The Pituitary gland
(Hypophysis Cerebri)
Gross Anatomy and Functional Localization
Done by
Dr.Rafid Remthan Al-Temimi
Clinical Radiology
CAMB,DMRD,M.B.Ch.B.,.
المرحلة
:
الثانية
المادة
:
التشريح
ج
امعة ذي قار
/
كلية الطب
الدكتور
رافد
رمثان التميمي
2
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Introduction
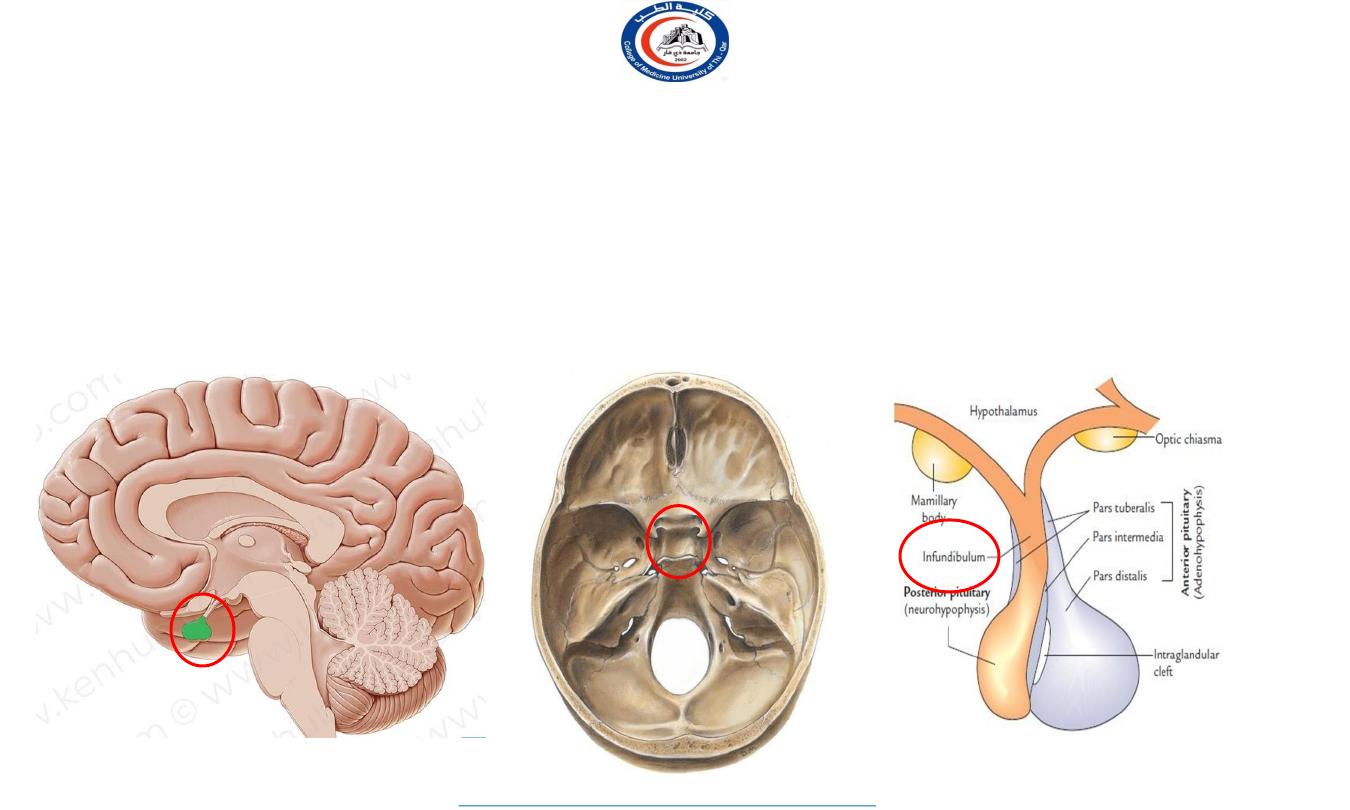
• The pituitary gland is a pea-shaped structure measuring about 0.5 inch in diameter that lies in the
hypophysial fossa
of the sphenoid bone and attaches to the hypothalamus by a stalk, the
infundibulum
.
• For long time pituitary gland was regarded as master endocrine gland due to its control over other gland,
but we now know that pituitary itself has master that is hypothalamus.
• Pituitary gland is also called as ‗hypophysis cerebri‘.(Hypo=under, physis= growth, cerebri=cerebrum)
PITUITARY GLAND
(POSITION)
3
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
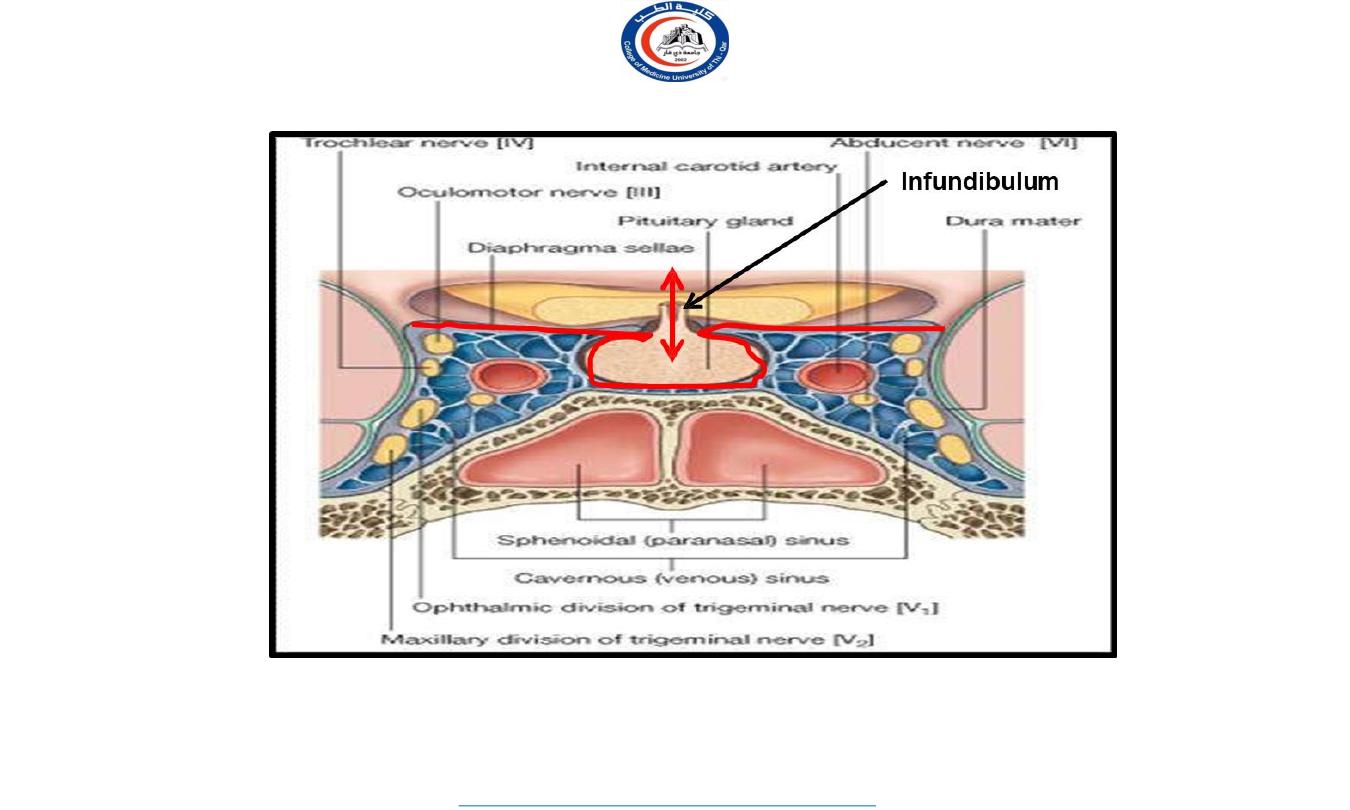
A fold of dura mater (Diaphragma sellae) covers the pituitary gland & has an opening for
passage of infundibulum (pituitary stalk) connecting the gland to hypothalamus.
