

holocrine secretion of sebum
Functions of sebum
lubricates and waterproofs the skin, and protects it
from drying; it is also mildly bactericidal and
fungistatic.
Free sebaceous glands may be found in the eyelid
(meibomian glands), mucous membranes (Fordyce
spots), nipple, perianal region and genitalia.

especially dihydrotestosterone, stimulate sebaceous
gland activity.
Human sebaceous glands contain 5-reductase, 3-
and 17-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, which
convert weaker androgens to dihydrotestosterone,
which in turn binds to specific receptors in
sebaceous glands, increasing sebum secretion.
The sebaceous glands react to maternal androgens
for a short time after birth

disorder of the pilosebaceous apparatus
characterized by comedones, papules, pustules, cysts
and scars.
all teenagers have some acne (acne vulgaris)
affects the sexes equally
ages of 12 and 14 years, tending to be earlier in
females.
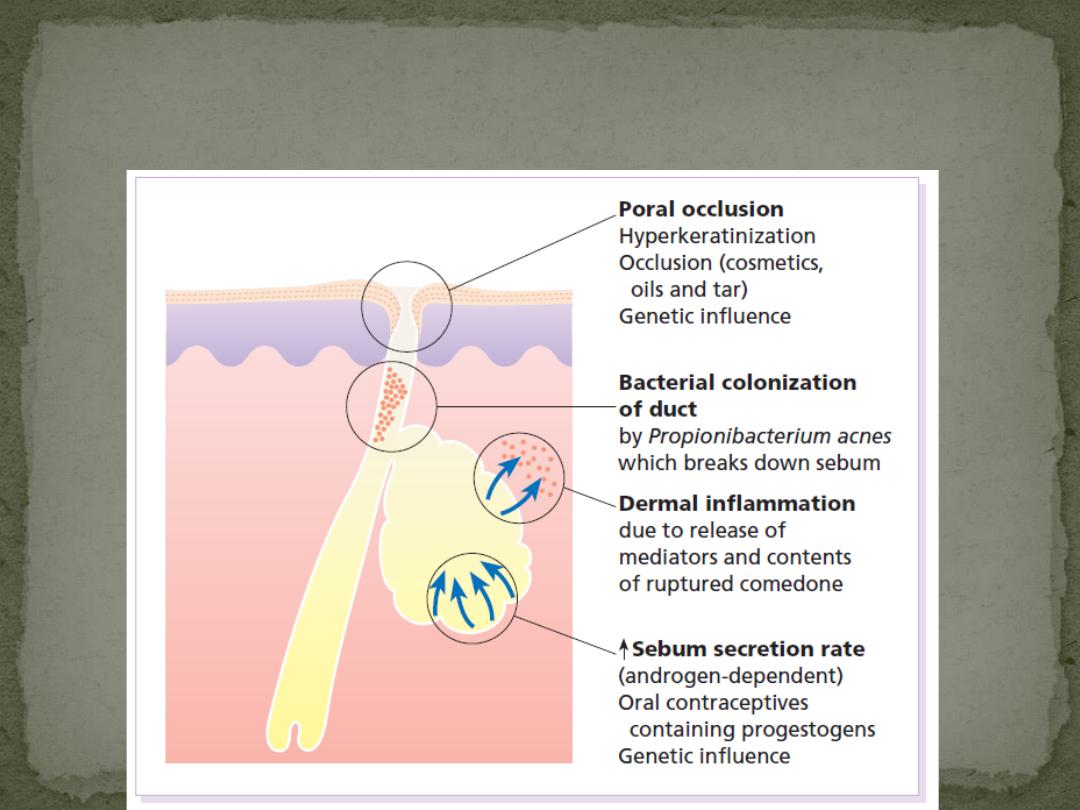
Pathological factors

Sebum
Sebum excretion is increased. However, this alone need not cause acne
Hormonal
Androgens (from the testes, ovaries, adrenals and sebaceous glands themselves) are
the main stimulants of sebum excretion,
Poral occlusion
Both genetic and environmental factors (e.g. some cosmetics) cause the epithelium to
overgrow the follicular surface.
Follicles then retain sebum that has an increased concentration of bacteria and free
fatty acids
Rupture of these follicles is associated with intense inflammation and tissue damage
Bacterial Propionibacterium acnes
normal skin commensal, plays a pathogenic part
Genetic
The condition is familial in about half of those with acne

1. Infantile acne
follow transplacental stimulation of a child’s sebaceous
glands by maternal androgens.
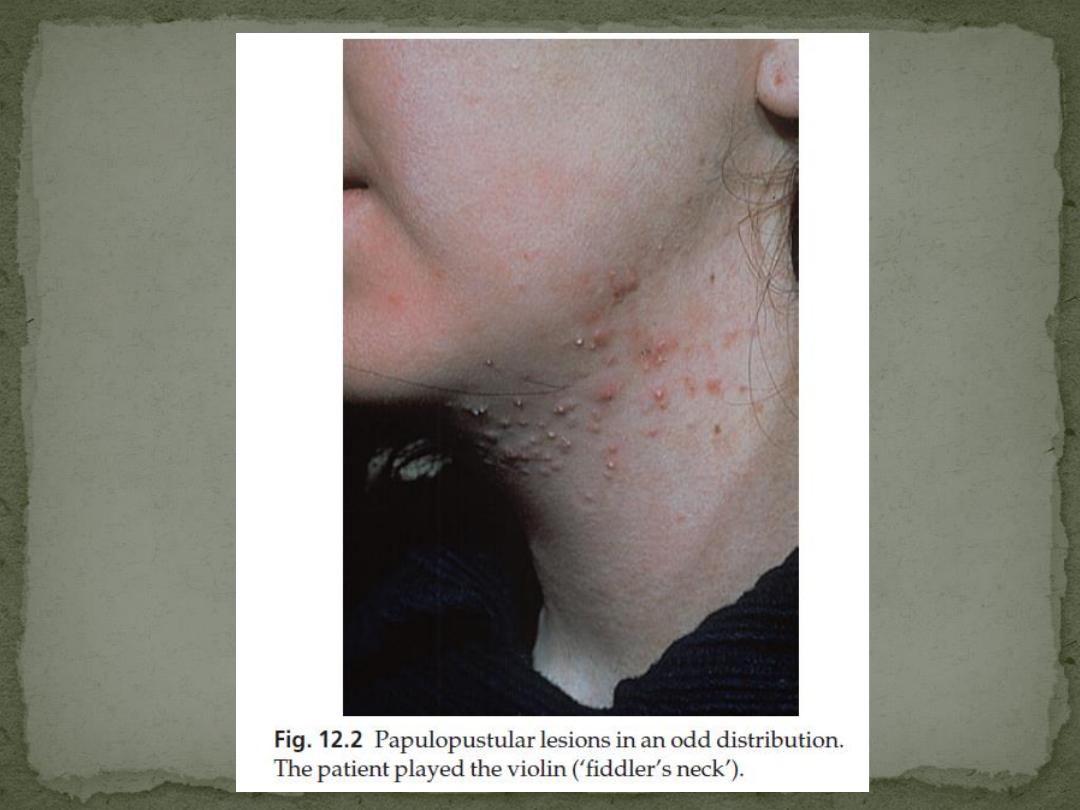
2. Mechanical
Excessive scrubbing, picking, or the rubbing of chin
straps or a fiddle

