Endo L3 adrenal prof. razaq alrubaee
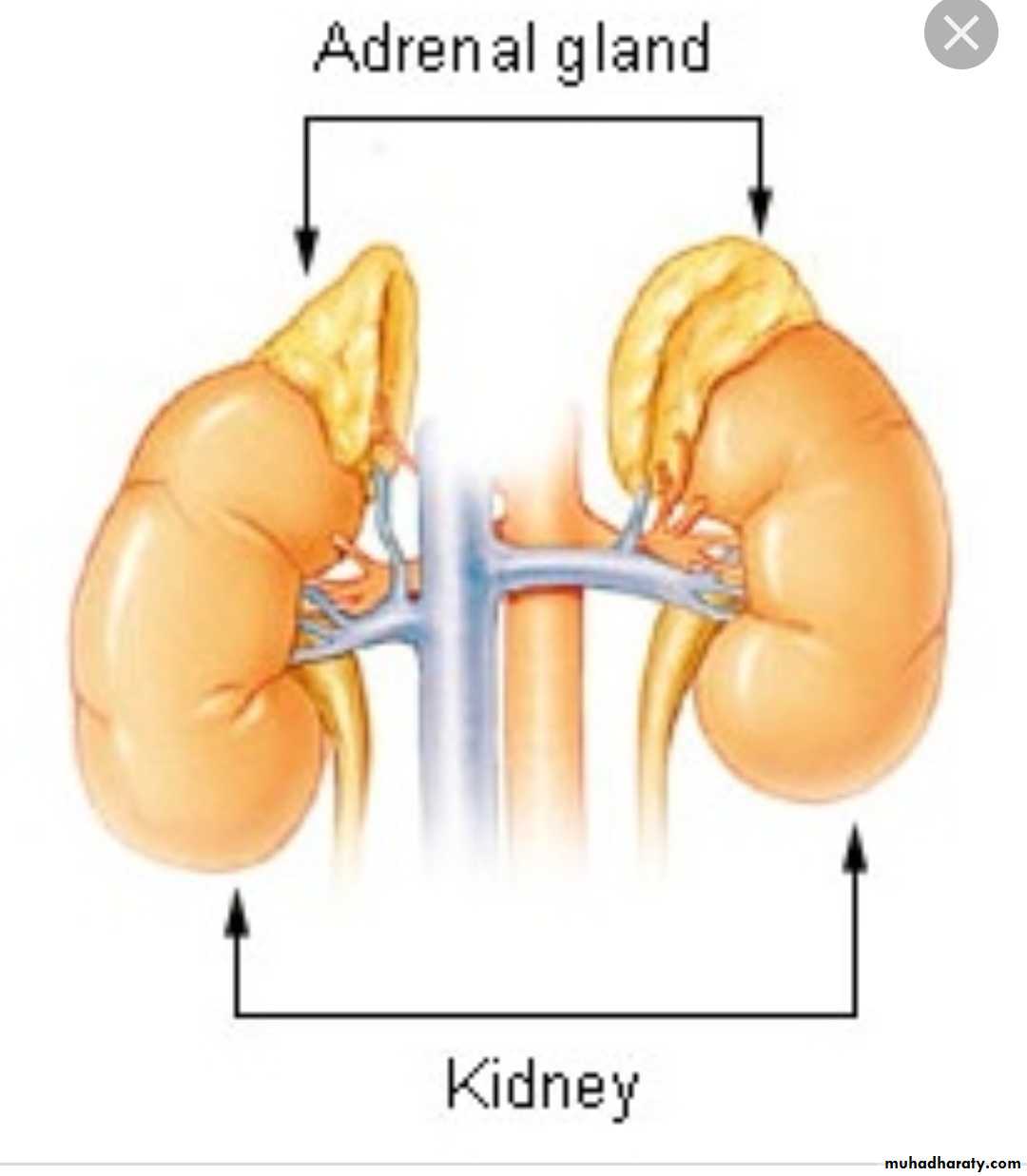
DISORDER OF ADRENAL LAND L3Adrenal gland consist of cortex & medulla
1-Cortexouter layer zona glomerularis(aldosterone secretion )
middle layer :zona fasiculata (glucocorticoid &cortizole )
inner layer :zona reticularis (androgen secretion )
2- medulla (epinephrine &norepinephrine )
01 نيسان، 20
201 نيسان، 20
3
CONGENITAL ADRENAL HYPERPLASIA (adrenal insufficiency CAH ):
Adrenal steroidoenesis01 نيسان، 20
4Adrenal steroidogenesis
CholesterolCholesterol desmolase
Pregninolone 17 OH pregninolone dehydroepiandrosterone
3 beta hydroxylsteroid dehydrogenasae DHEA
Progesterone
deoxycortisole Androsterone21 hydroxylase
11 beta hydroxylase 17 OH steroid deh ydrogenase
DeoxycorticosteroneCortisole testesterone
•
•
Corticosterone
18 oxydase