4
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
PITUITARY GLAND
(POSITION)
5
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
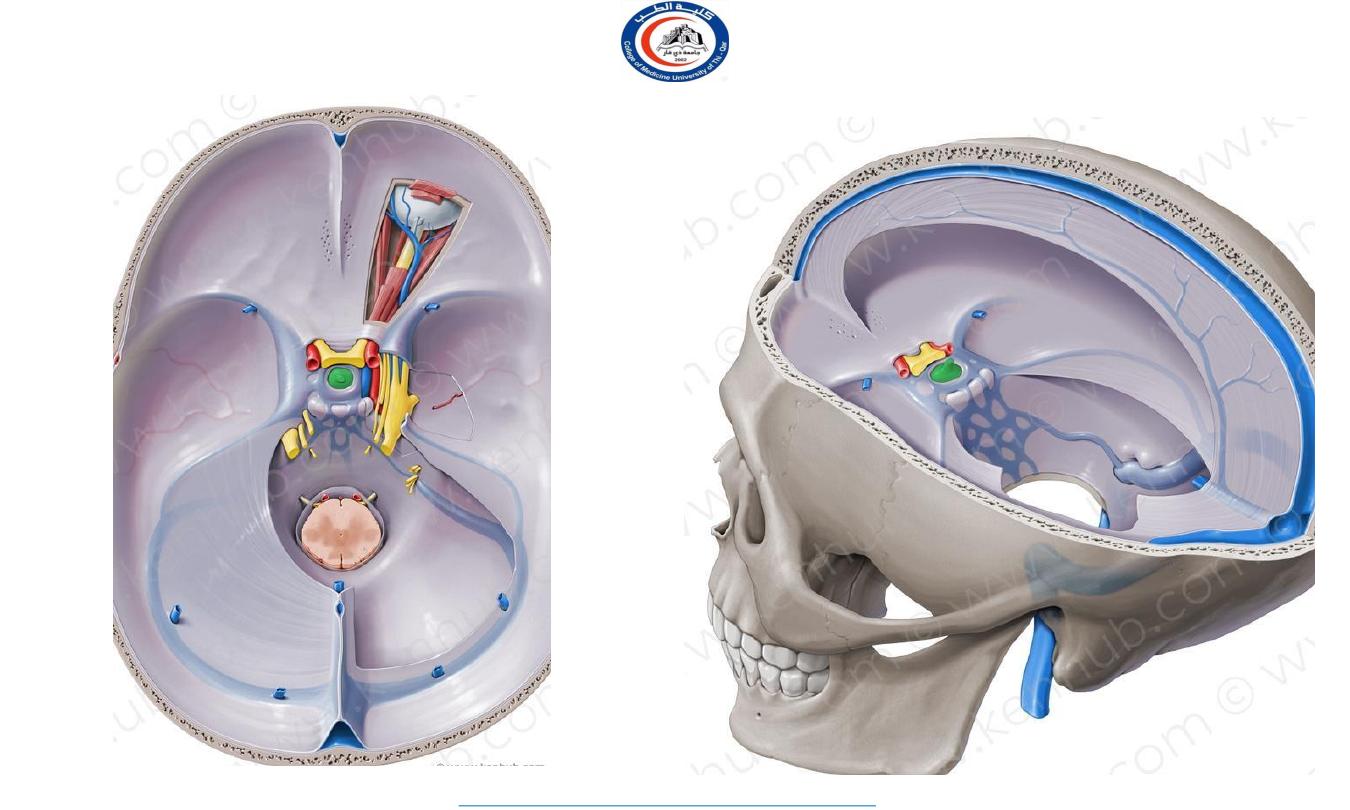
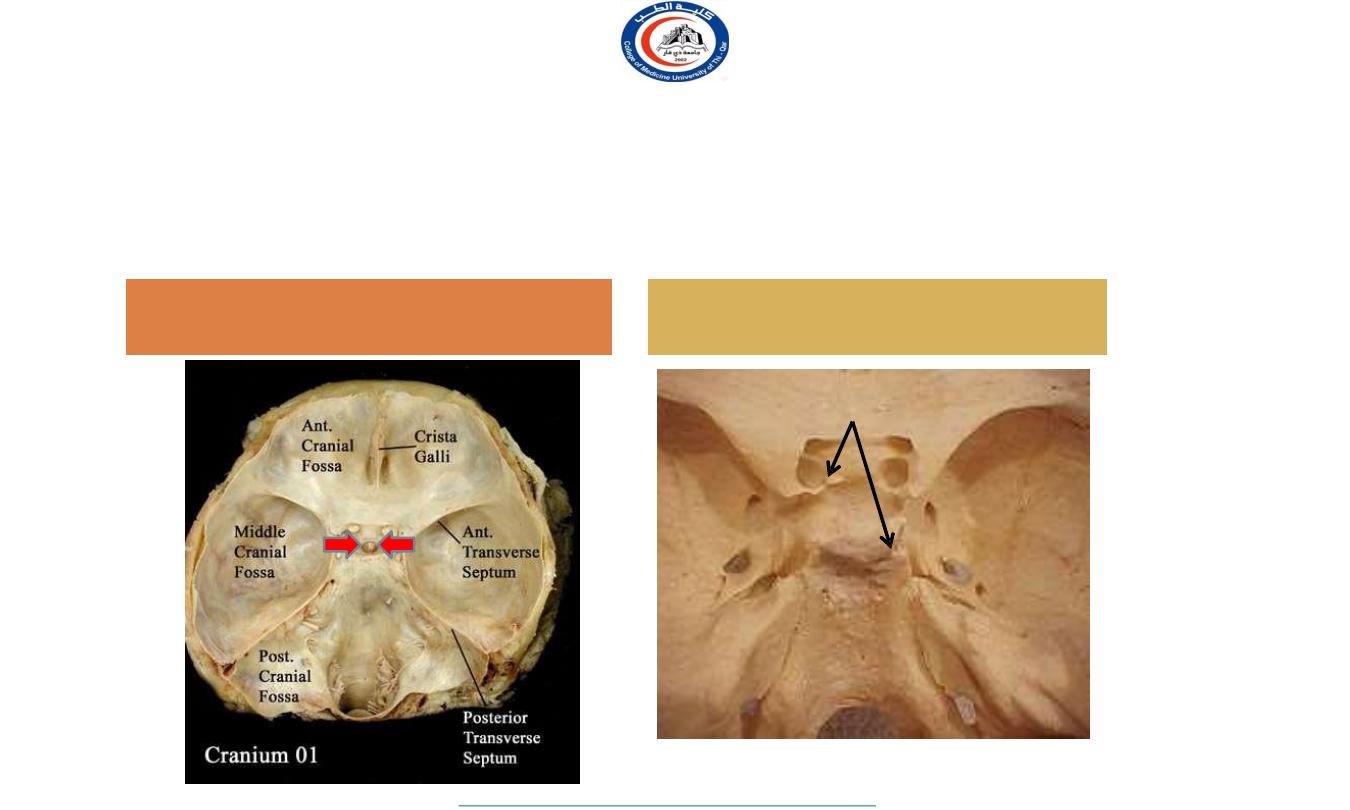
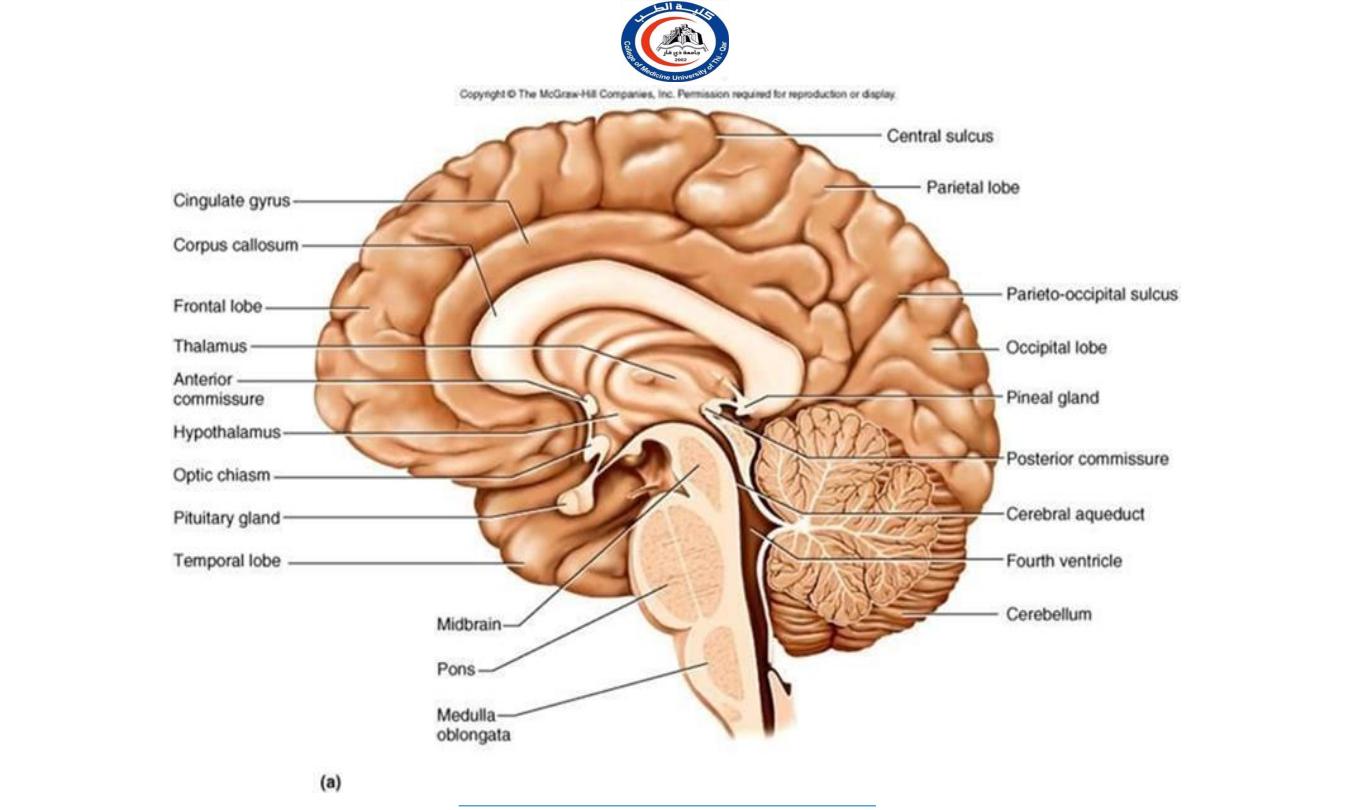
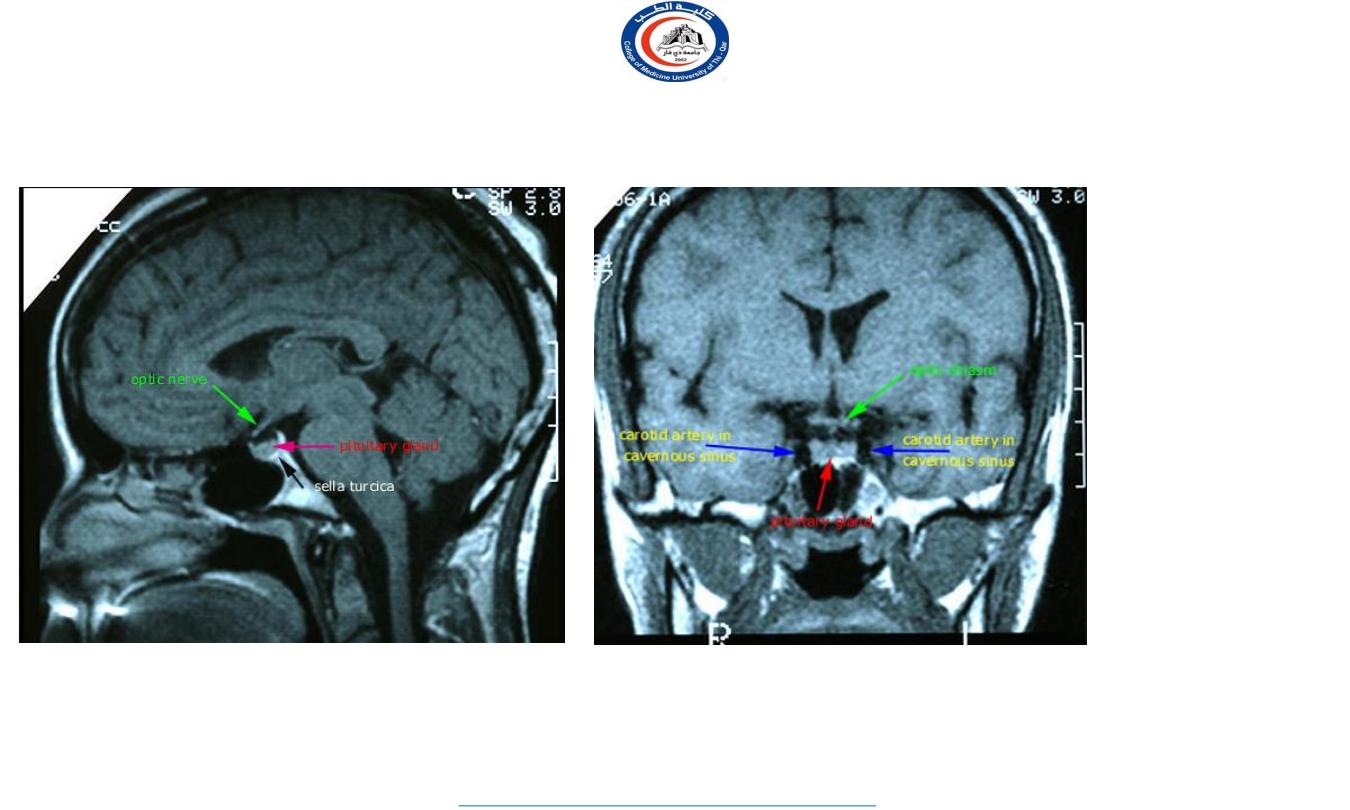
It lies in the middle cranial fossa
It is well protected in sella
turcica of body of sphenoid
Sella turcica
D
r.
Ak
ra
m
J
a
ff
a
r
The pituitary gland
(hypophysis cerebri)
•
•
•
