Pertussis (whooping cough)
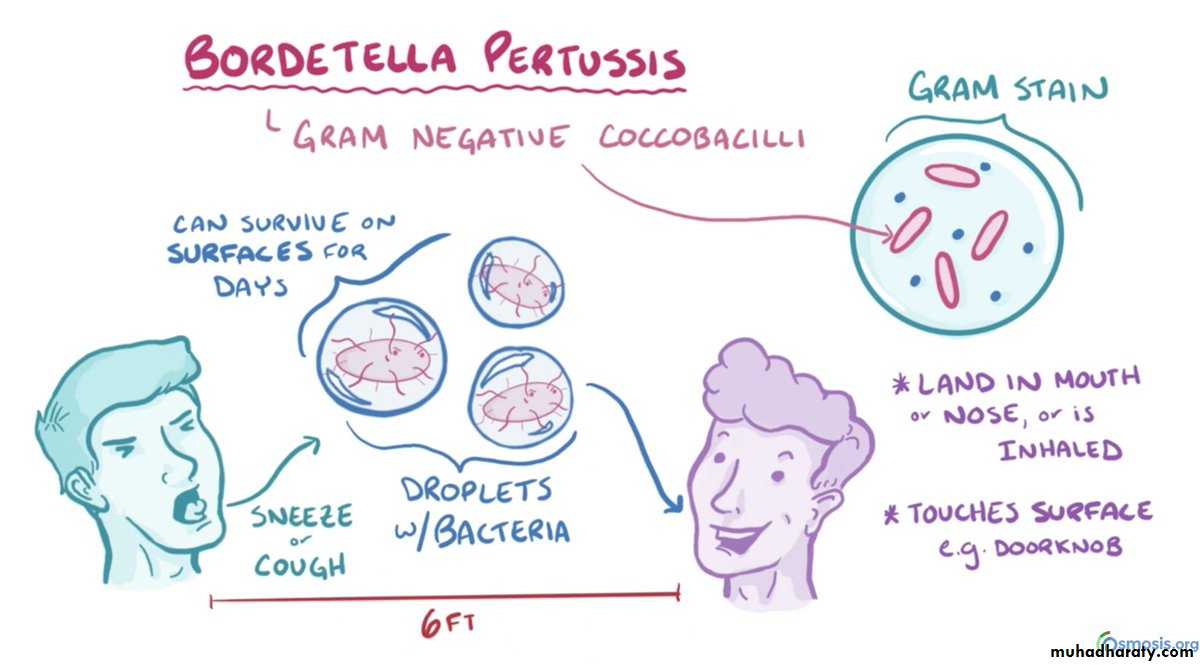
it is caused by Bordetella pertussis which is fastidious, gram-negative coccobacilli. Bordetella parapertussis is an occasional cause of sporadic pertussis .EPIDEMIOLOGY:
- It is extremely contagious, with attack rates 100% in close contacts.
- After intense exposure , the rate of subclinical infection is 80% in fully immunized or previously infected individuals.
- Neither natural disease nor vaccination provides complete or lifelong immunity against reinfection or disease.
- Mothers provide little protection to young infants.
Transmission is by droplets released during intense coughing especially in the catarrhal stage.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS:
Incubation period 3–12 days. Pertussis divided into 3 stages:1- The catarrhal stage (1–2 wk) :begins with congestion and rhinorrhea, low-grade fever, sneezing, lacrimation, conjunctivitis, & mild dry cough .
2- paroxysmal stage(2-6wk.): The cough begins as a dry, intermittent, irritative and progress into the paroxysms.
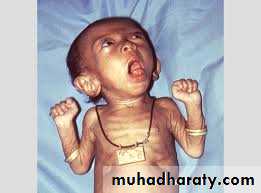
During attack of paroxysm, chin and chest held forward, tongue protruding maximally, face purple, until coughing ceases and a loud whoop(forcefull inspiratory gasp) follows.
This whoop not apparent in infant < 3 mo. of age & adults.
Infants <3 mo of age do not showing classical stages.
The catarrhal phase lasts only a few days. After that, young infant begins to choke, gasp, with face reddened.Cough may not be prominent & Whoop infrequently occurs.
Cyanosis can follow a coughing paroxysm, or apnea can occur without a cough. Apnea may be the only symptom .
Immunized children have foreshortening of all stages of pertussis.
