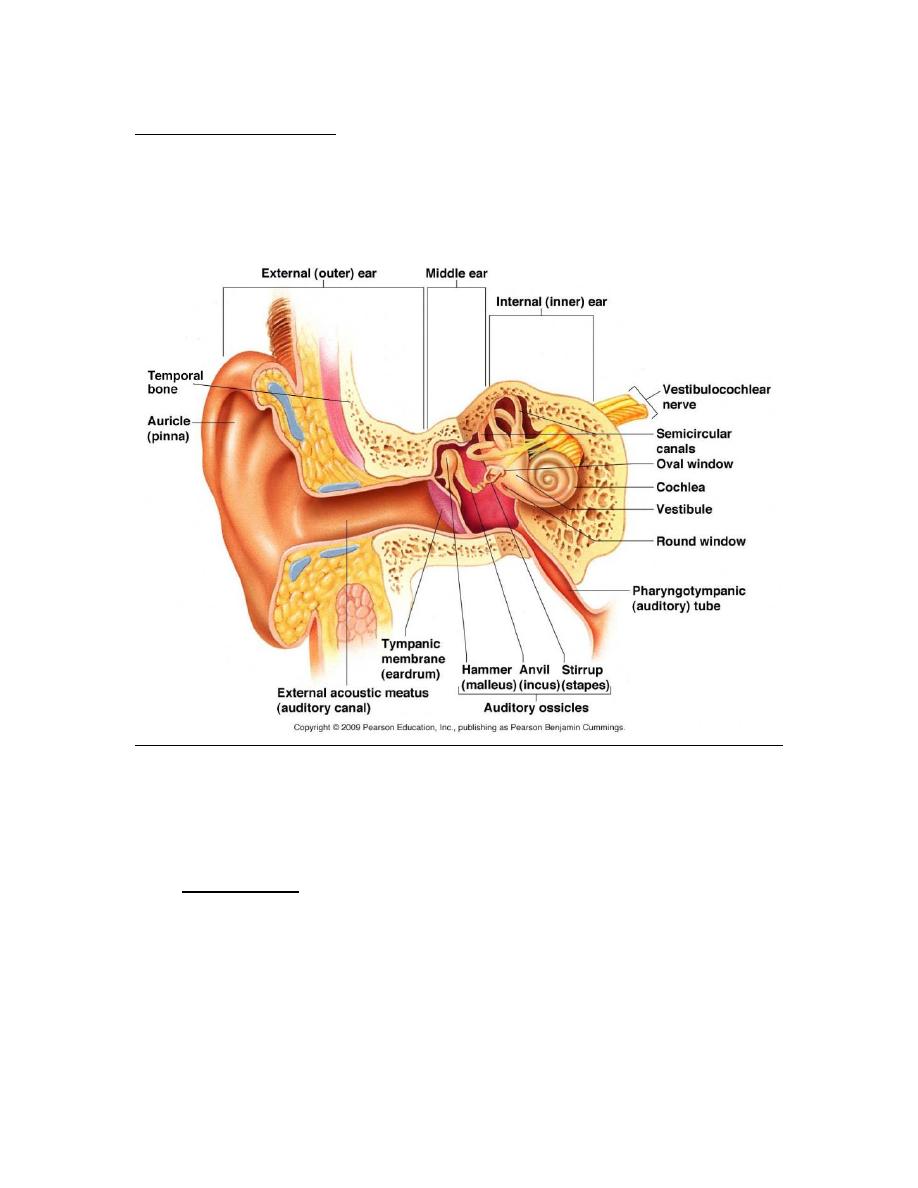
Anatomy of the ear:
1.
External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory
canal .
The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule,
the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
anterior surface of the auricle.

The length of external auditory canal about 2.5 cm, the
outer 1\3 is cartilage but inner 2\3 is bony.
Nerve supply
V, VII, IX, and X cranial Ns.
Lesser occipital n. c1.
