Endocrine system Dr.Razzaq L1
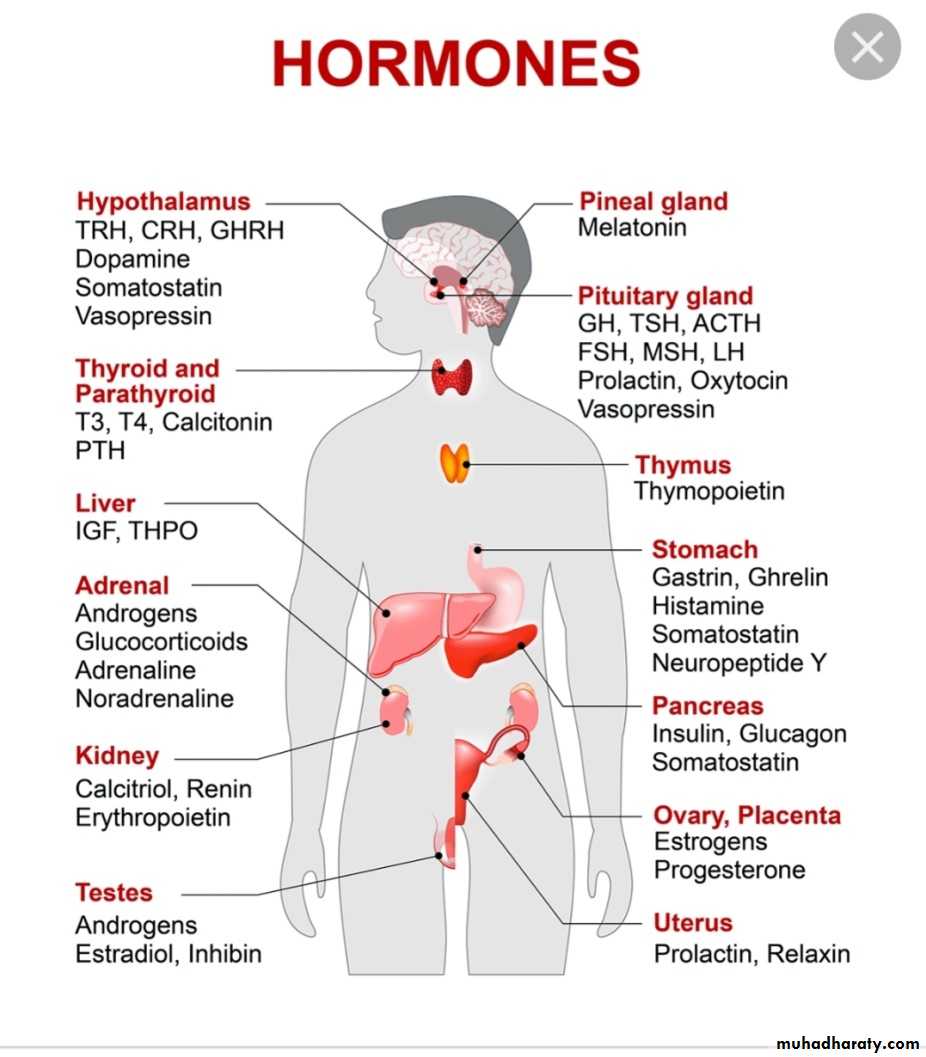
Hormones of hypothalamus and pituitary
The pituitary gland receive signals from hypothalamus & respond by sending pituitary hormones to target glands which produce hormones that provide negative feedback at level of hypothalamus and pituitaryHormones
Location
s\I(stimulate .inhibit)
Function
ACTH
Ant. pituitary
S
Production of glucocorticoid MC.miniralocorticoid.
androgen
ADH
Post. Pituitary
S
Water reabsorption from renal tubules
CRH. corticotropin releasing hor.
