Radiology
Technical consideration

Film Radiography
Image Generation
X-rays are a form of radiant energy that is similar in many
ways to visible light. X-rays differ from visible light in
that they have a very short wavelength and are able to
penetrate many substances that are opaque to light.

Regular x-rays (plain x-rays) account for about
80% of imaging examinations. X-ray
examinations, or plain x-rays, are made by an x-
ray beam passing through the patient. The x-rays
are absorbed in different amounts by the
various tissues or materials in the body. Most of
the beam is absorbed or scattered.

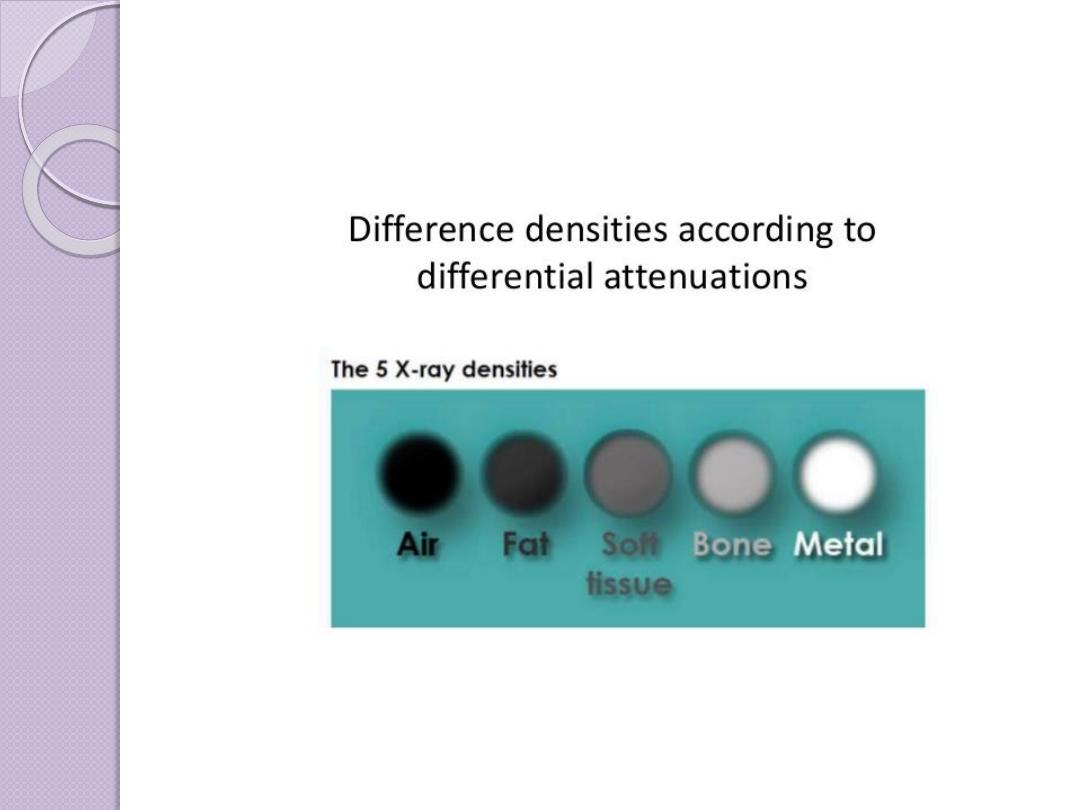
Basic radiographic densities
Principles of Interpretation
Conventional radiographs demonstrate
five basic
radiographic densities: air, fat, soft tissue,water, bone, and
metal
(or x-ray contrast agents). Air attenuates very
little of the x-ray beam, allowing nearly the full force of
the beam to blacken the image. Bone, metal, and
radiographic contrast agents attenuate a large
proportion of the x-ray beam, allowing very little
radiation through to blacken the image. Thus, bone,
metallic objects, and structures opacified by x-ray
contrast agents appear white on radiographs. Fat and
soft tissues attenuate intermediate amounts of the x-ray
beam, resulting in proportional degrees of image
blackening (shades of gray)
.
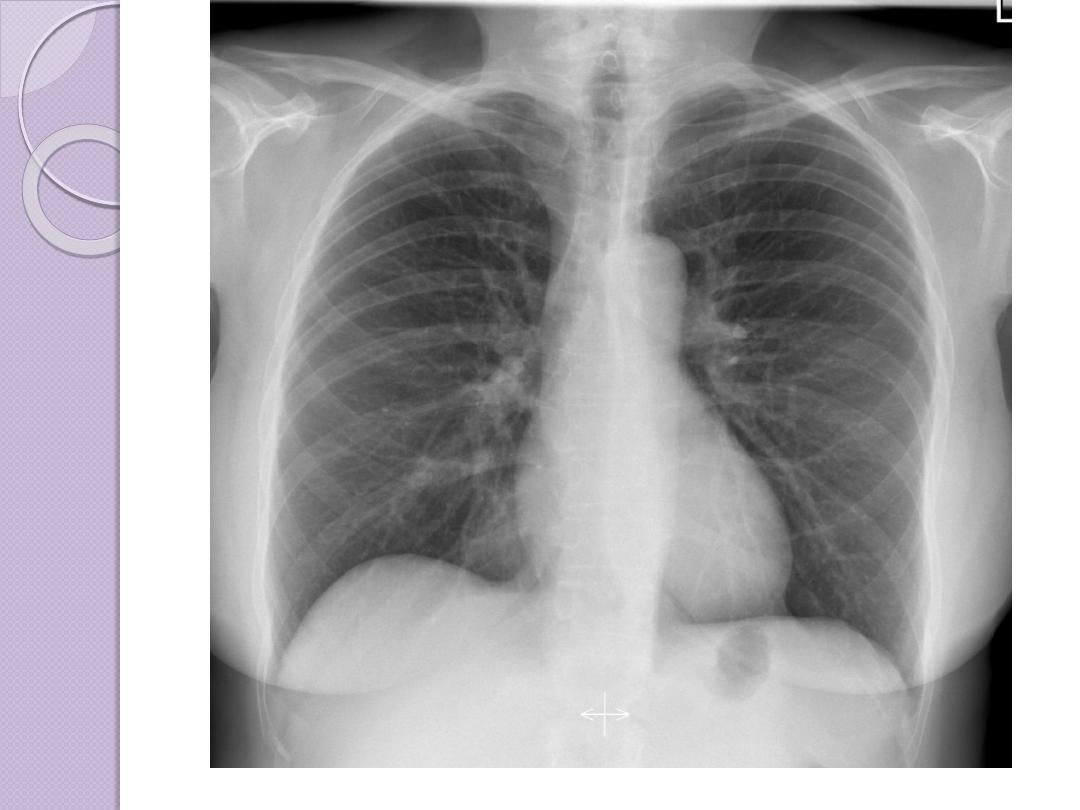