3- convalescent stage (≥2 wk) : the number, severity, and duration of episodes diminish. Chronic cough may persist for several months.
- Findings on physical examination are uninformative. Conjunctival hemorrhages and petechiae on the upper body are common.
DIAGNOSIS :
1- typical clinical presentation.2- Leukocytosis (15,000–100,000 cells/mm3) with absolute lymphocytosis .
2- Chest x-ray: showing perihilar infiltrate or edema and atelectasis. Pneumothorax & pneumomediastinum can be seen.
3- Isolation of B. pertussis in culture of specimen obtained by deep nasopharyngeal aspiration .
4- polymerase chain reaction.
5- serologic tests for detection of antibody to B. pertussis antigen in acute & convalescent samples.
COMPLICATIONS :
1- Apnea especially in infants < 3mo. of age .2- Secondary bacterial infections (such as otitis media and pneumonia) .
3- Bronchiectasis .4- conjunctival and scleral hemorrhages, epistaxis, hemorrhage in the central nervous system (CNS) and retina result from increased intrathoracic and intra-abdominal pressure during coughing .
5- pneumothorax and subcutaneous emphysema .
6- umbilical and inguinal hernias .
7- Seizures due to hypoxemia, intracranial hemorrhage or hyponatremia from excessive secretion of antidiuretic hormone during pneumonia can occur.TREATMENT :
Indications for hospitalisation :*infants < 3mo. of age are admitted to hospital almost without exception.
*Those between 3–6 mo if paroxysms are severe
*Those of any age if significant complications occur.
1-Supportive care:
- avoid provoking factors for cough like smoke, excessive stimulation .- Good hydration, adequate nutrition & avoid large volume feeding .
- For excessive secretion, frequent suction to clean airway & prevent aspiration .
2- Antibiotics:
- Azithromycin :it is drug of choice in neonates, 10mg/kg/day for 5days.Alternatives drugs are:
- Erythromycin 40 -50mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses for 14 days (associated with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in neonates) .Or Clarithromycin, Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ) .
