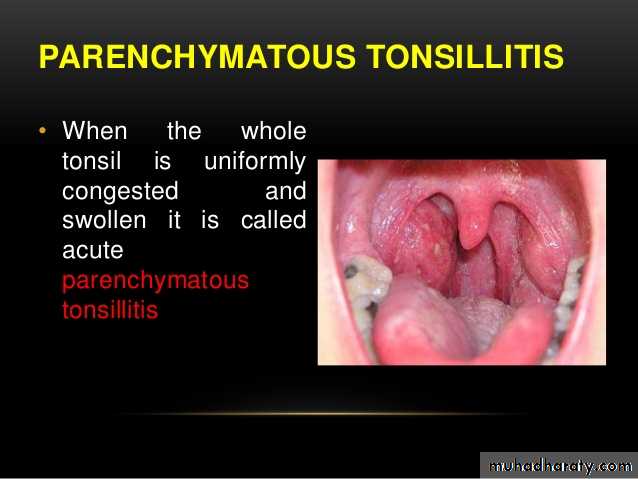
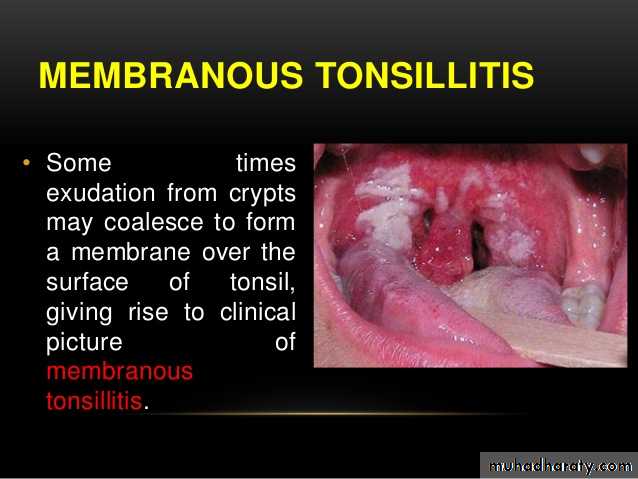
tonsillitis
Aetiology
Viral infection : 50%influenza ,parainfluenza, adenovirus, &
rhinovirus
Bacterial infection:
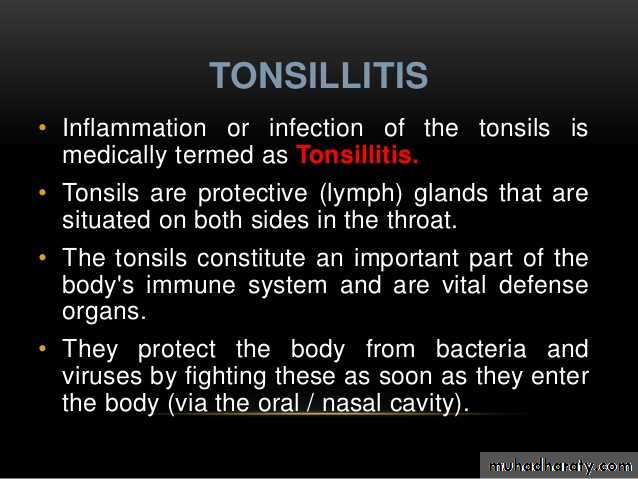
- B-haemolytic streptococcus
- Strept.pneumonia,
- H influenzae
- Staph. Aureus
- Moraxella catarrahlis
- Anaerobic organisms
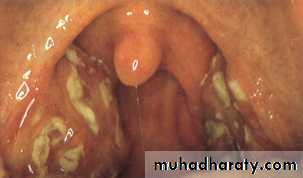
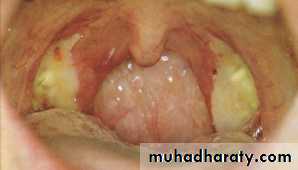
• Acute follicular ts. :
• Crypts of ts. filled with pus giving a spotted appearanceClinical features:
• Sorethroat
• Pyrexia
• Odynophagia
• Malaise
• Earache /referred otalgia
• Thickened speech
• In severe cases rigor & signs of toxaemia
• Appendicitis may simulated/ mesenteric adenitis.