Hypothalamus
S
Secretion of ACTH
FSH (female)
Ant. Pituitary
I
Secretion of estrogen from ovary
FSH (male)
Ant. Pit
S
Production of sperm from testes
GnRH
Hypothalamus
S
Secretion of LH &FSH
LH(female )
Ant. Pit
S
Ovulation and development of corpus luteum
LH(male )
Ant. Pit
S
Production and secretion of testosterone
Oxytocin
Post. Pit
S
Contraction of uterus at birth &release of milk from breast
TSH
Ant. Pit
S
Secretion of T3.T4
PRL prolactin
Post. Pit
S
Promotion of milk synthesis
Somatostatin
Hypothalamus
I
Secretion of GH&TSH
TRH( thyrotropin releasing hormone)
Hypothalamus
S
Secretion of TSH & prolactin
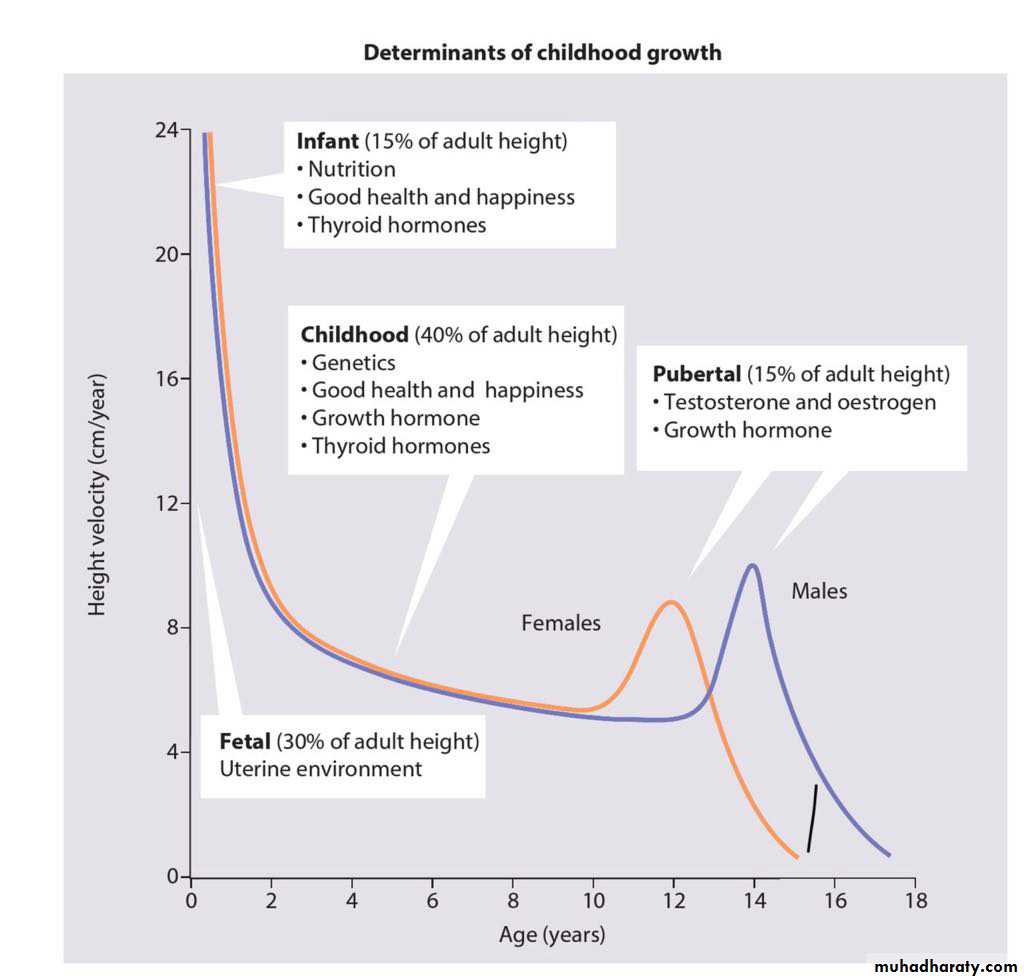
Growth hormone deficiency &insensitivity (hypopituitarism )
Hypopituitarism : denotes underproduction of GH growth hormone alone or in combination with deficiency of other pituitary hormones .