3- respiratory isolation of patient immediately & until 5days after initiation of macrolide therapy .
4- macrolide agents should be given to all close & household contacts regardless of age, history of immunization or symptoms.
PREVENTION :
DPT vaccine.Varicella (chickenpox)
Varicella-Zoster Virus(VZV)It is double-stranded DNA human herpesvirus.
It causes primary infection which is varicella (chickenpox). This infection result in lifelong latent infection of sensory ganglion neurons.
Reactivation of this latent infection causes herpes zoster (shingles).
EPIDEMIOLOGY :
- Patients with varicella are contagious from 24 to 48 hr before the rash appears and until vesicles are crusted, usually 3–7 days after onset of rash.Transmission by respiratory secretions and the fluid of skin lesions either by airborne spread or through direct contact.
Clinical manifestations
-Incubation period 10 to 21 days.
- Fever, malaise, anorexia, headache, and mild abdominal pain occur 24–48 hr before the rash appears. Fever persist during the 1st 2–4 days after the onset of the rash.
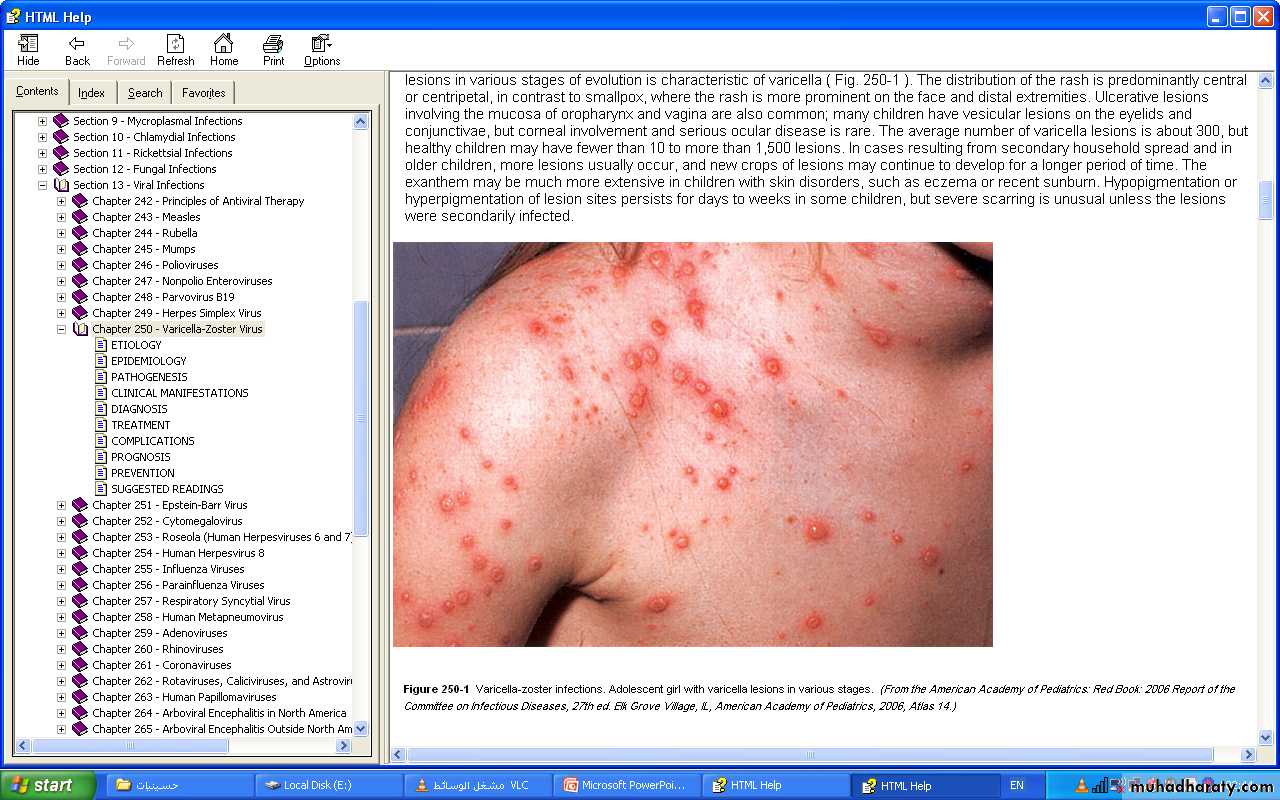
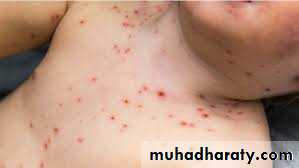
- Varicella rash appear first on the scalp, face, or trunk. Initially consists of intensely pruritic erythematous macules that evolve through the papular stage to form clear, fluid-filled vesicles. Clouding of the lesions begin in 24–48 hr.
The distribution of the rash is centripetal.
Neonatal Chickenpox :
Infants whose mothers develop varicella in the period from 5 days before to 2 days after delivery are at high risk for severe varicella, because the mother has not yet developed a significant antibody response. Those newborn given human V-Z Ig & if develop disease give acyclovir .If the mother develops varicella more than 5 days prior to delivery, infection is attenuated due to transmission of maternal antibody across the placenta.
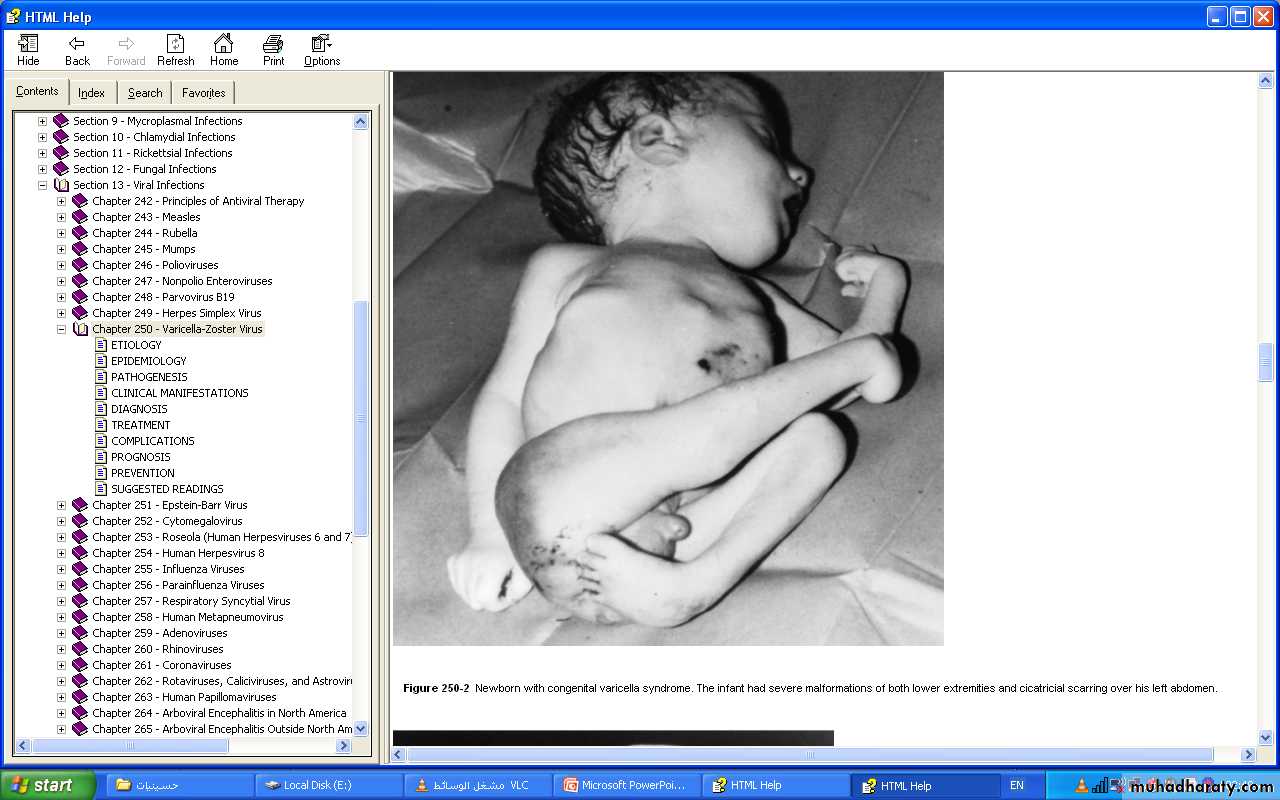
Congenital Varicella Syndrome (CVS):