Endocrine gland.
Situated in the hypophyseal fossa of the
body of the sphenoid bone.
Is closely related to the optic chiasma:
– Tumors may produce pressure effects
on the adjacent optic chiasma
visual defects.
Hypophyseal fossa
Optic
chiasma
Hypophysis
cerebri
6
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
PITUITARY GLAND (HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI)
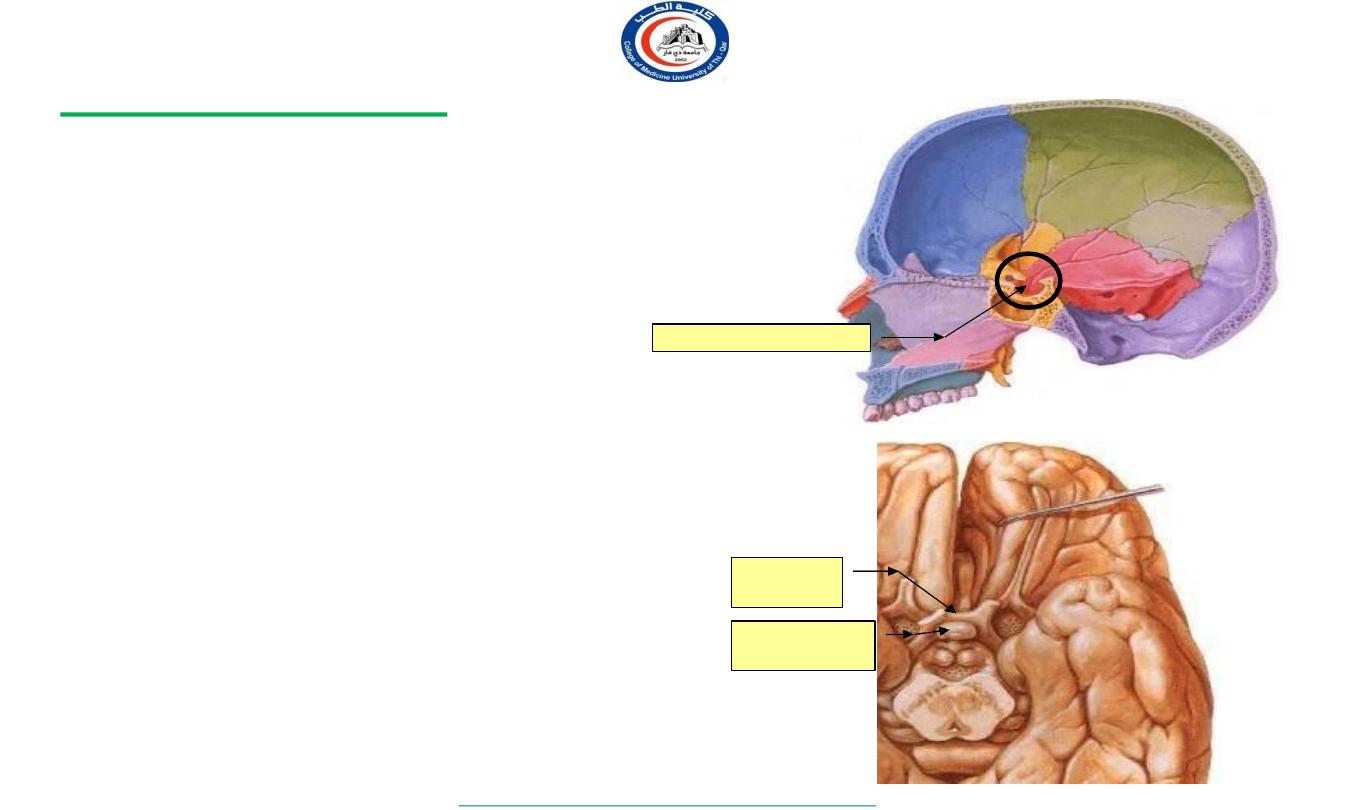
It is a small oval structure of 1 cm in diameter.