Greater auricular n. c2-c3.
Lymphatics
pre and post auricular lymph nodes.
Upper superficial cervical lymph nodes.
2.
Middle ear cleft: consists of
Eustachian tube pass from anterior wall of tympanic cavity
to the nasopharynx
the length of the tube about 3.7 cm
the lateral 1\3 is bony and the medial 2\3 is cartilaginous
with membrane.
Tympanic cavity this is biconcave disc shaped cavity ,
antero-posterior diameter 1.3 cm , height 1.5, the width is
2mm of the centre .
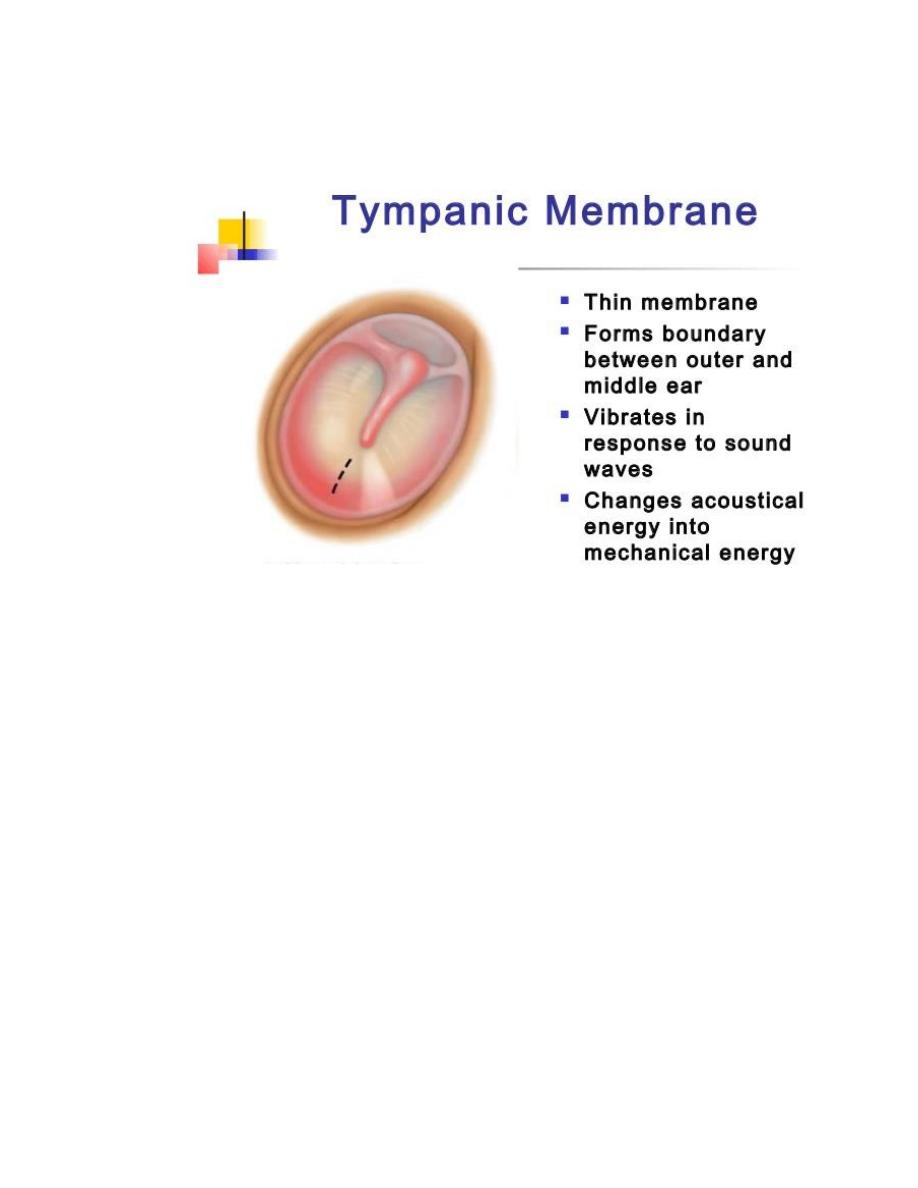
Tympanic membrane have 3 layers:
Outer epithelial layer.
Middle fibrous layer.
Inner mucosal layer.
Also the tympanic membrane divided in to 2 parts: the
lower part (pars tensa)contain middle fibrous layer &
upper part(pars flaccida) without fibrous layer and
,between them there is anterior and posterior
malleular folds.
Medial wall of tympanic cavity contain
i) Promontory is the bony projection covering the basal turn
of cochlea.
ii) Oval window occupied footplate of stapes
iii) Round window closed by membrane

iv) Facial n.
v) Horizontal semicircular canal.
Anterior wall of tympanic cavity contain 3 openings from
above.
1.canal of huguier (for chorda tympanic n.)
2.canal for tensor tympani muscle.
3.orifice of eustachian tube .
Posterior wall have opening as aditus connect epitympanum
to mastoid antrum, below aditus is the pyramid via its pass
tendon of stapedius muscle.
Ossicles
3 bones inside the tympa. Cavity:
1
.malleus has head, neck anterior and lateral processes and
handle.
2
.incus has body, short process and long process.
3
.stapes has head, neck, anterior and posterior crura and
footplate with held in oval window.
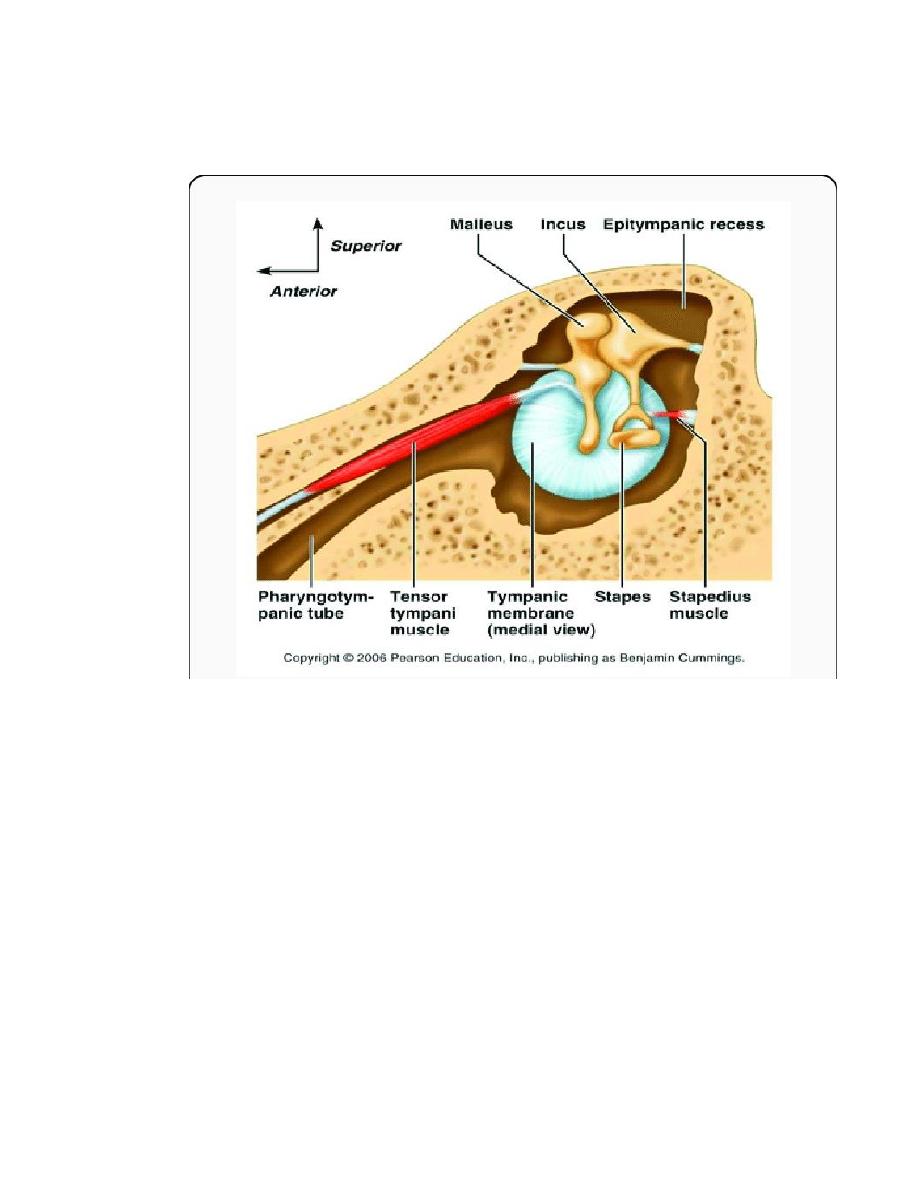
Intratympanic muscles :
1.tensor tympani m.
2.stapedius m.
3.
Aditus ad antrum , aditus is opening in the posterior wall
of tympanic cavity connect epitympanum to mastoid antrum
and mastoid air cells.
Relation of middle ear cleft to known the complication
1. Temporal lobe of brain.
2. Labyrinth(inner ear).
3. Facial n.
4. Lateral sinus(intracranial venous sinus).
5. Jugular bulb.
6. Cerebellum.
7. V & VI cranial ns.
Nerve supply of middle ear cleft :
Sensory from 1X n. via tympanic plexus with received also
from VIII N.
Motor 1.mandibular branch of V to tensor tympani muscle.
2.stapedial branch of VII n. to stapedius tendon
muscle.
Inner ear
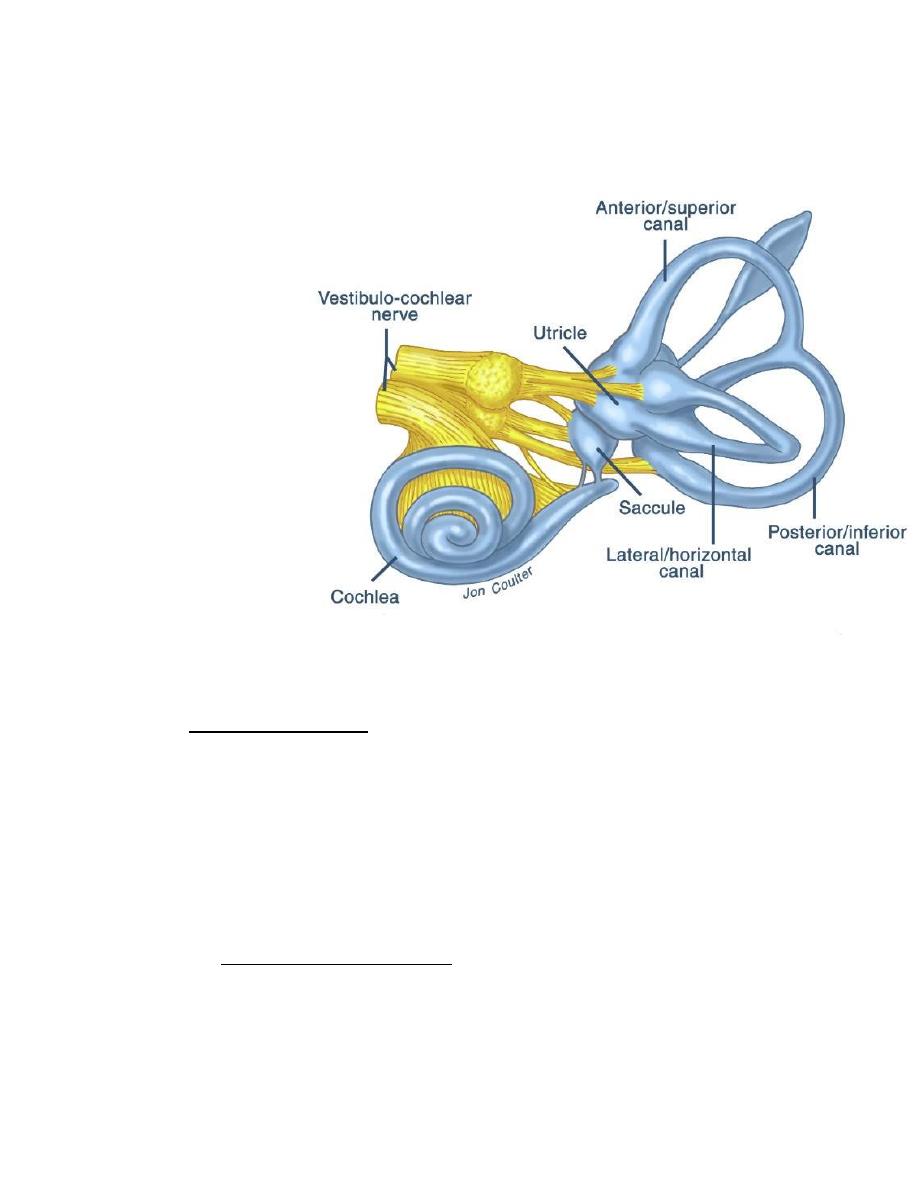
It lies in Temporal bone ,called labyrinth consist of:
Osseous labyrinth has 3 parts:
1. Vestibule =between middle ear & internal auditory
canal.
2. Bony semicircular canals =3 in no. posterior, superior
& lateral.
3. Cochlea = has 2 & half turns its snail shell in shape.
Membranous labyrinth consist of communicate sacs &
ducts within the bony labyrinth .
1. Saccule & utricle in the bony vestibule.
2. Membranous semicircular ducts in the bony
semicircular canals.
3. Cochlear duct in the bony cochlea.
These sacs containing endolymph .
Organ of conti
neuroepithelial structures arranged along
the inner edge of the basilar membrane of the
membranous labyrinth.
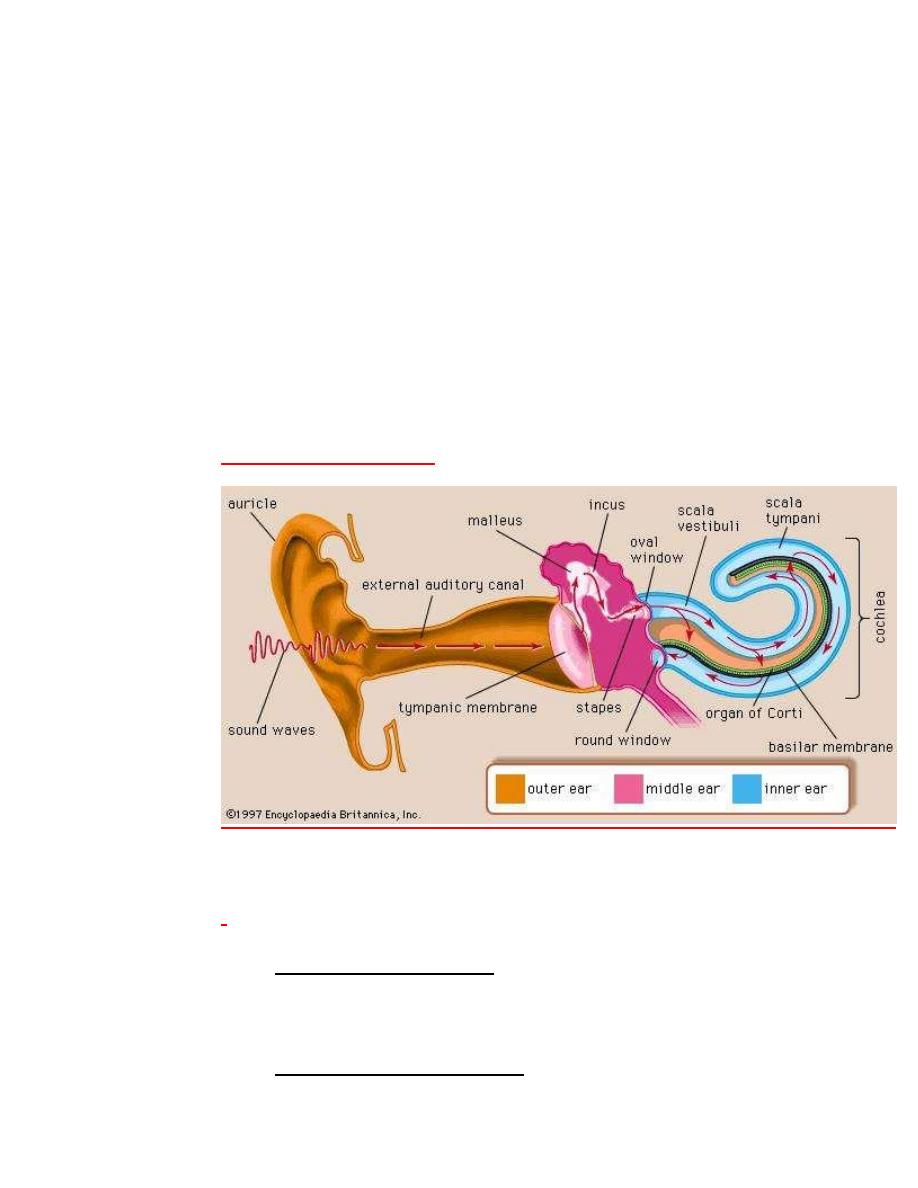
Physiology of hearing
For physiological purposes the ear is divided into 2 parts
1. Conductive apparatus these are external ear
,tympanic membrane ,chain of ossicles, eustachian
tube & labyrinth fluid .
2. Sensory neural apparatus

Organ of corti,auditory division of viii n. & central
connection.
Conduction of sound waves to the inner ear by one of
three ways
Ossicular chain
Directly via round window.
Bone conduction via s
CKUll
.
The acoustic energy is collected by large area of tympanic
membrane applied via the ossicles to the small area of
stapes footplate. The ratio of these areas 14:1 , also there
is lever action of the ossicular chain has mechanical
advantage 1.3:1 so both of them give advantage of 18:1
lead to increase in the force applied by stapes footplate
according to this ratio.
Tympanic muscles reflexes contraction of these muscles
lead to increase stiffness of middle ear apparatus ,
contraction reflex due to to exposed the ear to sound at
90 dB or above, that reflex protect the inner ear from
acoustic trauma .
there is NO reflexes in case of explosion because there is
no time for performance.
Functional examination of hearing
Tunning fork test forks of 256 hz and 512 hz are
commonly used .
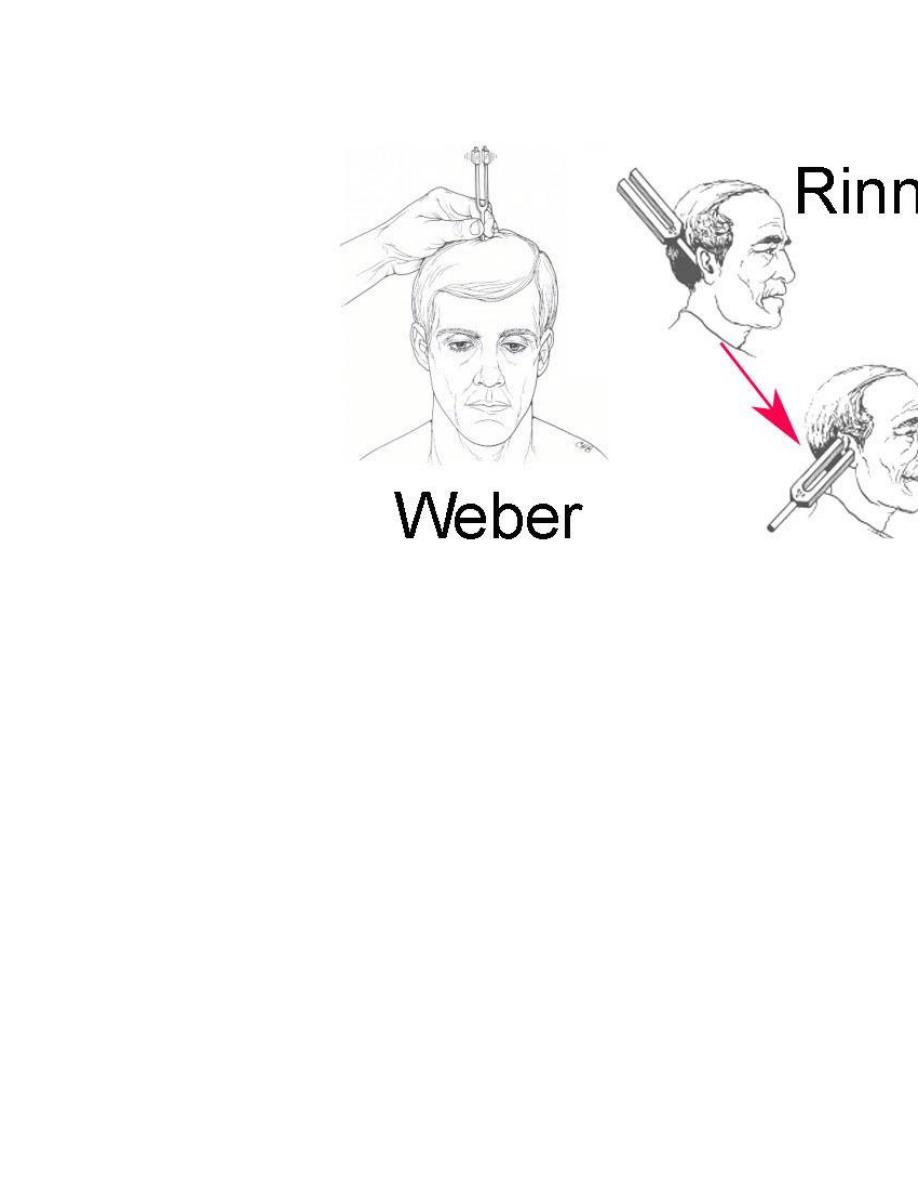
1. Rinne test
The patient is usually asked to say wether the vibrating
fork louder by air conduction(AC) close to the meatus , or
by bone conduction(BC) with base of fork on the mastoid
bone . so when the fork become inaudible by(AC)
transferring to (BC) the order is reversed start by (BC) then
(AC)
Normal subject =AC better than BC (rinne +ve)
Conductive deafness =BC better than AC (Rinne –ve)
Sensorineural deafness =AC better than BC (Rinne +ve)
often the bone conduction not heard.
2. Weber test
When the fork put on the forehead to see the difference
between the two ears , so in conductive deafness the
heard in or towards the deafened ear, but in SND the
sound heard towards better ear.
Rinne test become –ve when there is hearing loss in this
ear more than 30 dB., but in weber test we can see
lateralization of the sound to more conductive deaf ear
when the difference about 15 dB , so it is more sensitive
test.
3. Absolute bone conduction (ABC) test
Done by obstructing the external auditory meatus by
finger and compare between (BC) of patient & that of
examiner so seen if there is SNHL or not.
Pure tone audiometry
The most generally used technique which determined
threshold of hearing for tones of several seconds duration
. so the pure tones delivered to the ear under test via
suitable earphone(AC) or by vibrator applied to the
mastoid (BC)the frequency tested from (125 hz- 8000 hz)
and the intensities from (-10 dB to 120 dB)by this curve
we can see the type & degree of deafness in graph.
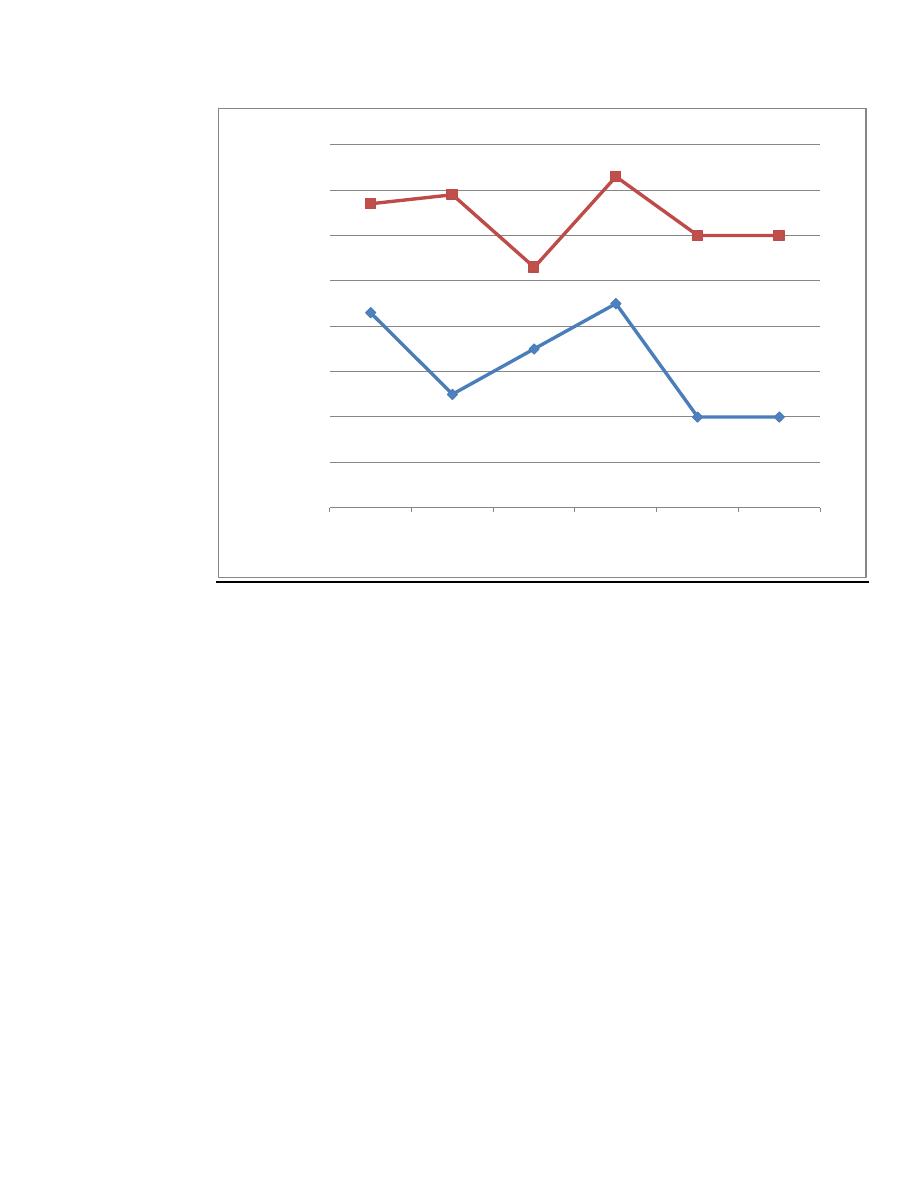
frequency in hz
250
500
1000
2000
4000
8000
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
Hearing
Level
In dB