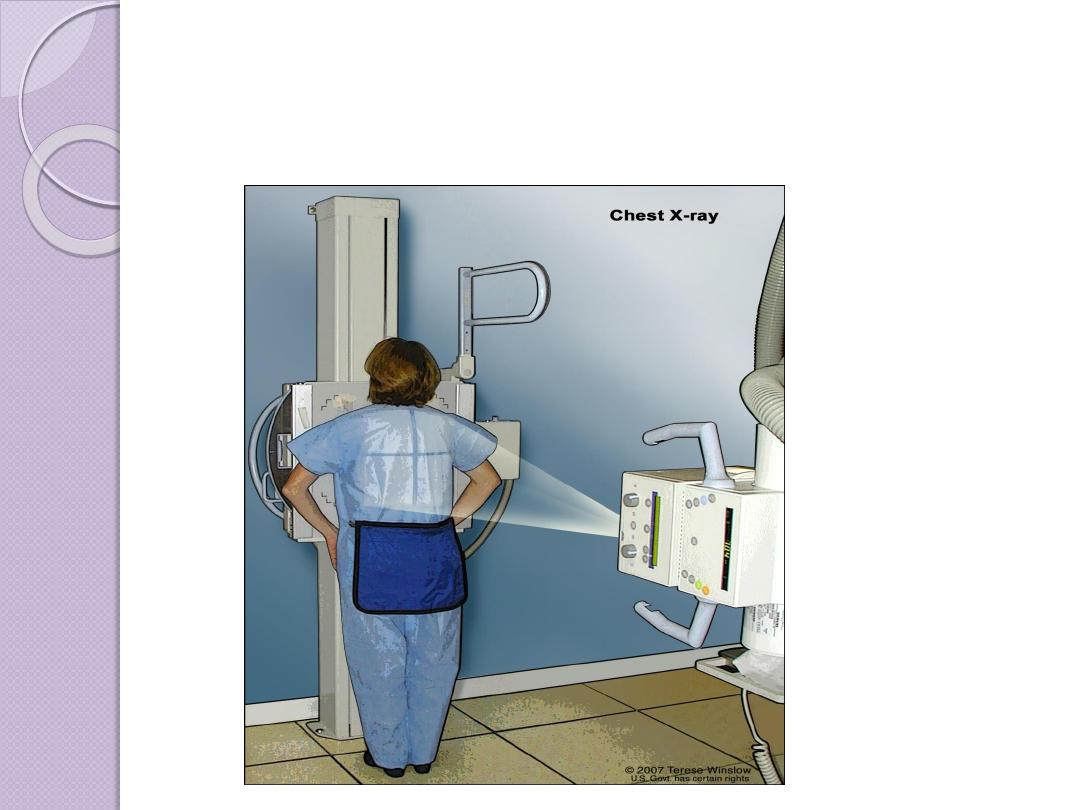
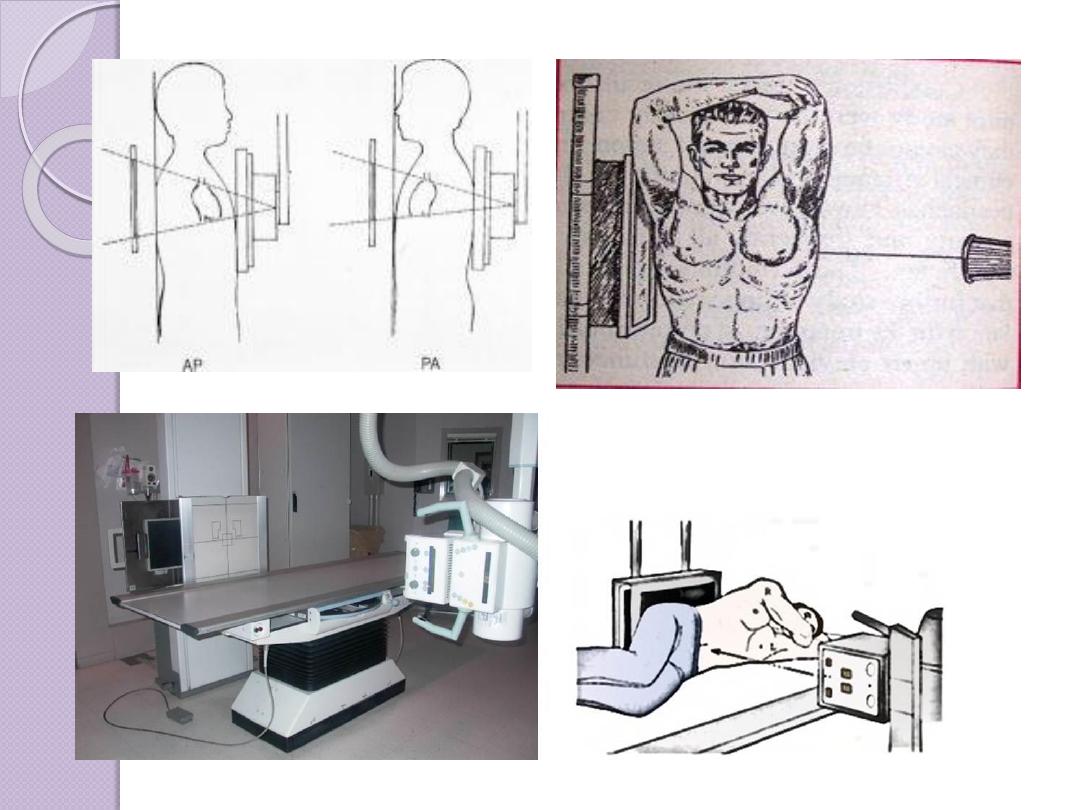
Radiographic Views
Chest and abdominal films are referred to as upright or
supine, depending on the position of the patient. In
addition, chest x-rays are usually described as
posteroanterior (PA) or anteroposterior (AP) or
lateral
These terms indicate the direction in which the x-ray
beam traversed the patient on its way to the detector.
PA means that the x-ray beam entered the posterior
aspect of the patient and exited anteriorly. AP means
that the beam direction through the patient was
anterior to posterior. A left lateral decubitus view is
one taken with the patient’s left side down.