It doubles its size during pregnancy.
It lies in the hypophyseal fossa of the body of sphenoid bone,
between optic chiasma (anteriorly) and mamillary bodies (posteriorly).
It lies in the middle cranial fossa
It is well protected in sella turcica of body of sphenoid
The ―master gland‖— controls three other endocrine glands
Better to think of the pituitary gland as the relay center—
Its function covers both endocrine target glands and nonendocrine target glands
7
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
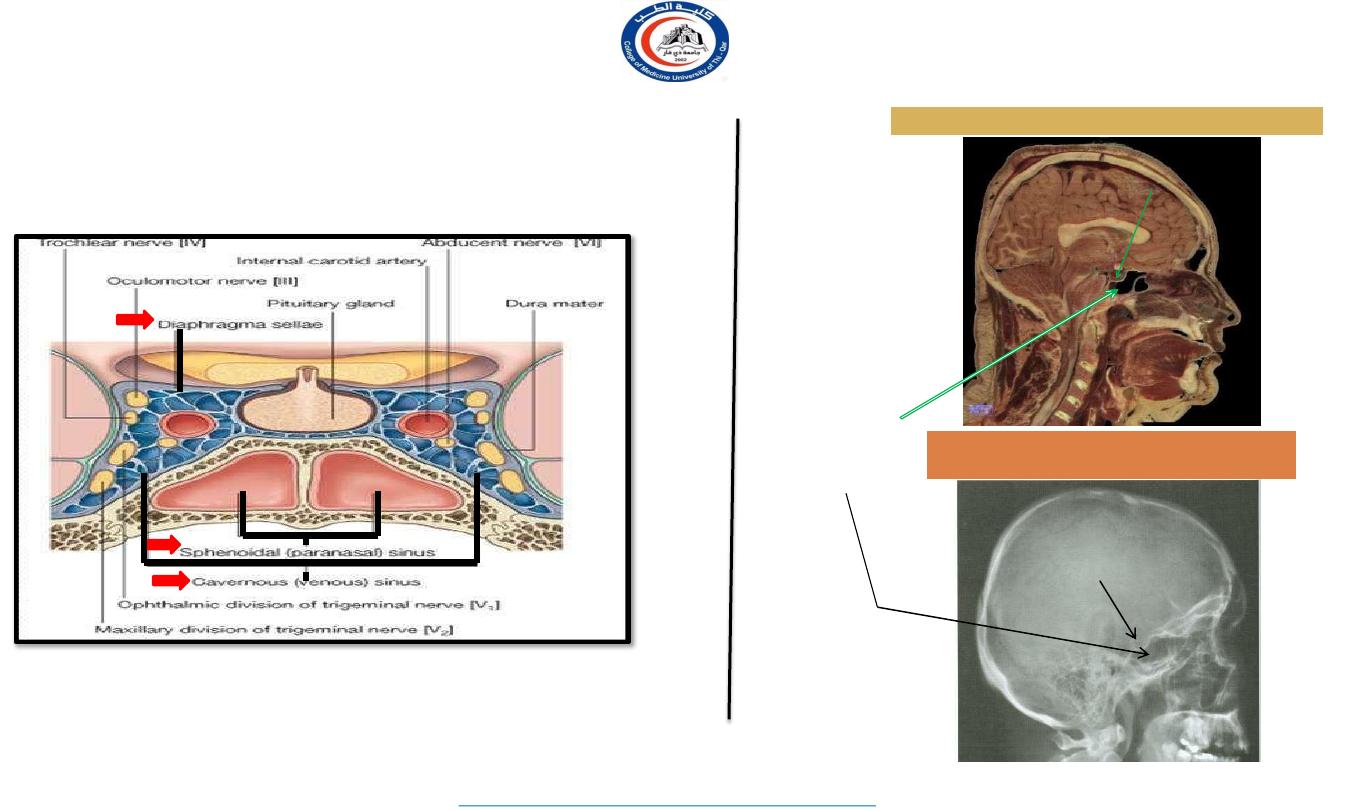
Important relations
housed in sella turcica of sphenoid bone
A fold of dura mater (Diaphragma sellae) covers the pituitary
gland and has an opening for passage of infundibulum (pituitary
stalk) connecting the gland to hypothalamus.
SUPERIOR
: Diaphragma sellae
INFERIOR
: Sphenoidal air sinuses
LATERAL
: Cavernous sinuses
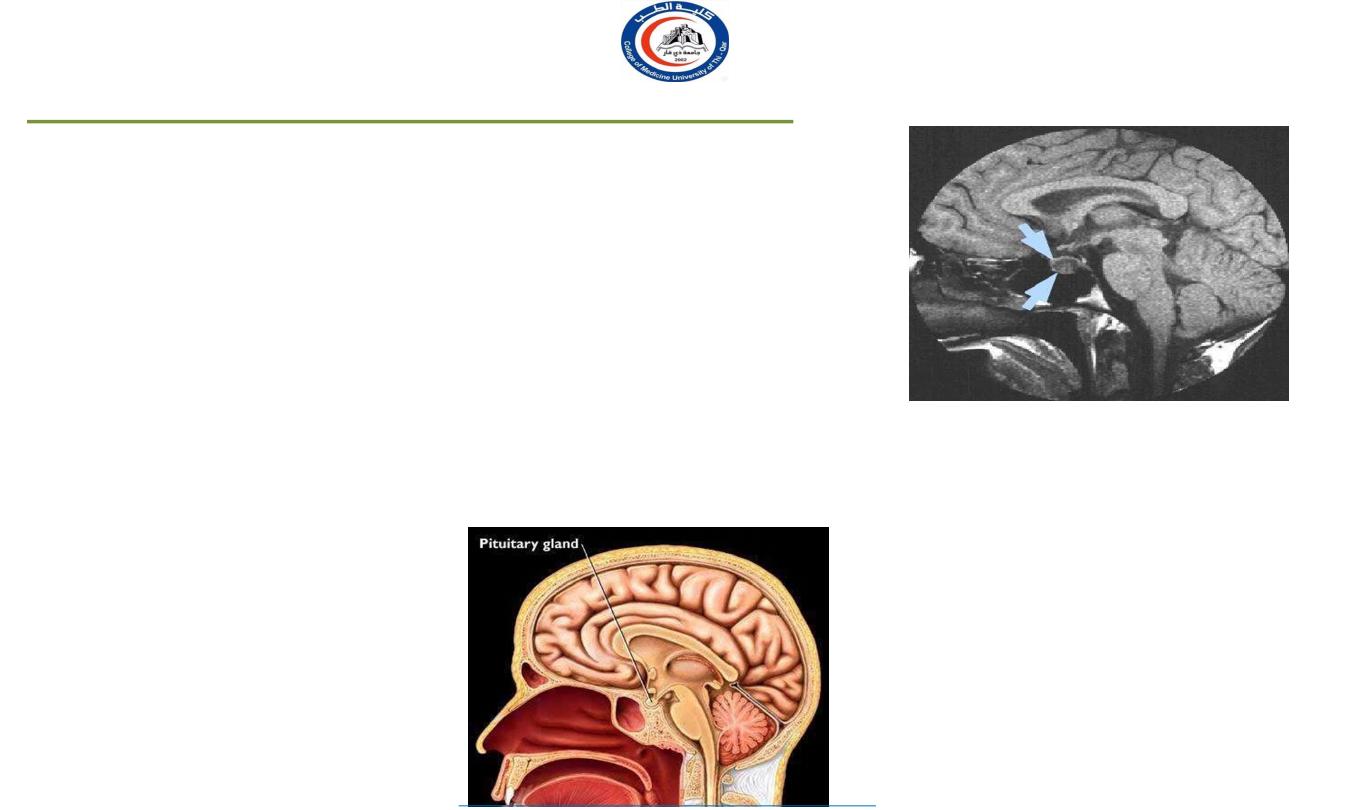
X-RAY SKULL: LATERAL VIEW
SAGITTAL SECTION OF HEAD &NECK
Hypophyseal fossa
Sphenoidal
air
sinus
Pituitary
gland
8
