Duplication of the ureter
Complete or incomplete duplication of the ureter is one of the most common congenital malformation of the urinary tract. Its more common in female & is usually bilateral.Types
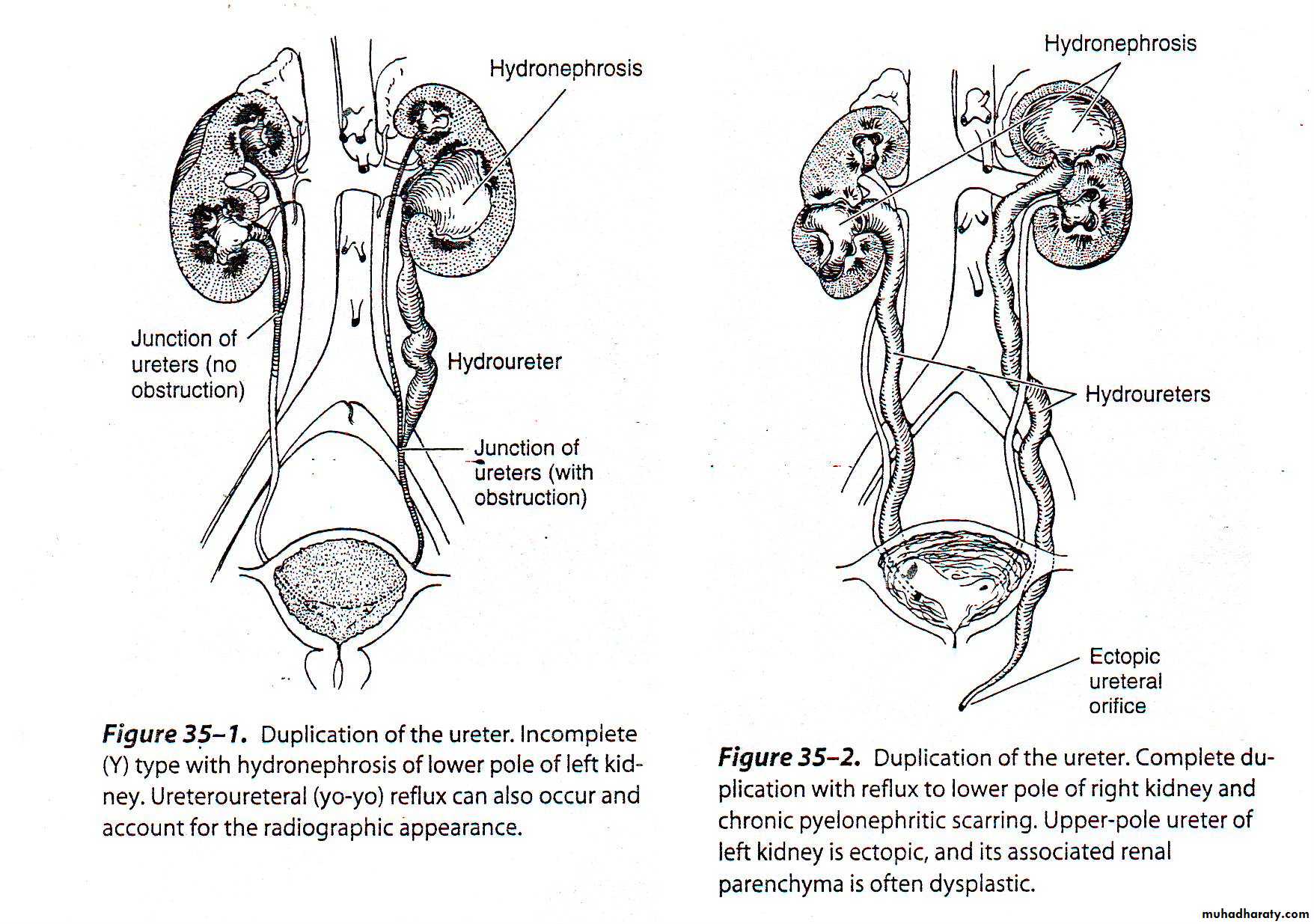
Incomplete : (Y) type of duplication is caused by branching of the ureter before it reach the metanephric blastema. Disorders of the peristalsis may occur near the point of union
Complete : duplication of ureter in which 2 ureteral buds lead to formation of 2 separate ureters & 2 separate renal pelvis.
The ureter draining the upper segment ending in the bladder medial & inferior to the ureter draining the lower renal segment so it libel to be ectopic or form ureterocele
Clinical finding
Patients may be asymptomatic or have recurrent UTI.In females, the ureter to the upper pole may be ectopic with an opening distal to the external sphincter.
Such patients have classical presentation of incontinence constant dribbling & normal voiding pattern.
In males the opening always proximal to the external sphincter so incontinence does not occur
Ectopic ureter in male mostly end to posterior urthera
Ultrasound,excretory urography & voiding cystourethrography usually diagnostic
Treatment is that of reflux if present.
Ureterureterostomy may be indicated if obstructed upper pole segment. & Heminephrectomy in cases of non functioning segment
Ureterocele
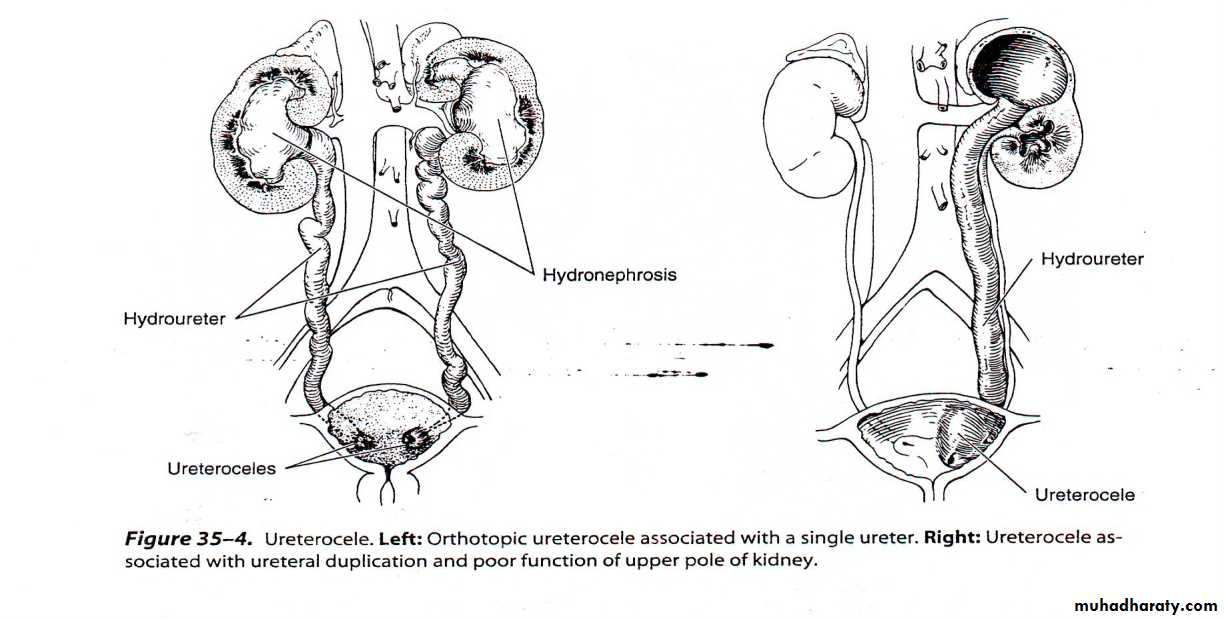
Sacculation or cystic dilatation of the terminal part of the ureter, due to incomplete canalization of the ureteral bud .classification
Ectopic ureterocele it most common
Orthotopic ureterocele it associated with single kidney system
Caecoureterocele very rare located in the urethra
the ectopic which is 4 times more common nearly always involve the upper pole of duplicated ureter.
Clinical finding.
Vary considerablyPatients usually present with
Infection (commonly)
bladder outlet obstruction
incontinence may be the initial complaint.