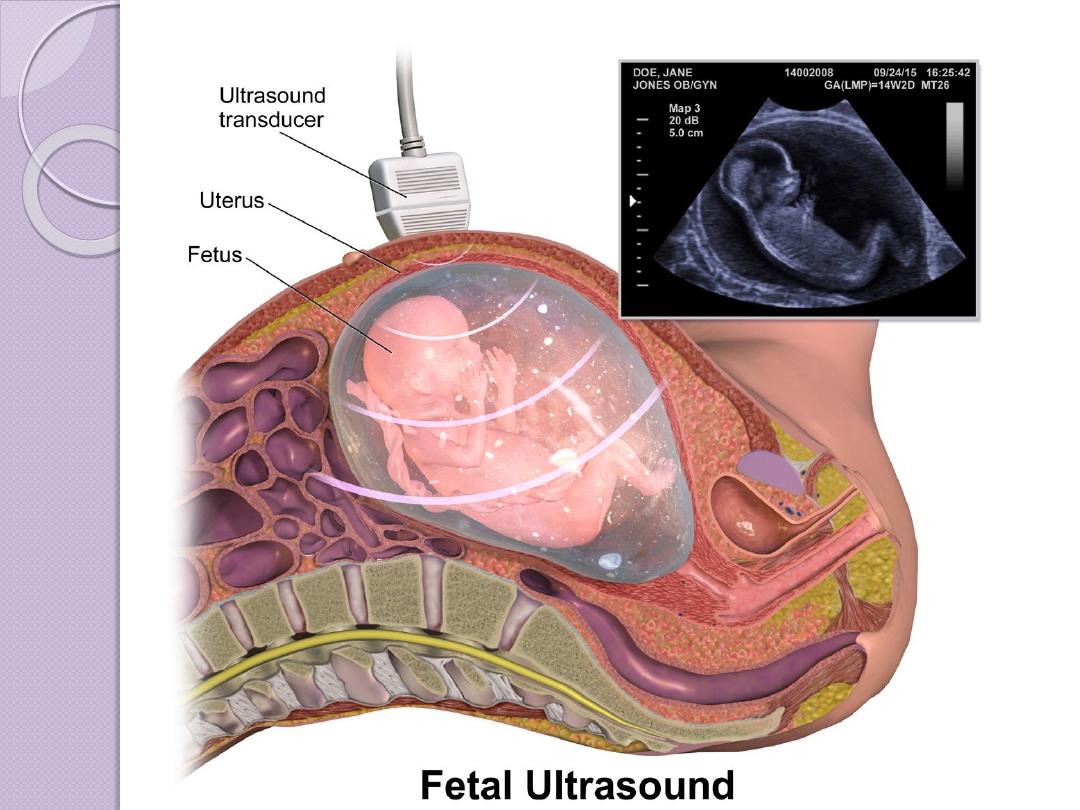
Ultrasound
Ultrasonography is made up of longitudinal waves of
frequency greater than 20,000 Hz
Pulsed ultrasonographic imaging sends an ultrasonic pulse
into the body and measures the time of echo return, which is
related to the distance to the reflecting surface.
Transducer is the main sonographic machine part which
made from a material which can change the electrical waves
to longitudinal sonographic waves (the range which is used
from 3 mega HZ which is used in general abdominal US to
10-12 MHZ) in superficial organs like ophthalmic
examination )
The reflection of the tissue interfaces are received again by
transducer and according to the amount of echoes received
the tissue brightness will be different from tissue to a tissue

Advantages of US
No ionizing radiation
SAFE (USED FOR FETAL
EXAMINATION )
Real time examination (biopsy )
Available, cheep, accessible .
Good soft tissue contrast in comparism
to x ray
Doppler examination for assessments of
vessels and blood flow without contrast

Disadvantages
Examiner dependant
Low spatial resolution
Gas shadow my obscure lesions
Not useful in boney lesions


4 d ultrasound


Computed Tomography
CT uses a computer to reconstruct mathematically a cross-
sectional image of the body from measurements of x-ray
transmission through thin slices of patient tissue. CT displays
each imaged slice separately, without the superimposition of
blurred structures that is seen with conventional
tomography. The x-ray beam is attenuated by absorption and
scatter as it passes through the patient. Sensitive detectors
on the opposite side of the patient measure x-ray
transmission through the slice. These measurements are
systematically repeated many times from different directi
ons

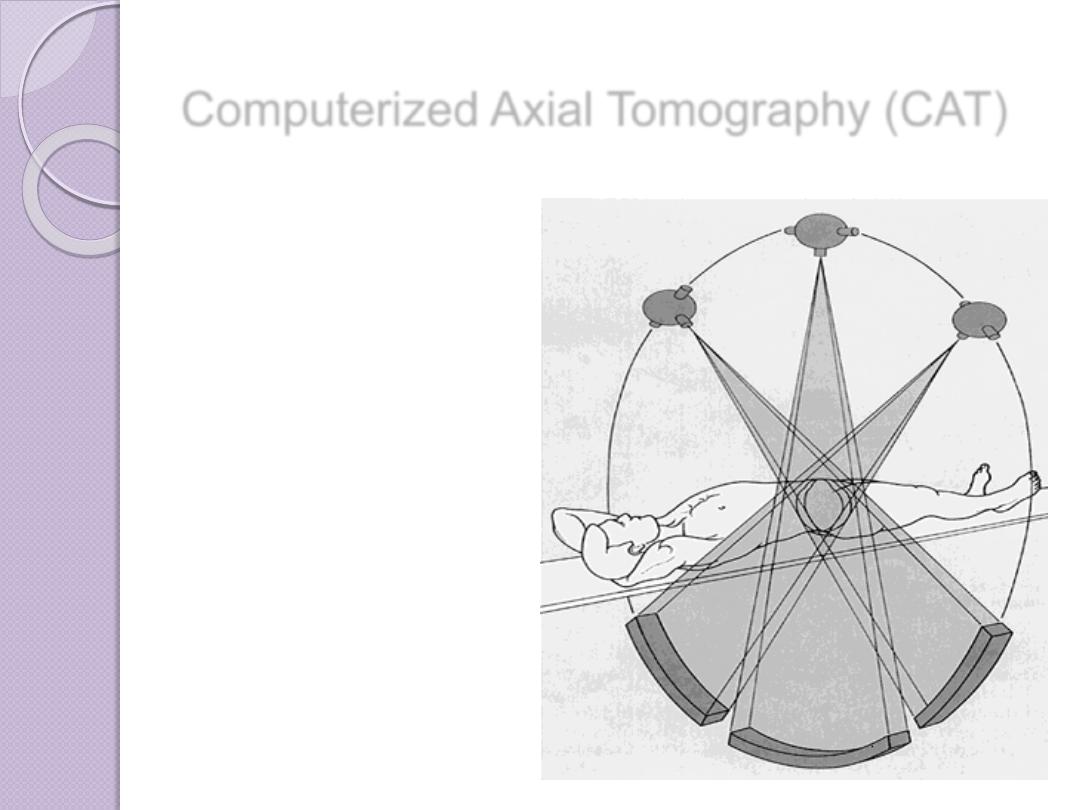
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT)
In this process a small beam of x-
ray is passed through a plane of the
body while the x-ray tube moves in
an arc or a circle around the body
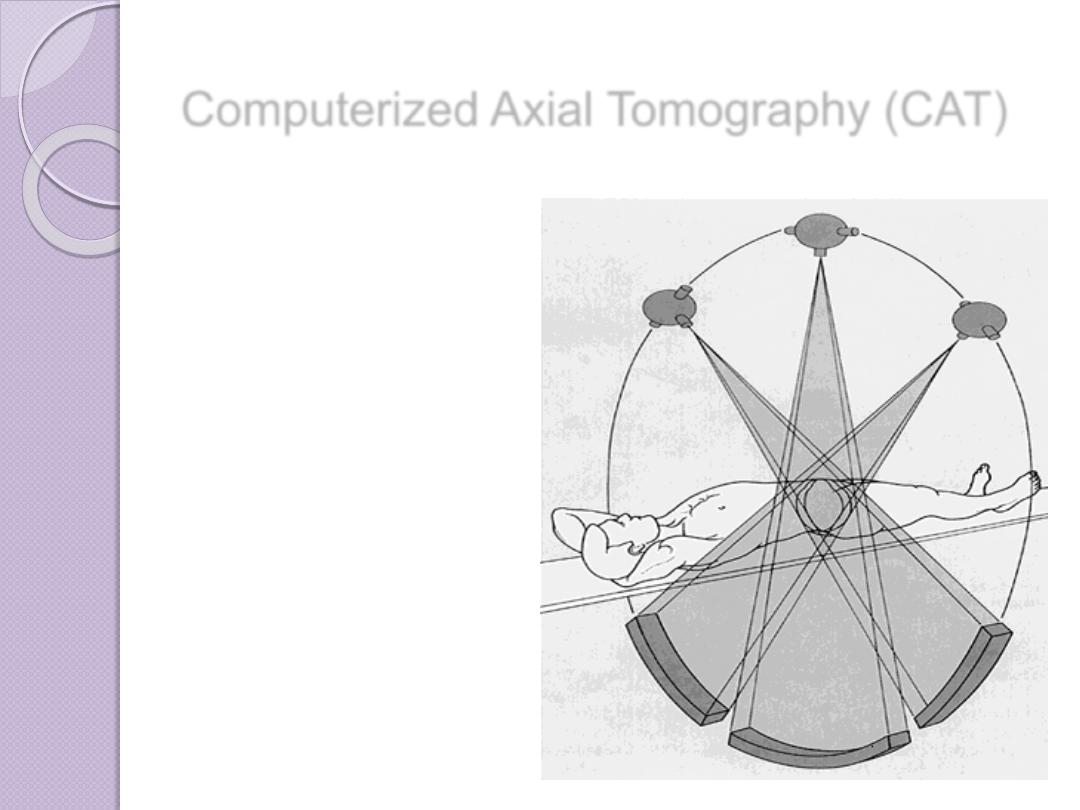
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT)
The amount of radiation absorbed
by different elements of the chosen
plane varies according to X ray
absorptions by different tissues
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT)
A computer stores a
large amount of data
from a selected region
of the body, making it
possible to determine
the spatial relationship
of the radiation-
absorbing structures
within it