Examination:
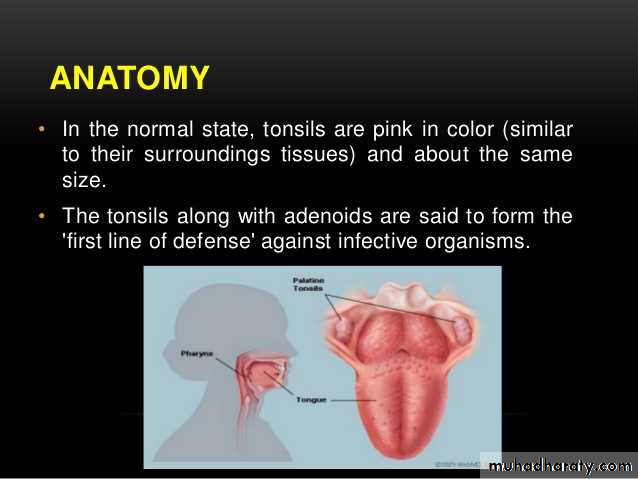
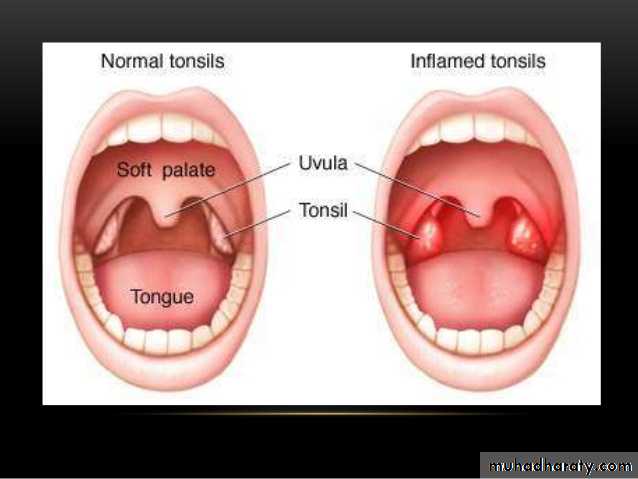
Congested & enlarged ts.Congested pillars.
Spots of pus or fibrin fill the crypts
Furred tongue & halitosis
Enlarged tender cx Ln.
Investigation:
• Throat swab for c/s• Complete blood feature
• Blood film / mono spot test (I.m.n.)
DDX:
• Scarlet fever
• Diphtheria
• Vincent`s infection
• Agranulocytosis
• I.M.N. ( glandular fever)
Treatment:
Bed rest , soft diet ,fluid intakeAnalgesic drug
Systemic AB.
Complications:
• Peritonsillar abscess• Parapharyngeal abscess
• Retropharyngeal abscess
• Edema of the larynx
• Acute rheumatism
• Acute nephritis
• Septicemia
• Acute OM.
Recurrent acute tonsillitis
Clinical features:
1. persistent or recurrent sore throat
2. marked ts. enlargment.
3. injected ant. pillars
4. halitosis
5. persistent cx. adenitis.
treatment:
tonsillectomy
tonsillectomy
Indications:1- recurrent ts. : 7//1 year
or 4//2 years
2- recurrent episodes of
peritonsillar abscess (2nd attack)
3- suspected neoplasm
( unilateral enlargement, or ulceration)
Contraindications:
• Recent ts. infection or URTI < 2wks
• Bleeding disorders
• Using of contraceptive pills
• Cleft palate
• Epidemics of poilo , viral infection (corona v.)
Complications of tonsillectomy:
• Peroperative:• 1- anaesthetic reaction
• 2- haemorrhage
• 3- damage to teeth, uvula, or
• to post. Pharyngeal wall
• 4- dislocation of the
• temporomandibular joint
B. Post operative:
Reactionary hemorrhage / 1st,24hsAnaesthetic complications
Secondary haemorrhage / 5th – 10th day
Infection of the ts. bed
Earache
Pneumonia
Tonsillar remanant
Post ts, haemorrhage
Reactionary (primary):
secondary
Reactionary haemorrhage:
~2%Within 24hs
Signs of the bleeding :
- obvious bleeding
- gurgling sound in throat during breathing
- repeated swallowing
- vomiting
- rising pulse rate & lowering of Blood p.
Management:
Blood sample for cross matchingIV, infusion
Identifying the bleeding site
Application of 1:1000 adrenaline soaked gauze or using hydrogen peroxide gurgle
If failed >>> 2nd anaesthesia >>stop the bleeding
Secondary haemorrhage
5th- 10th day
Infection
R/: admission & observation
Blood for cross match
AB.
H2O2 gargle (20 minutes waiting)
Adrenaline socked gauze in the fossa (20 minutes)
If failed 2nd anaesthesia/ suturing the pillars .
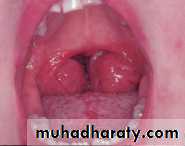
Post ts pictures ,healthy/infected
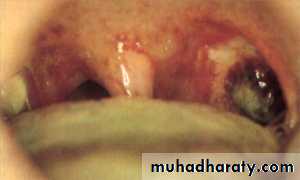
Peritonsillar abscess(quinsy)
Def;pus collects between ts. & sup. Cons.m.
Aetiology;
• - follows tonsillitis• - mostly unilateral
Clinical features:
• -Severe pain
• -pyrexia up to 40 C°
• -Headache & malaise
• -Trismus
• -Earache
• -Intense salivation
• -Thickened speech
• -Foetor oris
examination
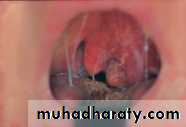
Marked hyperaemic edematous tonsil and palatal regionOedematous uvula & pushed towards other side
complications
Parapharyngeal abscessOedema of the larynx
septicemia
treatment
• 1. Conservative in early stage( cellulitis)
• - rest , AB. , analgesia
• 2. Surgery :
• - incision of the abscess
• - abscess-tonsillectomy