aldosterone
01 نيسان، 20
5
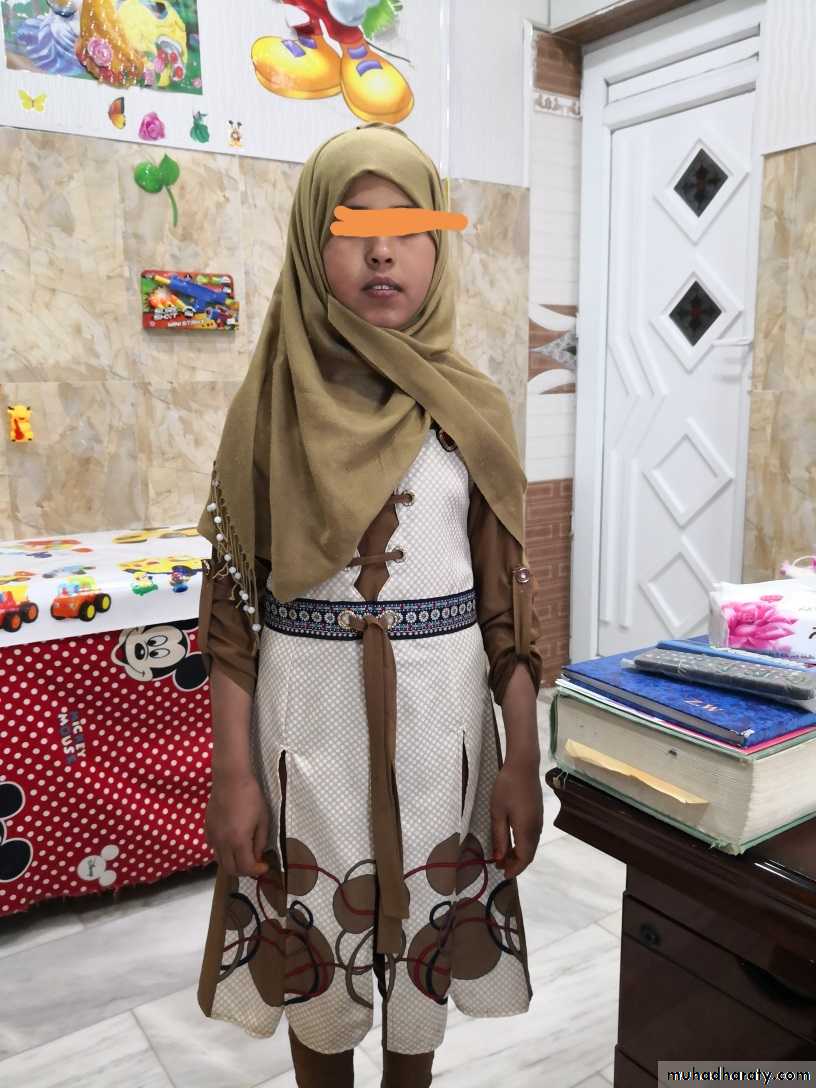
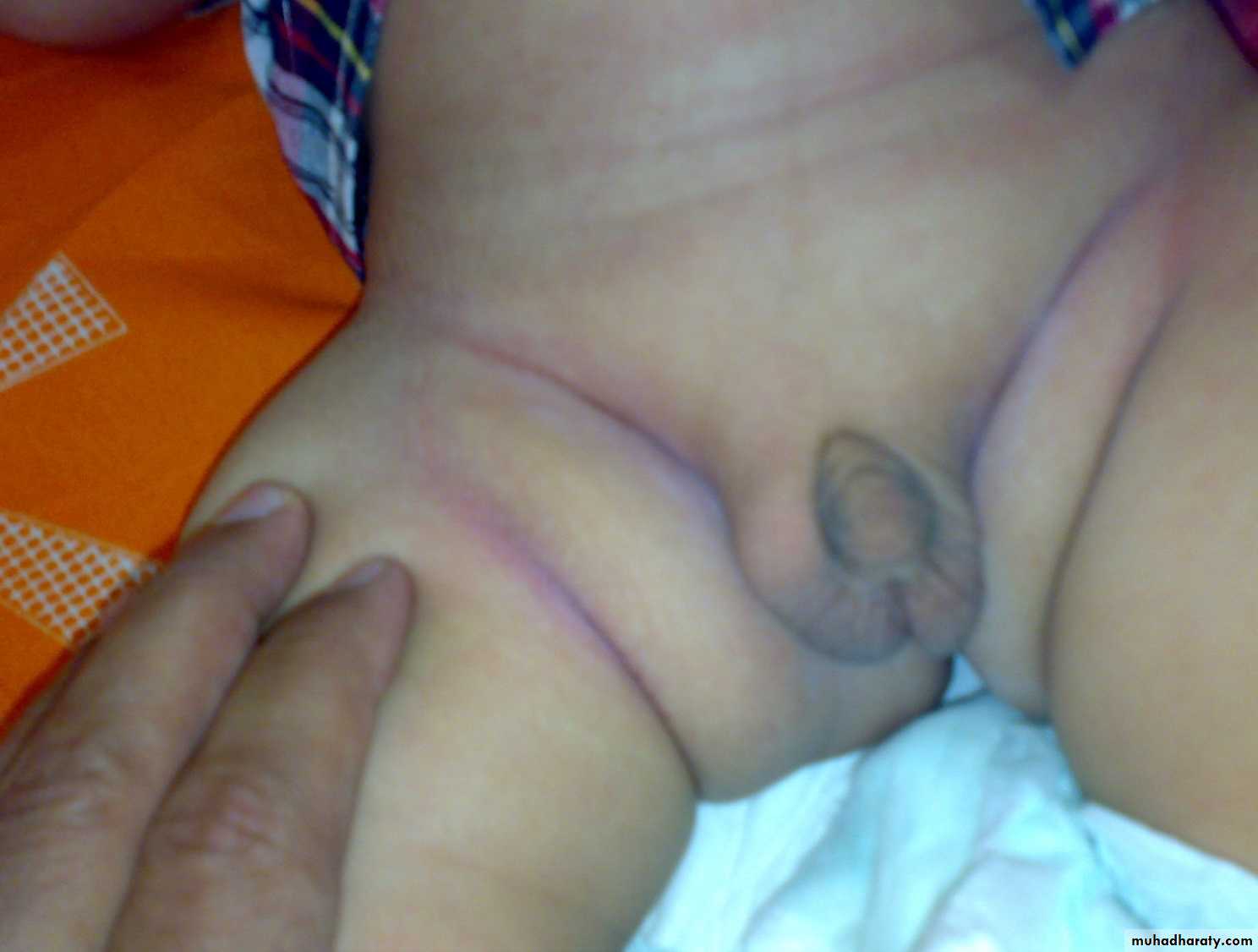
Ambiguous genitalia
01 نيسان، 206
A several of autosomal recessive disorder result from mutation of gene for enzymes mediating biochemical steps for production of mineralocorticoids ,glucocorticoids & sex hormones from cholesterol by adrenal gland
Most common types :
21 hydroxylase deficiency (>90% of cases)
11β hydroxylase def..
3βhydroxysteroid dehydrogenase def.
01 نيسان، 20
7Symptoms (depend on the form of CAH &sex of patient
Mineralocorticoid deficiency :• Vomiting due to salt loss(dehydration &death )
01 نيسان، 20
8
Excess androgen :
• Average size penis
• Ambiguous genitalia in females
• Early pubic hair & rapid growth in childhood
• Precocious puberty
• Excessive facial hair virilization
• Infertility due to anovulation
• Clitoromegaly
Undervirilization in XY male which can result in apparently female external genitals
01 نيسان، 20
9
Types:
1-salt losing : 21 hydroxylase def. most common2-salt retaining variety : either 11β hydroxylase or 17hydroxylase def.
01 نيسان، 2010
manifestations (depend on enzyme deficit ) with lab.findings
• Hypoglycemia ,hyperkalemia. hyponatremia (due to hypoaldosteronism ) repeated vomiting .dehydration• Low cortisole level
• High ACTH
• High 17 α hydroxyprogesterone in blood
01 نيسان، 20
11
• High 17 ketosteroid in urine
• Most definite (measure serum cortisol pre & after ACTH administration• Karyotyping to ascertain the sex of the child
• Antenatal diagnosis possible by chorionic villus sampling in 1st trimester & 17 OH in amniotic fluid in 2nd trimester
01 نيسان، 20
12Treatment.