3. Acne associated with virilization
4. Acne accompanying the polycystic ovarian
Syndrome
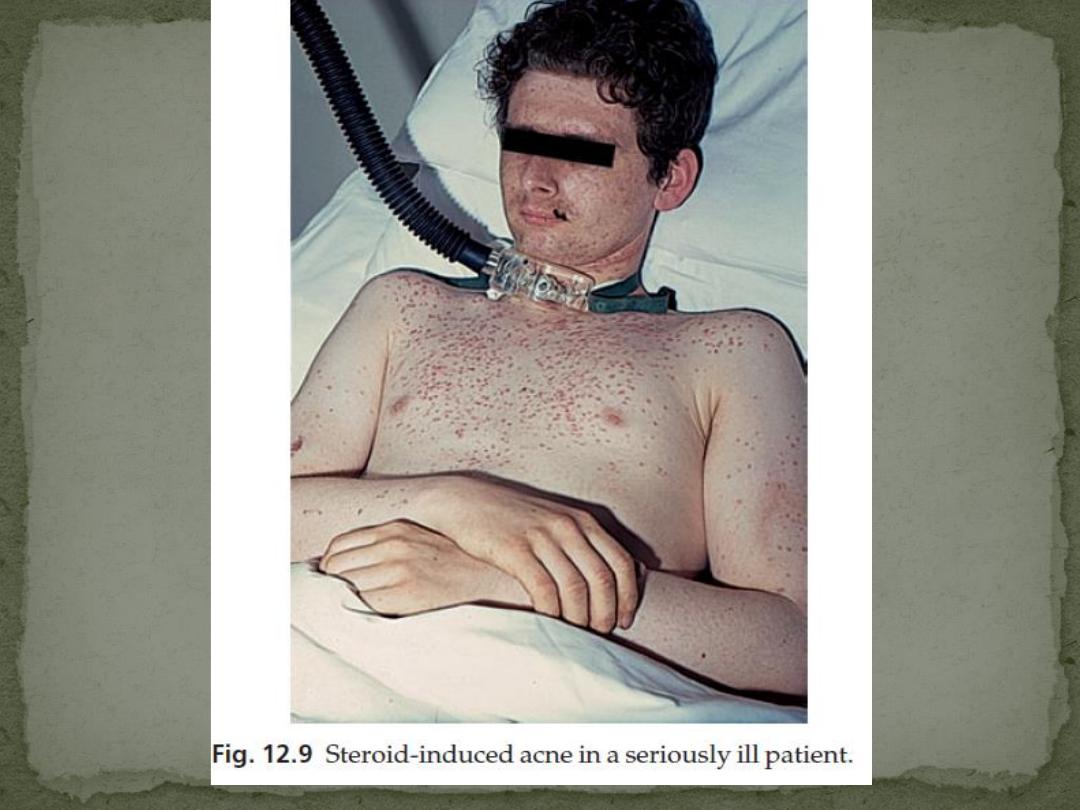
5. Drug-induced
Corticosteroids, androgenic and anabolic, steroids,
gonadotrophins, oral contraceptives, lithium, iodides,
bromides, antituberculosis and anticonvulsant therapy
can all cause an acneiform rash.
6. Tropical, Heat and humidity
7. Acne due to cosmetics