When pregnant women develop chickenpox early in pregnancy(1st 20 wk of pregnancy) , 2% of fetuses demonstrate CVS .Stigmata of CVS:
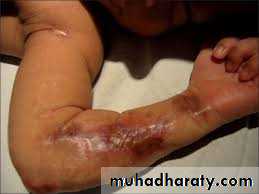
- Cicatrix (a zigzag scarring, in a dermatomal distribution), & hypopigmentation due to damage to sensory nerves.
- Microphthalmia, Cataracts ,Chorioretinitis &optic atrophy.
- Microcephaly, Hydrocephaly, & brain Calcifications .
- Hypoplasia of an extremity, Motor and sensory deficits , Absent deep tendon reflexes, Anal/urinary sphincter dysfunction.Diagnosis of CVS :
1- History of gestational chickenpox with stigmata in the fetus .2- PCR to detected viral DNA in tissue samples .
3- VZV IgM antibody detected in the cord blood sample.
TREATMENT: No specific treatment for CVS.
DIAGNOSIS :
1- Clinically2- Leukopenia with relative lymphocytosis .
3- Direct fluorescence assay to identify the virus from the cutaneous vesicular lesions .
4- PCR .
5- 4-folds rise in VZV-IgG antibodies .
COMPLICATIONS :
1- Secondary bacterial infections : include superficial impetigo, cellulitis, and subcutaneous abscesses .2- Encephalitis and Cerebellar Ataxia.
3- Reye syndrome: can associated with varicella especially if aspirin use as antipyretic .
4- Transverse mylitis & Gullian barre syndrome.
5-Pneumonia.6- others rare complications: hepatitis, nephrotic syndrome, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, myocarditis, pancreatitis, thrombocytopenia.
TREATMENT :
1- Aspirin should not be used as antipyretic in varicella .2- Calamine lotion for soothing pruritis, or use antihistamine .
3- Acyclovir : indicated for sever disease & in immunocompromised patients, I.V 10mg/kg/dose every 8hr.
Oral Acyclovir used for herpes zoster in children .
PREVENTION :
1-Varicella vaccine .2- Postexposure Prophylaxis :
varicella-zoster immune globulin (VZIG) given within 96hr. of exposure, indicated in :1- immunocompromised patients .
2- pregnant woman .3- Newborns whose mothers develop varicella 5 days before to 2 days after delivery .
4- premature infants <28 wk of gestation .5- high-risk patient in close contacts with patient have herpes zoster .