Orthopedic Surgery5th Stage
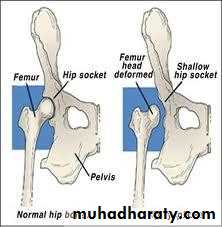
Developmental dysplasia of hip jointDefinitionDDH: It is abnormal development or abnormal formation of the hip joint inwhich the femoral head is not stable in the acetabulum
May occur during fetal development or at birth or after birth due to deviation in normal development of infantile growth period.Instability ↔ mal devop. of acetab
DDH include spectrum of disorders:1. Acetabular dysplasia without displacment of femoral head.2. Hip instability which either: subluxation Dislocation3. Teratological dislocation.
Incidence Neonatal instability At birth 5 -20\1000 At 3wk 1-2 \1000 female > male 7:1 Lt > Rt Bilateral 1:5
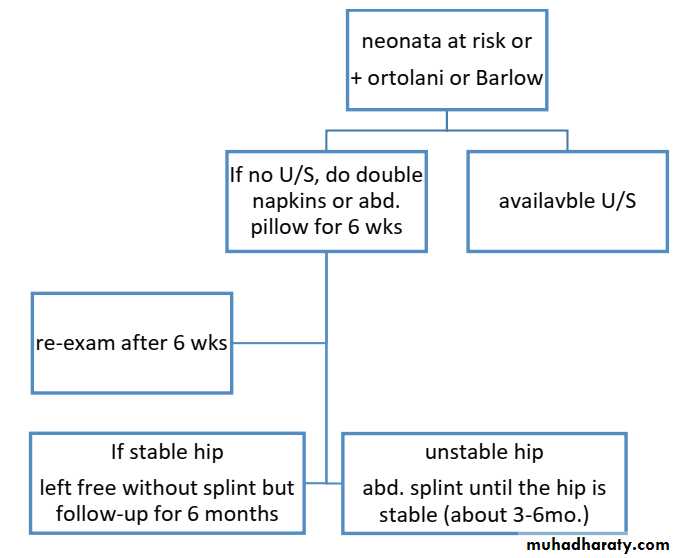
Aetiology1. Exact cause is unknown.2. Genetic factora. It run in families b. It run in population3. Hormonal factor.4. Intra uterin factorsa. Malpositionb. Large babyc. Oligohydramnios5. Post-natal factors.Child at risk1. Female2. Breech presentation.3. Postive family history.4. Other cong anomilies.5. First baby.They need extra care and they need frequent re-examination.
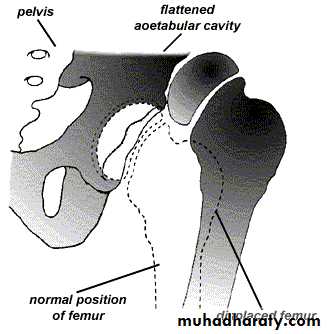
Pathology1. At birth: The hip normal in shape but the capsule is stretched andredundant.2. Infancy The head dislocated sup-lat. Acetab. is shallow and antev Delay app of epiph of head The head is anteverted3. At wt bearing intensification of all changes above increase antever of head and acetab false acetab hour-giass app.