• Aim:• 1-decrease rate of bone growth
• 2-stop virilisation,
• 3-prevent salt loss
• 4-attain normal puberty by steroid replacement &surgery if needed
01 نيسان، 20
13
• Immediate & vigorous fluid &electrolytes replacement
• supply enough glucocorticoid (natural hydrocortisone )to reduce hyperplasia & overproduction of androgen or mineralocorticoid• Replace enough mineralocorticoid (fludrocortisone )florinef (trade name )
01 نيسان، 20
14
Treatment
• Provide testesterone or estrogen at puberty if deficient• Optimize growth &bone maturation
• Hydrocortisone Na succinate 10-15 mg \m²\24hr TID
fludrocortisone (synthetic mineralocorticoid ) orally in dose 0.05-0.2 mg/day
01 نيسان، 20
15• Addison dsiaese : (acquired adrenal insufficiency ):
Occur as a part of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type-2(APS-2): which consist of Addison dis. autoimmune thyroiditis , or type 1 DM .Type 1 polyendocrinopathy : consist of : mucocutaneous candidiasis & various autoimmune endocrinopathies like hypoparathyroidism ,Adrenal insufficiency
01 نيسان، 20
16
Clinical features
Symptoms :• fatigue ,anorexia ,weight loss,myalgia &joint pain
• nausea ,vomiting
• Glucocorticoid deficiency
•
•
• Both glucocorticoid &mineralocorticoid
01 نيسان، 20
17
Signs
Signs :• Low blood pressure
• Skin or mucosal hyperpigmentation
•
• Both mineralo&glucocorticoid lack
• Excess of proopiomelanocortin –derived peptide
01 نيسان، 20
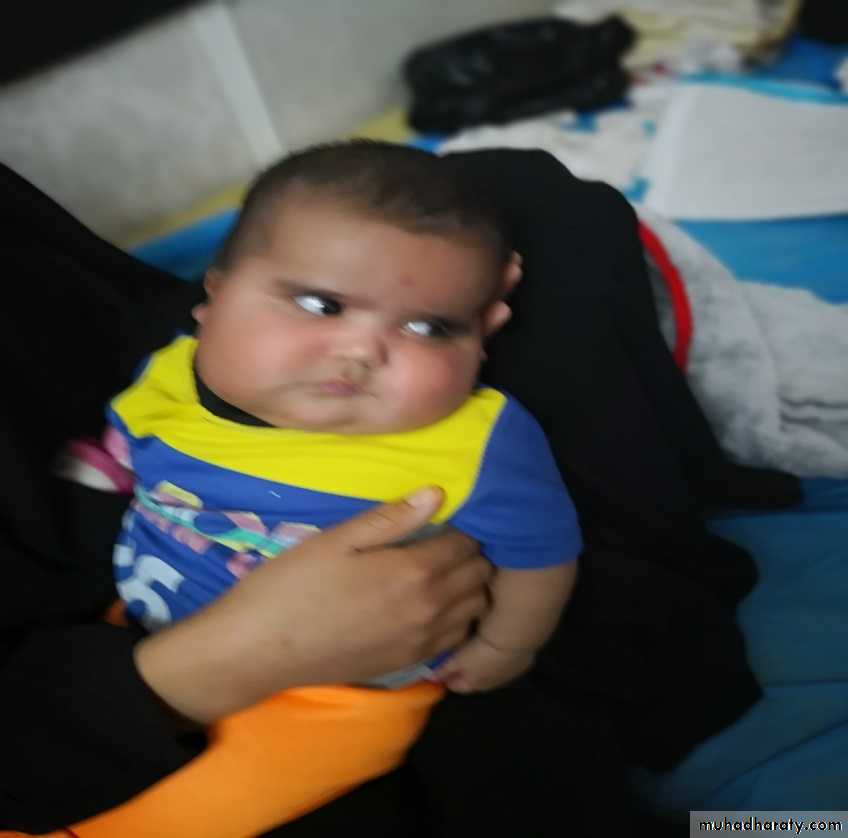
18zainab .14 yrs with dark skin recurent fainting bp60/40mmhg --Sugar 85mg./na 121mMOL/-k 5.5mMol
01 نيسان، 20
1901 نيسان، 20
20
Lab.findings
HyponatremiaHypoglycemia &ketosis
Hyperkalemia
Low cortisol level
Eosinophilia &lymphocytosis
High ACTH level
High plasma renin activty
01 نيسان، 20
21
• Treatment :
Correction of electrolyte abnormality with hypoglycemiaSteroid replacement. Hydrocortisone orally in daily dividing dose of 10-15 mg/m²/day
01 نيسان، 20
22• Cushing syndrome:
• excess of cortisol or other glucocorticoid due to either adrenal tumors or central pituitary involvement and or exogenous steroid usage (details in internal medicine lectures ).
01 نيسان، 20
23exogenous Steroid excess due to allergic airway disease
01 نيسان، 2024
Regarding adrenal insufficiency
• Precocious puberty• High ACTH
• Low plasma renin activity
• Low 17 ketosteroid in urine in CAH
• fludrocortisone is a meniralocorticoid used in CAH
• Slow growth in childhood
01 نيسان، 20
25