HU
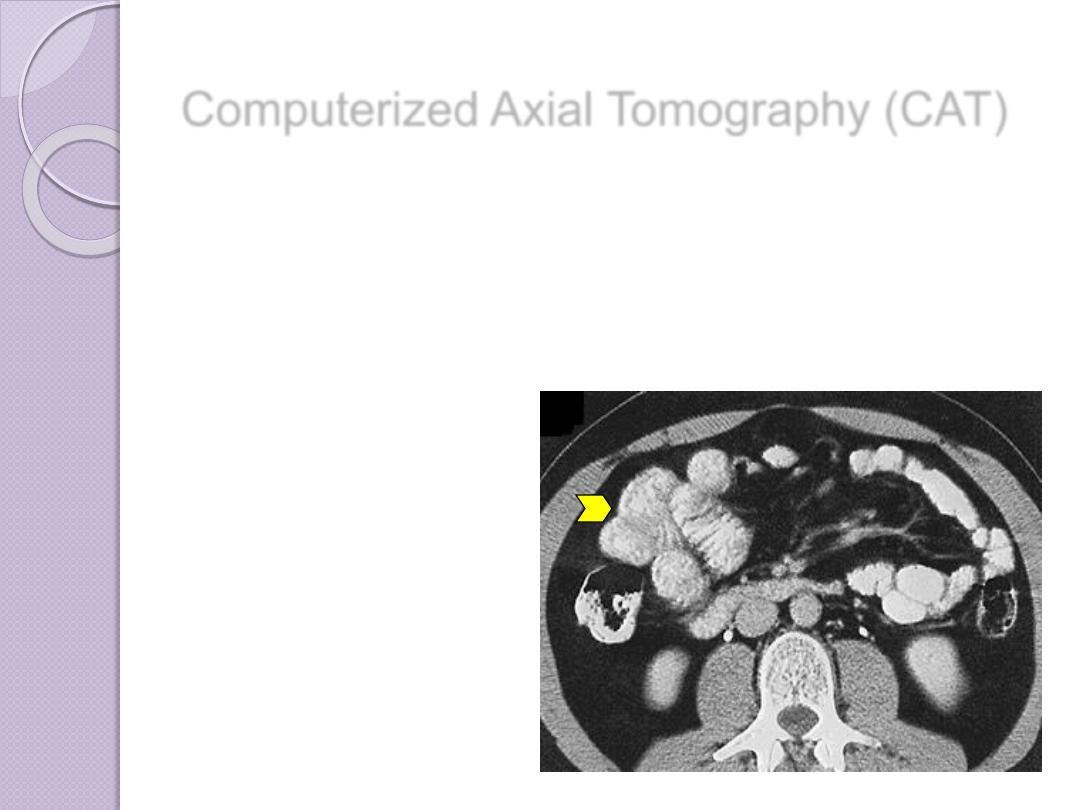
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT)
Important diagnostic
information about tissues
in the scanned regions of
interest is thereby made
Contrast enhancement
may be used
Contrast enhancement of
the bowel after oral
administration of barium

