Administration of intravenous fluids, morphine or other intravenous sedatives, and oxygen.
Placing the infant in a knee-chest position can elevate systemic vascular resistance with a resultant increase in pulmonary blood flow.
Intravenous β-blockers such as esmolol and α-agonists such as phenylephrine may also be used to temporize.
Intubation and positive pressure ventilation may also be used to attempt to increase oxygenation.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
Palliative ProceduresBlalock-Taussig shunt
In performance of a subclavian-pulmonary anastomosis, the incision is generally made on the side opposite that on which the aorta descends. Ideally, the subclavian branch of the innominate artery is used for the anastomosis.Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt
It requires interposition of a segment graft material between the subclavian artery and the pulmonary artery.Central Aortopulmonary Shunt
This includes interposition of a graft material between the ascending aorta and main (or right) pulmonary artery.Waterston shunt
It’s between the ascending aorta to right pulmonary artery.Potts shunt
It’s between the descending aorta to left pulmonary artery .
RV Outflow Tract Patch.
Is to relieve the pulmonary stenosis but leave the ventricular septal defect open.
Balloon Angioplasty of RV Outflow Tract.
Total CorrectionThe goals of Correction
1-To close the ventricular septal defect
2-To relieve right ventricular outflow obstruction
3-To repair any stenoses in the pulmonary arteries