pharynx
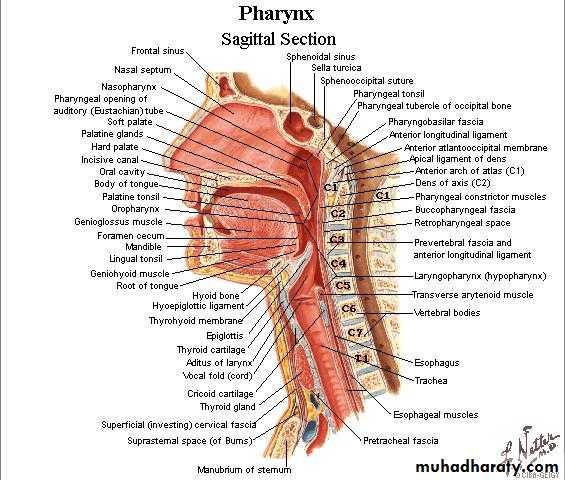
Funnel shaped musculomembranous tubeextended from the skull base to the oesophagus opposite the sixth cervical vertebra
Pharynx
• Nasopharynx• Oropharynx
• Hypopharynx.
Nasopharynx
• Pharyngeal opening of the eust.tube• Pharyngeal recess/ fossa of rosenmuller
• Nasopharyngeal tonsil
•
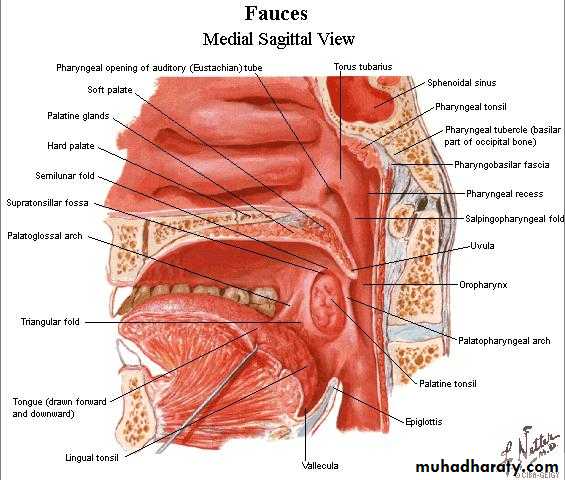
oropharynx
From soft palate to the upper border of the epiglottisLat. Wall contains palatoglossal , palatopharyngeal arches & palatine tonsil in between
hypopharynx
From upper border of epiglottis to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage.From 3rd to 6th cx. vert.
Supported by thyroid cartilage & thyrohyoid membrane