ADVANCES OF CT
Faster CT machines, due to multidetector
capabilities, have made imaging of
the
and
very
practical in a number of clinical
settings.The faster capability has allowed
the imaging of the heart with minimal
involuntary motion, which creates
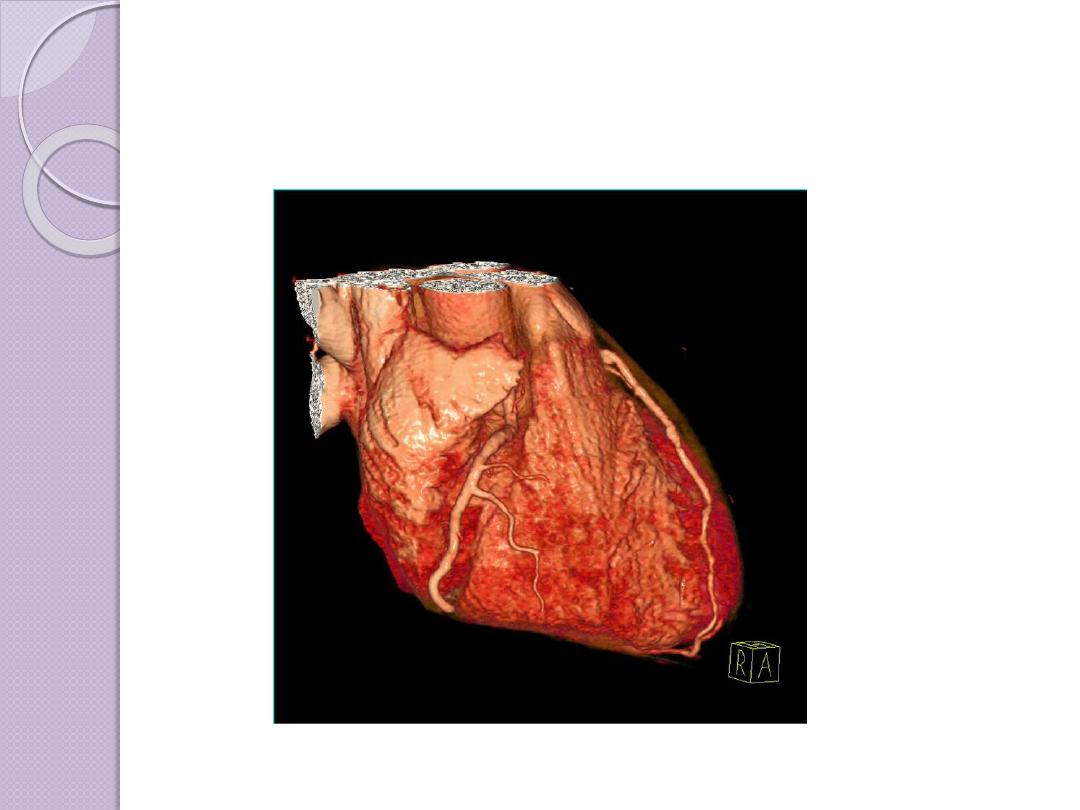
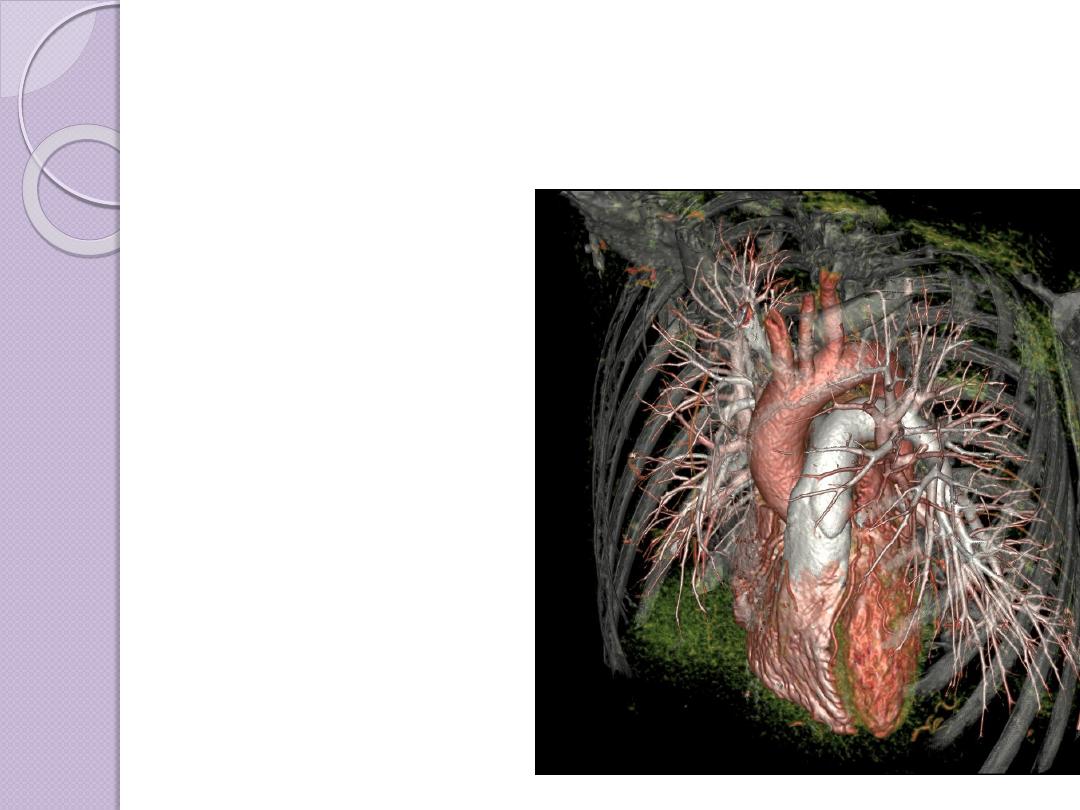
3D
RECONSTRUCTION
Multiplanar
reconstruction the
simplest method of
reconstruction. A
volume is built by
stacking the axial slices

Advantages of CT scan
CT is very good for imaging bony
structures and calcifications.
Good soft tissue and spatial resolution .
Short examination time ( suitable for
pediatric and some emergencies )
Suitable for Coronary and cardiac
examination ( advance multi
detector CT scan )

Disadvantages
Radiation single CT scan may give
radiation equivalent to more than 400
chest X ray
Contrast : CT scan may need injection of
contrast material which may cause some
adverse reactions or allergy in some
patients or it may be contraindicated in
some patients
CT scan have poor soft tissue contrast in
comparison to MRI
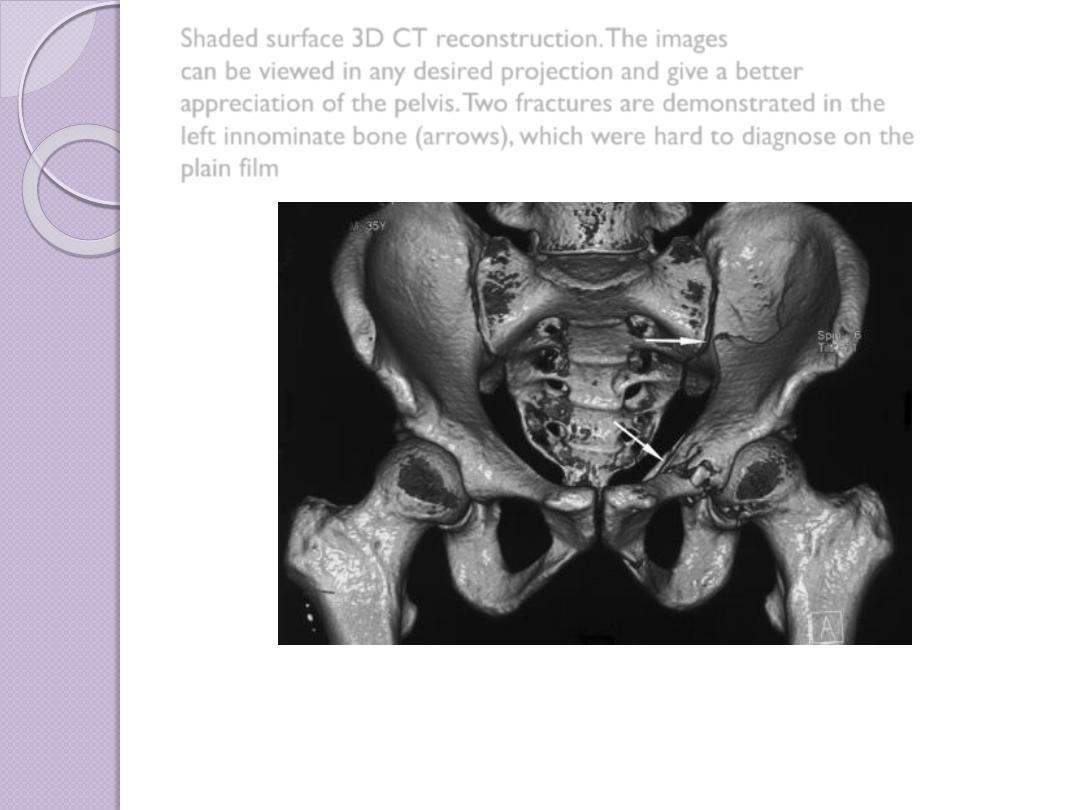
Shaded surface 3D CT reconstruction. The images
can be viewed in any desired projection and give a better
appreciation of the pelvis. Two fractures are demonstrated in the
left innominate bone (arrows), which were hard to diagnose on the
plain film
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Uses non-ionizing
radiation and has no
demonstrated adverse
biological effects
.
Magnetic resonance
images can be obtained in
any tissue plane
transverse
sagitttal
coronal
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
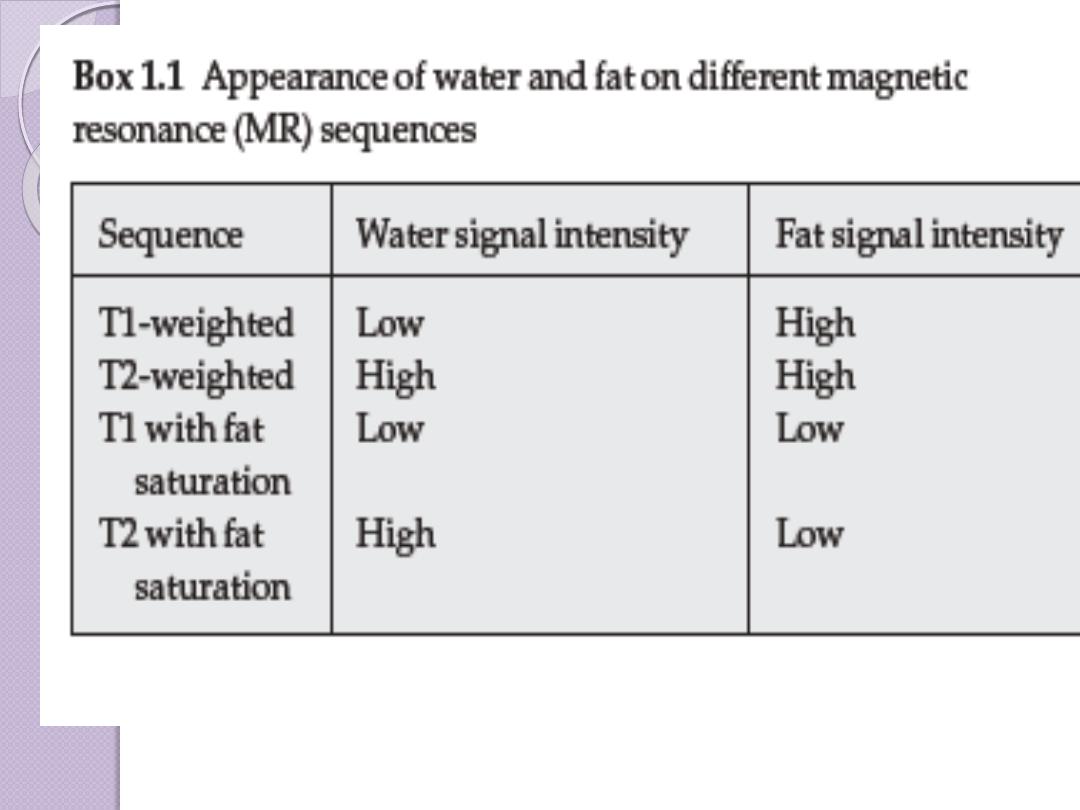
The appearance of
an MR image is a
function of the
chemical
composition of the
various types of
tissue
bone
fat
muscle

