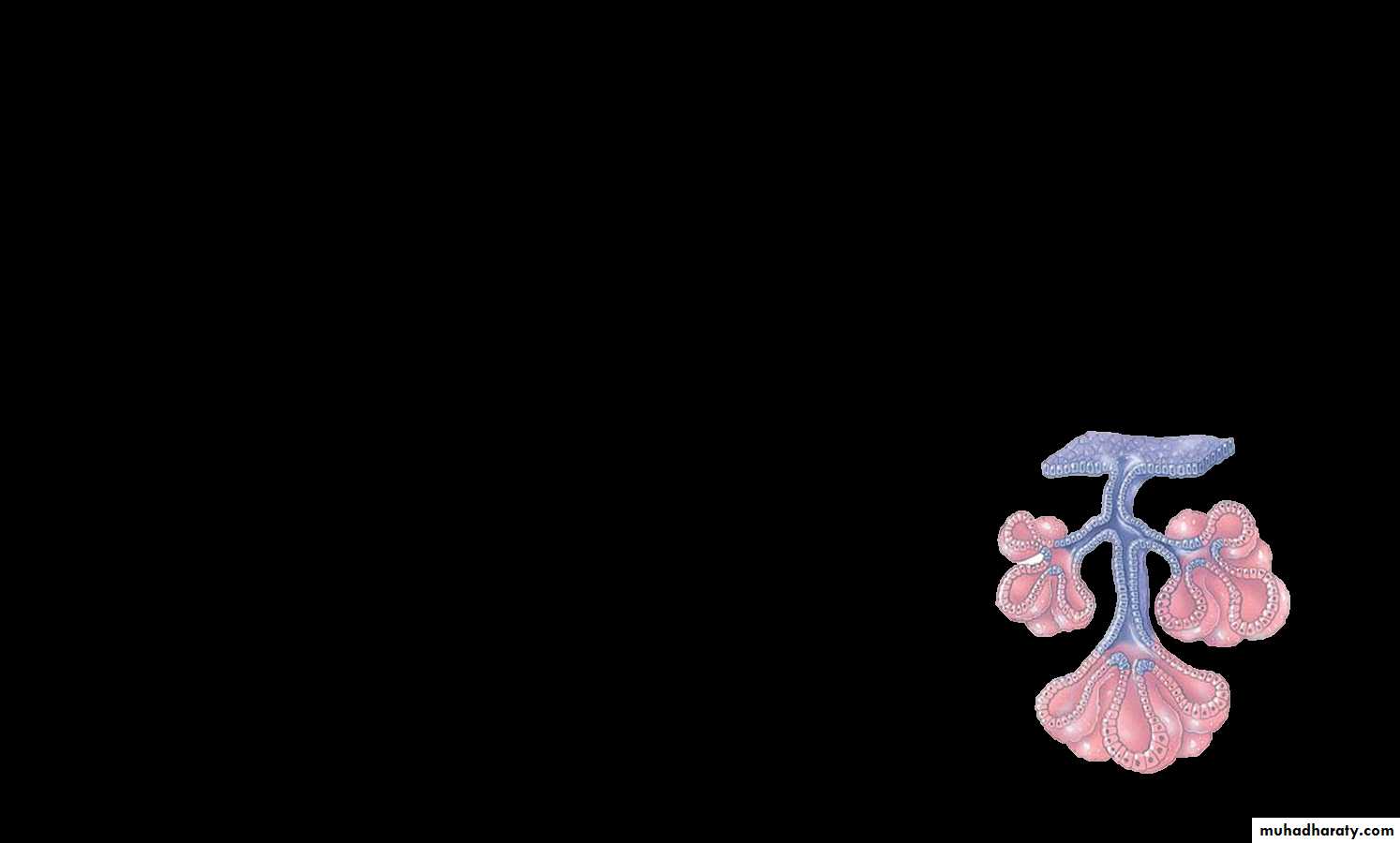Glandular epithelia
Glandular epithelia• Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion.
• The molecules to be secreted are generally stored in the cells in small membrane-bound vesicles called secretory granulesGlandular epithelial cells may be synthesize store, and secrete :
protein (e.g. Pancreas),
lipids (e.g. adrenal, sebaceous gland),
complexes of proteins and carbohydrates (e.g. salivary glands).
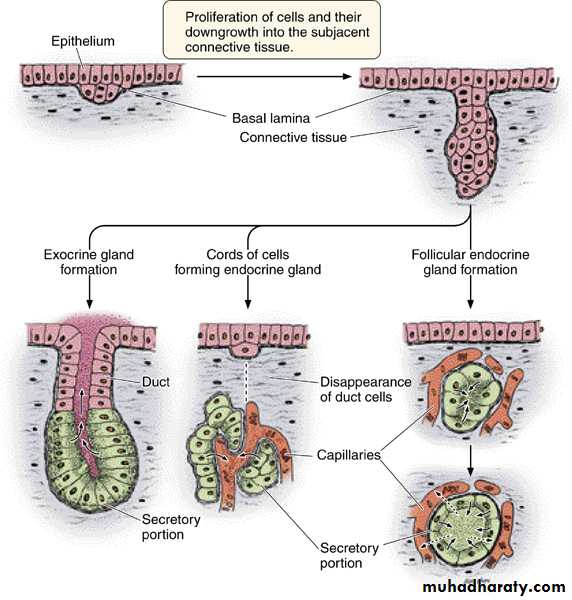
Formation of glands from covering epithelia. Epithelial cells proliferate and penetrate connective tissue.
