Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome( AIDS)(HIV)
Etiology
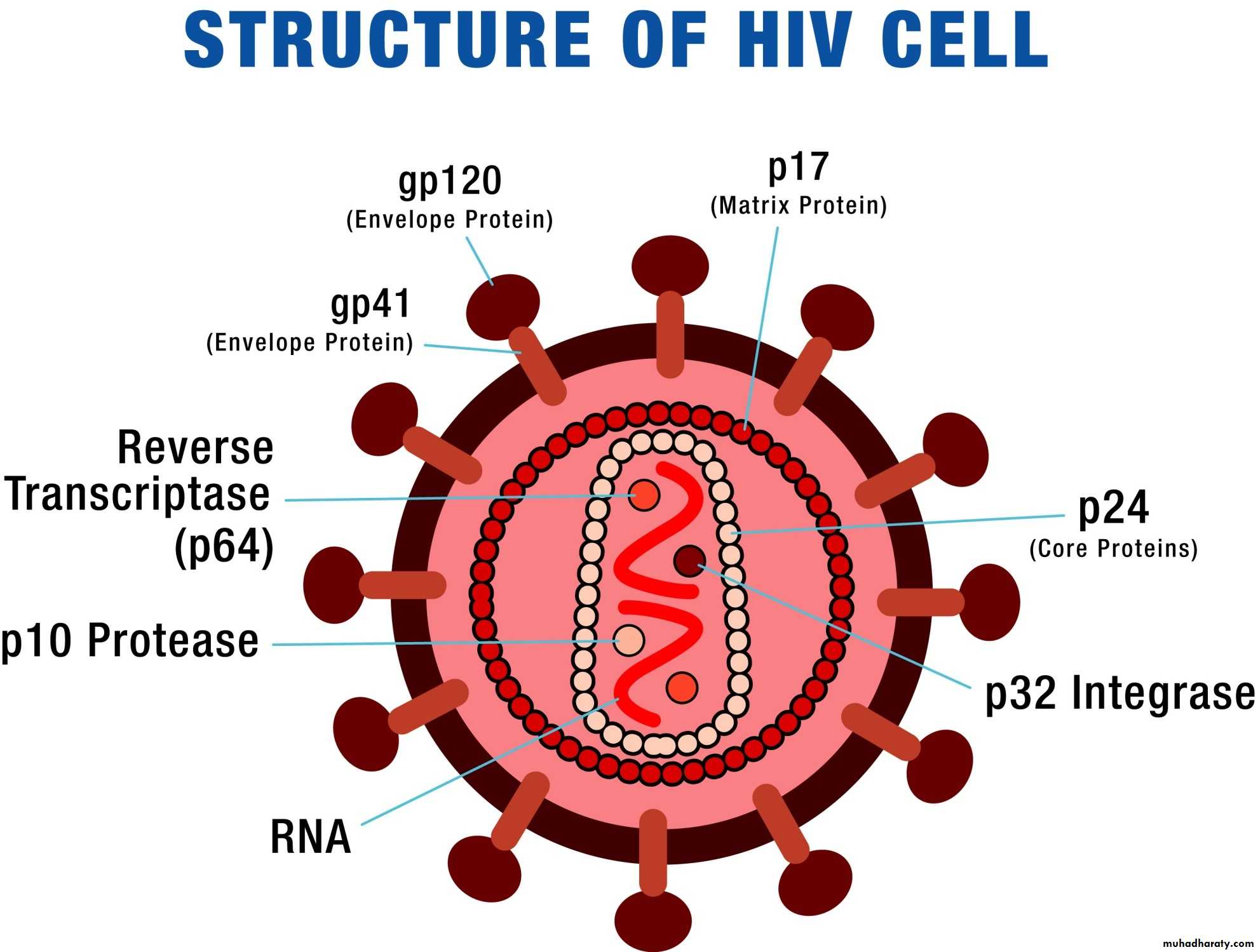
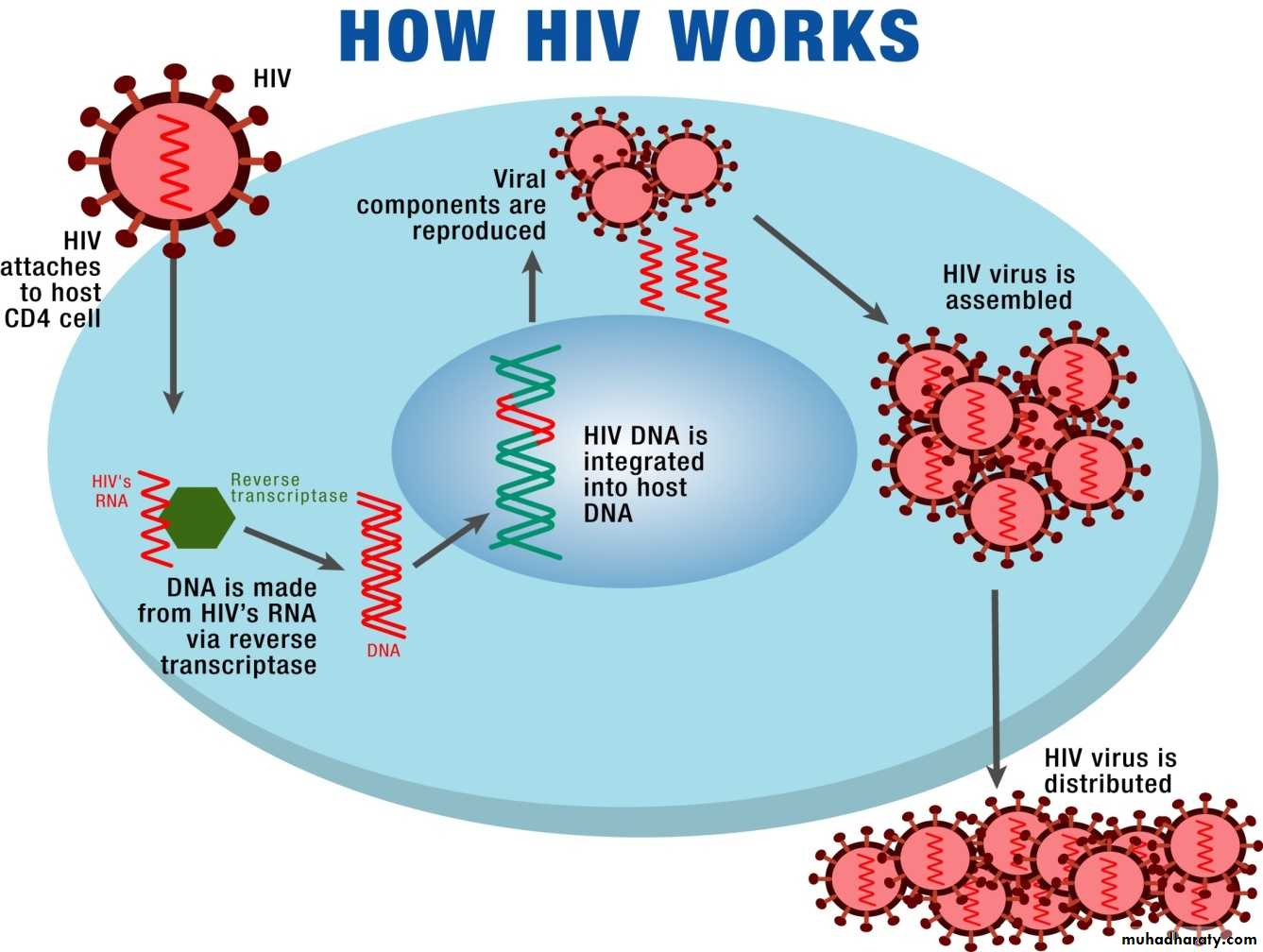
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1 and HIV-2) HIV-2 is a rare cause of infection in children. HIV is single stranded RNA .Transmission