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
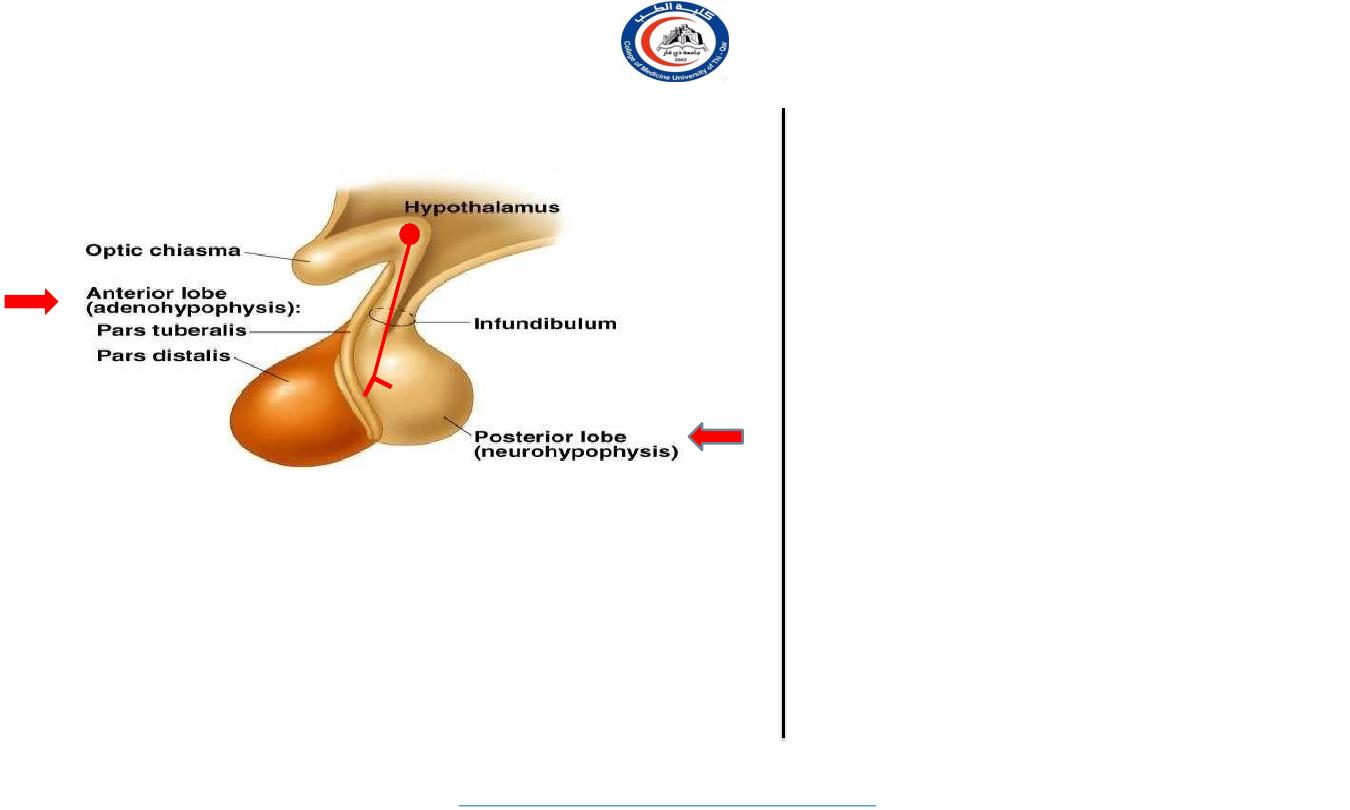
Subdivisions of pituitary gland
The gland is subdivided into:
1) Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis):
true gland, secretes hormones
2)Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis):
connected to hypothalamus
through hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract, stores hormones secreted
by hypothalamic nuclei
Adenohypophysis
(pituitary)
arises from hypophyseal (
Rathke’s)
pouch (outgrowth of pharynx)
Neurohypophysis
(pituitary)
arises from brain;
Magnocellular neurons
– supraoptic
and paraventricular nuclei; Nerve
endings.
Suspended from hypothalamus by stalk
(infundibulum)
9
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
10
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
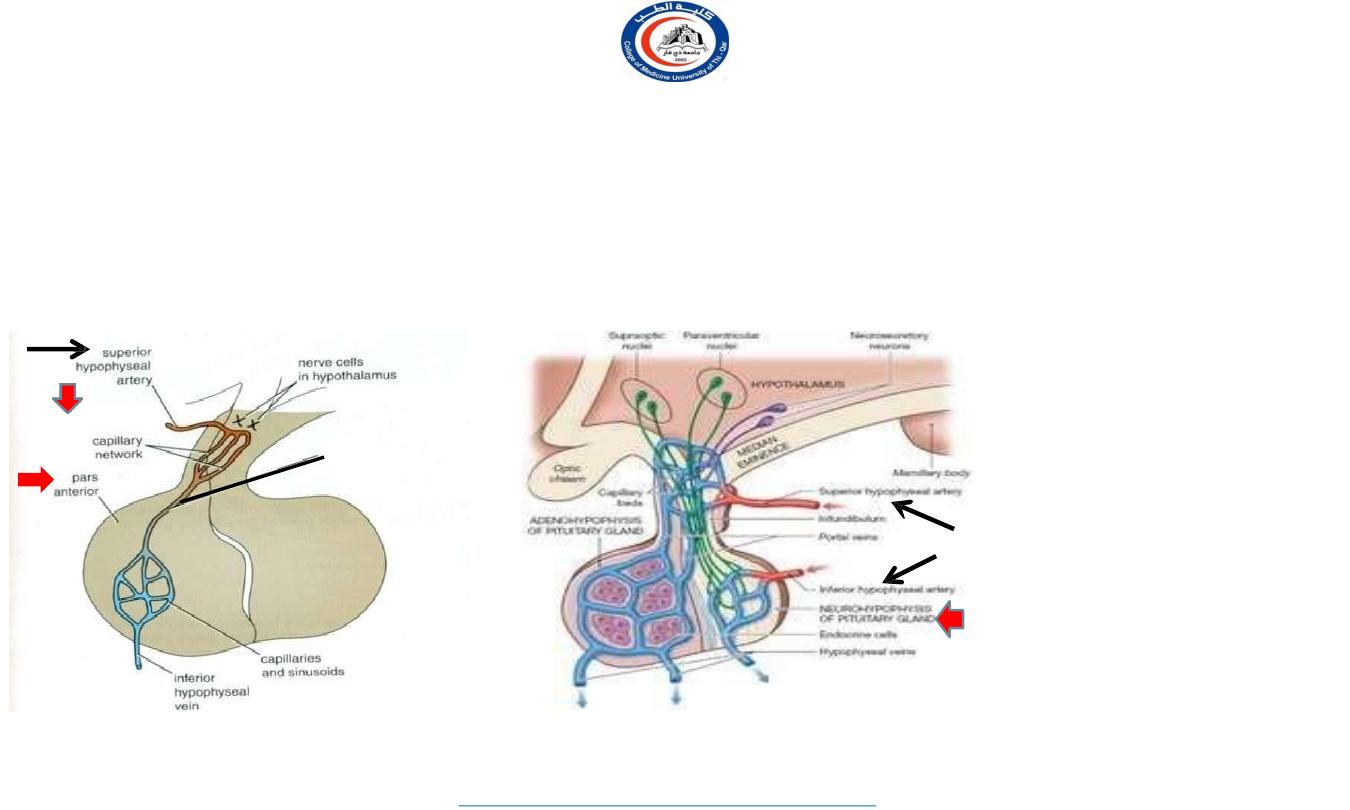
blood supply of pituitary gland
arteries:
superior and inferior hypophyseal arteries (branches of internal carotid artery)
veins:
hypophyseal veins drain into cavernous sinuses.