Clinical featuresEvery new born should examine for sign of instability
Neonate
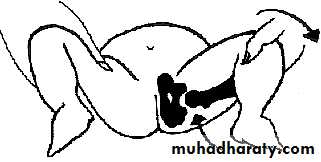
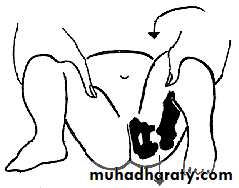
Ortolanis testBarlows testInfancy
Symp
- difficult to apply napkins- asymmetrical skin creases- click during hip movement- short limb- delay walking
Signs
If unilat- asymmetry- Short leg- Missing of head in groinIf bilateral- wide perineal gab- Little abduction
walking age
SignsIf unilat: limpingIf bilate: wadling gaite
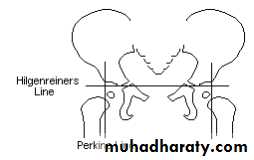
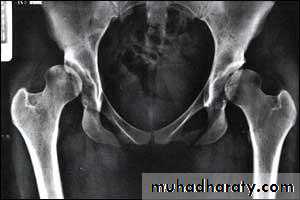
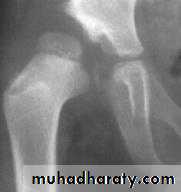
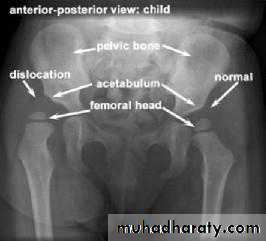
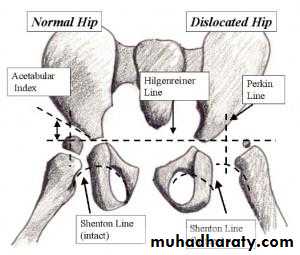
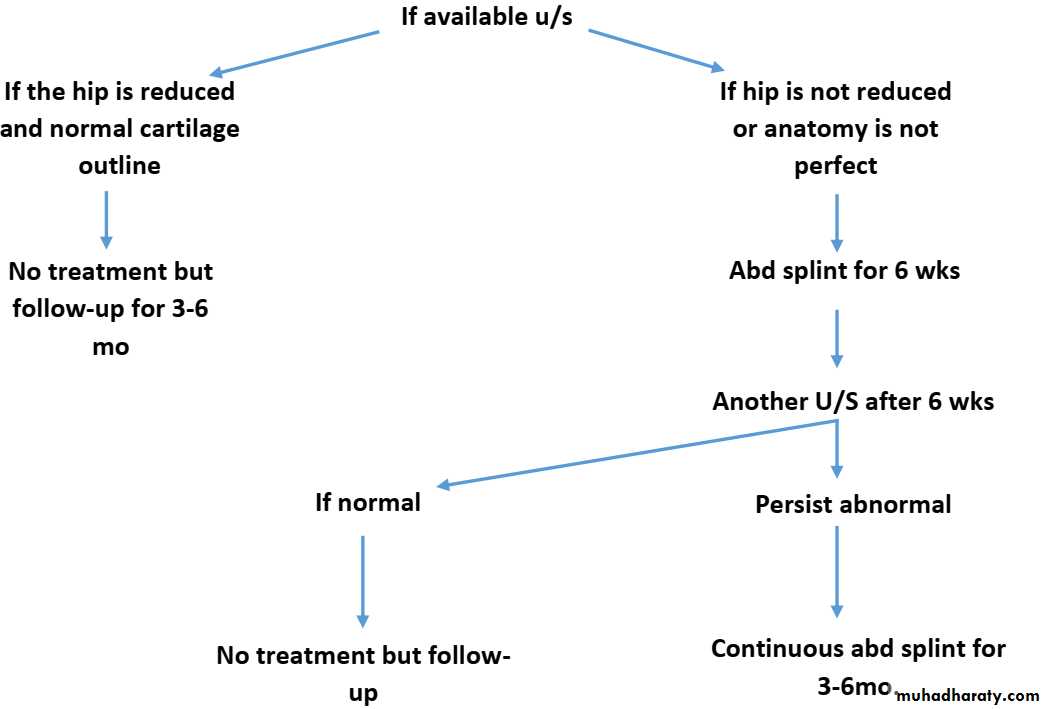