*vertical transmission from mother to child: before delivery (intrauterine), during delivery (intrapartum), or after delivery (postpartum through breastfeeding).*Transfusions of infected blood or blood products
*sexual contact
Clinical Manifestations:
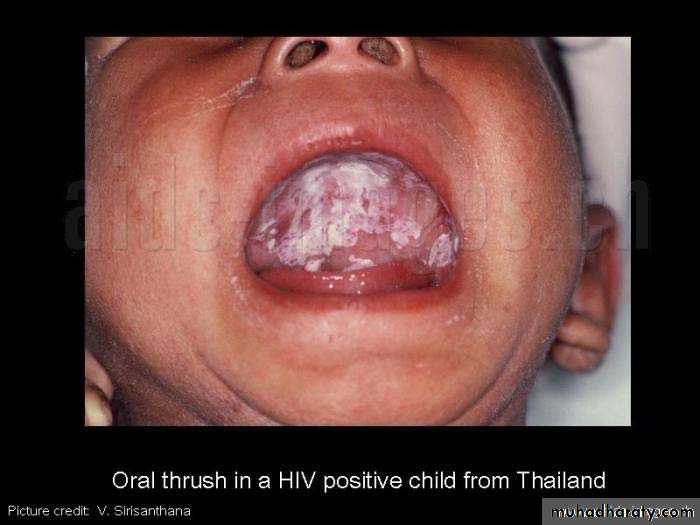
*May be normal at birth .*LAP and HSM ,FTT, chronic or recurrent diarrhea and oral thrush .