Congenital hypopituitarism growth hormone defciency )
Clinical features :The child usually normal size and weight at birth .may have neonatal emergencies like apnea .seizures .jaundice, cyanosis or Sever hypoglycemia with or without seizures prolonged neonatal jaundice is common .nystagmus may suggest septooptic dysplasia . micropenis in boys can be clue for GH def.
Physical exam:
head is round & face is short & broad ,prominent frontal bones eyes somewhat are bulging .mandible and chin are underdeveloped ,delayed teeth eruption and often crowded , short neck and small larynx , high pitch voice which remain high after puberty
Evaluation of suspected growth hor. Def.
Growth related history &physical examGrowth failure
Short stature
GHD affect 1in 3500 child
Image & other evaluation
Clinical diagnosis
Bone age ( delayed )
MRI,CT evaluate hypothamic pituitary region
Lab . finding
Measures GH with stimulation , IGF-1 test
Rationale for treatment
Replacement with GHTshould be started as soon as GHD is diagnosis
Diagnosis :
determined by low or absent level of GH in response to stimulation with insulin , arginine clonidine ,or glucagon to establish low level of GH <10 ng\ml and also necessary to evaluate others pituitary hormones deficiency like ACTH, TSH cortisol ,gonadotropin .
Treatment
recombinant hGH available since 1982 usually given in a dose 0.18-0.3 mg/kg/wk during childhood and higher dose needed during puberty. Therapy should continued until near final height is achieved and treatment discontinued if he or she tall enough or growth rate < I inch /year and bone age >14 yr in girls &>16 years in boys
Indication of GH therapy :
1-GHD 6-Prader willi syndrome
2-Turner syndrome 7-SHOX gene abnormality
( short stature homebox)
8-Noonan syndrome
3-Chronic renal failure 5-Small for gestational age
4-Idiopathic short stature
Adverse effect of GH therapy .include
pseudotumor cerbri .gynecomastia ,slipped capital femoral epiphysis & worsening scoliosis
Growth hormone insensitivity (LARON syndrome)
autosomal recessive disease.Is a condition that occur when the body unable to utilize GH , and characterized by short stature ,hypoglycemia ,near normal at birth ,delayed puberty & short limbs (arms &legs) with obesity .other signs include small genitals ,thin fragile hair those people have low risk of cancer and type II diabetes .
Diagnosis :
S&S , GH usually high and reduced level of IGF1 & genetic study to show abnormality in GH gene
Treatment : no current cure for Laron syndrome & only available treatment is subcutaneously injection of IGF1 (mecasermin)(Iplex)
Prognosis :generally good d not affect life span
Constitutional Growth delay
: one of the variant of normal growth . length & weight normal at birth , growth is normal for the first 4-12 months , height sustained at low percentile during childhood .
., the pubertal growth spurt delayed and eventual normal stature , normal bone age . GH response to provocative test tend to be lower than in children with a more typical timing of puberty . the prognosis of those children to achieve normal adult height is guarded
HYPERPITUITARISM ( TALL STATURE )
Either primary or secondaryTable showed differential diagnosis of tall stature & overgrowth syndromes
FETAL OVERGROWTH :
Maternal DM
cerebral gigantisim (Sotos syndrome)
Beckwith Wiedemann
Postnatal overgrowth leading to childhood tall stature
Nonendocrine causes
Familial (constitutional tall stature )
Exogenous obesity
Cerebral gigantism sotos syndrome
Marfan synd.
Bekwith wiedmann synd.
Klinfelter syndrome
Homocystinuria
Endocrine cause
Excess GH secretion
Precocious puberty
Hyperthyroidism
Mc Cune –Albright syndrome
Postnatal overgrowth leading to adult tall stature
FamilialMarfan
Klinfelter
Excess GH
XXY
ACTH or cortisol deficiency
Test question
Regarding Growth hormoneA - hypopitiutarism mean deficiency of all pituitary mormones
B- growth hormone deficient child usually small at birth
C- high pitch voice of GH deficient child usually corrected after puberty
D—treatment with GH usually stopped after 15 yr of age
E—laron syndrome have low risk of cancer