
Fifth Stage
Dermatology
Dr. Hadaf – Lecture 7
1
Papulosquamous disorders
Lichen planus
•
A common pruritic inflammatory disease of the skin &
/mucosa, nail & hair follicles that resemble lichen.
Pathogenesis
•
Thought to be an auto immune process with unknown
trigger
If the trigger is known then it is called lichenoid reaction
•
Exposure to medicines, dyes, other chemicals as gold, antimalarials, antibiotics,
diuretics.
•
Diseases such as hepatitis C
Epidemiology
•
Race: no racial predisposition
•
Sex: Female to male ratio 3:2
•
Age: more than 2/3 are 30-60 years age, although
can occur at any age
Clinical presentation
•
3 types of lesions
•
1- skin lesions
•
2- mouth lesions
•
3- other manifestations hair & nail lesions
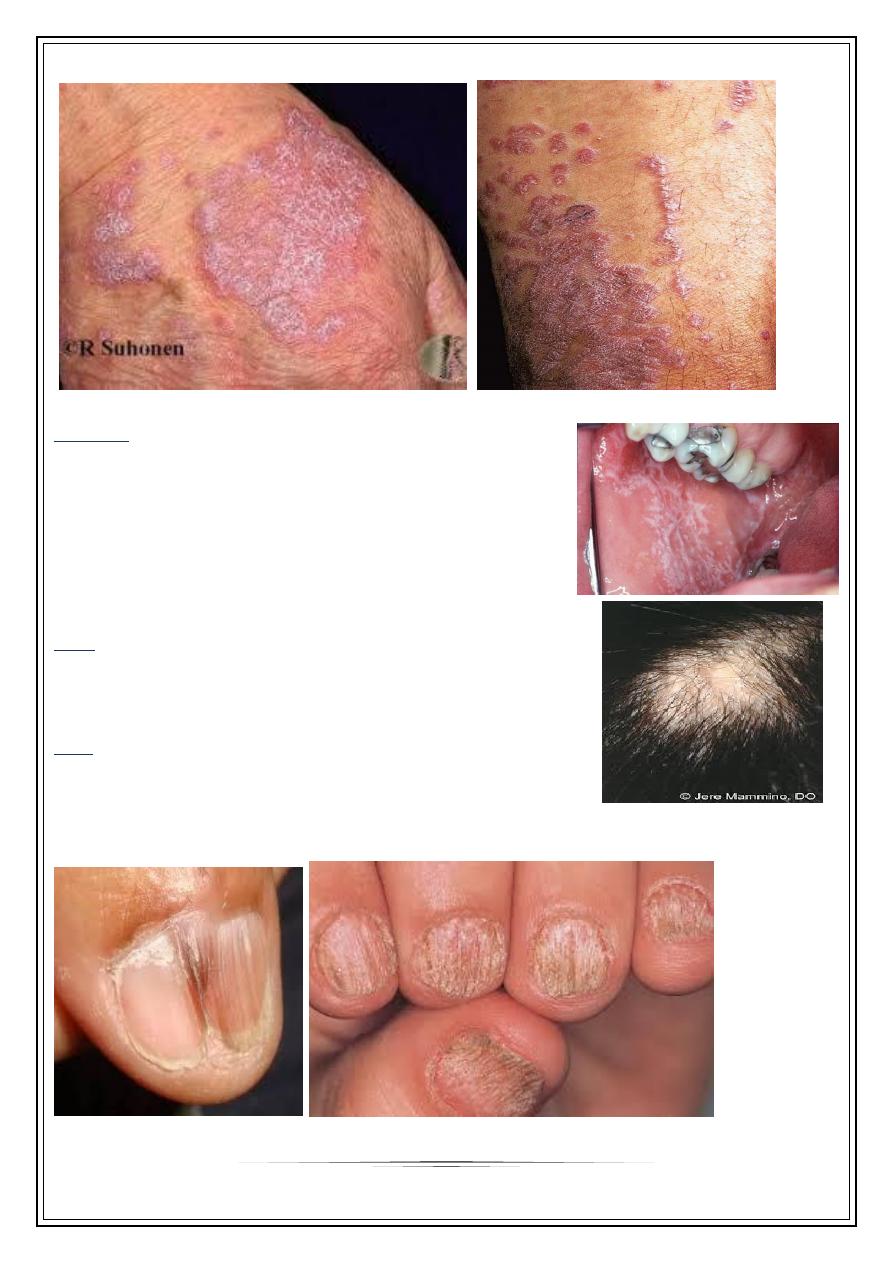
Skin lesions
•
Characteristic; almost pathognomonic primary lesions:
small, violaceous, flat-topped, polygonal papules.
•
Described as the 5 Ps disease:
•
Pruritic, polygonal, purplish, plane, papules
•
The surface is dry, shiny with whitish streaks
or puncta called Wickham’s striae
•
Sites: flexor wrists, med. thighs,
•
trunk, shins, dorsal hands &
glans penis
•
Positive Koebner phenomenon
•
prominent itching
2
Mucosa
Mucous membrane involvement: 50% of patients,
asymptomatic
White lacy lines & dots, or small plaques
Usually inside cheeks, lips
Sometimes may be the sole manifestation (oral LP)
Genital mucosa may show same picture
Hair
70-80% are females leading
to scarring alopecia
Nail
In 5-10% of patients
May be the only manifestation esp. children
Longitudinal ridging, splitting , onychlysis, red lunula
Pterygium formation is characteristic of LP
3
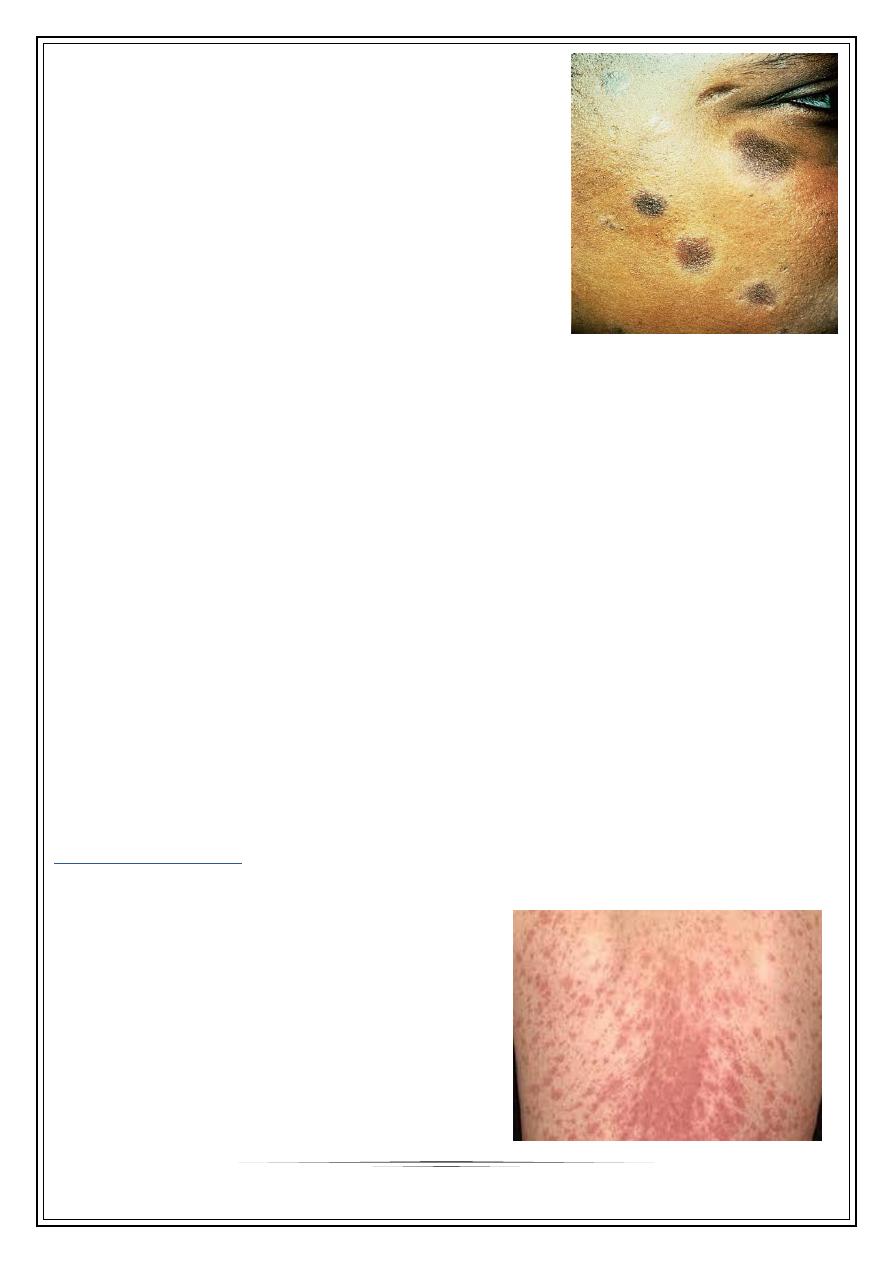
Actinic lichen planus
mostly middle east, sun exposed skin, in spring or
summer.
Adolescents & young adults
Face is target organ; forehead, cheeks, & lips
Annular, hyperpigmented plaques with hypopigmented
margin, & minimal itching
Diagnosis
•
1- Clinical
•
2- histopathology
Prognosis
Individual lesions may last months
The disease itself may last for 1 year
Hyperpigmentation usually follow resolution
Recurrence rate is 1 in 6
Treatment
May be difficult
1)Limited lesions by superpotent topical or intralesional steroids
2)Indications of systemic steroids:
Extensive lesions
nail destruction
painful erosive oral lesions.
3)phototherpy: PUVA+ narrow-band UVB
4)Retinoids: in hypertrophic types
5) Antihistamines to relieve itching
Pityriasis rosea
Mild inflammatory exanthem characterized by pinkish, macular & papular lesions;
begin as discrete, then
become confluent.
Epidemiology
Mainly children & young adults.
More in spring & autumn
Women more than men
Herpes virus 6 & 7 implicated in etiology
Not contagious, 2% recurrence rate
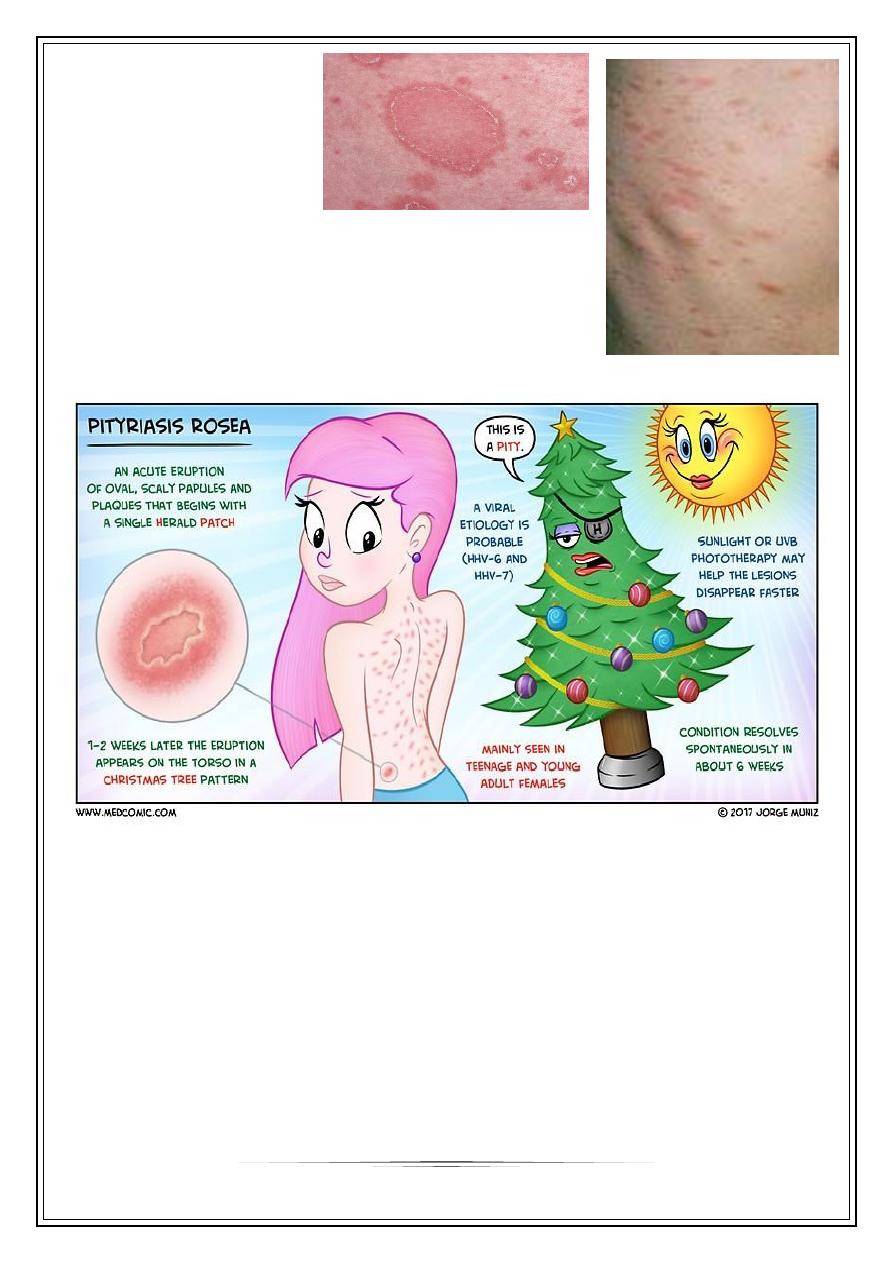
4
Begin with herald patch
which is larger, redder, more
scaly than remaining rash;
Which consist of oval or
circinate patches covered with dry, crinkled, surface,
desquamates leaving a collarette scale
Mainly trunk, extremities, neck
Inverted Christmas tree pattern
Mild pruritus & constitutional symptoms
Prognosis
•
Last 6-8 weeks & resolve spontaneously
•
Sometimes they leave post inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Treatment
Most cases no treatment is required
To shorten the course or decrease itching:
1- UVB in erythema doses
2-Corticosteroids are the standard therapy
3-Oral antihistamines
4-Emollients to relieve dryness & irritation
5-Erythromycine 250mg q.d.s for 2 weeks
5
REACTIVE ERYTHEMA
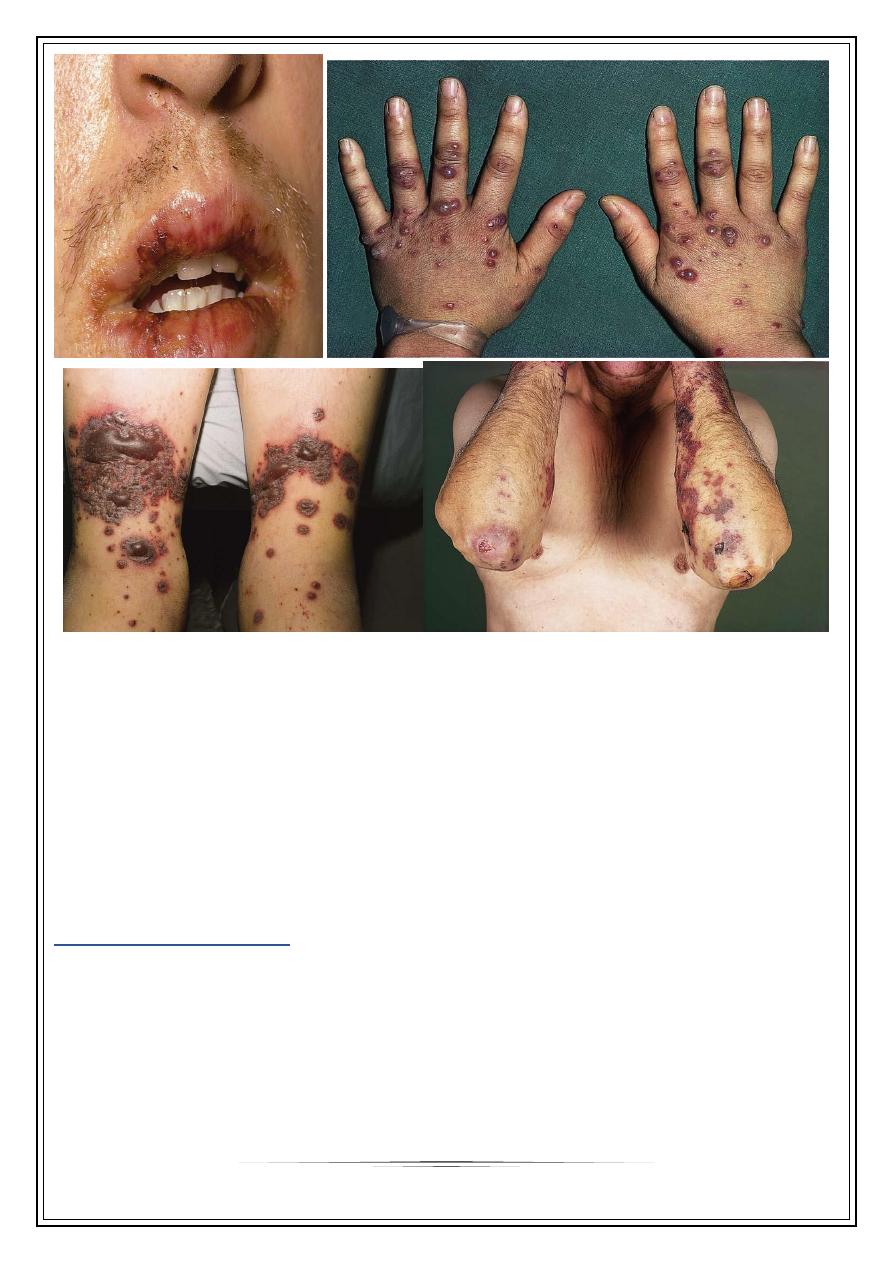
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORMI
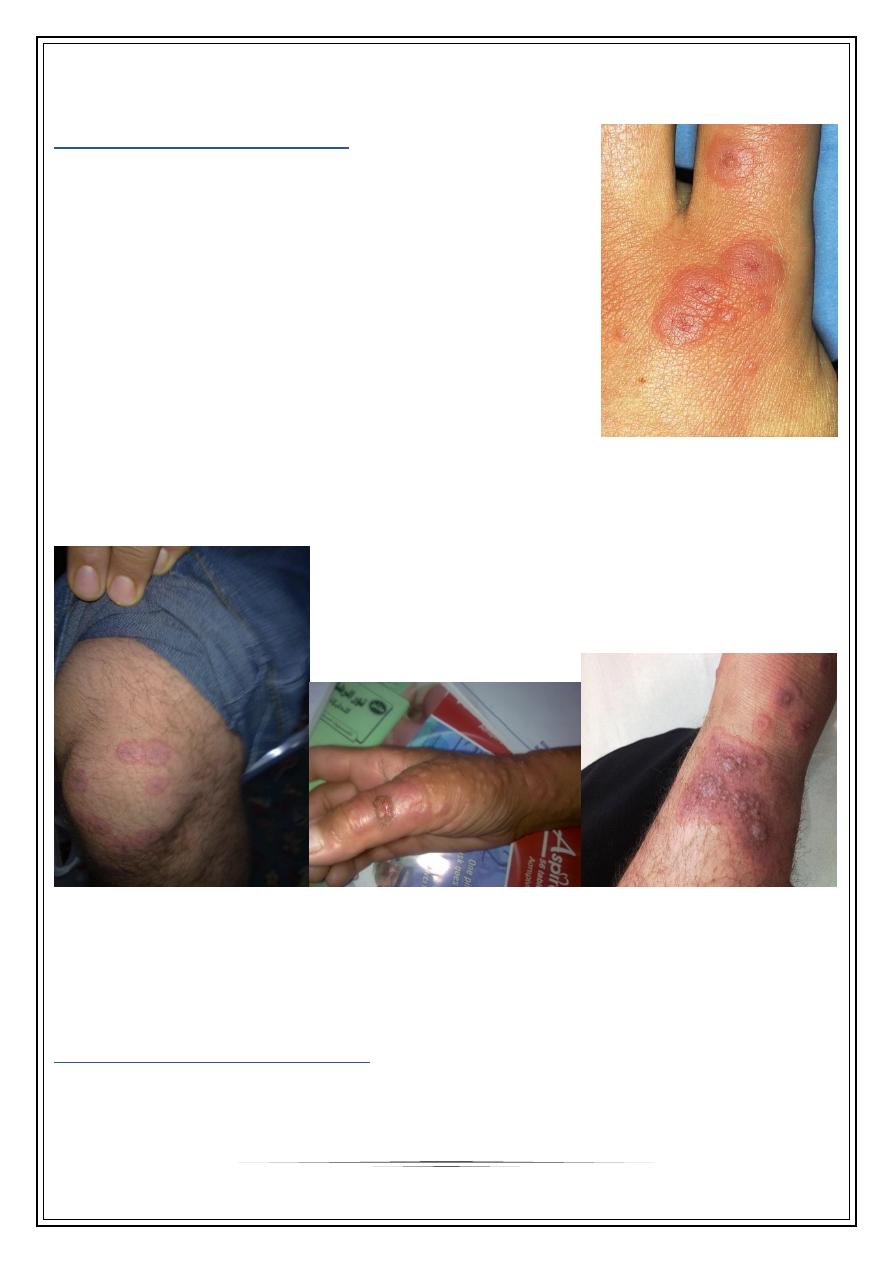
A reaction pattern of multiform erythematous lesions.
ETIOLOGY
1-Viral: preceding oral herpes 1-2 weeks previously, also
orf, mycoplasma, hepatitis A,B,C.
2-bacterial, fungal, & parasitic infection.
3-Drugs: sulfa, NSAID, anticonvulsants, & others
4-Pregnancy
5-Malignancy or its treatment with radiotherapy
Start as sharply marginated, erythematous macule.
Become raised edematous papules over 24-48 hours.
A ring of erythema forms around the periphery, with flatter, purpuric dusky center,
giving” target lesions” of 3 zones
Bilateral, symmetrical, & acral distribution
Mostly starting on dorsa of hands
Sites of predilection are extensor limbs, face, elbows, knees, palms & soles
Steven johnson syndrome
a severe variant with bullous lesions, fever & extensive mucosal involvement.
May be complicated by:
asphyxia, blindness
6
Treatment
Most cases are self-limited with symptomatic treatment.
Remove precipitating factors.
Recurrent HHV infection may be prevented by oral acyclovir 200mg 3-5 times/day.
Steven-Johnson may require aggressive treatment: I.V. gamma globuline, good nutrition,
fluid & electrolyte balance, prevent secondary infection,+ high dose short course
systemic steroids & good nursing care for eyes & mouth.
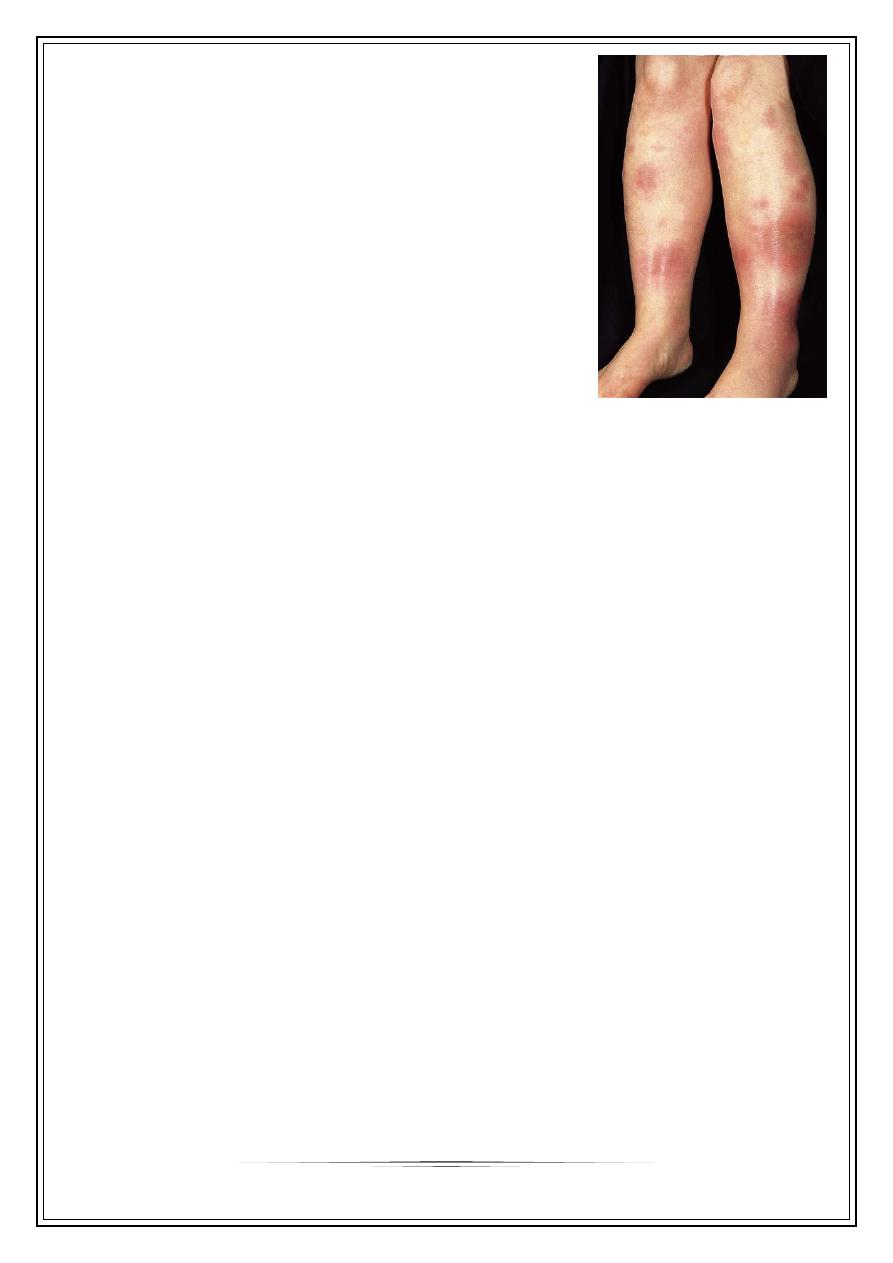
Erythema nodosum
Inflammation of subcutaneous fat (panniculitis), elicited by many factors:
1) Bacterial infection: as T.B, strept., brucella, leprosy, yersinia.
2) viral, mycoplasma, rickettsia,& chlamydia
3)Fungal as coccidiomycosis
4)malignancy, sarcoidosis, ulcerative colitis, Behcet disease
5)drugs: sulfa & oral contraceptives.
7
Clinical features
Characteristic lesion is a tender red nodule , alone or
grouped on shins or forearms.
Other areas as thighs, face, breast.
Bilateral, symmetrical lesions.
Mostly in young adult women
Acute onset, frequently with constitutional symptoms
Resolve within few days leaving bruise like
The whole course last 6-8 weeks
Diagnosis
Thorough history
physical examination
Chest x-ray
Throat culture
ASO titre
Treatment
Simple consisting of bed rest, NSAID as aspirin, indomethacin, ibuprofen
Systemic steroids not used
Potassium iodide in a dose of 400-900 mg/day but not for more than 6 months
Thank you,,,