*Recurrent bacterial infection
*Chronic parotid swelling.
Recurrent bacterial infection like strep. Infection , salmonella spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Atypical Mycobacterial infection :(mycobacterium avium complex )
Fungal infection like oral candidiasis.Pneumocystic carinii pneumonia.
*Viral infections: Herpes virus ;(recurrent gingivostomatitis , Varicella zoster , CMV ).
• *Respiratory tract manifestation:• OM or sinusitis are very common
• LIP(lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis )
• Strept.pneumonia.
*Skin manifestation: seborrhea dermatitis ,eczema, and molesecum contagiusum .
*Hematologic and Malignant DiseasesAnemia ,leukopenia , &thrombocytopenia.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Diagnosis
All infants born to HIV-infected mothers test antibody-positive at birth because of passive transfer of maternal HIV antibody across the placenta during gestation.To establish a definitive serologic diagnosis, the test should be repeated after 18 months.
*Viral diagnostic assay: HIV DNA PCR, HIV RNA PCR,& HIV culture → used for detection of HIV in children less than 18 months.
Treatment
The currently available therapy does not eradicate the virus and cure the patient; instead it suppresses the virus and changes the course of the disease to a chronic process.• 1. Anti-retroviral Therapies
• - Reverse transcriptase inhibitors:• * Nucleoside (or nucleotide) reverse transcriptase inhibitors→ Lamivudine, Zidovudine.
• * Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Protease inhibitors
2. Supportive therapy.
• Nutritional support, oral hygiene• Immunizations, prophylactic antibiotics
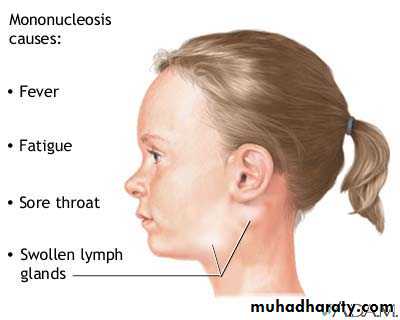
Infectious mononucleosis (glandular fever)
Etiology
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Epidemiology
It is transmitted in oral secretions by close contact such as kissing or exchange of saliva from child to child.
EBV is shed in oral secretions for >6 mo after acute infection.
Clinical Manifestations
I-P 30-50 days.Malaise, fatigue , fever and headache, sore throat , nausea and abdominal pain are main presentations .
This prodromal period may last 1-2 wk.
Rapid splenic enlargement causing Lt. upper quadrant abdominal discomfort and tenderness.
On physical examination:
Generalized LAP > 90% of casesSplenomegaly in 50 % of cases
Hepatomegaly in 10 % of cases
Epitrochlear LAP.
Hepatitis and jaundice uncommon.