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
At the atomic level, water and adipose are
composed of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and
phosphorus atoms. The
hydrogen atom
contains a proton and an orbiting electron.
A spinning charged particle (the proton) produces a local
magnetic field

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
In the absence of any external forces,
the magnetic moments of protons in
tissue are oriented randomly
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
If the protons are placed in a strong
magnetic field, their magnetic dipoles
align
with
and
against
the strong
magnet

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) combines a strong
magnetic field
and
radiofrequency
(RF) energy to study the distribution and behaviour of hydrogen protons
in fat and water
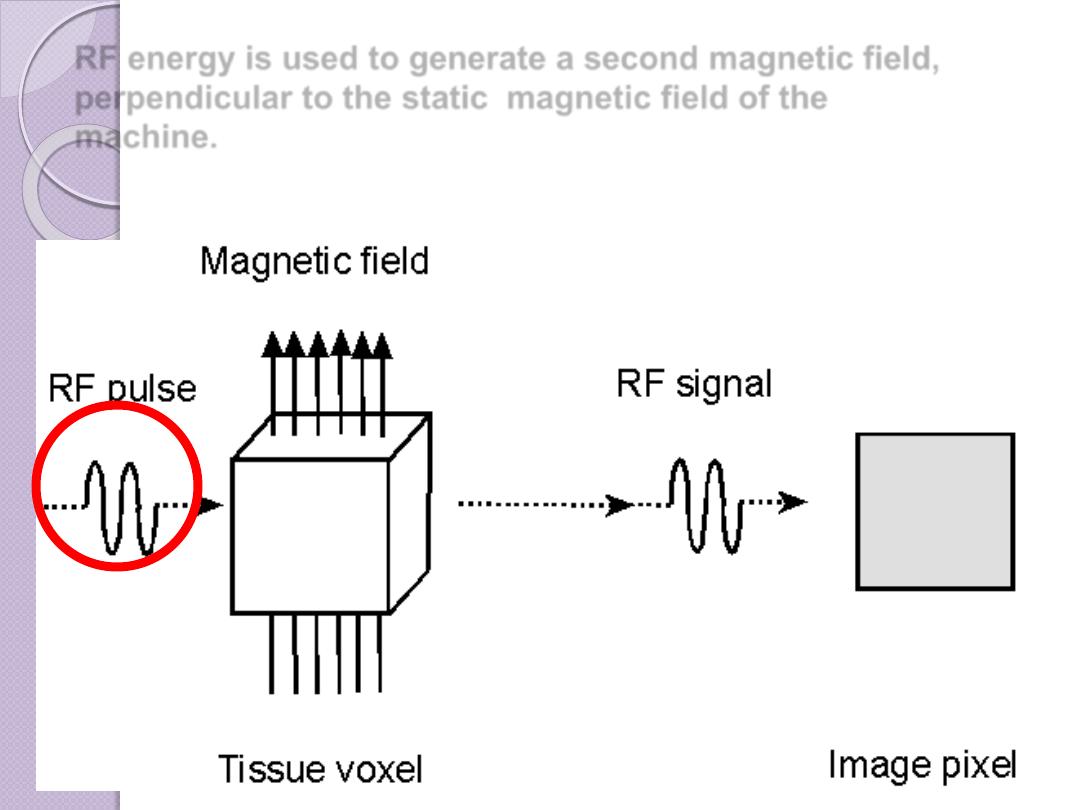
RF energy is used to generate a second magnetic field,
perpendicular to the static magnetic field of the
machine.
The result of this second
magnetic field is to rotate or
flip the protons away from the
static magnetic
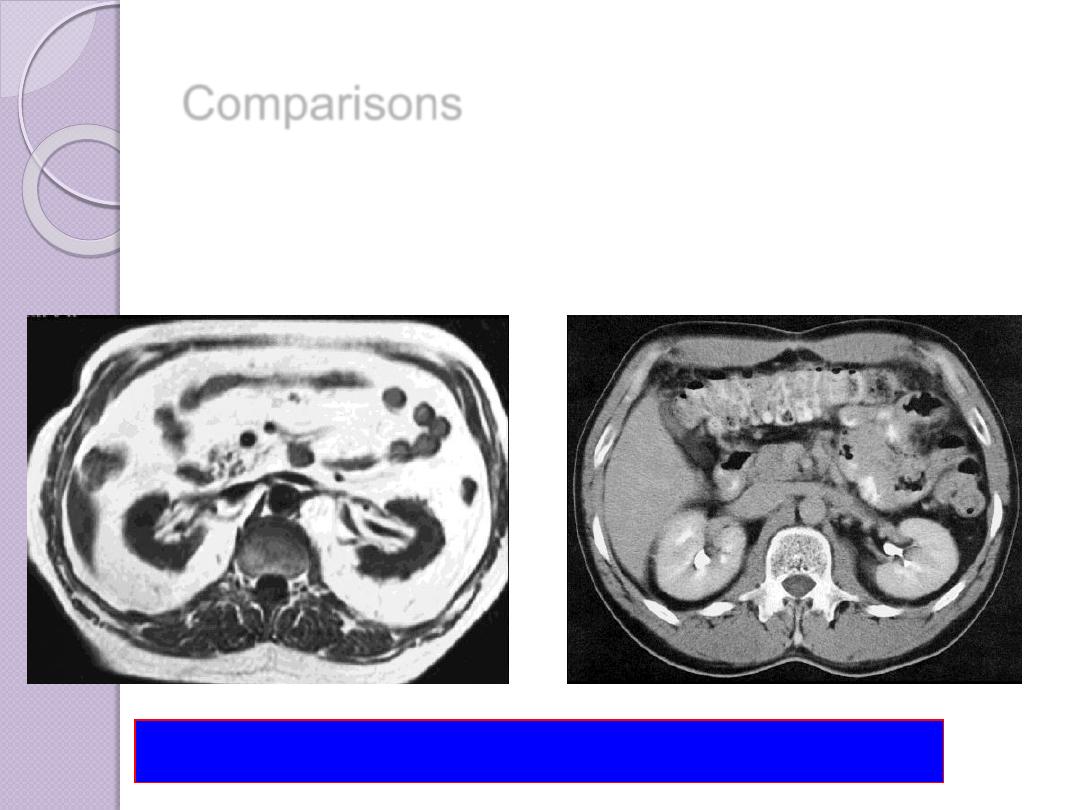
Comparisons
MRI image
CT image
abdomen
Compare bone and soft tissue density