They may–or may not–maintain contact with the surface. When contact is maintained, exocrine glands are formed; without contact, endocrine glands are formed.
Type of Glandular epithelia
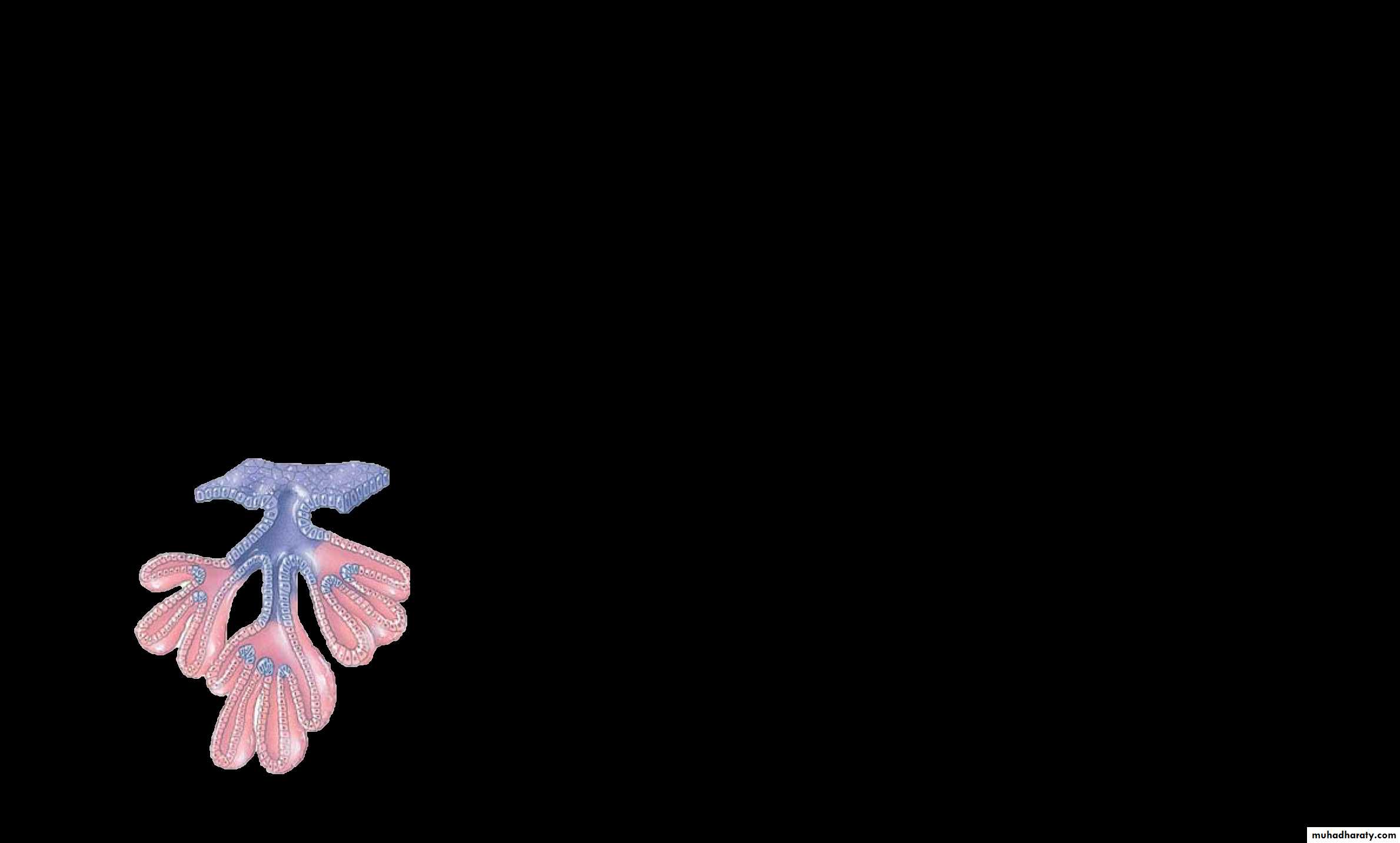
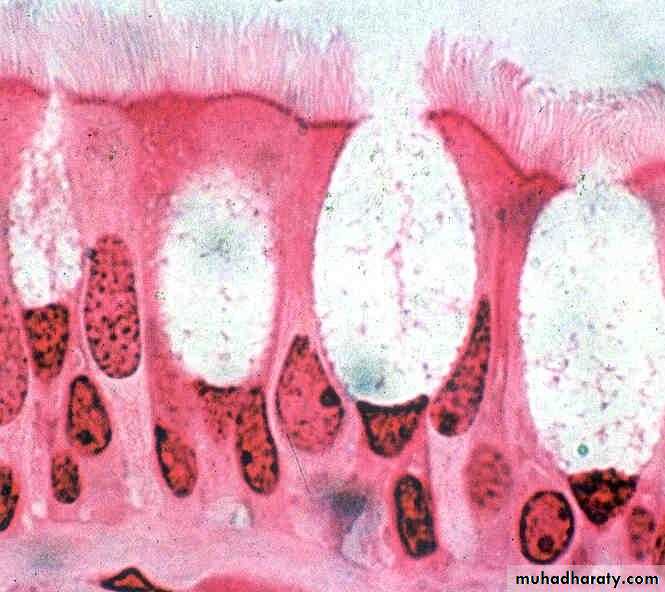
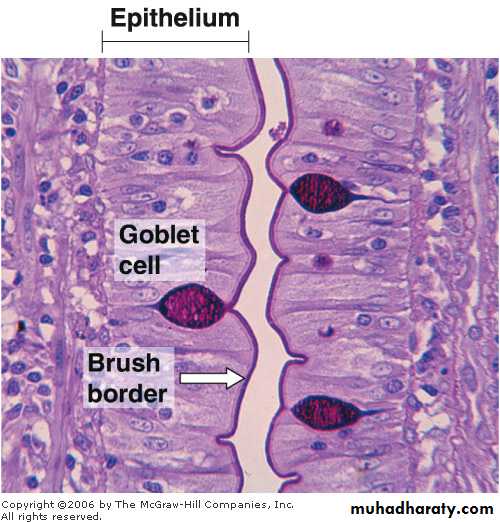
1. According to the number of the cells forming the gland1-unicellular glands: consist of isolated glandular cells, an example of a unicellular gland is the goblet cell of the lining of the small intestine or of the respiratory tract.