Imaging1. U/S in the neonatal period. Should done for every child at risk and every hip with sign of instability2. X-ray signs In neonate → Von rosens line In infancy → Shentons line Perkins line Acetabular roof angle Smal epiphysis In child hood → false acetabulum3. Arthrography
4. C.T SCA
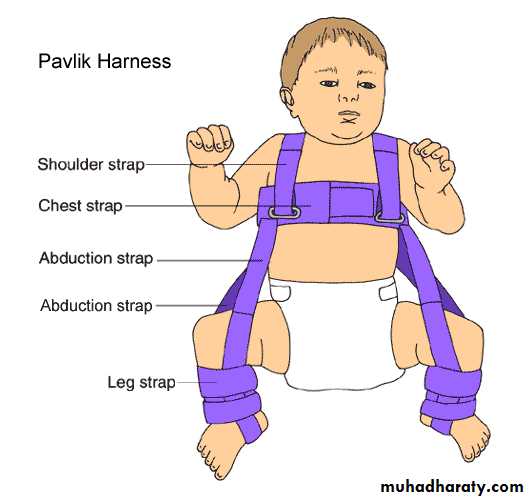
Treatmentfirst 6 months
SplintageObjective: to hold hip flexed andabductedTypes: Pavlik harness Vonrosen splint Cast splintGolden rules: Proper reduction Avoid extreme postion Allow slight mov
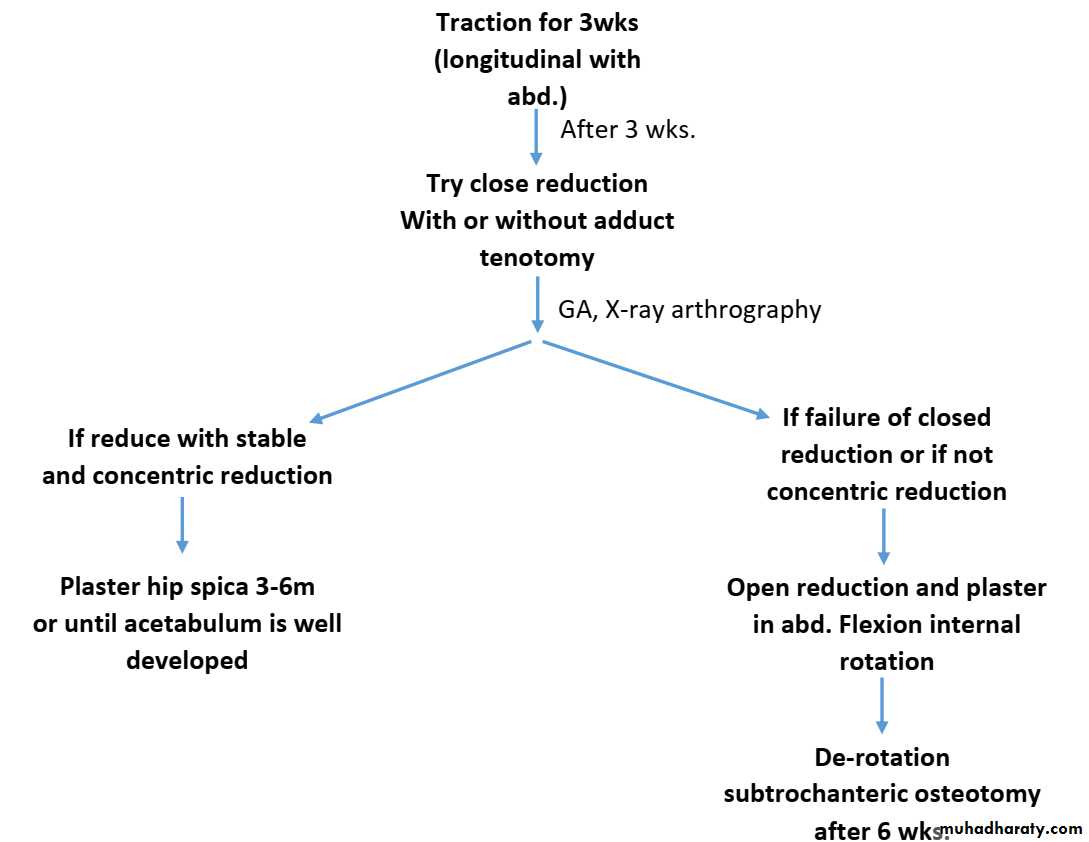
6 – 18 months (missed dislocation)
Pt 18m – 4y
Obstacles for close reduction1. Redundent capsule2. Psoas tendon (hour –glass deformity)3. Hypertrophic lig. Teres.4. Inverted limbus.
