1
College of Medicine
Dept. of Medical physics 2019-2020
Heat and cold in medicine /CH 4
*****************************************************************
Physical Basis of Heat and Temperature
As molecules of all materials are moving so they have kinetic energy. The average
kinetic energy of an ideal gas can be shown to be directly proportional with temperature.
An increase of temperature of any material means an increase in the energy of molecules
of that material. If enough heat added to a solid, it melts, forming a liquid. The liquid may
be changed to a gas by adding more heat. Adding still more heat converts gas to ions.
While adding heat to substance increase its molecular kinetic energy, which increase
its temperature, the reverse is also true, heat can be removed from a substance to lower the
temperature,
Thermometry & Temperature scales:
—
Thermometry is instrument to measurement heat while temperature scales represented
unit of measuring the temperature.
—
Temperature is difficult to measure directly, so we usually measure it indirectly by
measuring one of many physical properties that change with temp. .
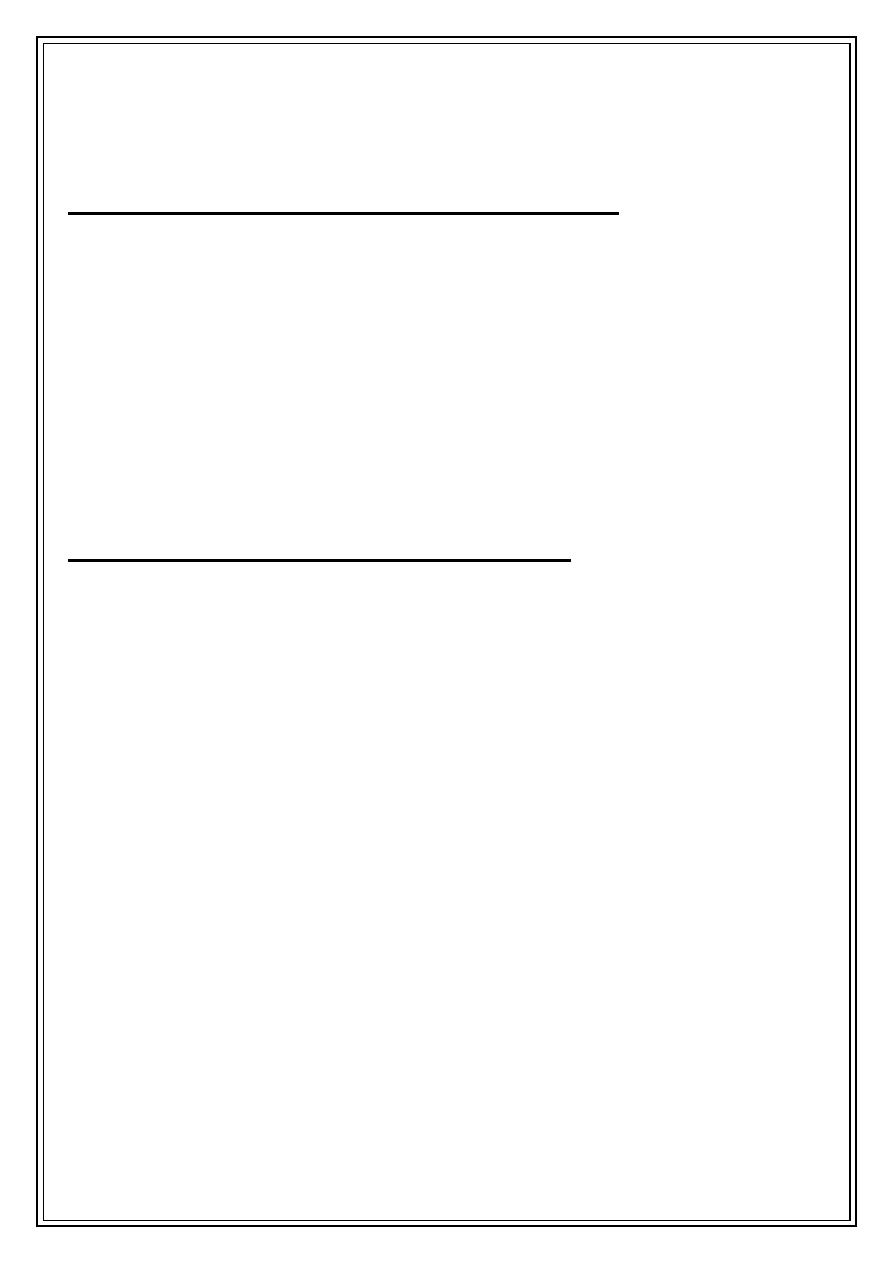
1-Fahrenheit scale (°F): in this scale the freezing temp. is 32°F and boiling point is
212°F ,and normal body temp. is about 98.6°F .
2-The Celsius (°C): the freezing point is 0°C and the boiling point is 100°C, in
between is divided into 100 divisions.
3-The Kalvin scale(°K):or the absolute scale this scale has the same divisions as
the Celsius but takes the 0° K at the absolute zero which is=-273.15°C.
2
To change °C to °F
[°C= (°F-32) 5/9] or [°F=°C (9/5)+32]
Also °C=°K-273 or °K=°C+273
3
Types of thermometers
1-Glass-liquid thermometer
This called a glass fever thermometer. This thermometer composed of glass capillary
tube ends with a bulb a store for liquid, the liquid can be mercury or (alcohol for low
temperature measurement). The principle behind this thermometer is that an increase in
the temperature of different materials usually causes them to expand different amounts.
When the thermometer is heated the liquid inside will expand more than the glass causing
the liquid to raise in the capillary, for mercury it expands 1.8% from (0- 100°C).As the
fever temp. is needed to be precise it has a thin capillary less than 0.1mm in diameter,
which makes the mercury to rise higher per degree.
That it would be very difficult to read if it were not designed for visibility. Two
things increase the visibility of the capillary: the glass case acts as a magnifying glass
and an opaque white backing in used.
In addition to that the fever thermometer has a restriction above the bulb making the
mercury not to return if the thermometer is exposed to low temp. unless the thermometer
is moved rapidly with proper snap of the wrist. The temperature is usually taken underneath
the tongue or in the rectum. Since the thermometer is usually considerably colder than the
body its lowers the temperature of the surrounding tissue when it is first inserted. It takes
several minutes before the temperature of the tissue rise to the original value.
2- Thermistor
It's composed from a bridge of four resistances with a source of electricity. These
resistors are in balance and one of them is used for temp. measurement (resistor T).This
resistor as any other resistance changing with heat but this particular resistance has the
property of rapid change with heat (5 %/°C).A bridge circuit with a thermistor in one of
the legs, initially the four resistors are equal, the bridge is balanced, by symmetry, the
voltages at each end of the meter are equal and no current flows through the meter. A temp.
change causes the thermistor resistance to change . This unbalance the bridge, the voltages
at each end of the meter become un equal, causing a current to flow through the meter and
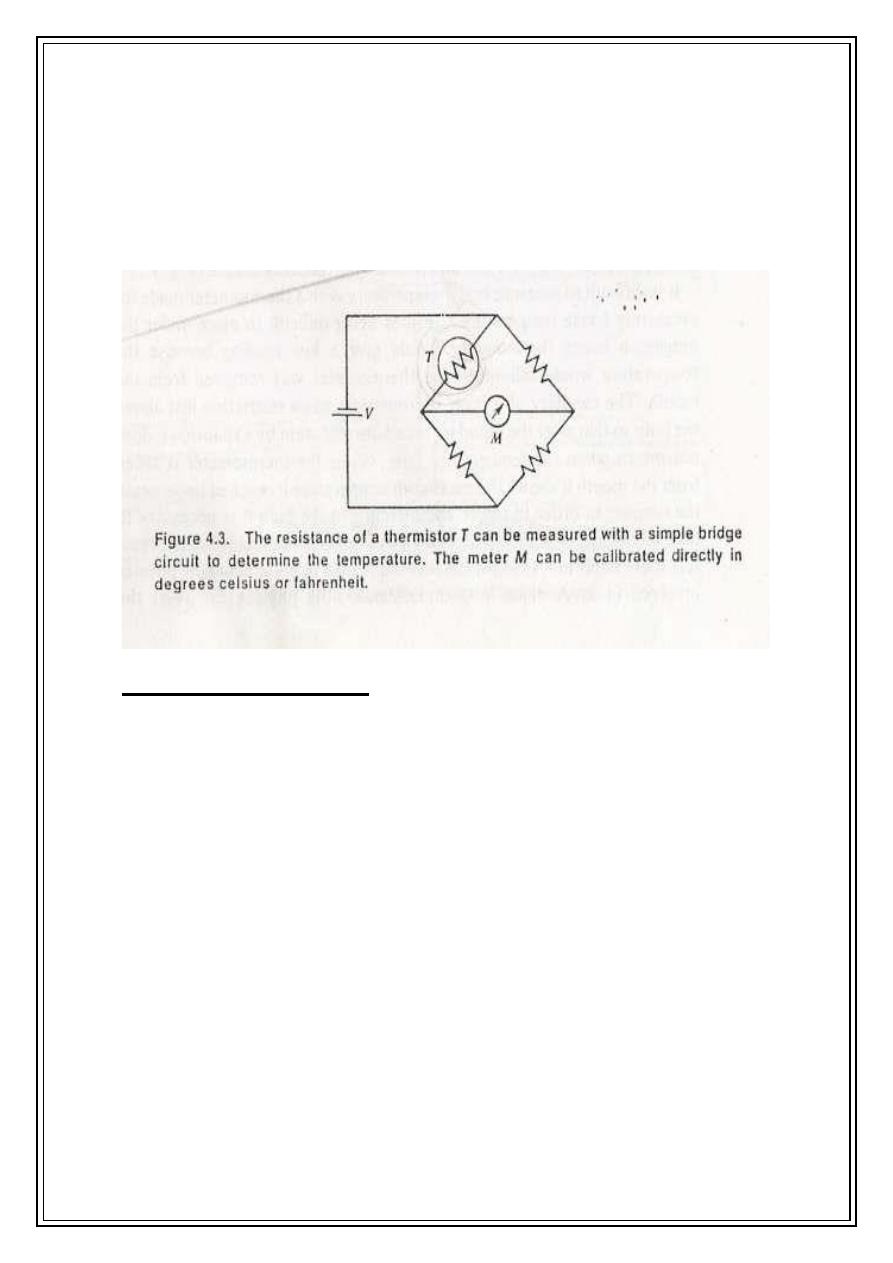
4
the resulting meter deflection can be calibrated for temp. with thermistors it is easy to
measure temp. changes of 0.01°C . therefore are used quite often in medicine because of
their sensitivity.
Thermistors are placed in the nose to monitor the breathing rate of patients by
showing the temp. change between inspired cool air and expired warm air (pneumograph).
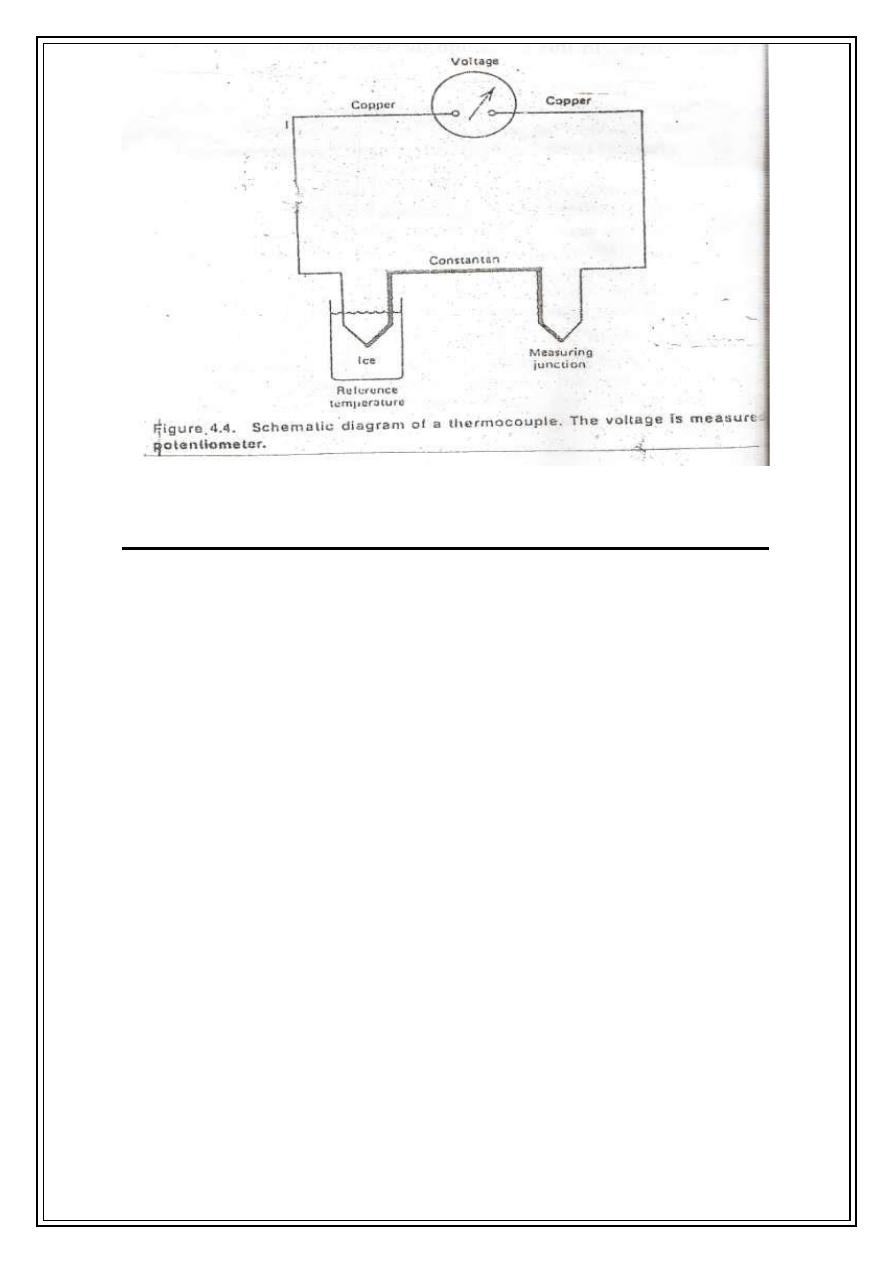
3-Thermocouple:-
Consist of two junctions of two different metals. If the two junctions are at different
temp.. A voltage is produced that depends on the temp. difference. Usually one of the
junctions is kept at a reference temp. such as in an ice-water bath. The copper -constantan
thermocouple can be used to temp. from -190 to 300°C. For 100°C temp. difference, the
voltage produced is only about 0.004V.Thermocouple can be made small enough to
measure the temp of individual cells.
5
Thermograph-mapping the body's temperature:
The temperature of body's surface is different in different parts. Depending on
▪ External physical factors and internal metabolic.
▪ Blood supply to the skin.
Measurement of surface temp. is useful to diagnosis of some diseases, which may change
locally the skin temp.. The body heat can give infrared radiation (IR) of long waves, which
are not visible unlike the red-hot object which is visible. By using this principle the
thermograph instrument was designed to measure the radiation emitted from a part of the
body.
There are two techniques to measurement the body’s temperature they are:
▪ A basic thermographic unit used to measure the radiation emitted from a part
of the body
▪ A commercial instrument used in clinical thermography.
Clothing affects skin temperature so that must be removed before thermography.
Heat radiation power can be measured by Stefan-Boltzman law for the total radiative power
per surface area:
W= e σT
4
6
Where
T: is the absolute temp. of the body
e: is the emissivity depends upon the emitter material and its temp. for radiation from
body e is almost 1.
σ: is the Stefan –Boltzmann constant=5.7×10
-12
W/cm
2
°K
4
Example:
a. what is the power radiated per square centimeters from
skin at a temp. of 306°K.?
W= e σT
4
= (5.7×10
-12
)(306)
4
= 0.05W/cm
2
b. what is the power radiated from a nude body 1.75m
2
(1.75×10
4
cm
2
) in area?
W= (0.05) (1.75×10
4
cm
2
) = 875 W
Thermography usually is taken in a rather cold room to increase the temp. difference
between region of poor and normal blood supply consequently the contrast improved the
machine can detect 0.2°C
Temp. difference and record the thermogram in two seconds. The procedure takes
about 20 min at room temp. (20-21 °C).
o Usage of thermograph:
❖ It was found that the most breast cancers has 1°C higher than that the other
side(healthy)(since the tumor often increase the blood flow) and it was thought that this
will be good procedure for early breast cancer detection.
It was found that one of three thousands women, have abnormal thermogram of the
breast and less than 1% has shown cancer.
X-ray mammography has shown much more successful results to detect breast tumor
of less than 1cm in diameter, but they present a radiation hazard to the body.
Biopsy gives information only about the material excised.
❖ Thermography is useful in the study of blood circulation in the head, differences in the
blood supply between left and right of the patient, which may reflect problems.
❖ In diabetic patients the study of blood supply in legs is important. The presence of hot spots
in the foot can be determined before of ulcer forms and preventative measure can be taken,
studies show a reduction of 20% in limb amputation of diabetic patients.
7
Heat therapy
Heat was recognized as therapeutic agent several thousand years ago. It has two
primary therapeutic effects:
1- An increase in metabolism resulting in relaxation of the blood
capillaries (vasodilation).
2- An increase in blood supply to cool down the heated area.
Heat production for therapy:
1- The conductive method
Heat can transfer by conduction. The quantity of heat transfer depends on the temp.
difference, the time of contact, the area of contact, and the thermal conductivity of the
materials. This can be done by several ways such as hot bath, hot packs, and electric heating
pad. This can lead to local surface heating and using in the treatment of arthritis, neuritis,
strains, sinusitis and back pain.
2-Radiant heat (IR)
Heat radiation can be achieved by using infrared radiation (IR); it penetrates about 3mm in
the skin. It can be produced glowing coils and by 250 watts incandescent lamps. The
wavelengths used are between (800-40000nm) an excessive exposures can cause reddening
and sometimes swelling longer exposure can cause skin browning or hardening. It is
considered to be more effective than conductive heating because it can penetrate deeper.
3-Diathermy
Short wave diathermy utilized electromagnetic wave in radio range (=10m) and
microwave range (12cm).
Heat from diathermy penetrates deeper into the body than radiant and conductive heat, thus
it is useful for internal heating and has been used in the treatment of inflammation of
skeleton, bursitis and neuralgia.
Different methods are used for transferring the electromagnetic energy into the body:
A- The part of the body to be treated is placed between two plates (electrodes)
connected with high frequency power supply. The charged particles of the tissue will
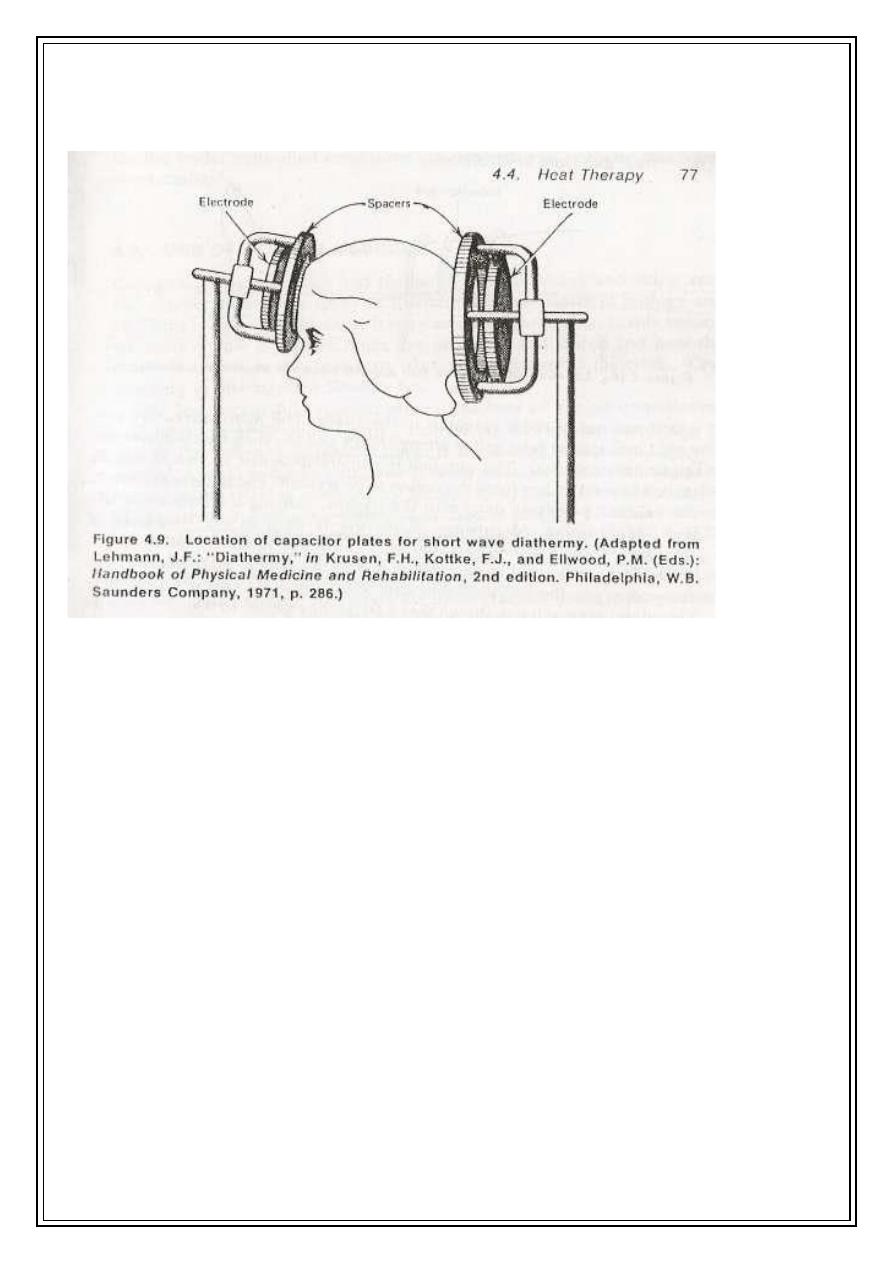
8
be attracted to one plate and to other depending upon the sign of the alternating
voltage on the plate. This movement will produce resistive (joule) heating (book fig
4.9).
B- By transferring short wave energy into the body by magnetic induction. This can be
done by either placing a coil around the region to be treated or by (pancake) coil placed
near the part of the body to be treated. The alternating current in the coil produces an
alternating magnetic field in the tissue. Consequently an alternating (eddy) current are
induced, producing joule heating in the region b treated.
Short wave diathermy can penetrate deep into tissue. It can be used in relieving muscle
spasms, protruded intervertebral disc pain, joints with minimal soft tissue coverage such as
knee, elbow.

9
C- Microwave diathermy can be produced in special tube called (magnetron) and emitted
from the applicator (antenna) which can be placed several inches from the region to be
treated.
Microwave can penetrate deeper into the tissue causing heating. It is used in fractures,
sprains, strains, bursitis, and injuries to tendons. The frequency used is 900MHz, which is
found more effective than other frequencies in therapy. It causes more uniform heating
around bony region.
4-Ultrasonic waves
These waves are different from electromagnetic waves. It produces mechanical vibration
inside tissue. It is the same as the sound waves but it has much higher frequencies about
1MHz with power
of several watts per centimeter. It can move the tissue particles
backward and forward with high frequency, in doing so it can increase the kinetic energy
consequently it heats the tissue.
Ultrasound can be produced by special transducers placed in direct contact with the skin.
It is used for reliving tightness and scarring
occurring in joint disease. It can dispose more
heat in bones as bones are better absorber for ultrasonic energy than soft tissue. It is also
used in deep therapy. Heat therapy has also been used in cancer treatment in combination
with radiotherapy. The tumor is heated about 42°C for approximately 30 minutes, and the
radiation treatment is given after heat treatment.
10
Cryogenics
Cryogenics is the science and technology of producing and using of very low temp.,
it is effects in biology and called cryobiology.
Low temp. can be produced by liquefying gases. It was succeeded to produce liquid air (-
196 °C) in 1877 and liquid helium (-269°C) in 1908.For solid carbon dioxide it is (-79°C)
and liquid nitrogen (-196°C).These cold liquids have many medical and biological
advantages. The storages of liquefied gases are rather difficult because it can take heat
rapidly from the environment by conduction, convection, and radiation.
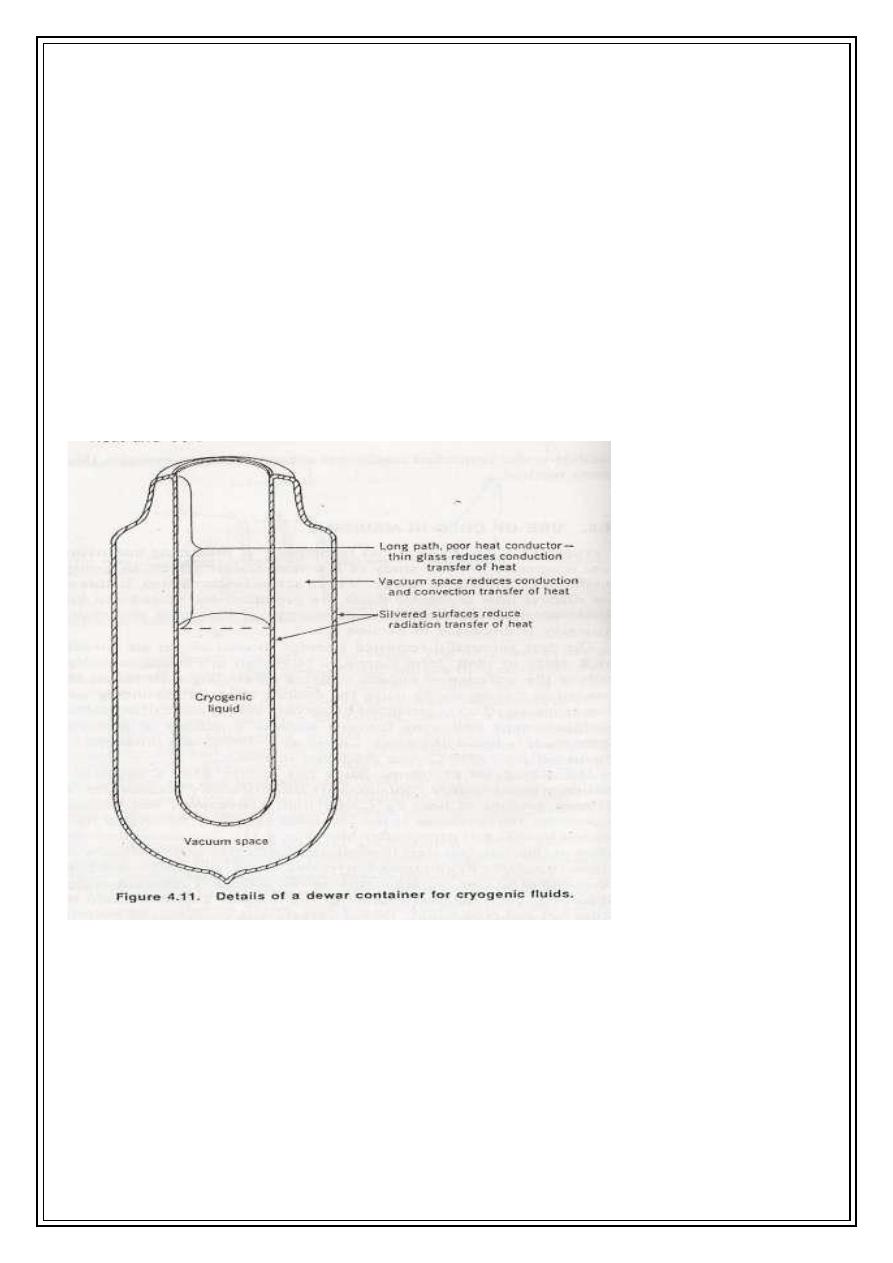
A special container has been designed by Dewar (1892) and its named after his death, this
composed from two cylindrical bottles made of glass or stainless steel one inside the other
and a vacuum in between this can prevent heat transfer by conduction and convection the
two bottles are both silvered so that radiation striking the surface is reflected rather than
absorbed they are as good reflector and poor radiation for heat, the contact between them
is made only at the top to minimize heat losses by conduction.
Low temperatures have been used for long term preservation of blood, sperm, bone
marrow and tissue. The idea of using cryogenic methods to cool the body into a state of
suspended animation so that it can pass time without aging.
For conventional blood storage it can be stored with anticoagulant at 4°C, about 1% of
the red blood cells hemolyze (break) each day so the blood will not be suitable for use after
21 day, for rare blood types this storage time is insufficient and makes maintaining an
adequate supply difficult. Also some preservation materials (protective agents) added such
as glycerol or dimethyl sulfoxide improves the cell survival. Sometimes and especially in
blood these materials can present a problem to remove them from the blood.
Blood can store for a much longer if it frozen rapidly. Two techniques are used for this:
a- thin-walled containers
The container with thin walls is constructed so that the blood volume between the walls is
small. After it is filled with blood it is quickly inserted into a liquid nitrogen bath. The
frozen blood can be stored indefinitely at the temperature of liquid nitrogen (-196°C).
11
b- the 'blood sand' method
blood is sprayed onto a liquid nitrogen surface and freezes into small droplets. The droplets
are about the size of grains of sand hence the name 'blood-sand'. The droplets are collected
and then stored in special containers, usually at the temperature of liquid nitrogen.
The preservation of large tissue like bone, muscles is still under searches as storage of
them involves some problems:
1- Because of its large physical dimensions it is difficult to cool down all the cells at the
same rate.
2- Adding and removing protective agents is difficult. Some work has been carried out to
preserve cornea and skin.
12
Cryosurgery
The cryogenic methods are used to destroy cells called cryosurgery. It has several
advantages:
1-Cause a little bleeding
2-The volume of the tissue destroyed can be controlled
3-Little pain because low temp. desensitize the nerves
One of the first uses of cryosurgery is in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease; (shaking
palsy). A disease associated with the basal ganglion of the brain. This disease causes
uncontrolled tremors in the arms and legs. It is possible to stop it by destroying parts of the
thalamus of the brain that controls nerve impulse to the other part of the nerve system. In
cryosurgery using a cryoknife. it desired to treat Parkinson's disease by destructively
freezing the appropriate region in the thalamus. the vacuum jacket acts as an insulator for
the walls of the variable temperature probe (cannula)in the treatment of Parkinsone's
disease the tip of the probe its cooled to(-10°C) and moved into appropriate regions of
the thalamus causing temporary freezing of these region. The frozen areas recover if the
probe tip is removed in less than 30 sec. the patient must be conscious during the procedure
so that the surgeon can observe when the shaking stops; this means that the probe has
reached the correct region of the thalamus. This region is then destroyed by freezing for
several minutes at temperature near -85
o
C. After freezing. the tip is warmed and removed,
the destroyed tissue will form a cyst which does not interferes with the normal body
function and successful results were obtained in more than 90% of cases.
Safety with Cryogenics
• Containers must be securely fixed.
• Pressure-reducing regulator must be used.
• Cryogenic fluid causes “freeze burns”.
• Adequate ventilation is required.
• Open flame and smoking are prohibited
• Special care for oxygen since it is highly flammable.