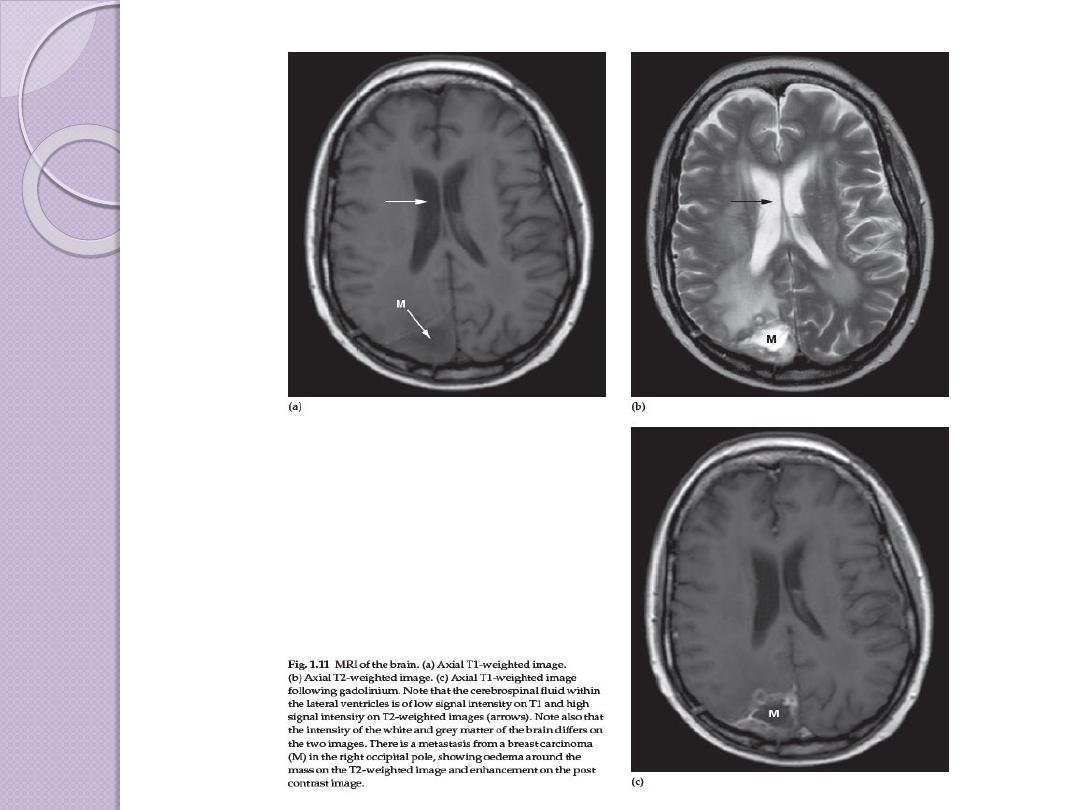
Brain Tumor Imaging
What’s changed between these images?
T
1
-weighted Sagittal
T
1
-weighted Axial
T
2
-weighted Axial

Advantage of MRI
Non ionizing radiation
Multiplanar images (cross section , saggital
and coronal views )
The ability of imaging vessels without
contrast (MR angiography )
Have a good soft tissue contrast

Contraindication of MRI
Patient with pacemaker
Patient with bullet injury or ferromagnetic
F.B ,or surgical clip (because of heat and
missile effect )
Pregnancy especially first trimester
Claustrophobia reported that between 1
% and 10 % of patients experience some
degree of claustrophobia which in the
extreme cases results in their refusal to
proceed with the scan

DISADVANTAGES OF MRI
Expensive
Long scan times
Audible noise (65-115dB)
Isolation of patient (claustrophobia,
monitoring of ill patients)
Exclusion of patients with pacemakers
and certain implants

•Monitoring equipment
•Infusion pumps
•Credit cards
•Cellular telephones
•Any electronic device
THE CHANGING MAGNETIC FIELDS
CAN DO DAMAGE TO
:

•Gold
•Silver
•Digital watches
•Eyeglass frames
•Snaps/zippers fastened to clothing
•Dental work
•IUCD
THE FOLLOWING ARE
(USUALLY*) OKAY:

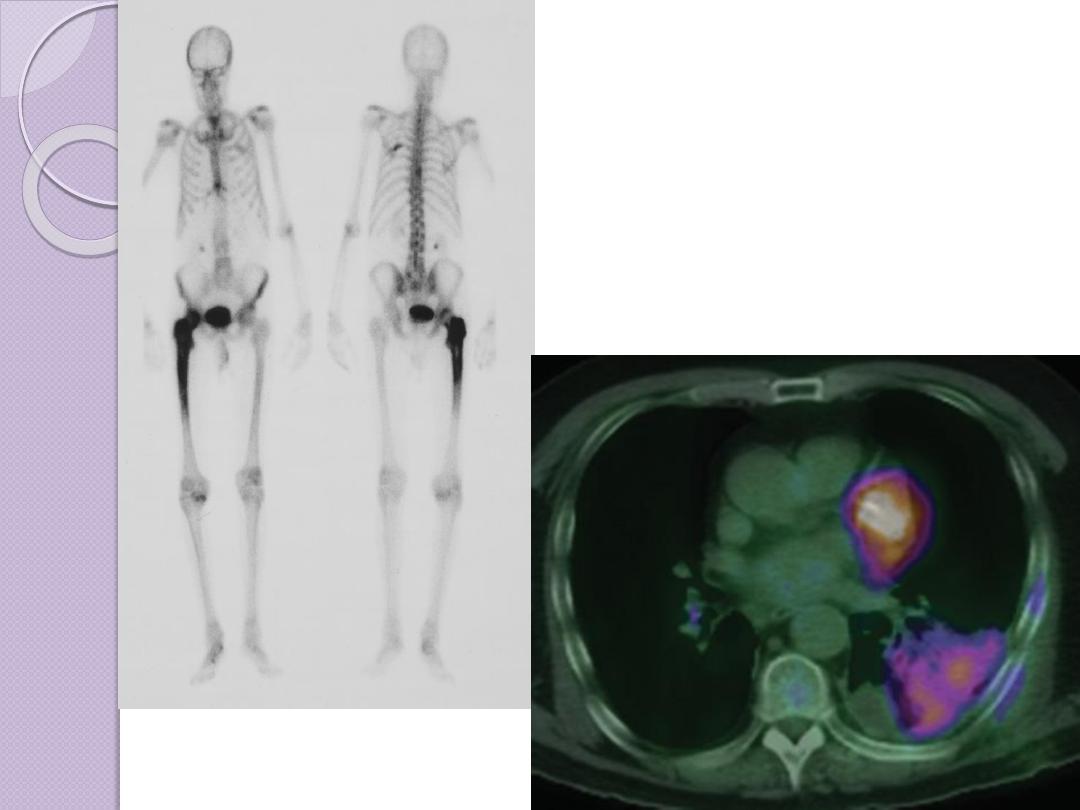
NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Nuclear medicine images are made by giving the patient
a short-lived radioactive material. The most
commonly used radionuclides decay rapidly and have
half-lives of only hours. Most materials administered
are not detectable within a day or so after
administration.
Nuclear medicine images are made by a gamma camera
or positron emission scanner that records radiation
emanating from the patient and makes an image of
the distribution of the radioactive material . The
major advantage of nuclear medicine is its ability to
obtain an image of physiologic function. For example,
virtually no other imaging technique can assess
regional pulmonary ventilation or hepatobiliary
function.

Ionizing Radiation
Although many patients benefit from radiation’s ability to destroy cancer
cells or capture real-time images of the human body, radiation can harm
healthy cells wherever it enters the body. It is well documented that
ionizing radiation can cause damage ranging from uncontrollable cell
replication to cell death
X-ray and gamma waves have the highest energy, and thus can pass
through the human body. When these waves of energy enter a cell, their
wavelengths may collide with the electrons of the cells’ atoms, possibly
resulting in damage to the cell.
When an x-ray’s wavelength of energy collides with an atom’s electron,
the electron may be bumped out of its orbit leaving the atom with an
unbalanced charge and in an unsteady state. In this state, the atom is
called a radical. Like H2O2 , This process is called ionization.

Ionization of an Atom

Radiation effect
Unstable radicals seek a reaction to stabilize
them, making them highly chemically reactive. The
radicals react with and alter the chemical bonds
within a cell, particularly interrupting bonds
within DNA molecules and those between water
molecules’ hydrogen and oxygen atoms
DNA damage
DNA molecules are susceptible to both direct
and indirect radiation damage. Direct damage
occurs when the radiation energy directly breaks
DNA bonds; indirect damage occurs when
radiation-generated radicals break DNA bonds

DNA Damage

Infants and children
As children are more radiosensitive than
adults and their longer life expectancy
gives greater opportunity for the
radiation detriment to be expressed,
special care must be taken to ensure that
any radiation doses to children are
justified by the diagnostic information to
be gained as a result of the procedure.

RADIATION PROTECTION
OF STAFF AND PUBLIC
Almost anything that will help to reduce patient doses, use non
ionizing examinations will also tend to reduce staff dose
Monitoring of radiology department and staff by dosimeter
badges is very helpful in protection of radiologist and staff .
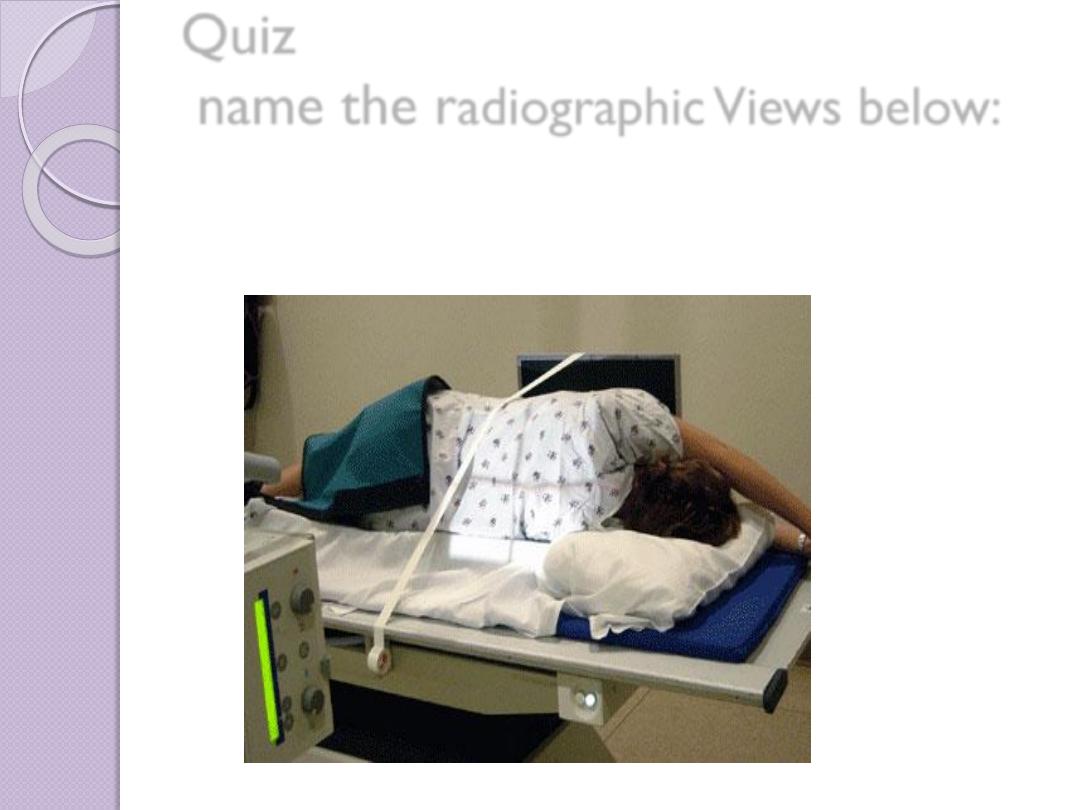
Quiz
name the r
adiographic Views below: