HYPERTENSIVE DISORDERS IN PREGNANCY
CLASSIFICATIONA: gestational hypertension and or proteinuria developing during pregnancy, labor or the puerperium in a previously normotensive non proteinuria woman
1.gestational hypertension (without proteinuria)
2.gestational proteinuria (without hypertension)
3.gestational proteinuria hypertension (pre-eclampsia)
B: chronic hypertension (before week 20 of pregnancy) and chronic renal disease (proteinuria before week 20 of pregnancy)
1.chronic hypertension (without proteinuria)
2.chronic renal disease (proteinuria with or without hypertension)
3.chronic hypertension with superimposed pre-eclampsia (new onset protein )
C:unclassified hypertension and or proteinuria
D:eclampsia.early onset pre-eclampsia( before 20 weeks) occur in molar pregnancy and antiphospholipid syndrome
Definition
Hypertension in pregnancy: measures in sitting position.diastolic Bp more than 110 mmHg on any one occasion or
.diastolic BP more than 90 mmHg on two or more consecutive occasions more than 4 hours apart
Proteinuria in pregnancy
.one 24 hour collection with total protein excretion more than 300 mg per 24 hours or
.two clean catch midstream or catheter specimens of urine collected more than 4 hours apart with 2 + on reagent strip
RISK FACTORS FOR PRE ECLAMPSIA
.first pregnancy
.multiparous with pre-eclampsia in previous pregnancy or ten years or more since last pregnancy
.age 40 years or more .BMI of 35 or more
.family history of pre eclampsia in the mother or sister
.booking diastolic blood pressure of 80 mmHg or more