The arteries
The inferior hypophyseal:
supplies posterior lobe of pituitary gland.
The superior hypophyseal:
supplies infundibulum & forms a capillary network from which vessels pass
downward and form sinusoids into the anterior lobe of pituitary gland (hypophyseal portal system).
a hypothalamo-
hypophseal
portal vessel
Infundibulum
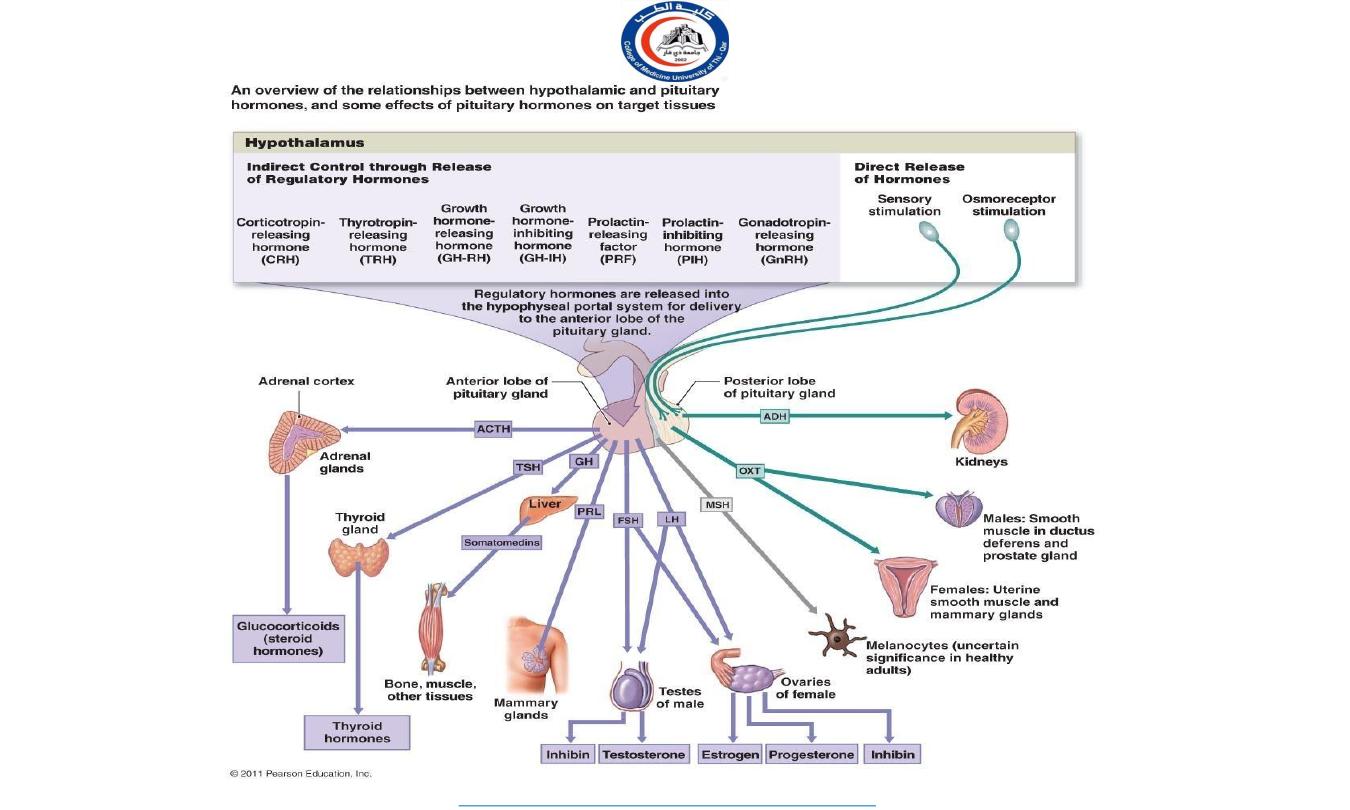
Hormone-releasing and inhibiting factors produced by hypothalamus use hypophyseal portal system of vessels to
reach the anterior lobe of pituitary gland
11
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
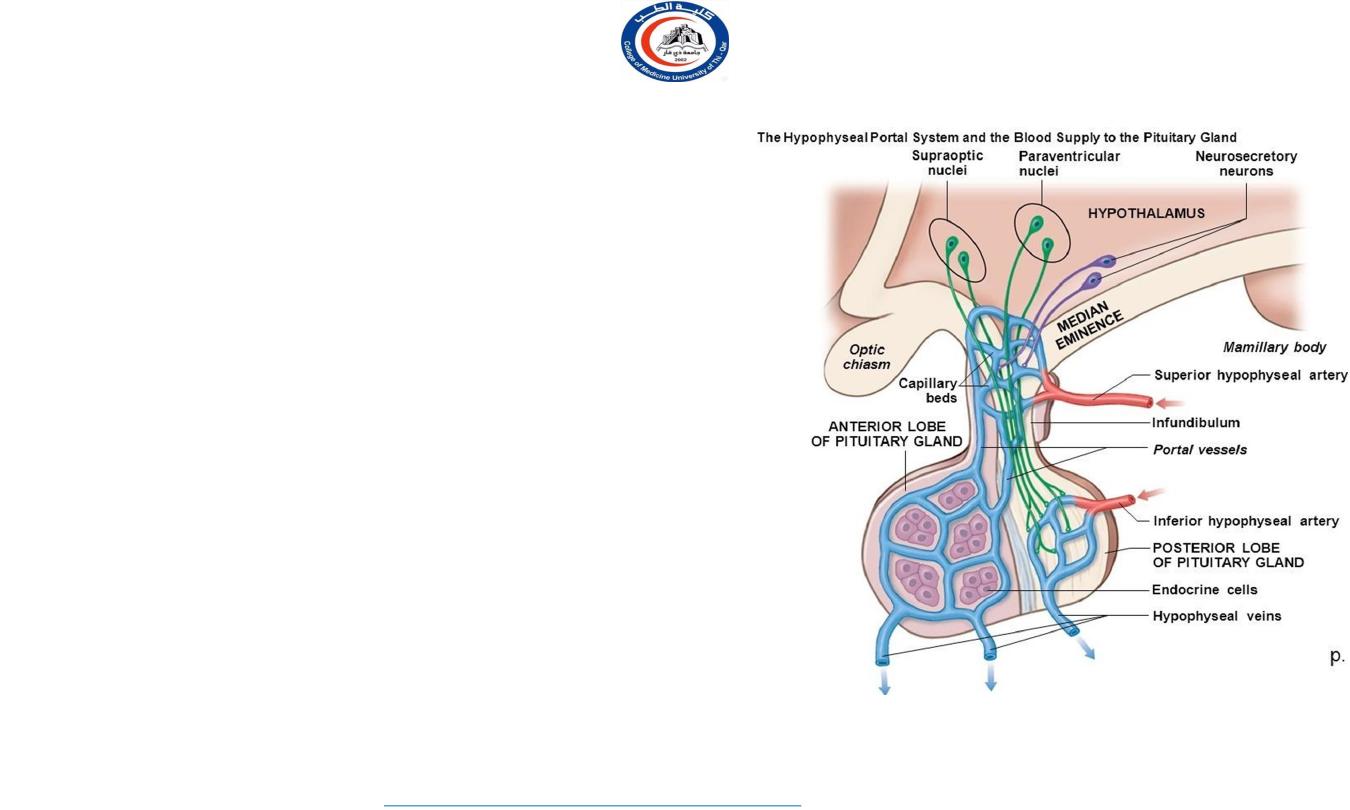
Hypophyseal Portal System
• The hypophyseal portal system is formed on each side from the
superior hypophyseal artery, which is a branch of the internal
carotid artery.
• The artery enters the median eminence and divides into tufts of
capillaries. These capillaries drain into long and short
descending vessels that end in the anterior lobe of the
hypophysis by dividing into vascular sinusoids that pass
between the secretory cells of the anterior lobe.
• Neurosecretory cells situated mainly in the medial zone of the
hypothalamus are responsible for the production of the
releasing hormones and release-inhibitory hormones. The
hormones are packaged into granules and are transported along
the axons of these cells into the median eminence and
infundibulum. Here, the granules are released by exocytosis
onto fenestrated capillaries at the upper end of the
hypophyseal portal system
• The portal system carries the releasing hormones and the
release- inhibiting hormones to the secretory cells of the
anterior lobe of the hypophysis.
12
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
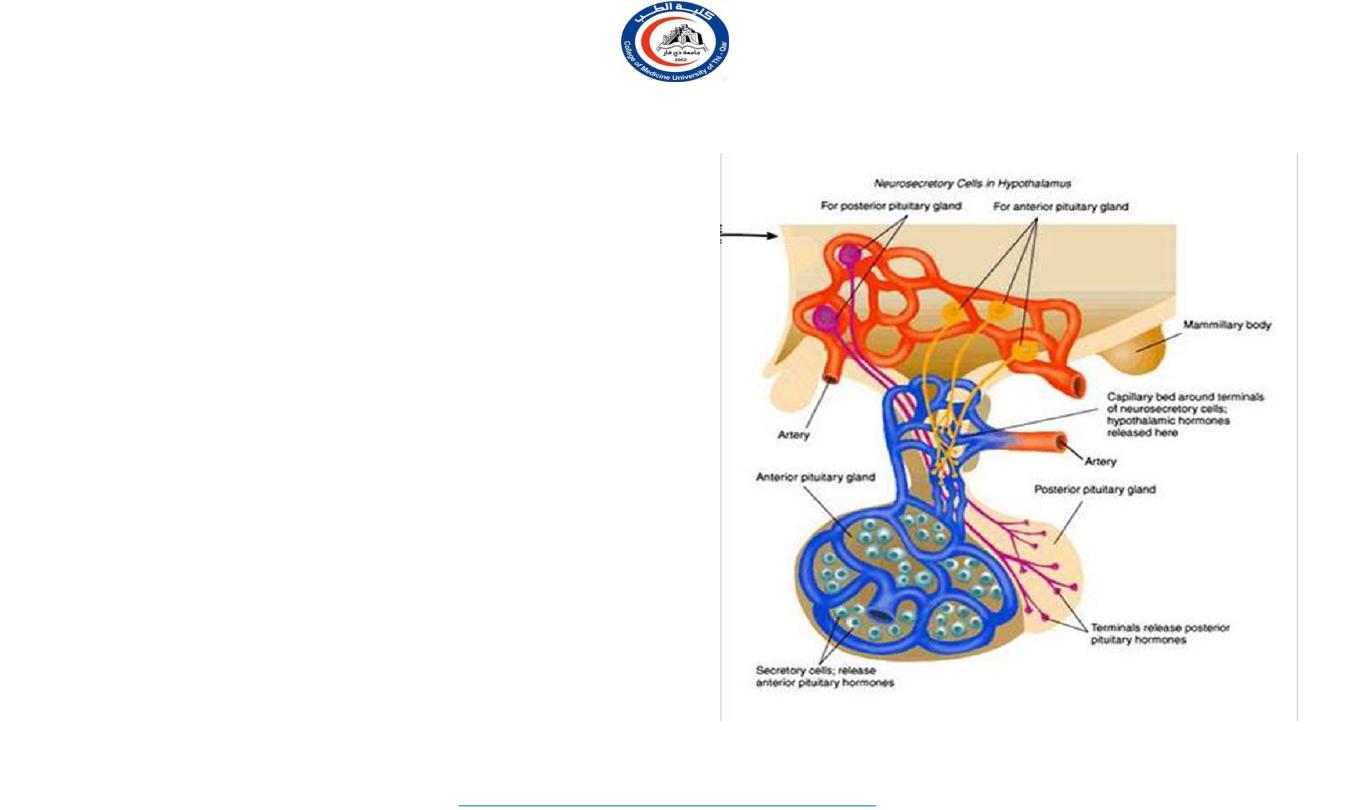
ANTERIOR LOBE OF PITUITARY
13
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Hormone-releasing & inhibiting factors
produced by hypothalamus use hypophyseal
portal system of vessels to reach the anterior
lobe of pituitary gland

Anterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary:
connected to the hypothalamus by hypothalmoanterior pituitary portal vessels.
The anterior pituitary produces six peptide hormones:
1.
FSH
(follicle stimulating hormone)
2.
LH
(luteinizing hormone)
The above two are called
gonadotropins
3.
TSH
(thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin)
4.
ACTH
(adrenocorticotropic hormone)
5.
GH
(growth hormone; somatotropin or somatotropic
hormone)
6.
PRL
(prolactin)
Tropic (trophic) hormones-- target other endocrine
glands to release their own hormones;
14
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

Glycoprotein hormone family
– TSH, FSH, LH
1.
TSH
– to stimulate the secretion of thyroid hormone
2.
FSH & LH
–important for the function of the testes and the ovaries
FSH– growth of ovarian follicles and formation of sperm