Nerve supply
• Motor:• * cranial part of the XI nerve & vagus n (X)
• ** glossopharyngeal n (IX) to
• stylopharyngeus muscle only
• 2. Sensory :
• - maxillary n from the nasal part
• - glossopharyngeal n.---oral part
• - internal laryngeal n of the vagus from the
• laryngeal part
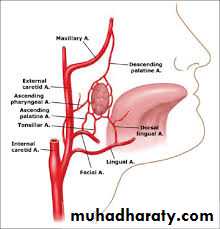
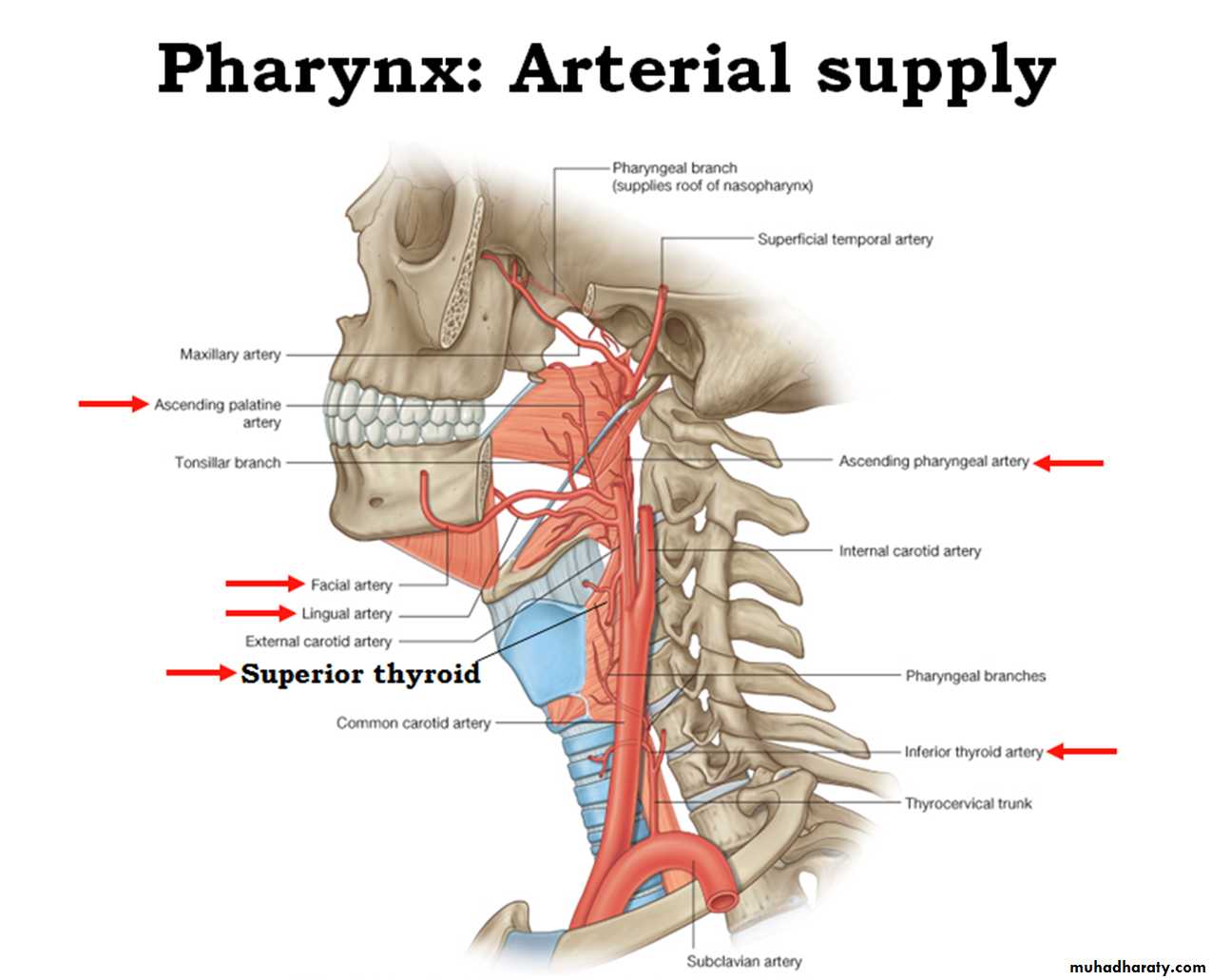
Blood supply
• Ascending pharyngeal a.
• Ascending palatine
• Facial a.
• Maxillary a
• Lingual a
Veinous drainage : pharyngeal pluxes to int.jug.v.
Lymphatic drainage:#- deep cx. Ln.
#- retropharyngeal
#- parapharyngeal Ln
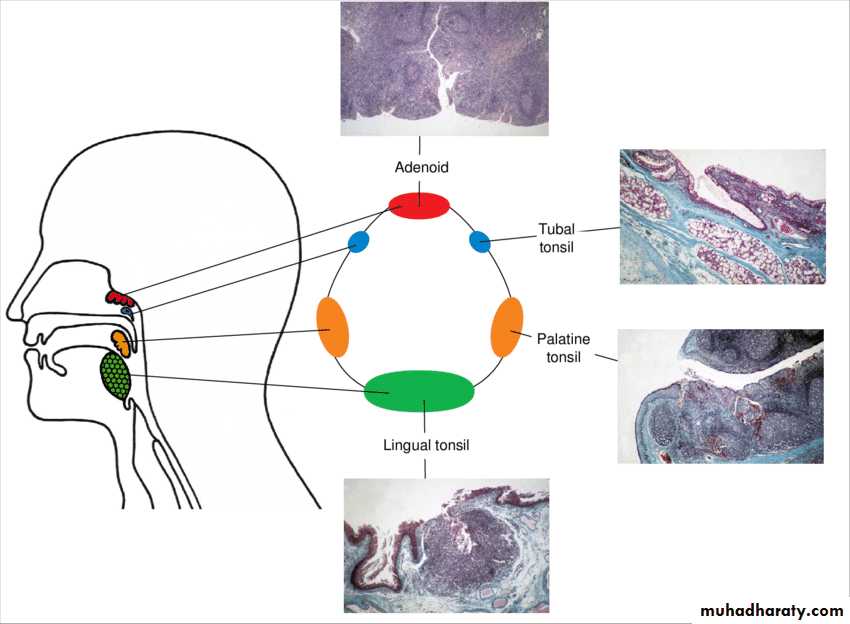
- subepithelial lym. t. (Waldeyer`s ring):
1-palatine ts.