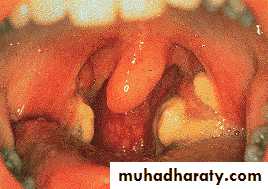
Sore throat
moderate to severe pharyngitis with marked tonsillar enlargement, occasionally with exudates.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
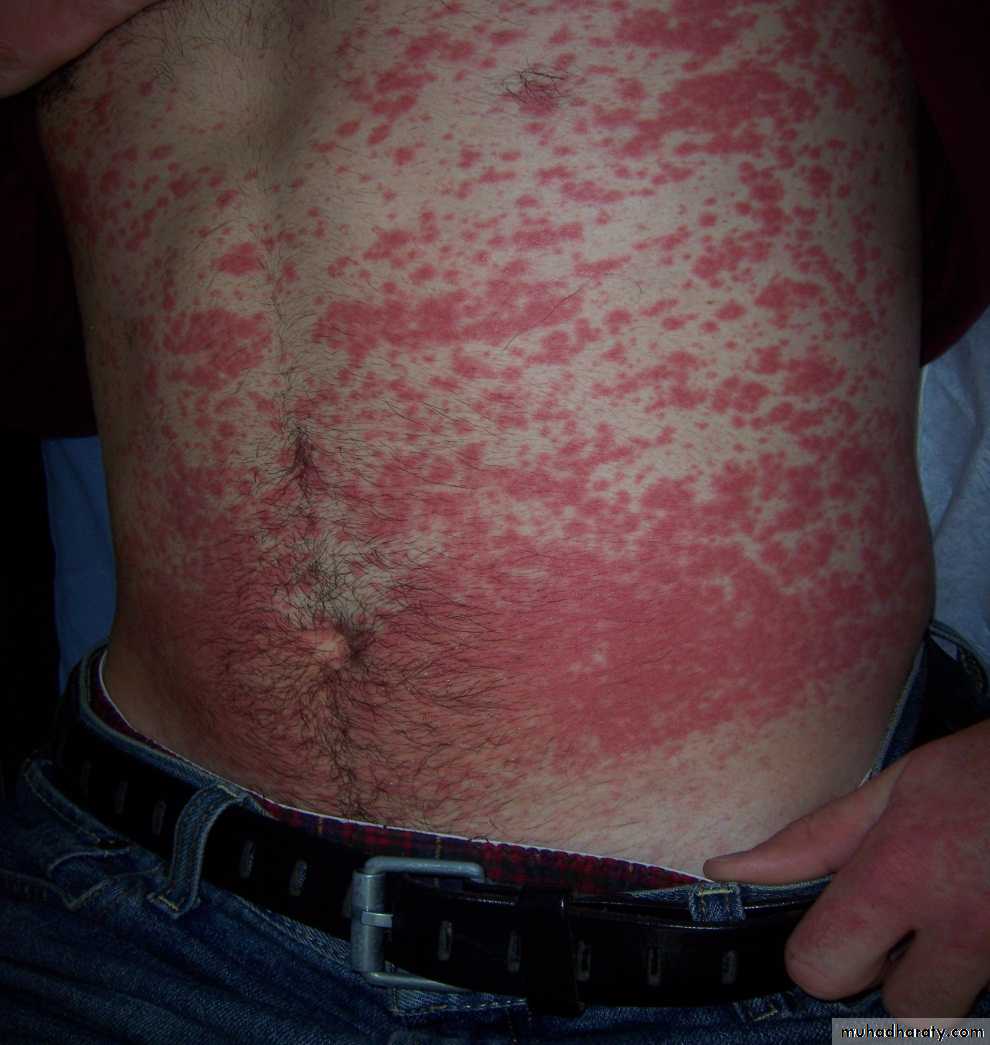
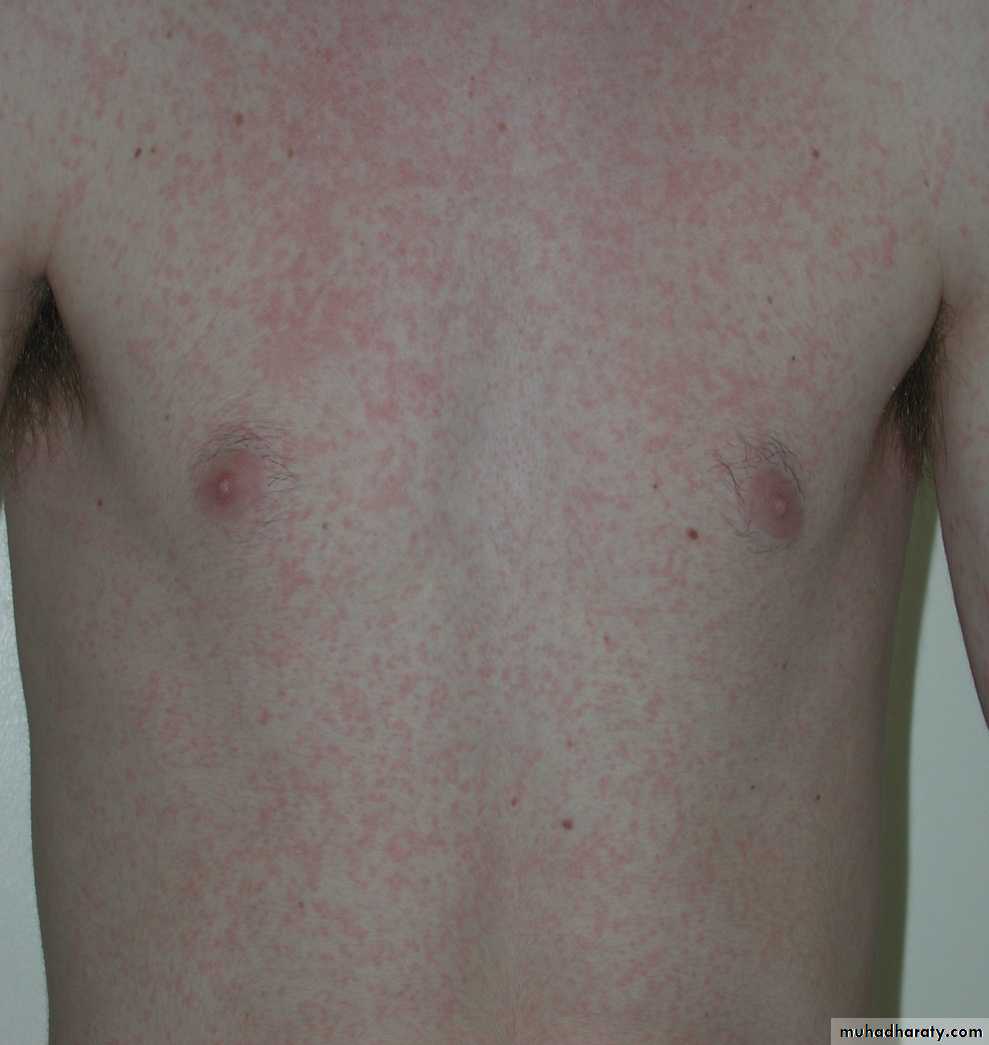
19Maculopapular rash.
80% of cases will experience rash if treated with ampicillin or amoxicillin.Diagnosis.
1. Typical signs and symptoms.
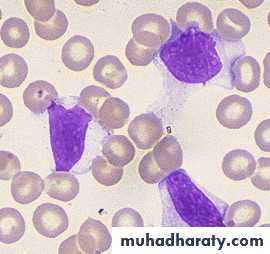
2. Atypical lymphocytosis > 20% -40% of the total number.
3. leukocytosis
• 4. Specific test:
*Paul-Bunnell-Davidsohn test: detect Heterophile antibodies (Paul-Bunnell antibodies)Titers greater than 1:28 or 1:40 are considered positive.
*EBV-specific antibody testing: IgM & IgG AB.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment.High doses of acyclovir, with or without corticosteroids, decreases viral replication and oropharyngeal shedding but does not reduce the severity or duration of symptoms.
Symptomatic therapy & Bed rest.
Avoid abdominal trauma to avoid splenic rupture .Avoid exercise for 2-3 wks. or while splenomegaly present .
Indications for corticosteroids include:
1.airway obstruction2.thrombocytopenia with hemorrhaging
3.autoimmune hemolytic anemia
4.seizures and meningitis.
A recommended dosage is prednisone, 1 mg/kg/ 24 hr, for 7 days &tapered over 7 days .
Complications
*Splenic rupture during 2nd wks.*Airway obstruction
*Ataxia and seizure
*Meningitis , facial palsy and encephalitis
*Guillain barre` syndrome
*Hemolytic anemia with +ve combs` test
*Aplastic anemia ( rare )
*Myocarditis , parotitis ,orchitis.