2-Multi-cellular glands: are composed of clusters of cells. The term gland however, is usually used to designate large complex aggregation of glandular epithelia cells, such as in the salivary glands and the pancreas glands
Goblet cell
2. According to the mode of secretion
Exocrine glands retain their connection with the surface epithelium from which they originated. This connection takes the form of tubular ducts lined epithelial cells through which the glandular secretions pass to reach the surface.Endocrine glands: are ductless, and thus their secretory products are released directly into the bloodstream or the lymphatic system، for distribution to target organs. These glands can be differentiated according to cell grouping:
1- the agglomerated cells form anastomosing cords interspersed between dilated blood capillaries (e.g. Adrenal glands, parathyroid, anterior lobe of the pituitary).
2- the cell lines a vesicles or follicles filled with non cellular material, between them capillaries are present (e.g. Thyroid gland).
Mixed glands: these are characterized by having both exocrine and endocrine parts (eg. Pancreas)
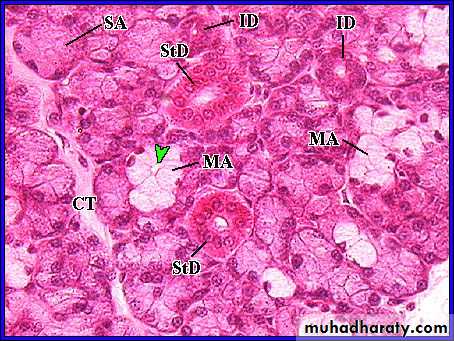
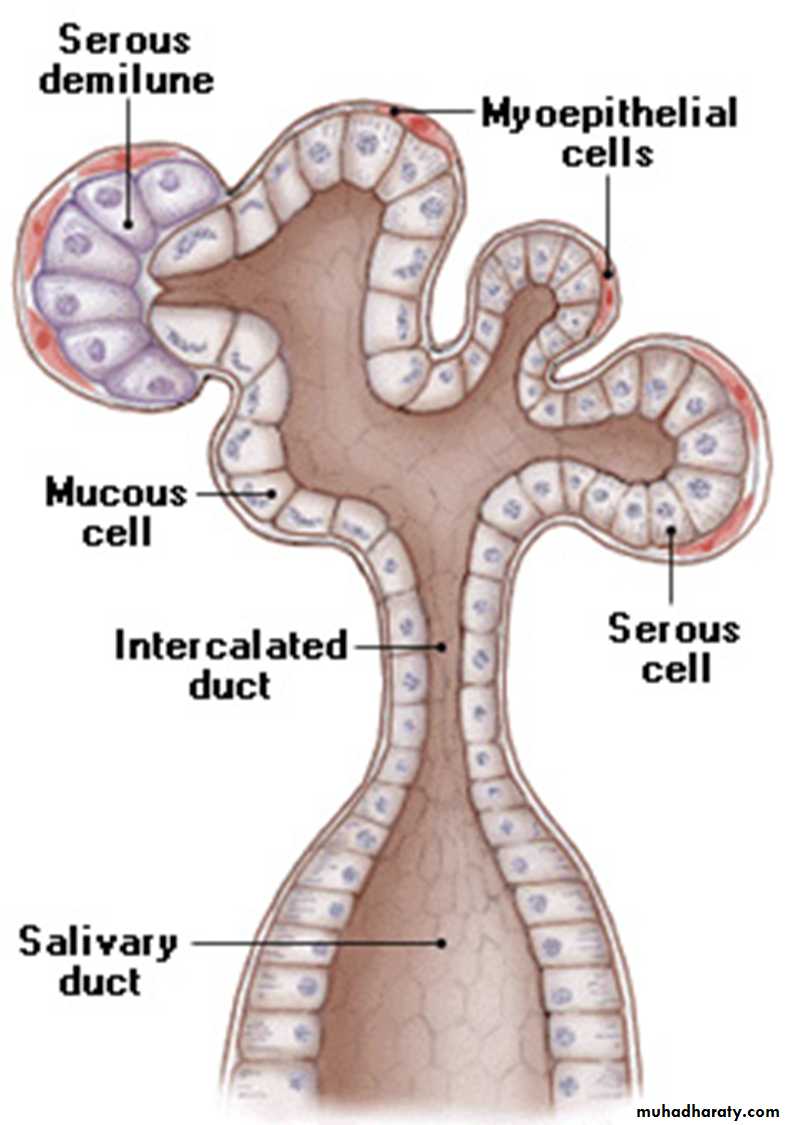