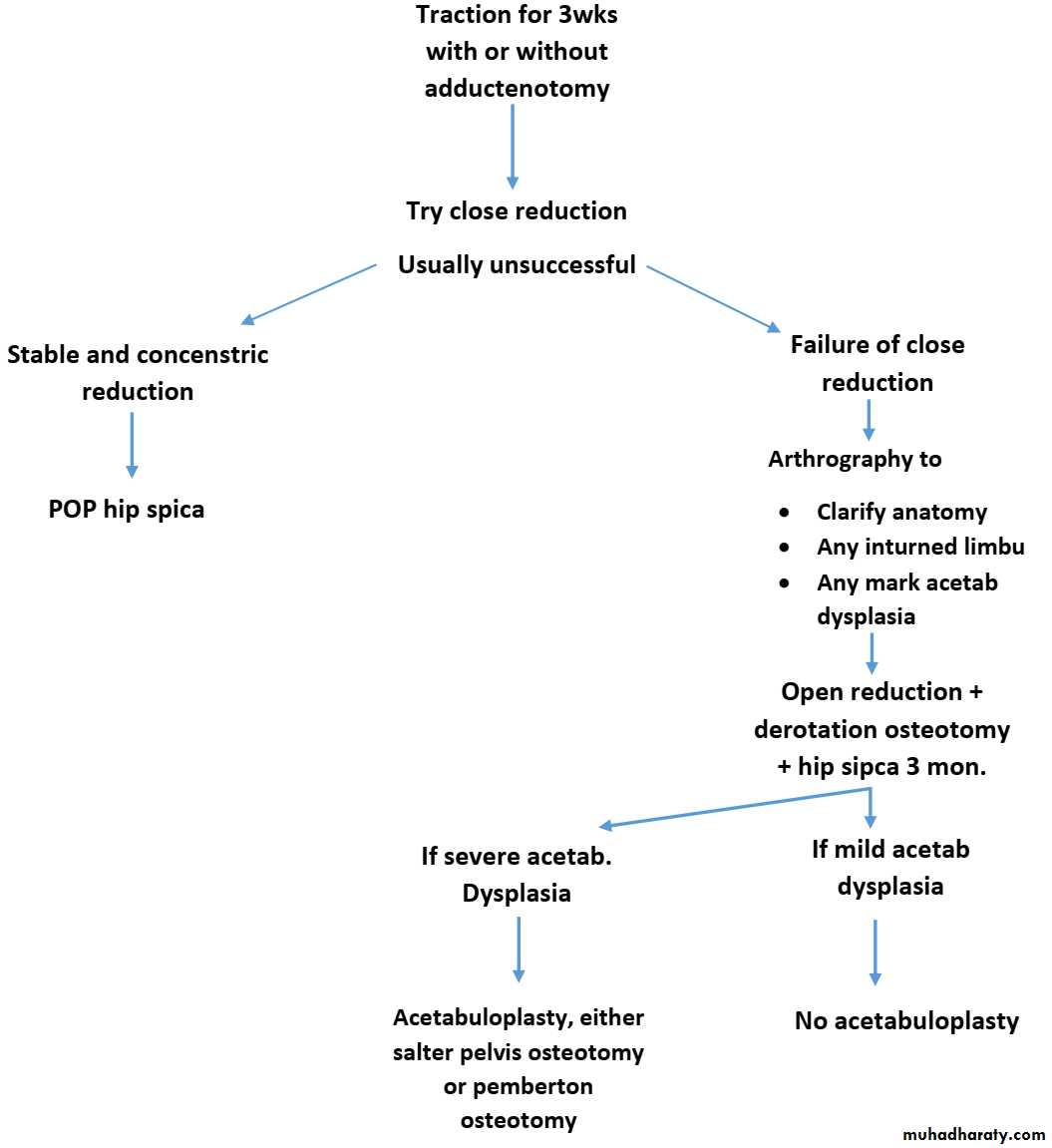
Pt > 4y
If pt 4-8 y + unilat: OR + derotation osteotomy + acetabuloplasty If pt 4-8 y + bilat: no treatment at this time If pt > 8y: no treatment