LH (in women)– induce ovulation and the formation of the corpus
luteum; stimulate the ovarian production of estrogen and progesterone
LH (in men)– stimulates the production of Testosterone; what
cells?
3.
Prolactin
Stimulates breast development and lactogenesis
May be involved in development of Leydig cells in pre-pubertal males
Immunomodulatory effects– stimulates T cell functions
Prolactin receptors in thymus
15
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
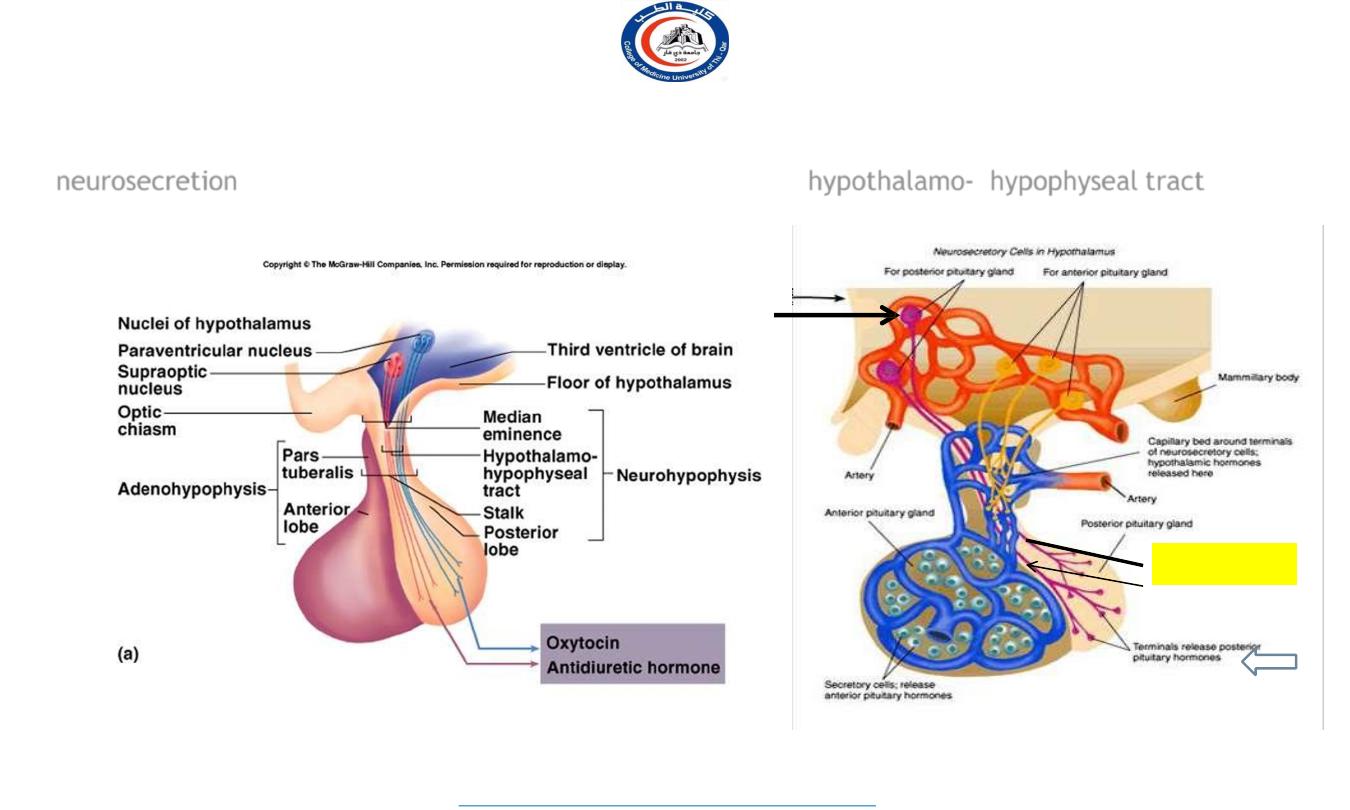
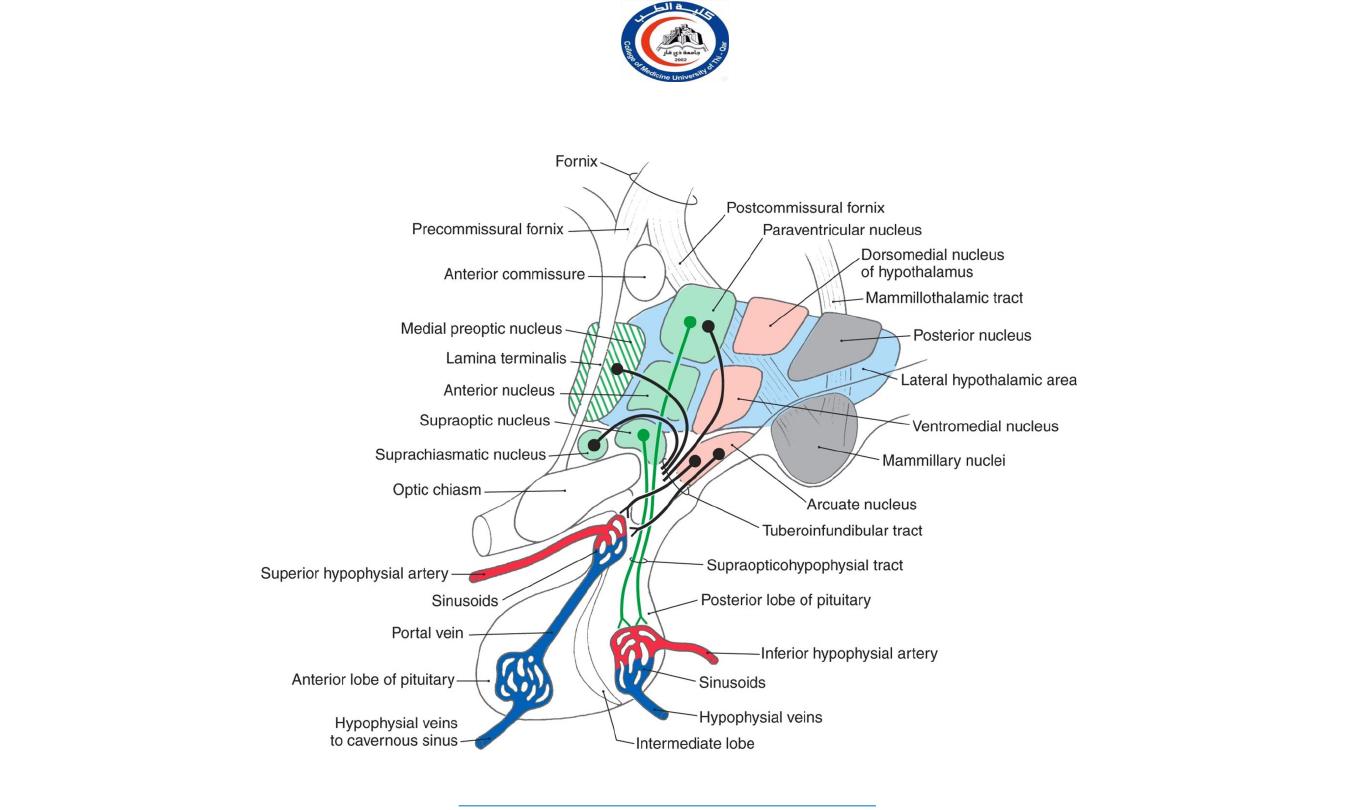
Posterior lobe of pituitary
Axons of supraoptic and paraventricular cells of hypothalamus send their secretion
(
neurosecretion
) to posterior lobe of pituitary gland through
hypothalamo- hypophyseal tract
Hypothalamo-
hypophyseal tract
16
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
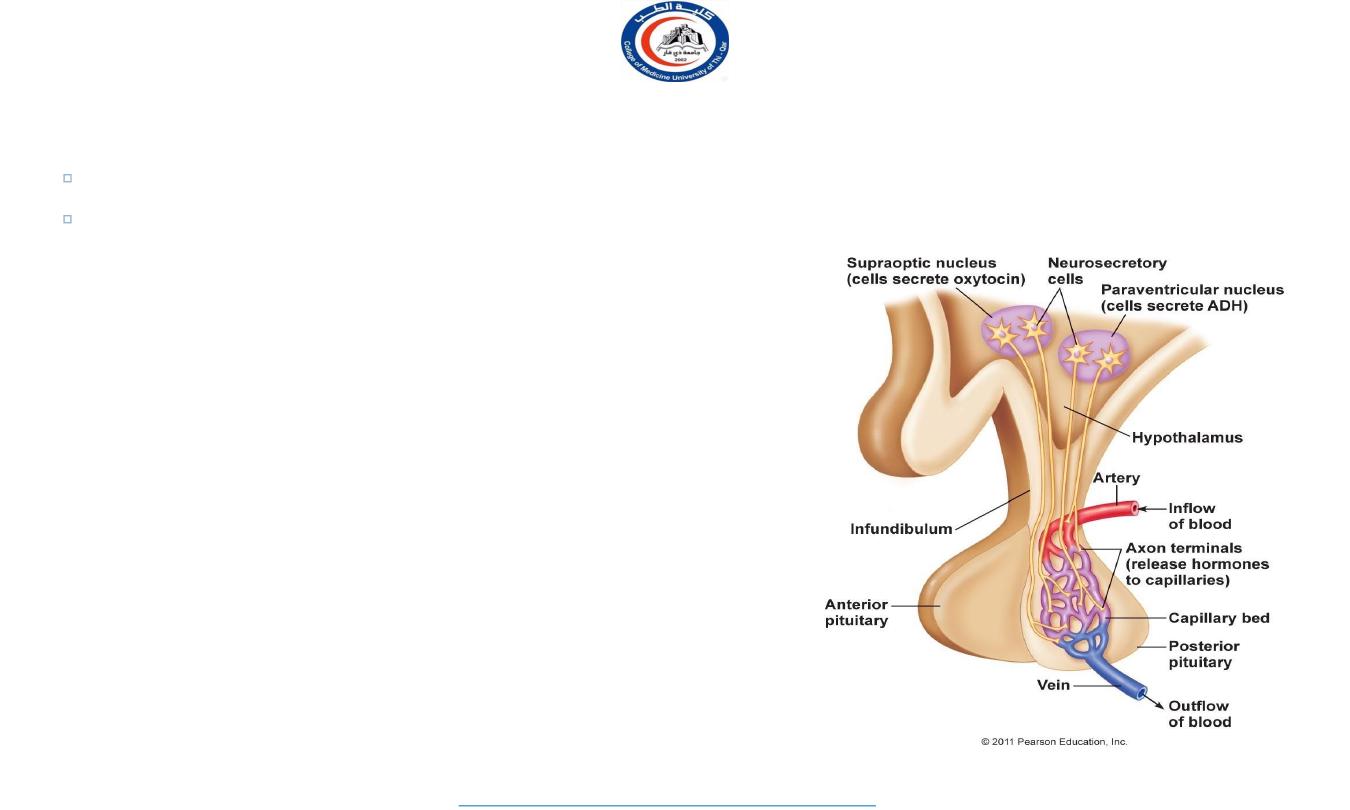
Posterior Pituitary Hormones
OT (oxytocin) and ADH
produced in hypothalamus
transported by
hypothalamo- hypophyseal tract
to posterior lobe (stores/releases hormones)
Hormone Actions: Posterior Lobe
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone)
Target organ/tissue-- ?
water retention, reduce urine
also functions as neurotransmitter
Oxytocin
labor contractions, lactation (milk ejection)
possible role in
sperm transport . . .
emotional bonding
2-31
17
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
18
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
19
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
20
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

Done by
Dr. Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi Clinical Radiology CABM ,DMRD,MBCHB,
21
Thank you with best wishes
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