2-n/p ts ( adenoid)
3- lingual ts.
4- tubal ts.
5- lateral pharyngeal band.
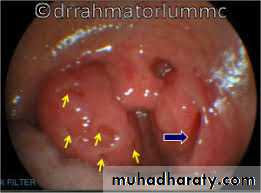
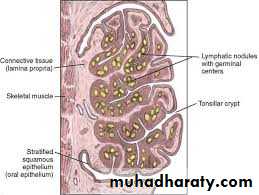
Palatine tonsil
Two masses of lymphoid tissue located in the lat. wall of the oropharynx between ant. & post. Faucial pillarsThe free medial surface project into the cavity of pharynx and pitted by numerous small opening lead into crypts in which the mucous glands are secreting
Lat. Surface covered by fibrous tissue called capsule
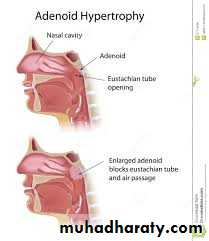
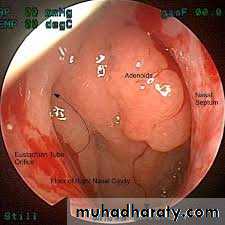
adenoid
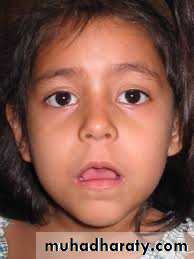
Hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil sufficient to produce symptoms .- most commonly between 3 & 6 years.
- atrophy begins after 10 years / completes before 20 years.
Symptoms &signs
• Due to hypertrophy :• 1. nasal obstruction causing :
• a- mouth breathing
• b- difficulty in eating
• c- noisy breathing & eating
• d- drooling
• e- snoring
• f- toneless voice
• Eustachian tube obstruction:
• a- deafness
• b- Secretory o. m.
• B. Due to inflammation:
• nasal discharge & post nasal drip
• ( egg- white plug of mucus seen behind uvula on gagging is almost diagnostic) .
• O.M.
• rhinosinusitis
• Cx. Lymphadenitis.
C. Generalized disturbances:
mental dullnessApathy
Nocturnal enuresis .
diagnosis
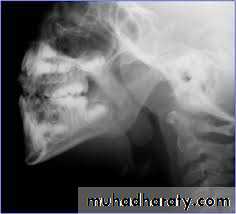
Symptoms, signs & examination by postnasal mirror in quite young children .X-ray of post nasal space .
Endoscope.
DDX. :
• Other causes of nasal obstruction
intrinsic rhinitis
F.B.
hypertrophy of posterior end of the inf. Turbinate.
Nasal septal deviation .
Congenital choanal atresia
Sinusitis
Antrochoanal polyp.
• Orthodontoic abnormalities / high arch palate.
• Thorn Waldt`s disease / cystic persistence of the median furrow of the n/ph tonsil.treatment
A- conservative / no marked symptoms & signs- decongestant nasal drop
- fresh air breathing & postural exercise
- nose blowing training
B- adenoidectomy
Indications of adenoidectomy
1- obstructive sleep apnea .
2- significant hearing loss.
3- repeated tonsillitis ,sinusitis or otitis media.