
Giardiasis
Dr. Mohamed Ghalib
Internal medicine
TUCOM
5
th
year

•
Giardiasis is a common cause of nonbloody diarrhea in
returning travelers.
•
G. lamblia and Giardia intestinalis are found worldwide,
including in the United States. However, giardiasis is most
commonly diagnosed in travelers returning from Latin
America, Southeast Asia, or the Middle East. Transmission
is by the fecal-oral route in the setting of contaminated
food or water or public swimming areas, or by person-to-
person contact in certain risk populations such as men
who have sex with men.
•
It is usually a self-limited diarrheal illness that lasts 2 to 4
weeks but may persist longer. Rarely, individuals have
associated fevers, nausea, or vomiting. The diagnosis is
made by microscopic examination of stool for cysts or
trophozoites or by an antigen detection test.

•
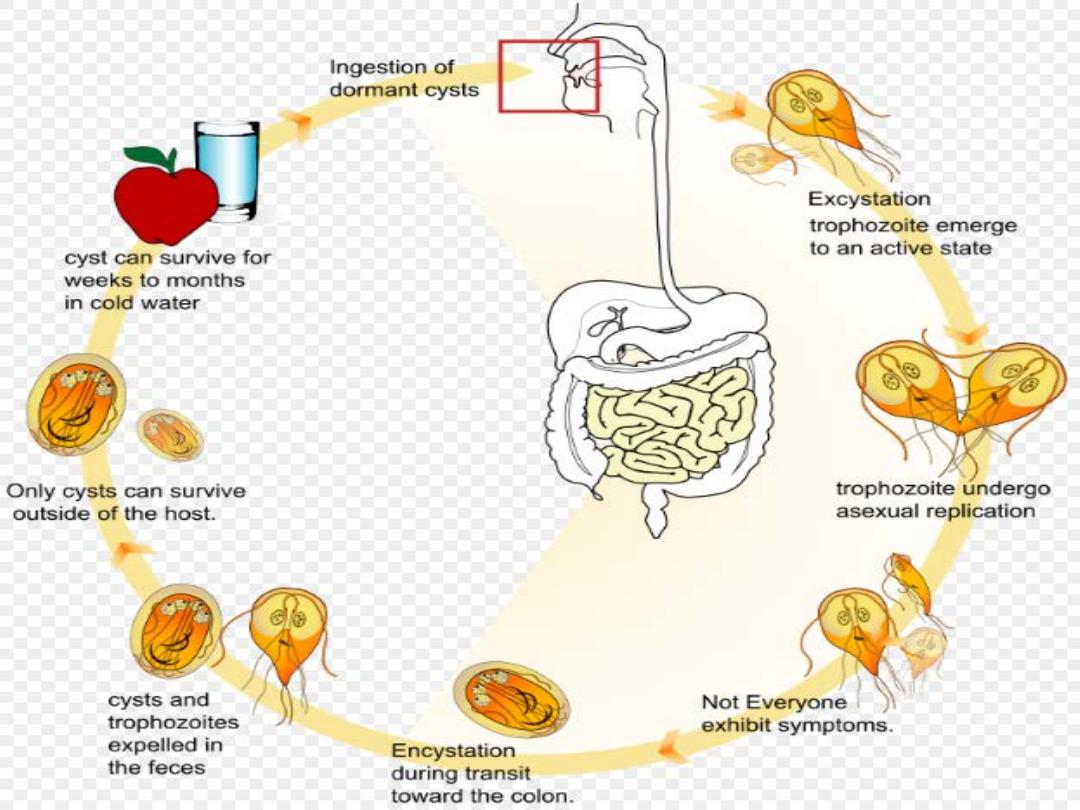
Infection with Giardia lamblia is found
worldwide and is common in the tropics. It
particularly affects children, tourists and
immunosuppressed individuals, and is the
parasite most commonly imported into the UK.
In cystic form, it remains viable in water for up
to 3 months and infection usually occurs by
ingesting contaminated water. Its flagellar
trophozoite form attaches to the duodenal and
jejunal mucosa, causing inflammation.

Clinical features and investigations
•
After an incubation period of 1–3 weeks, there is diarrhoea,
abdominal pain, weakness, anorexia, nausea and vomiting.
•
Chronic diarrhoea and malabsorption may occur, with bulky stools
that float.
•
On examination, there may be abdominal distension and
tenderness.
•
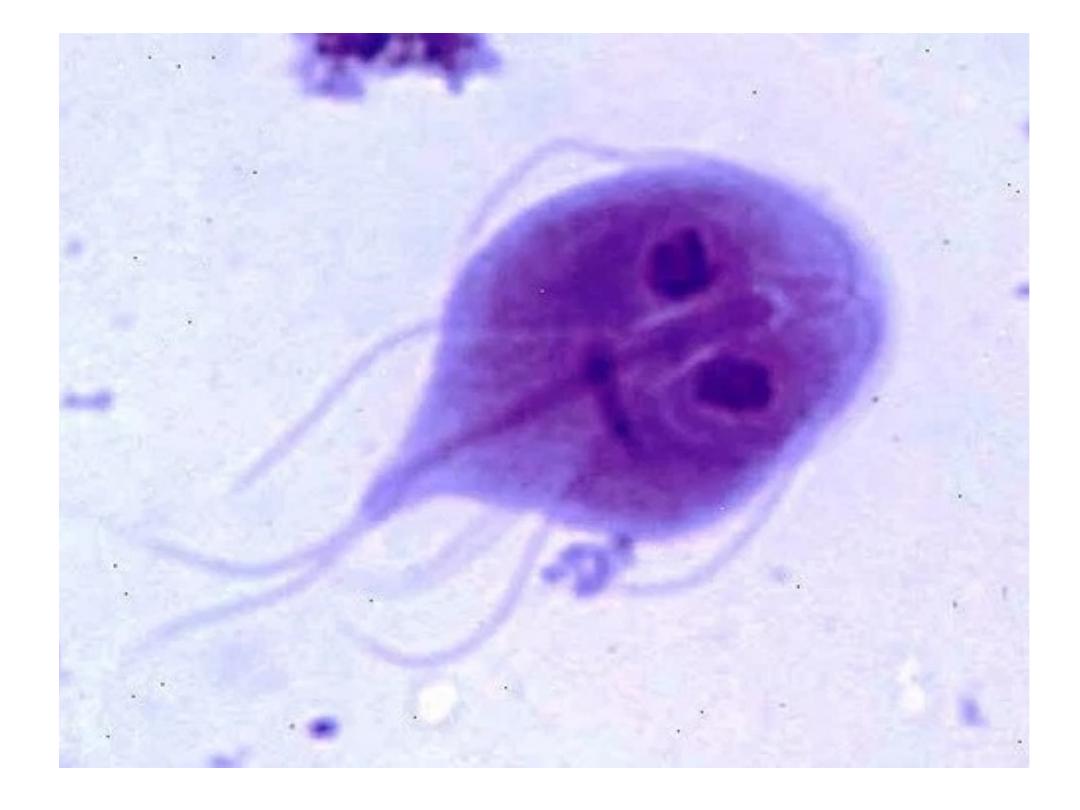
Stools obtained at 2–3-day intervals should be examined for cysts.
•
Duodenal or jejunal aspiration by endoscopy gives a higher
diagnostic yield.
•
The ‘string test’ may be used, in which one end of a piece of string
is passed into the duodenum by swallowing and retrieved after an
overnight fast; expressed fluid is then examined for the presence
of G. lamblia trophozoites.
•
A number of stool antigen detection tests are available.
•
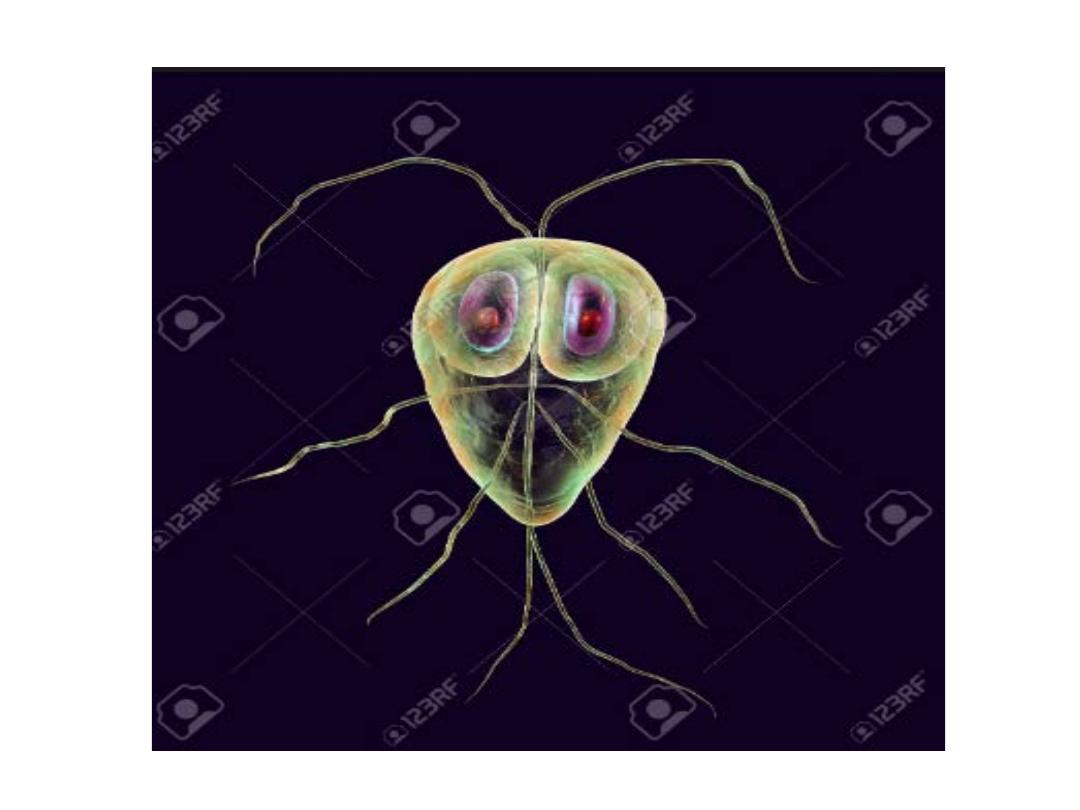
Jejunal biopsy specimens may show G. lamblia on the epithelial
surface.

Management
•
Treatment is with a single dose of tinidazole 2 g,
metronidazole 400 mg 3 times daily for 10 days,
or nitazoxanide 500 mg orally twice daily for 3
days.

•
THANKS