CT - connective tissueID - intercalated ductMA - mucous aciniSA - serous aciniStD - striated ductsgreen arrowheads - lumen of mucous acini
3- According to the type of the duct
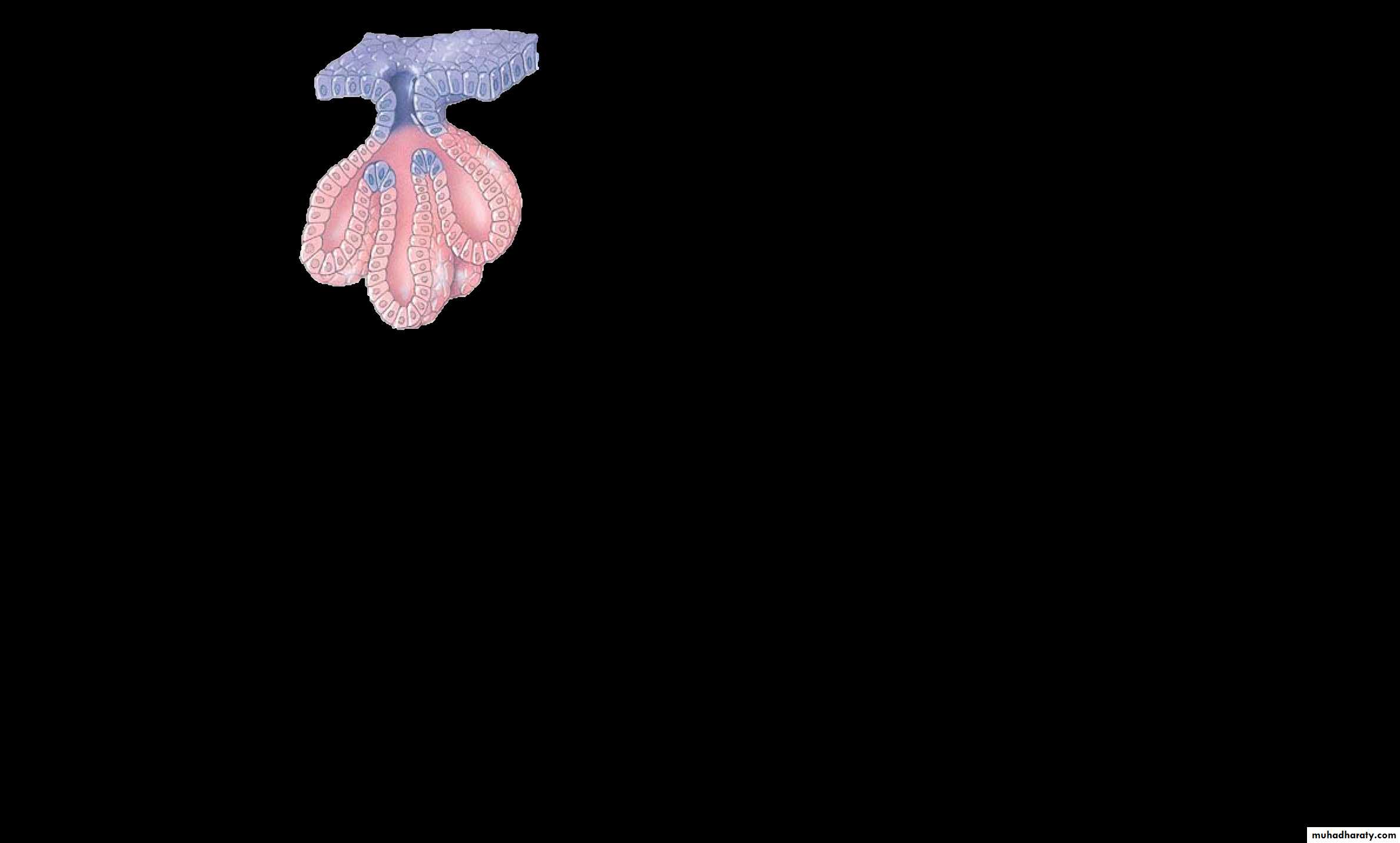
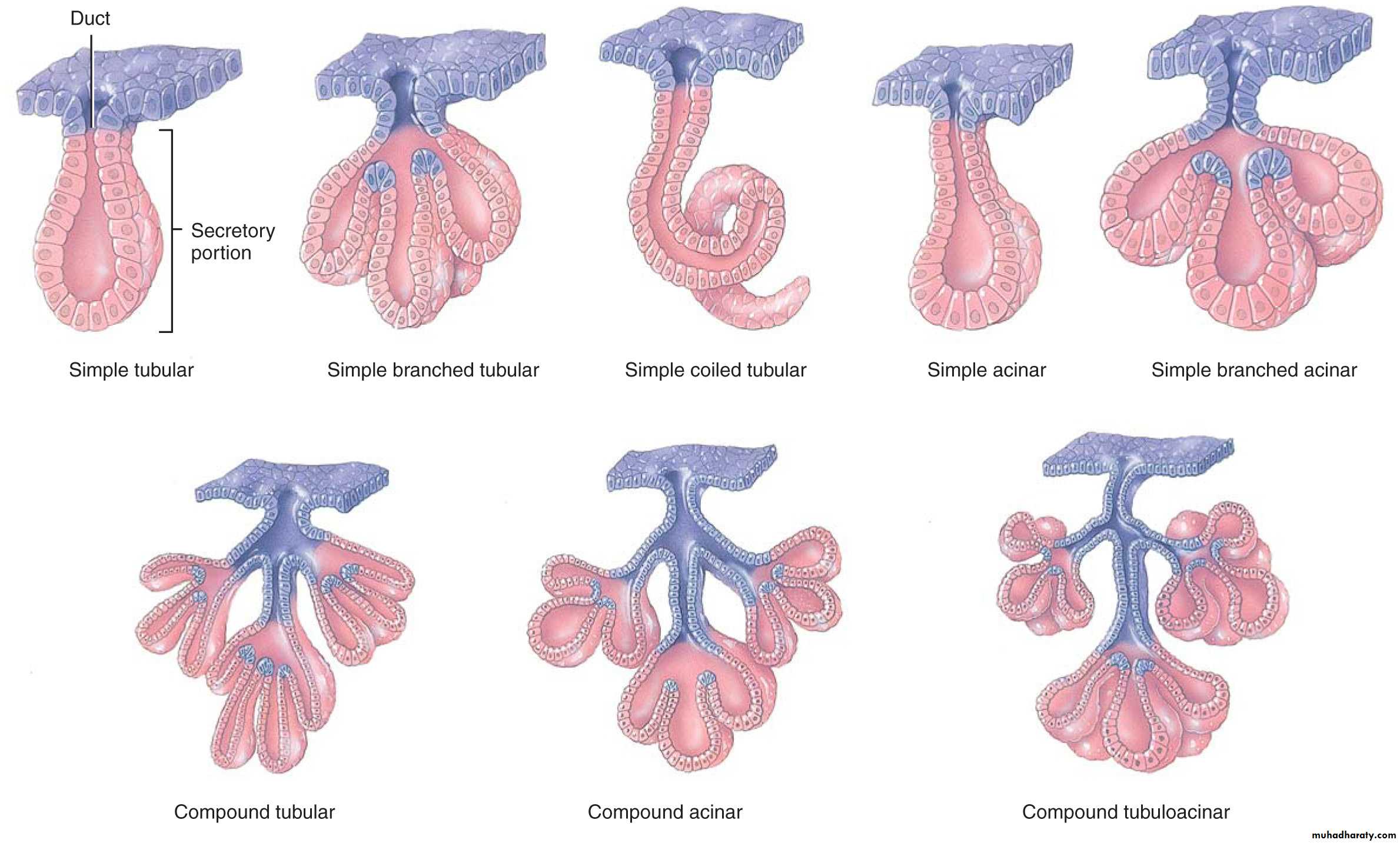
• -Simple multi-cellular gland has only one unbranched duct, according to the shape of the secretory portion these glands are further classified into:• A-Simple tubular glands are consists:
1- Simple straight tubular glands: present in small intestine (crypts of Lieberkuhn)
2-Simple branched tubular glands: the secretory part is branched• e.g. In stomach
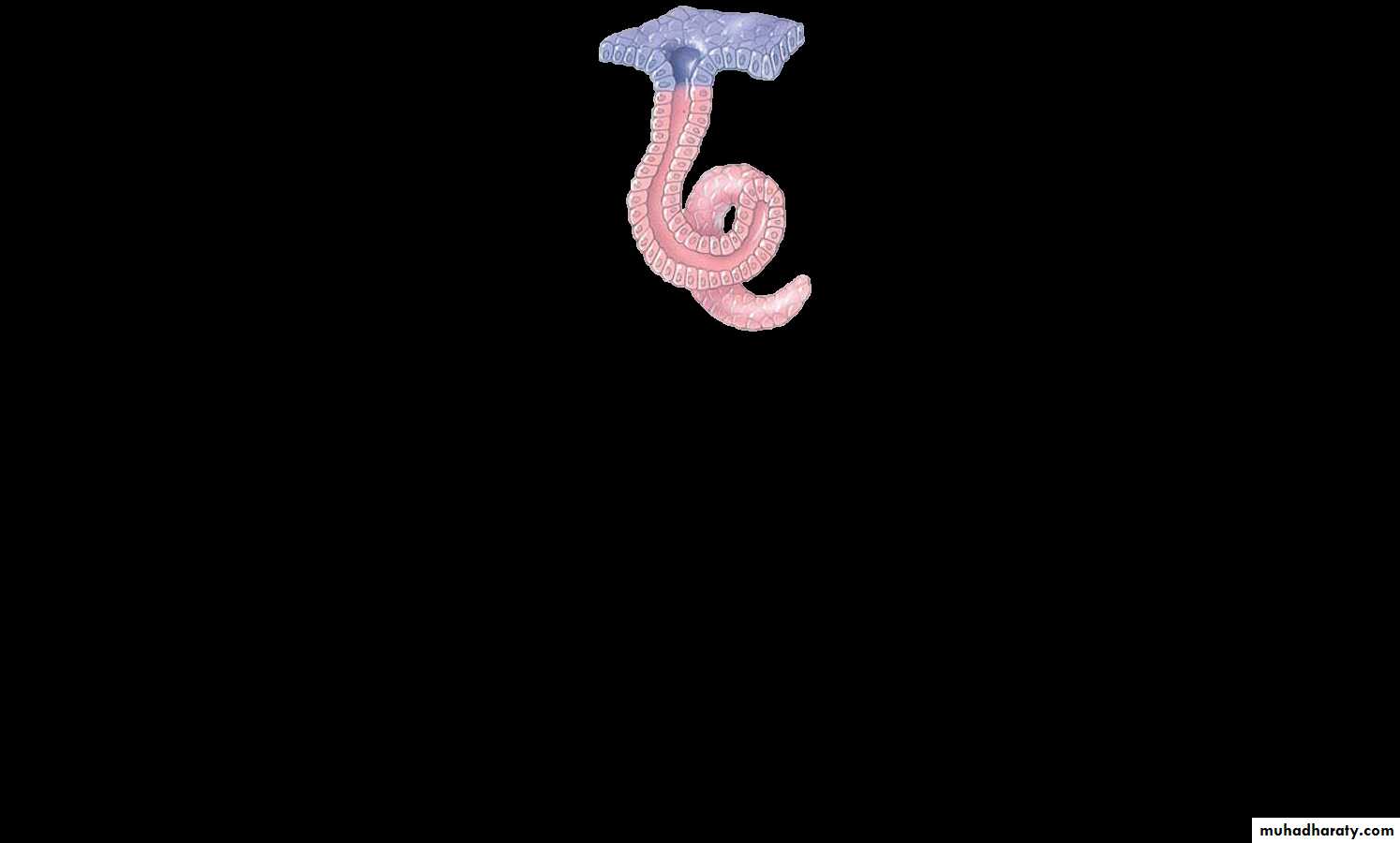
3-Simple coiled tubular glands: the secretory part is very long tubular and coiled
• e.g. in sweat gland
B-Simple alveolar glands: the secretory part of this gland expand to form sacs or alveoli or acinar
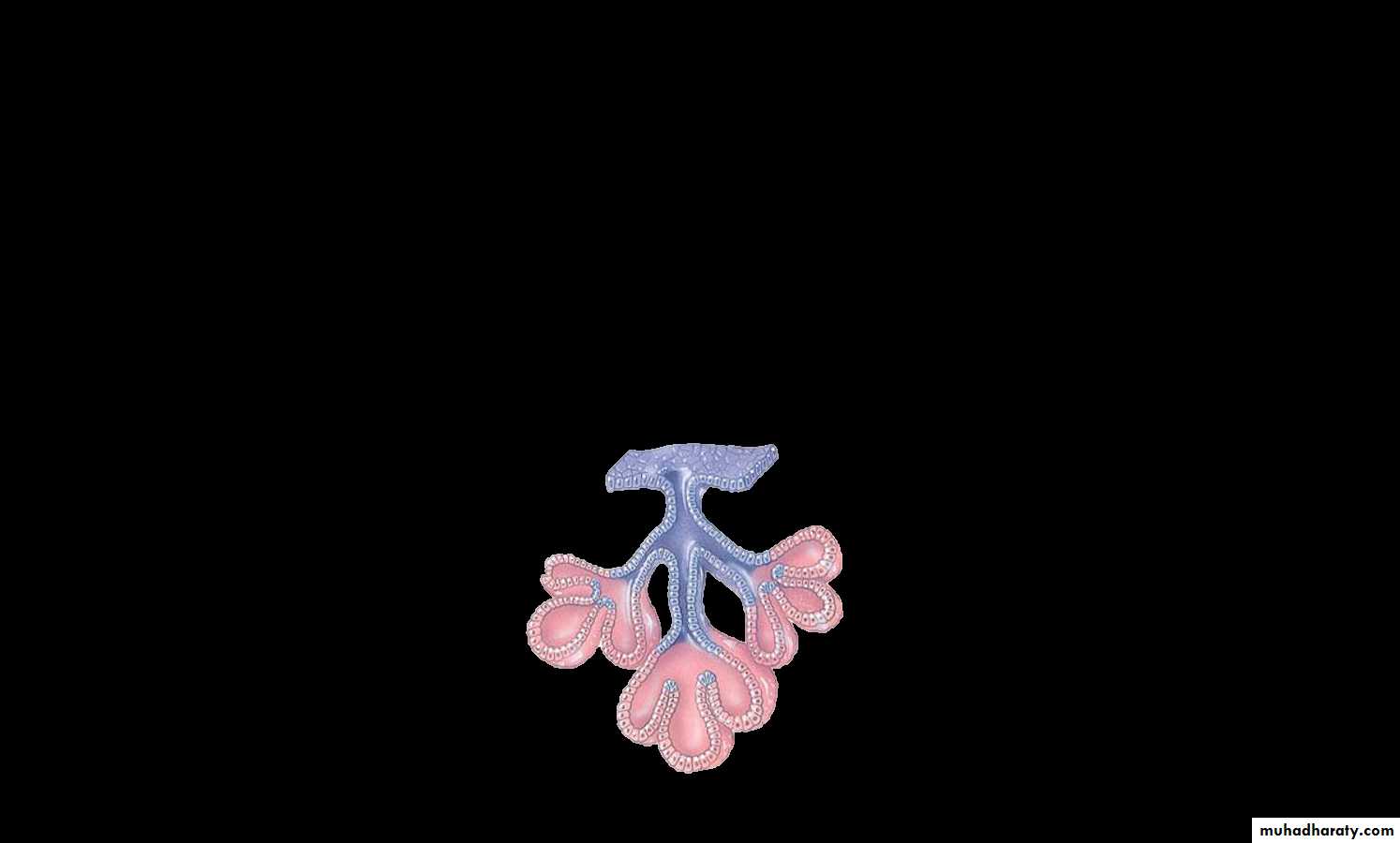
Compound multi-cellular glands have ducts that branch repeatedly.
Compound tubular gland: the functional (secretory) part is tubular in shape eg. The kidney and mouth cavity glands, Brunner's glands (mucous glands) of the duodenum.Compound alveolar acinar
the secretory part is alveoli e.g. mammary and salivary glandsCompound tubuloacinar
some organs have both endocrine and exocrine function and one cell type may function both ways e.g. in the liver (secrete bile into the duct system also secrete some of their products into the bloodstream).4- According to the way in which the secretory products leave the cell
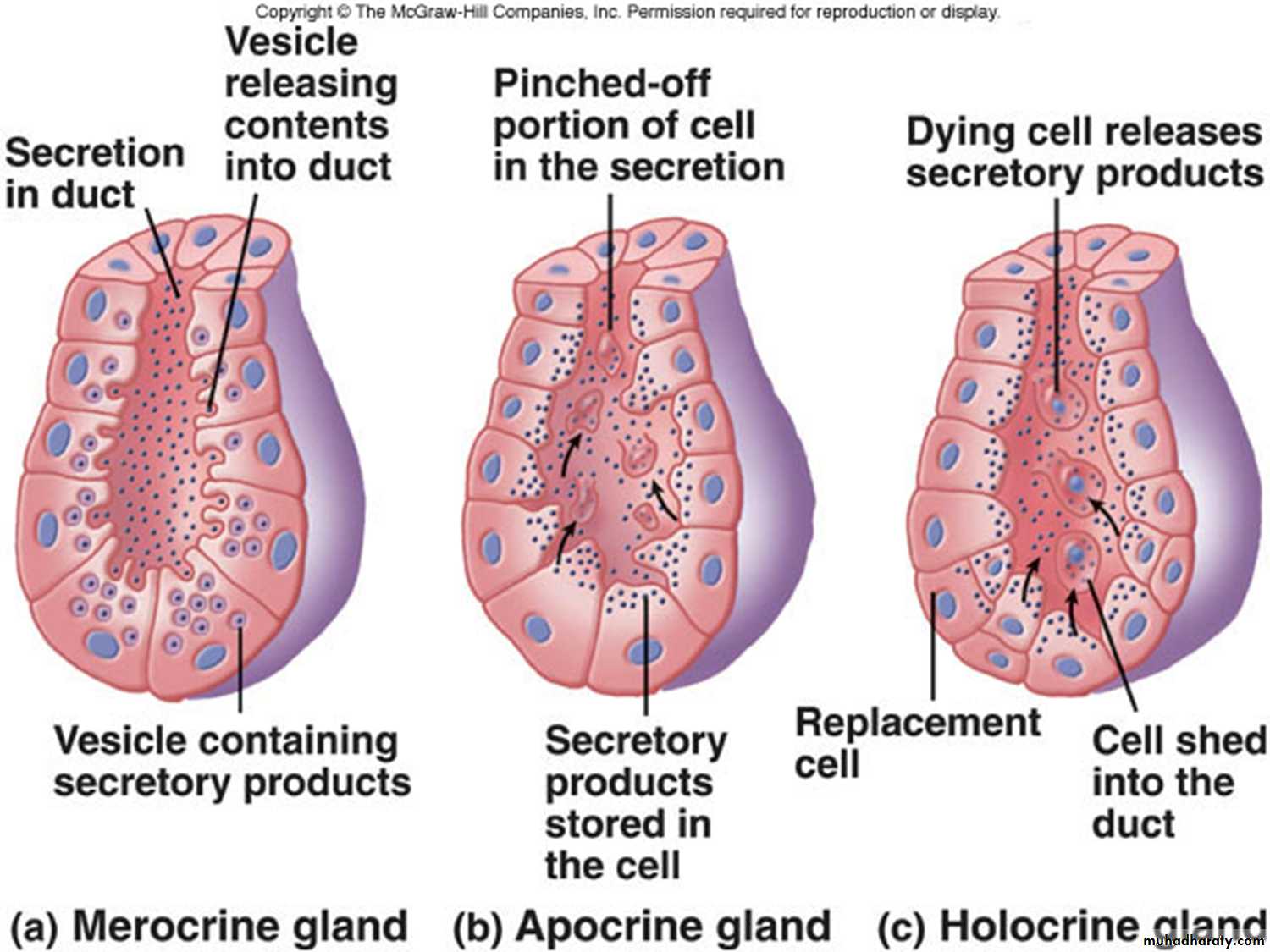
Merocrine : during secretion the secretory cells remain intact and the secretion is released by exocytosis (e.g. Salivary glands and pancreas) with no loss of other cellular material.Holocrine: (e.g. sebaceous gland) the product of secretion is shed with the whole cell a process that involves destruction of the secretion filled cells.
Apocrine: In an intermediate type- the gland secretory product is discharged together with parts of the apical cytoplasm after that the cell will regenerate e.g. Mammary glands
5- According to the type of secretion
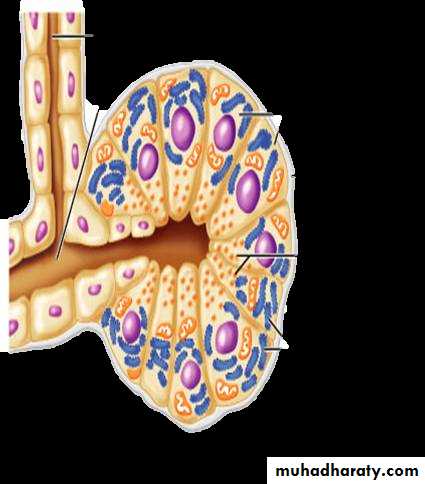
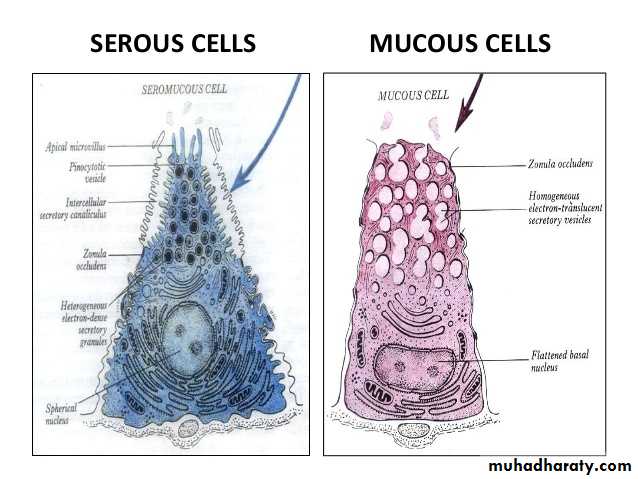
serous glands: they secrete watery albuminous material e.g: parotid gland and pancreas , gastric chief cells and paneth cells of intestinal crypts.• lined with pyramid shape cells
• The boundaries between the cells are not very clear• The nuclei are round euchromatic showing clear nucleus
• The basal cytoplasm is basophilic because its rich in RER and Golgi complex
• The apical cytoplasm is granulated these granules are called zymogen
• The lumen is very small
The cell are characterize by the following histological characteristics:
Mucos gland: it secret mucus substance e.g. sublingual gland. The mucus alveoli have the following histological characteristics
• The alveoli are lined by columnar shape cells
• The boundaries between the cells are clear
• The apical cytoplasm is pale
• The nucleus is flattened based in location because of the heavy weight of mucin material
• The basal cytoplasm is rich in RER and Golgi complex
• The lumen is larger of that of serous glands
Mixed gland: in this type of glands both serous and mucous alveoli are present in addition to that some of the mucous alveoli are surrounded from one side by serous cells forming a crescent; these cells are also called (serous demilunes).
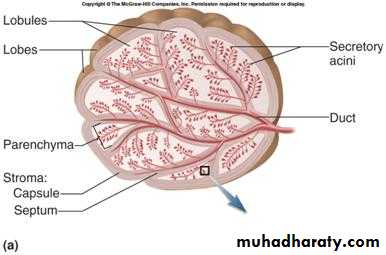
Multicellular glands usually have a surrounding capsule of connective tissue and septa that divides the glands into lobules. These lobules then subdivide, and in this way the connective tissue separates and binds the glandular components together, blood vessels and nerves also penetrate and subdivide in the gland.