Occasionally ureterocele may prolapsed through the female urethra.
Calculi can develop secondary to urinary stasis.
Ultrasound may be diagnostic,
excretory urography may show cobra head appearance,
voiding cystourethrography should always be part of the workup to exclude reflux.
Treatment.
Vary from heminephrectomy & ureterectomy,
vesical reconstruction & reimplantation of the ureter or just transurethral incision of the ureterocele.
Depend on the degree of obstruction & age of presentation
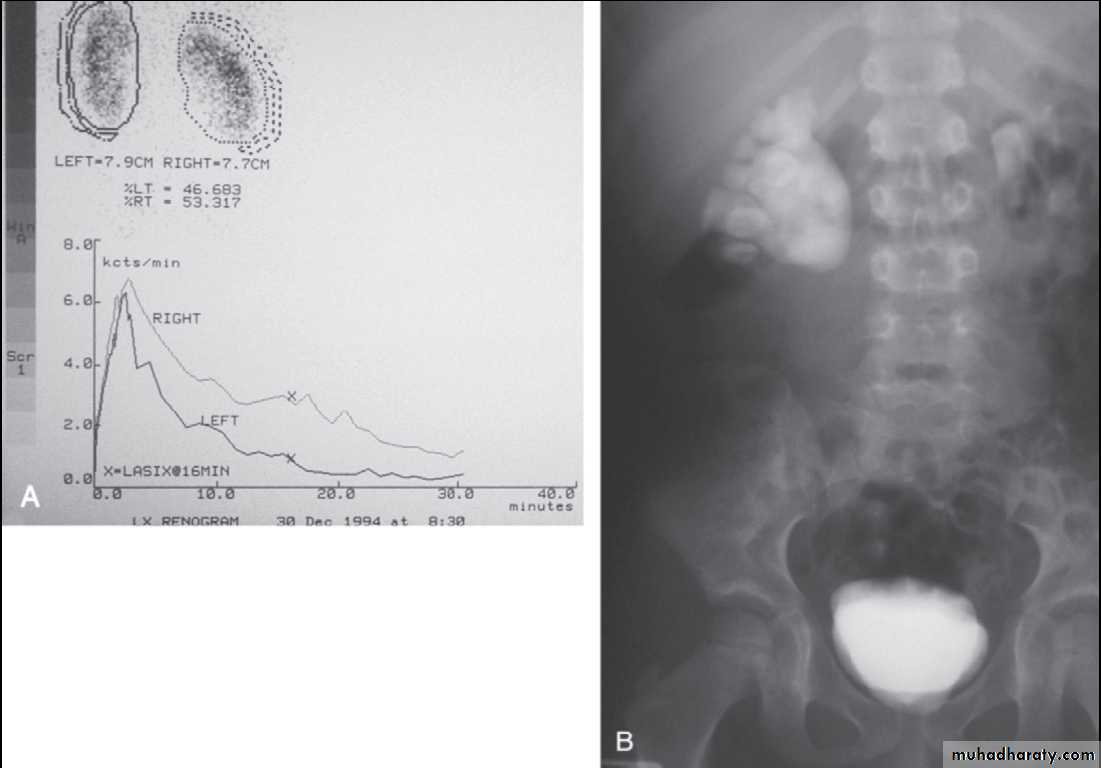
Obstruction of ureteropelvic junction
(PUJ obstruction)PUJ obstruction is probably the most common congenital abnormality of the ureter
It is seen more often in boys than girls (2:1 ratio) &, in unilateral cases more often on the left than right side (5:2 ratio)
Bilateral obstruction in 10-15% of cases & specially common in infants
Etiology
1-Intrinsic (commonest)
Mostly due to a peristaltic segment
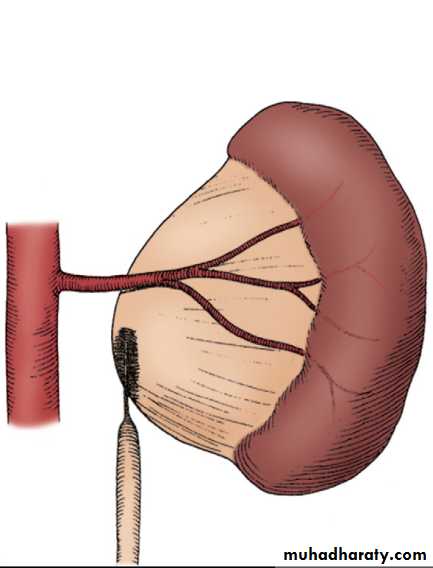
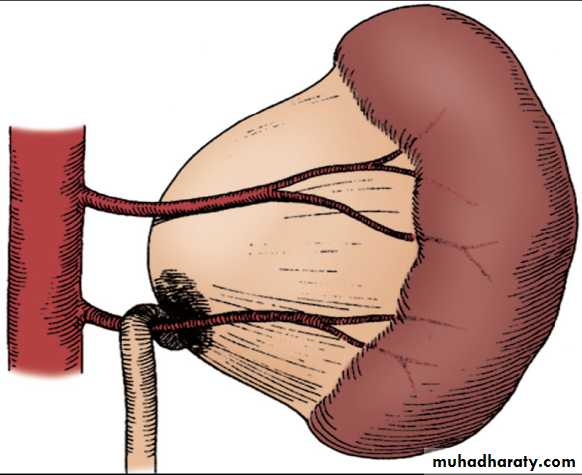
2- Extrinsic
An aberrant ,accessory ,or early-branching lower polevessel
Secondary upj obstruction
incidence of VUR + UPJ obstruction about 9-18%
Associated Anomalies
UPJ obst. Is most common associ. anomaly in other kidney it aacount in 10-40%Renal dysplasia and multicystic dysplastic kidney are second common
Upj obstr.+svere VUR may also present
Clinical findings.
Vary depending on the patient's age at diagnosis.
Infant mostly asymptomatic discovered by prenatal maternal uls but can present with failure to feeding difficulties thrive sepsis pain hematuria
Young child present with recurrent UTI in about 30%
older children have episodic of flank or upper abdominal pain some time vomiting due to intermittent UPJ obstruction is a prominent
Diagnosis
In neonatal and infants by maternal uls or finding of flank mass
(dilatation of collecting system, to differentiate it from , multicystic kidney& level of obstruction)
IVP (diagnostic)
Treatment.
Asymptomatic PUJ obstruction conservative follow up every 3 month by IVP to degree of dilatation &obst. Of UPJ if deteriorate then surgery .
symptom
Indications for surgery (pyeloplasty)
Early surgery may prevent future UTI, stones, or other
complications
Early surgery is recommended for patients who have kidneys with
-diminished function,
-massive hydronephrosis,
-infections, or stones
Acquired diseases of the ureter
Nearly all acquired diseases of the ureter are obstructive in natureTheir clinical manifestations, effects on the kidney,
complications, & treatment are similar to those described previously.
The lesions can be broadly categorized as either intrinsic or extrinsic
Intrinsic ureteral obstruction
The most common causes are as follow.
1 – ureteral stones.
2- transitional cell tumor of the ureter.
3- chronic inflammatory changes of the ureteral wall
(due to tuberculoses or schistosomiasis) leading to contracture or insufficient peristalsis
Extrinsic ureteral obstruction
The most frequent causes are1- sever constipation, seen primarily in children
2- secondary obstruction
3- benign gynecological disorders
4- local neoplastic infiltration
5- pelvic lymphadenopathy
6- iatrogenic ureteral injuries
7- retroperitoneal fibrosis
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Chronic inflammatory process involve the retroperitoneal tissue over the lower lumber vertebrae may engulf & obstruct the ureter
Causes:-
mostly idiopathic
malignant disease
medications, most notably methysergide
Symptoms.
Are non specific & include low back pain, malaise, anorexia, weight loss, & in sever cases uremia.
Diagnosis
Excretory urography.
There is medial deviation of the ureter with proximal dilatation.
Ultrasound for diagnosis &follow up
Treatment
Conservative : Spontaneous regression has been reported
Medical : trial of cortecosroid
Surgery : (ureterolysis)