.booking proteinuria of equal or more than 1 +on more than one occasion or quantified at equal or more than 0.3g\24 hour
.multiple pregnancy
. certain underlying medical condition :pe existing hypertension ,preexisting renal disease ,preexisting diabetes ,antiphospholipid antibodies
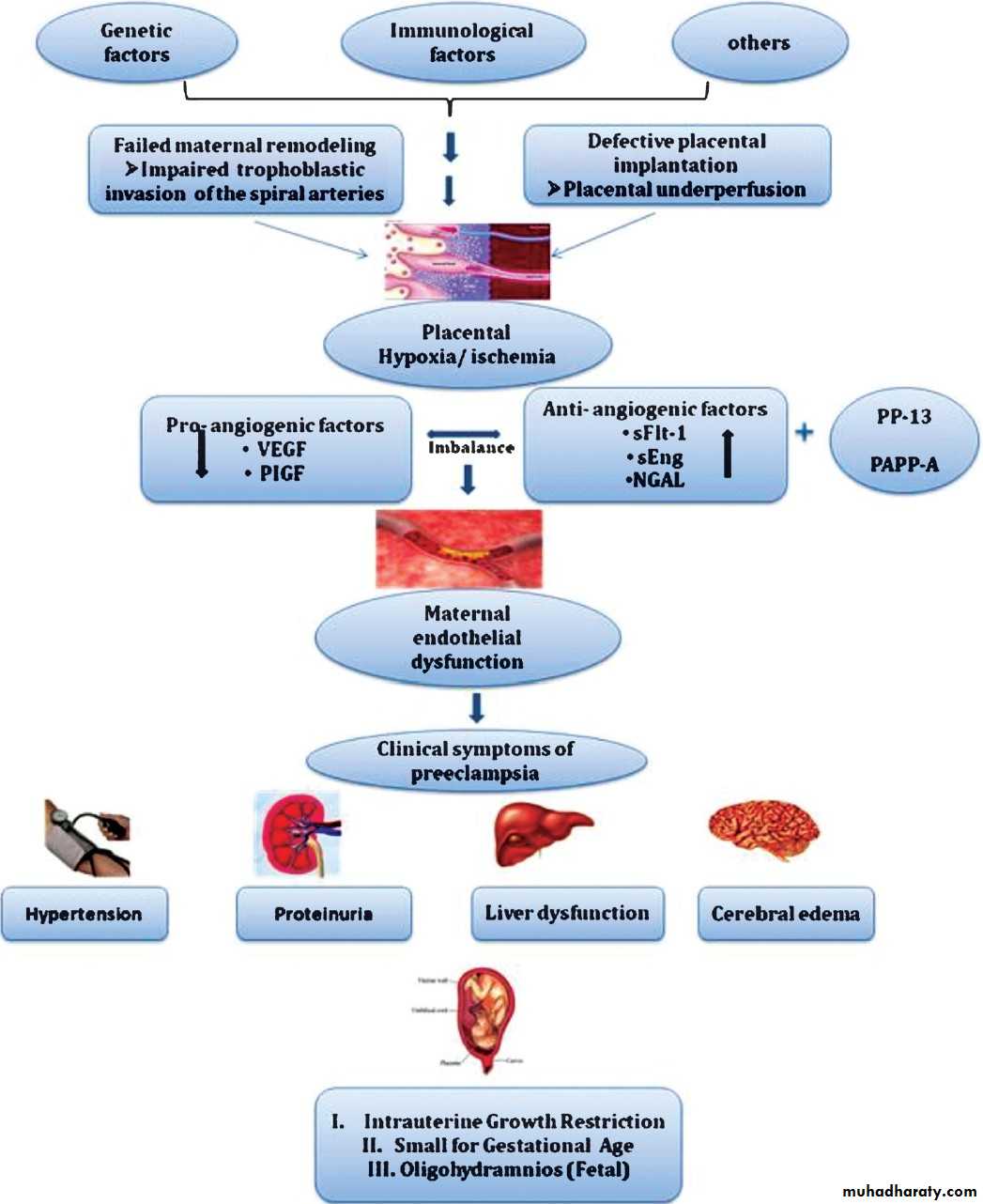
AETIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
This disease occur only in pregnancy suggesting that the presence of trophoblastic tissue that provides the stimulus for the disorder. Defective trophoblast invasion results in relative under perfusion of the placenta and this releases a factors into the maternal circulation that targets the vascular endothelium (variety of growth factors ,cytokines ,oxidative factors ) .as the target of the disease is vascular endothelial so its multisystem disorders.
.the pathophysiology is mainly of two stages disorders
1.abnormal placentation in first half of pregnancy
2.maternal response to this abnormality (in the second half of pregnancy
Genetic predisposition
↓Abnormal immunological response
↓
Deficient trophoblast invasion
↓
Hypo perfused placenta
↓
Circulatory factors
↓
Vascular endothelial activation
↓
Clinical manifestations of the disease
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
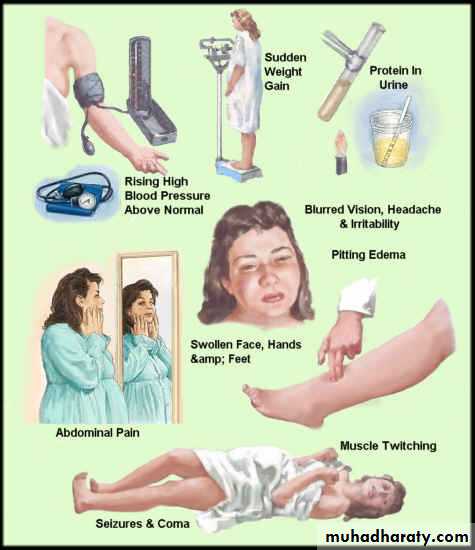
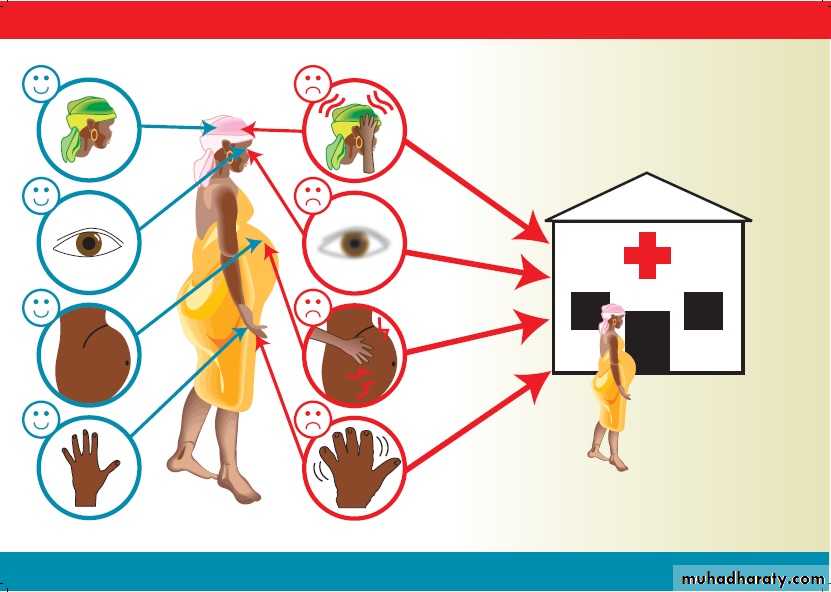
. because woman with pre-eclampsia may be asymptomatic, much antenatal care is directed towards screening for this condition. general vague flu like illness.
. frontal headache, visual disturbance and epigastric pain. . hypertension is usually the first sign but some time transient until late stage
. edema in nondependent part (face and hand ),while leg edema can be present in healthy pregnant
.epigastric tenderness indicate liver involvement
Hyperreflexia and clonus in sever case
Urine testing for protein
.rapid or sudden weight gain
LABORATARY INVESTIGATION
.FBC :relative high Hb due to haemoconcentration,TCP,anemia if hemolysis in sever cases
Coagulation profile: mild prolongation of PT and APTT
Biochemistry: increase urate, increase urea and creatinine, abnormal LFTs(increase transaminases),increase LDH ,increase protein in urine (more than 300/24 hour )
MANAGEMENT OF PRE ECLAMPIA :
.no cure other than end of pregnancy by delivery of the fetus and the placenta.so the aimed of treatment is control the disease during pregnancy and avoid complication and delivery of survival infant with minimal trauma to intact mother
. management plan depend on the severity of the disease and complications. gestational age and fetal wellbeing
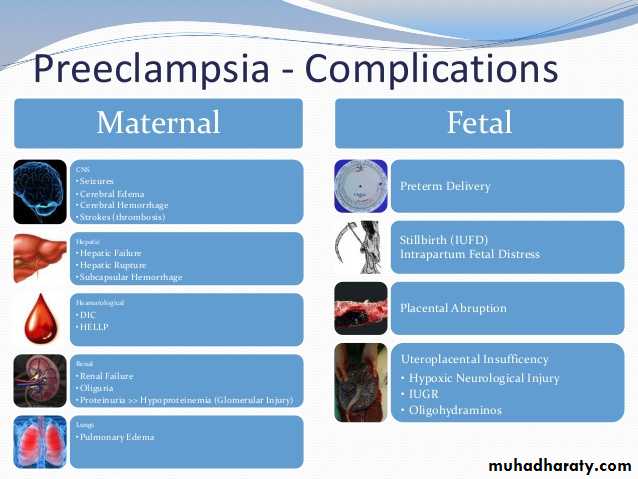
.sever complications of preeclampsia: eclampsia
HELLP
Cerebral hemorrhage
IUGR and fetal compromise
. renal failure
. placenta abruption
. Outpatient management of pre-eclampsia:
Appropriate if Bp less160 systolic and less 110 diastolic and can be controlled, no or low proteinuria, asymptomaticWarn about development of symptoms
Extra rest
Salt in moderation
1-2 \week review of Bp and urine
Regular checking body weight
Weekly review of blood biochemistry
Inpatient management
.sever hypertension 160/110 or less but with significant proteinuria symptomatic patient ,if there is complications4 hour Bp
24 hour urine collection for protein
Daily urine analysis
Daily fetal assessment with CTG
Regular blood test every 2-3 days
Doppler /liquor volume depending on severity
Antihypertensive medications
. Labetalol:.alph and beta adrenergic blocker
.few side effect ,avoided in asthma
.IV labetalol has important role in management acute sever hypertension and in intrapartum
Methyldopa:
.safe and few side effect.oral use
Nifedipine:
.calcium channel blocker
.tachycardia ,headache , flushing are known side effect.
.used as second line of treatment
Hydralazine:
.safe
.tachycardia ,headache ,diarrhea are known side effect
Mainly used as infusion for intra partum or acute sever hypertension
.can be used oral as second line
INDICATIONS OF DELIVERY IN PRE ECLAMPSIA
. term pregnancy
. sever uncontrolled hypertension despite maximum recommended doses of two antihypertensive drugs
. hemolysis with TCP and elevated ALT
. progressive symptoms (headache, visual disturbance, epigastric pain)
. pulmonary edema
.renal compromise with oliguria
Eclampsia
Fetal distress (diagnose by BPPS,NST,Doppler )