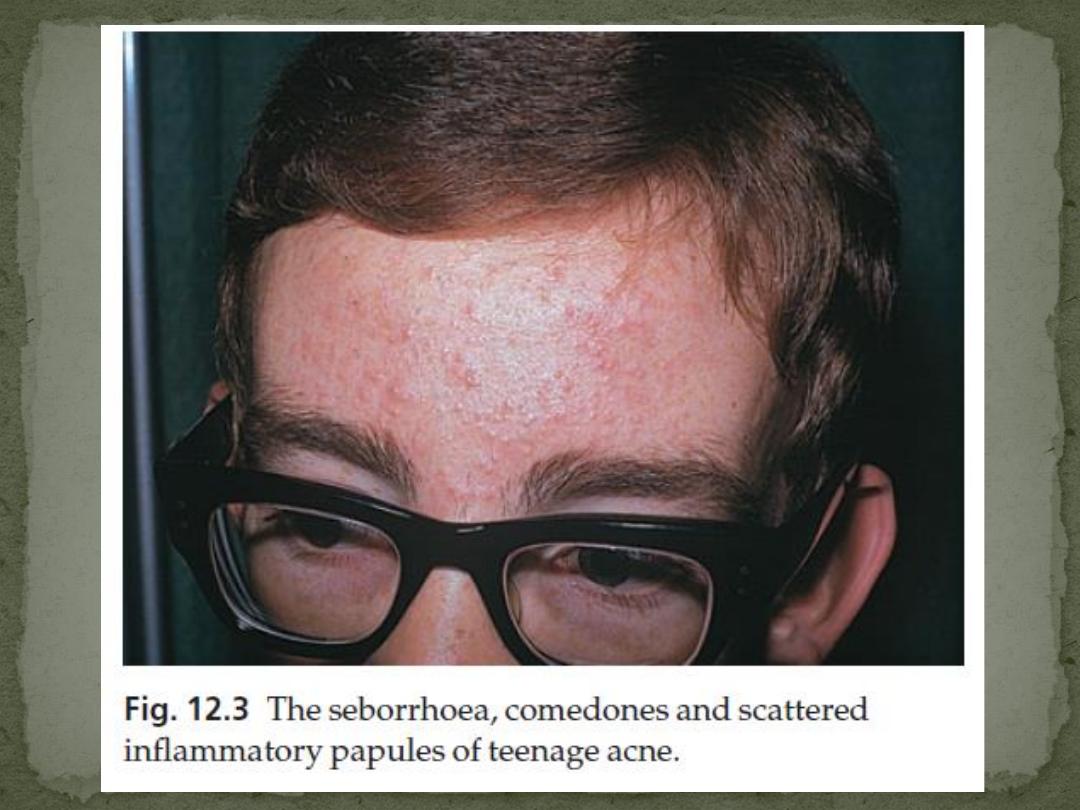
face, shoulders, upper chest and back.
Seborrhoea is often present
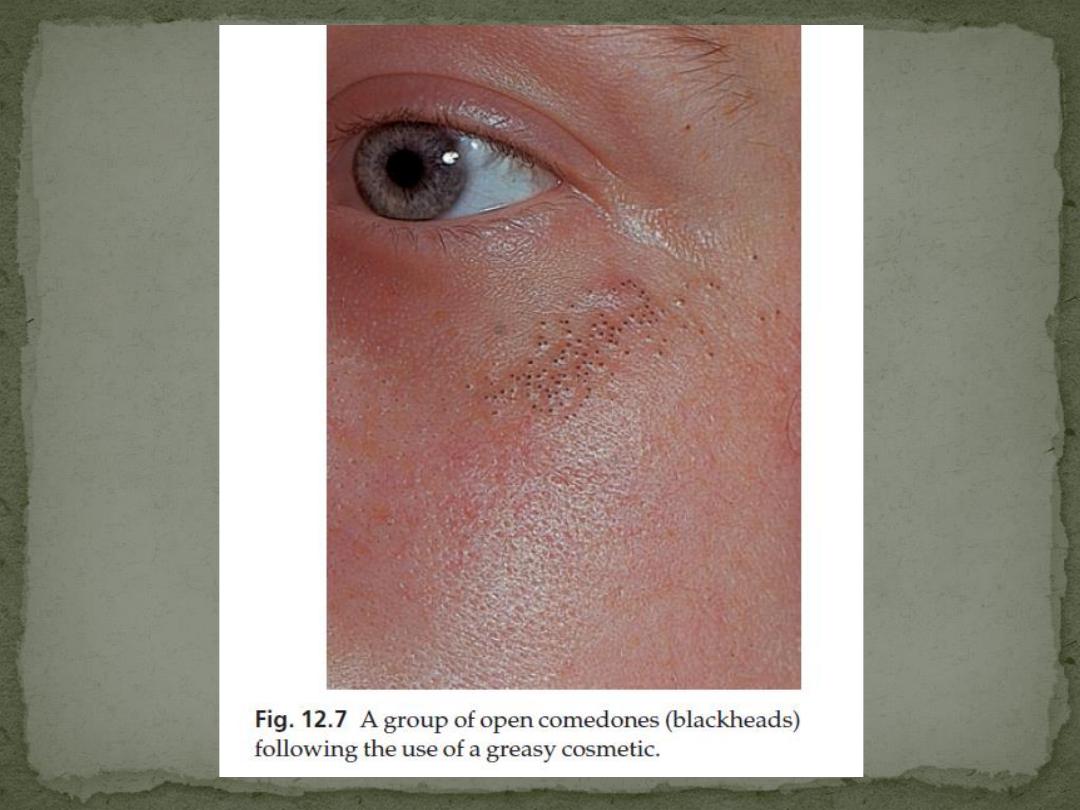
Open comedones (blackheads) because of the plugging by
keratin and sebum of the pilosebaceous orifice
closed comedones (whiteheads), caused by overgrowth of
the follicle openings by surrounding epithelium
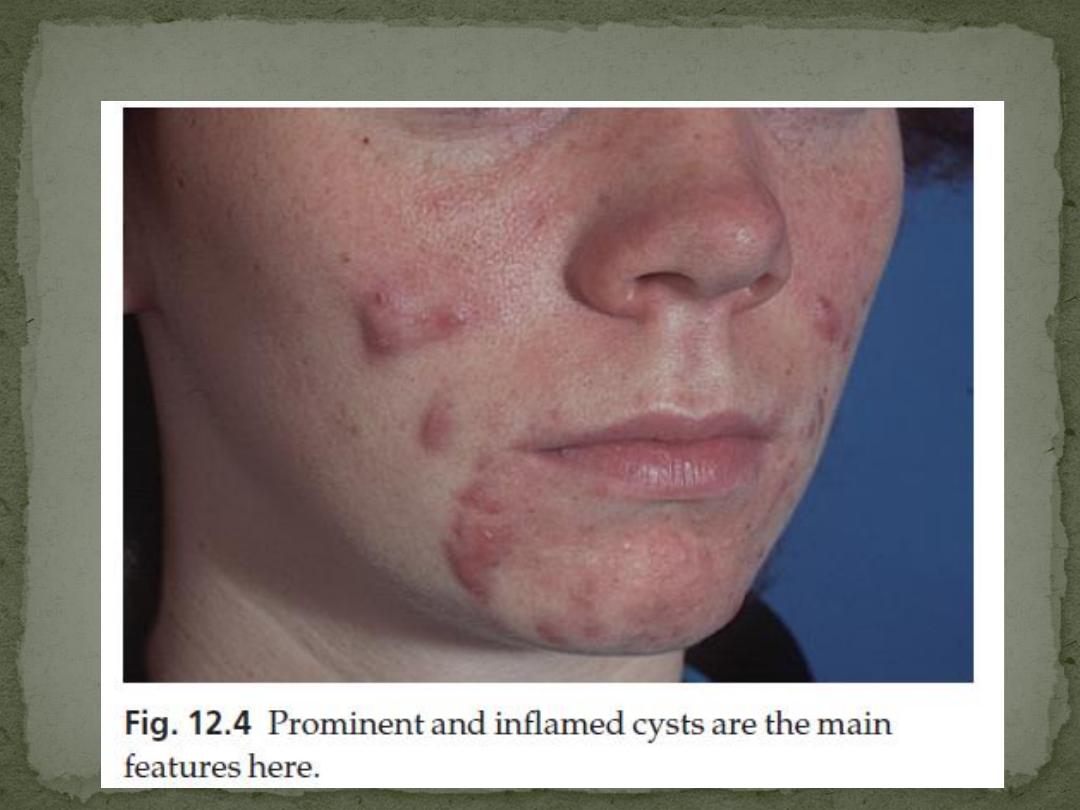
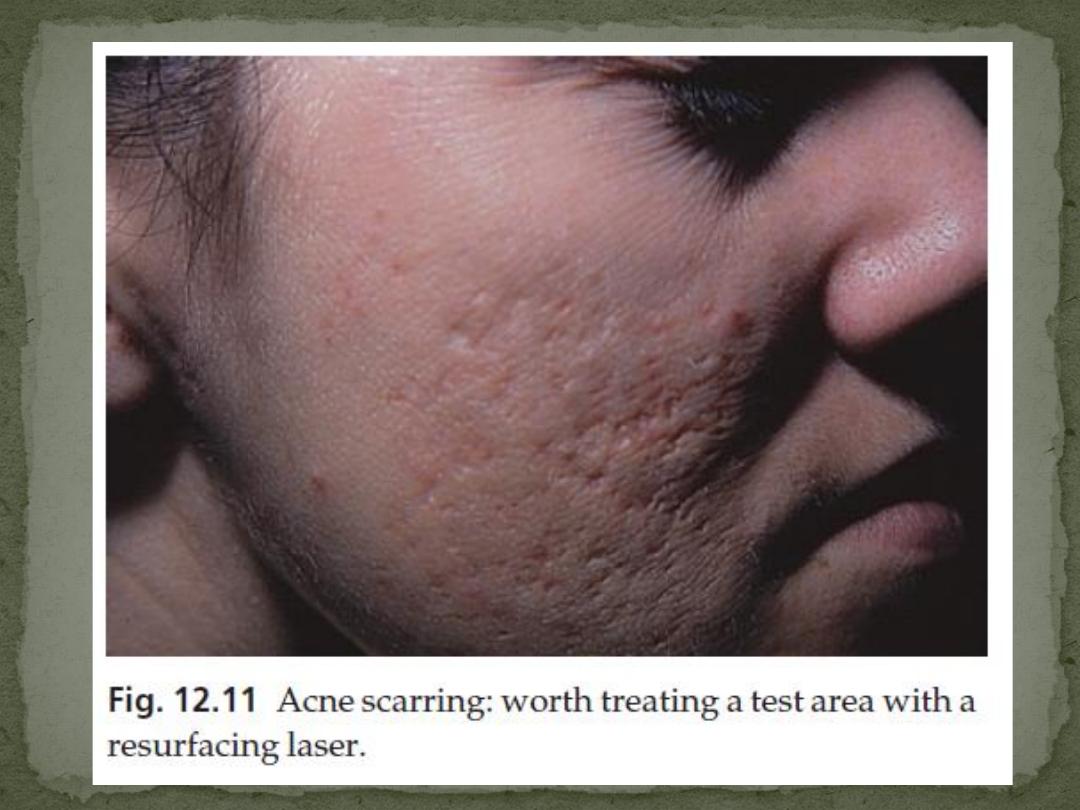
Inflammatory papules, nodules and cysts
Depressed or hypertrophic scarring
post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Psychological depression is common

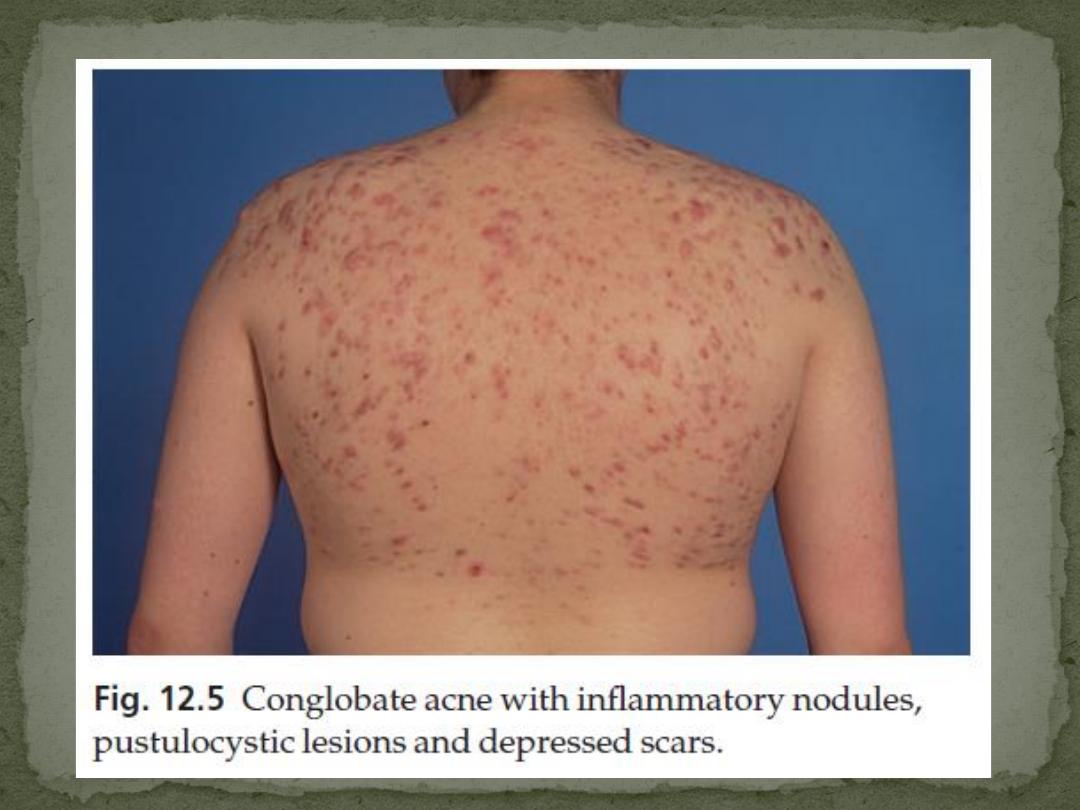
Acne Conglobate
is severe form of acne
abscesses or cysts with intercommunicating sinuses
that contain thick serosanguinous fluid or pus
On resolution, it leaves deeply pitted or hypertrophic
scars, sometimes joined by keloidal bridges
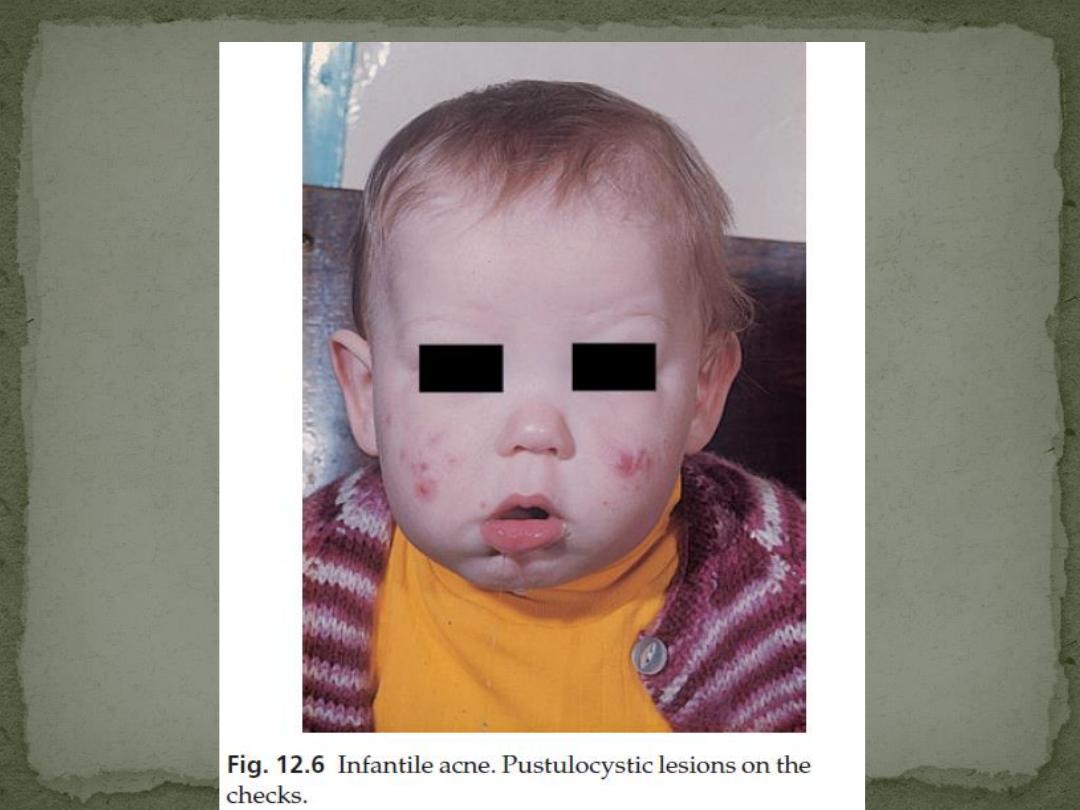
Infantile Acne
present at or appears soon after birth and may last up
to 3 years

Fulminans Acne
conglobate acne is accompanied by fever, joint pains and a
high erythrocyte sedimentation
rate (ESR)
Excoriated Acne
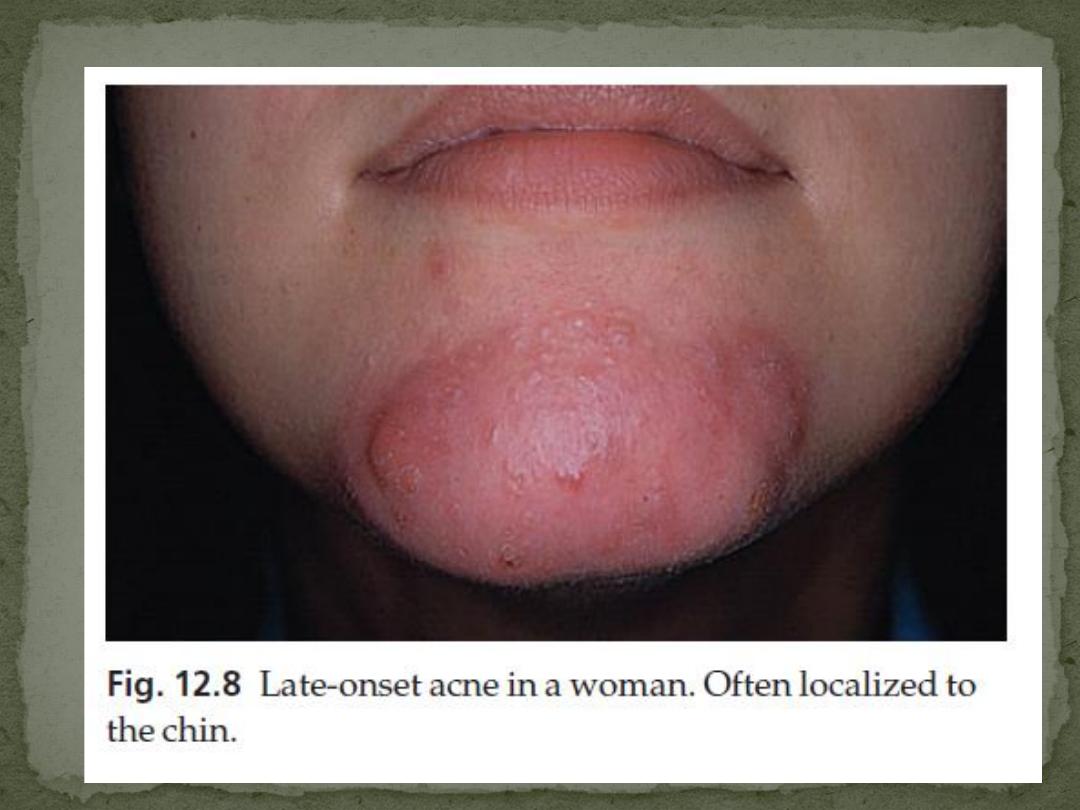
Late onset Acne
Women, limited to the chin, Nodular and cystic
lesions predominate
It is stubborn and persisten
Tropical Acne
Drug-induced Acne
Hormonal induced Acne

Acne vulgaris clears by the age of 23–25 years in 90%
of patients
5% of women and 1% of men still need treatment in
their thirties or even forties.

No need usually
Cultures are occasionally needed to exclude a
pyogenic infection, an anaerobic infection or Gram-
negative folliculitis
exclude an androgen-secreting tumour of the
adrenals, ovaries or testes, and to rule out congenital
adrenal hyperplasia caused by 21-hydroxylase
deficiency, polycystic ovarian syndrome

Rosacea
Pyogenic folliculitis
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Pseudofolliculitis
barbae

1.
General measures
regular encouragement worthwhile
underlying cause should be removed or treated.
2. Local treatment
3. Systemic treatment
Antibiotics
Hormonal

Regular gentle cleansing with soap and water to
remove surface sebum.
Benzoyl peroxide
Is an antibacterial agent
most effective for inflammatory lesions not affected
by propionibacterial antibiotic resistance
start with a 2.5% or 5% preparation, moving up to 10%
if necessary.

Retinoids.
normalize follicular keratinization
down-regulate TLR2 expression
reduce sebum production
effective against comedones
Side effects are skin irritation and photosensitivity
applied overnight on alternate nights
stop temporarily if irritation
worth increasing the strength of tretinoin after 6 weeks if it
has been well tolerated
Contraindication
Concomitant eczema and Pregnant women

Azelaic acid
bactericidal for P. acne
anti-inflammatory
inhibits the formation of comedones
It should be applied twice daily, but not used for more than 6
months at a time
Topical antibiotics
topical clindamycin, erythromycin and sulfacetamide
antibacterial resistance of P. acnes is a most erythromycin-
resistant strains being cross-resistant to clindamycin
Combining antibiotics with benzoyl peroxide reduces P. acnes
numbers and the likelihood of resistant strains Emerging
The addition of zinc acetate complex to erythromycin enhances
the antibiotic’s anti-inflammatory effect
Cosmetic camouflage

Oxytetracycline and tetracycline.
starting dosage for an adult is 500 mg twice daily, but up to
1.5 g/day may be needed in resistant cases.
Used not less than 3 months and may be needed for 1–2
years, or even longer.
It should be taken on an empty stomach, 1 h before meals
or 4 h after food, as the absorption of these tetracyclines is
decreased by milk, antacids and calcium, iron and
magnesium salts.
maintenance dosage being 250–500 mg/ day.
serious side-effects are rare, although candidal
vulvovaginitis may force a change to a narrower spectrum
antibiotic such as erythromycin.

Minocycline
50 mg twice daily or 100 mg once or twice daily is now preferred by
many dermatologists
Absorption is not significantly affected by food or drink.
Minocycline is much more lipophilic than oxytetracycline and so
probably concentrates better in the sebaceous glands.
can cause abnormalities of liver function and a lupus-like syndrome.
Rarely, the long-term administration of minocycline causes a greyish
pigmentation, like a bruise, especially on the faces of those with actinic
damage and over the shins.
Doxycycline
100 mg once or twice daily is a cheaper alternative to minocycline
more frequently associated with phototoxic skin reactions.
Contraindications
Tetracyclines should not be taken in pregnancy or by children under 12
years as they are deposited in growing bone and developing teeth,
causing stained teeth and dental hypoplasia.

Erythromycin
Is the next antibiotic of choice
is preferable to tetracyclines in women who might become
pregnant.
Its major drawbacks are nausea and the widespread
development of resistant Proprionibacteria, which leads to
therapeutic failure.
Trimethoprim
with or without sulfamethoxazole
by some as a third-line antibiotic for acne, when a
tetracycline and erythromycin have not helped. White
blood cell counts should be monitored.
Ampicillin is another alternative.

Isotretinoin
is an oral retinoid
inhibits sebum excretion, the growth of P. acnes and
acute inflammatory processes.
reserved for severe nodulocystic acne, unresponsive to
the measures outlined above.
It is routinely given for 4–6 months only, in a dosage of
0.5–1 mg/kg body weight/day
A full blood count, liver function tests and fasting lipid
levels should be checked before the start of the course,
and then 1 and 4 months after starting the drug.

Isotretinoin is highly teratogenic
Effective contraception must be taken for 1 month
before, throughout and for 1 month after treatment.
Tests for pregnancy are carried out monthly while the
drug is being taken only a single month’s supply of the
drug should be prescribed at a time
Treatment should start on day 3 of the patient’s next
menstrual cycle following a negative pregnancy test.

Other side-effects of isotretinoin include:
1.
Depression rarely lead to suicide
2.
a dry skin, dry and inflamed lips and eyes,
nosebleeds,
3.
facial erythema, muscle aches
4.
hyperlipidaemia and hair loss
these are reversible and often tolerable, especially if
the acne is doing well.
5. Rarer and potentially more serious side-effects
include changes in night-time vision and hearing loss


Rosacea affects the face of adults, usually women.
peak incidence is in the thirties and forties, it can also
be seen in the young or old.
It may coexist with acne but is distinct from it.

The cause is still unknown.
Rosacea is often seen in those who flush easily in
response to warmth, spicy food, alcohol or
embarrassment.
No pharmacological defect has been found that
explains these flushing attacks.
Psychological abnormalities, including neuroticism
and depression, are more often secondary to the skin
condition than their cause.
Sebum excretion rate and skin microbiology are
normal

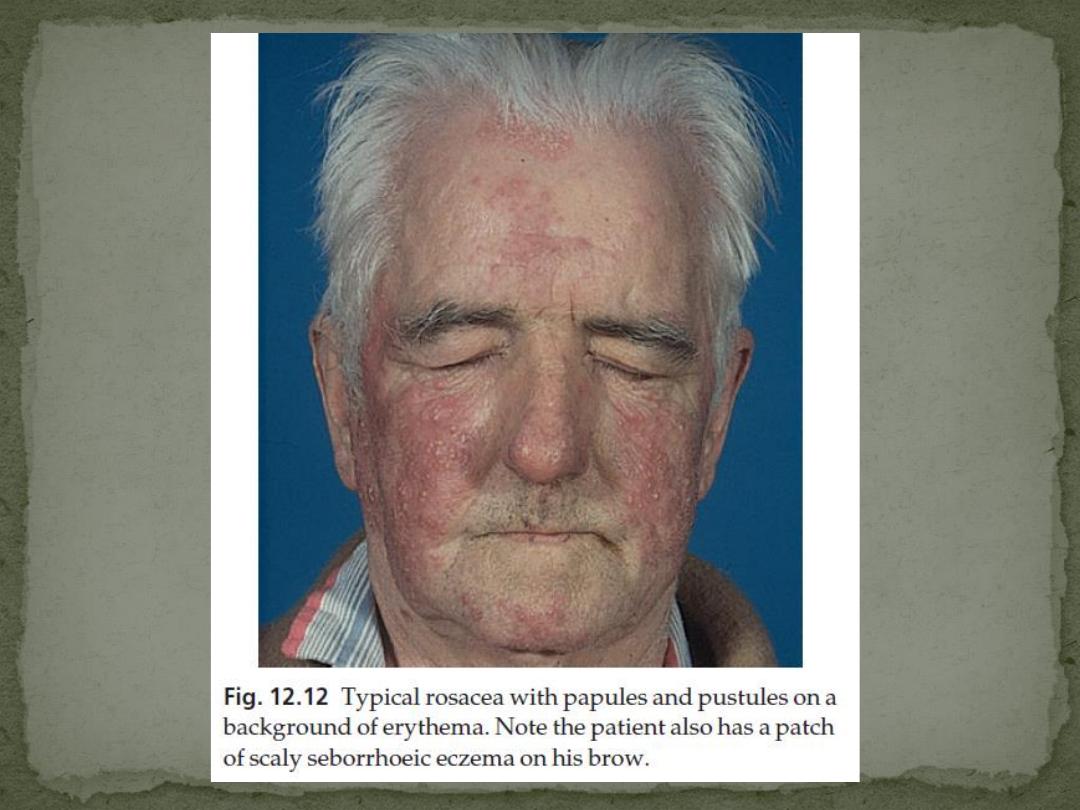
The cheeks, nose, centre of forehead and chin are most
commonly affected
the periorbital and perioral areas are spared
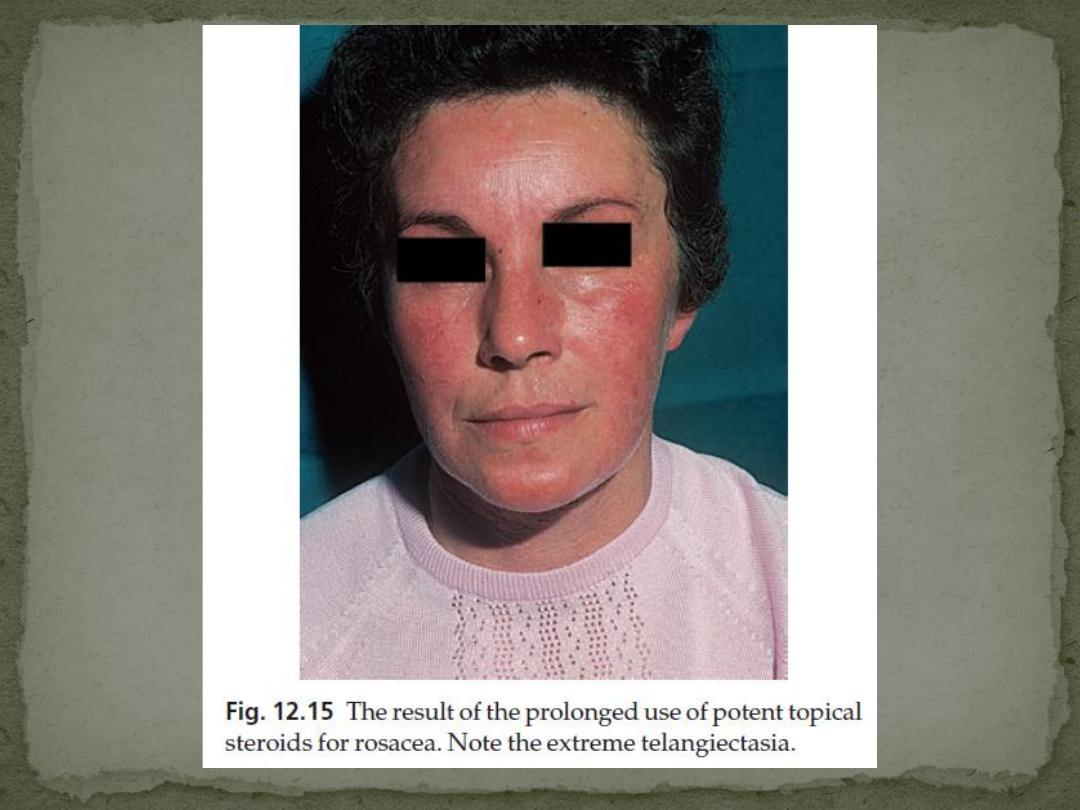
Intermittent flushing is followed by a fixed erythema
and telangiectases.
Discrete domed inflamed papules, papulopustules
and, rarely, plaques or nodules develop.
no comedones or seborrhoea.
It is usually symmetrical.
Its course is prolonged, with exacerbations and
remissions.

Blepharitis
conjunctivitis
Keratitis
Rhinophyma
Lymphoedema, below the eyes and on the forehead
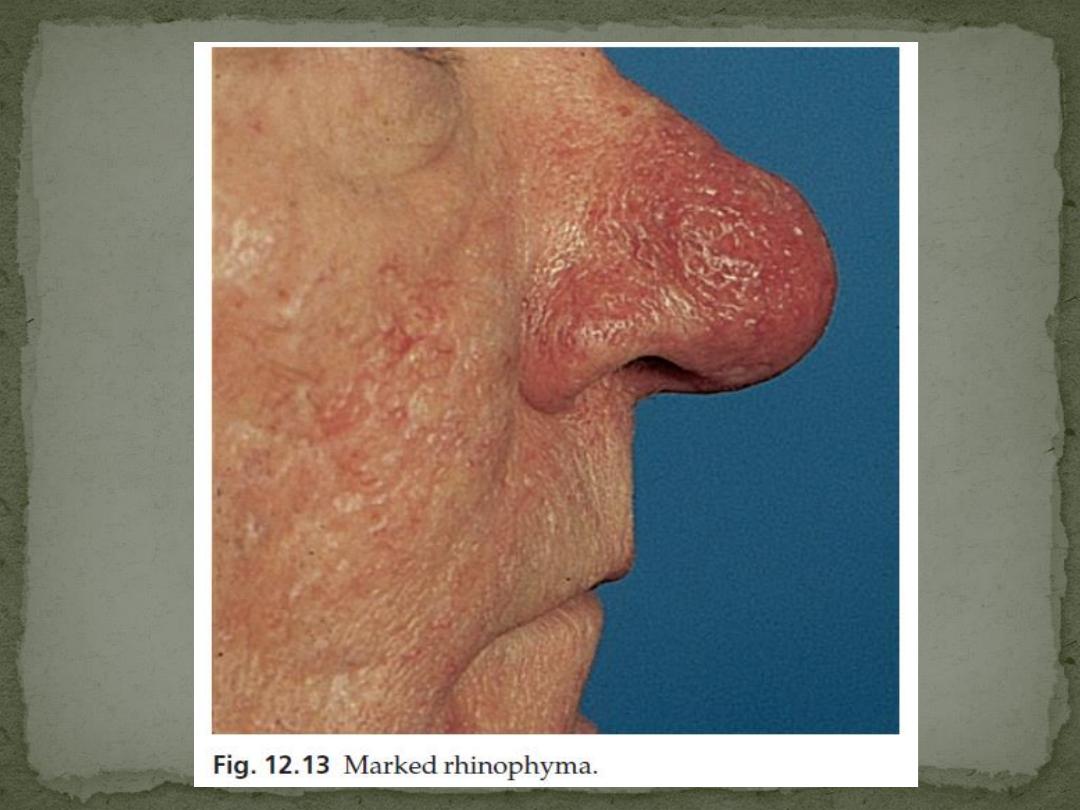

Acne
Rosacea differs from it by:
1.
its background of erythema and telangiectases
2.
absence of comedones
3.
distribution of the lesions is central face but not the
trunk.
4.
usually appears after adolescence.

Sun-damaged skin with or without acne cosmetica
causes most diagnostic difficulty
Remember, rosacea affects primarily the central, less
mobile parts of the face, whereas sun damage and acne
cosmetica are more generalized over the face
The flushing of rosacea can be confused with:
1.
menopausal symptoms
2.
carcinoid syndrome
3.
Superior vena caval obstruction

Seborrhoeic eczema
perioral dermatitis
systemic lupus erythematosus
photodermatitis
they do not show the papulopustules of rosacea
Rosacea and topical steroids go badly together
Papulopustular rosacea
Systemic
tetracyclines as for acne are the traditional treatment and are
usually effective.
Erythromycin is the antibiotic of second choice.
Courses should last for at least 10 weeks and, after gaining
control with 500–1000 mg/day, the dosage can be cut to 250
mg/day
The condition recurs in about half of the patients within 2 years,
but repeated antibiotic courses, rather than prolonged
maintenance ones, are generally recommended
Rarely, systemic metronidazole or isotretinoin is needed for
stubborn rosacea

Topical
Topical 0.75% metronidazole gel, 15% azelaic acid and
sulfacetamide/sulphur lotions applied once or twice
daily
are nearly as effective as oral tetracycline and often
prolong remission
Sunscreens help if sun exposure is an aggravating
factor
changes in diet or drinking habits are seldom of value

relatively common, 1 in 3000
Autosomal dominant
There are two main types:
Von Recklinghausen’s neurofibromatosis (NF1; 85% of
all cases)
Bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis (NF2)

Cause
Mutation of NF1 gene, localized to chromosome 17q11.1.
The NF1 gene is a tumour suppressor gene, the product
of which, neurofibromin, interacts with the product of
the RAS proto-oncogene. This may explain the
susceptibility of NF1 patients to a variety of tumours.
Inheritence as autosomal dominant trait
about half of index cases have no preceding family
history.

The physical signs include the following.
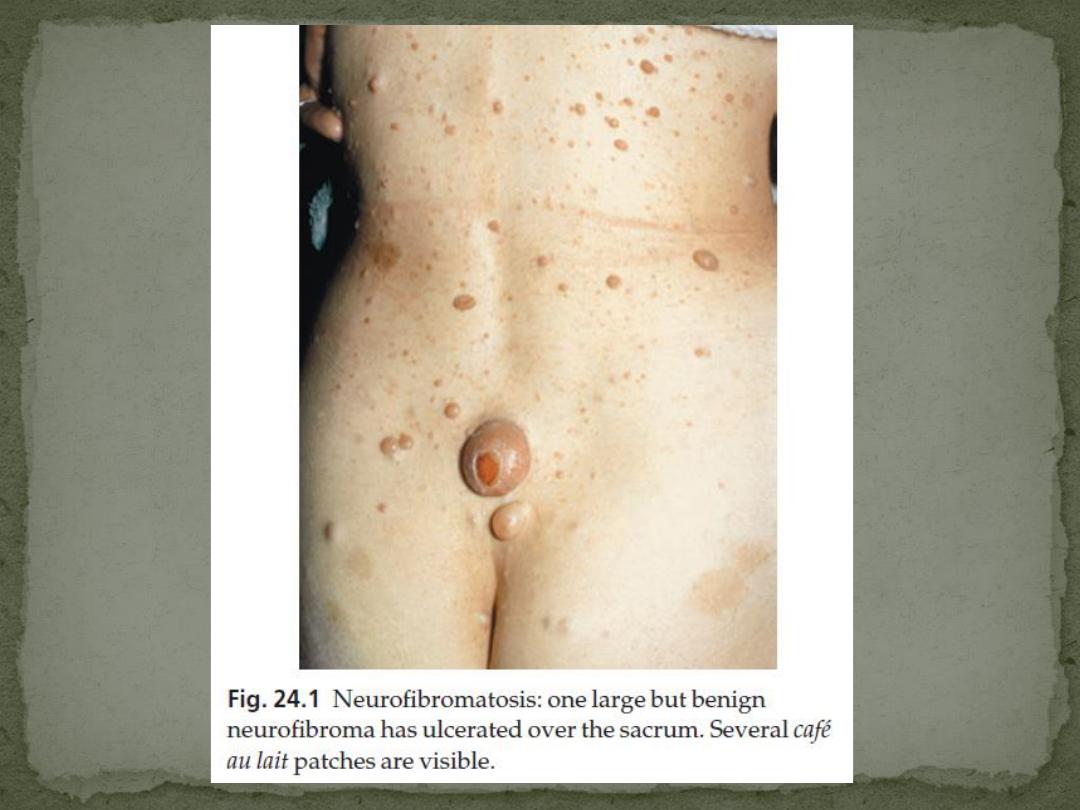
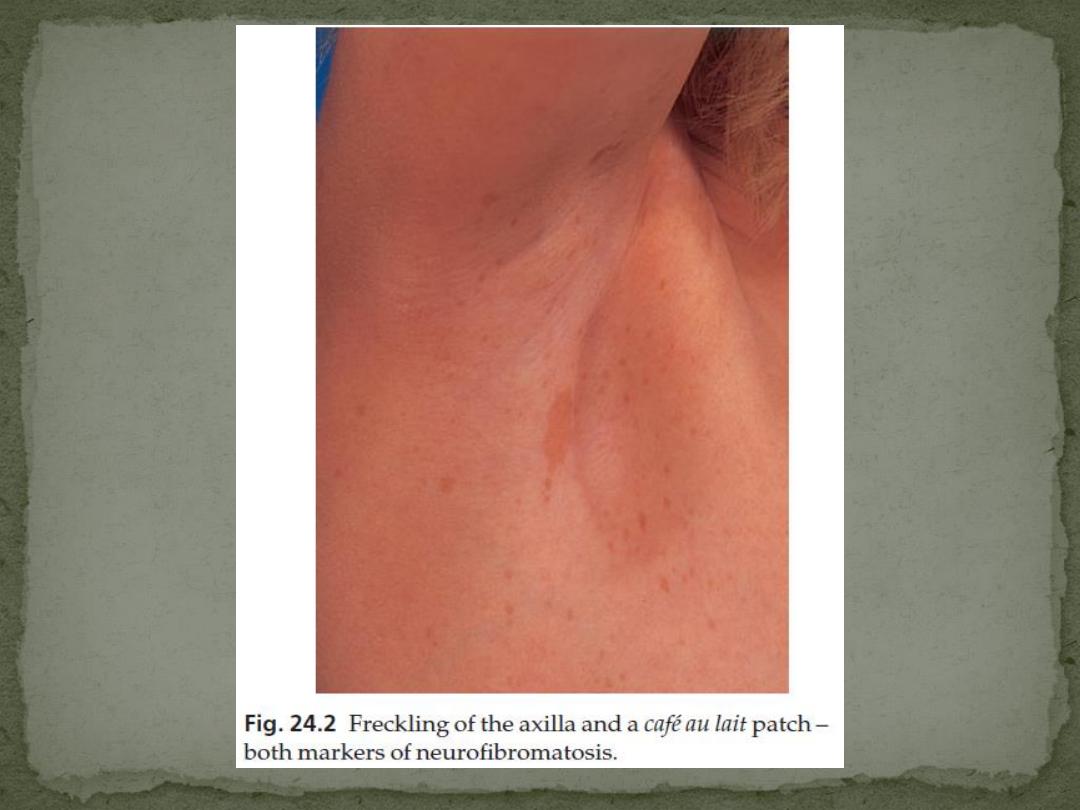
1. Café au lait patches
Six or more (light brown oval macules, usually developing in the first
year of life.
2. Axillary freckling
in two-thirds of affected individuals (Crowe’s sign).
3. Neurofibromas
Any number
some small and superficial, others larger and deeper
Most are dome-like nodules, but others are irregular raised plaques.
Some are firm, some soft and compressible through a deficient dermis
(‘button-hole’ sign); others feel ‘knotty’ or ‘wormy’.
may not appear until puberty and become larger and more numerous
with age.
4. Lisch nodules
Small circular pigmented hamartomas of the iris, appear in early
childhood.
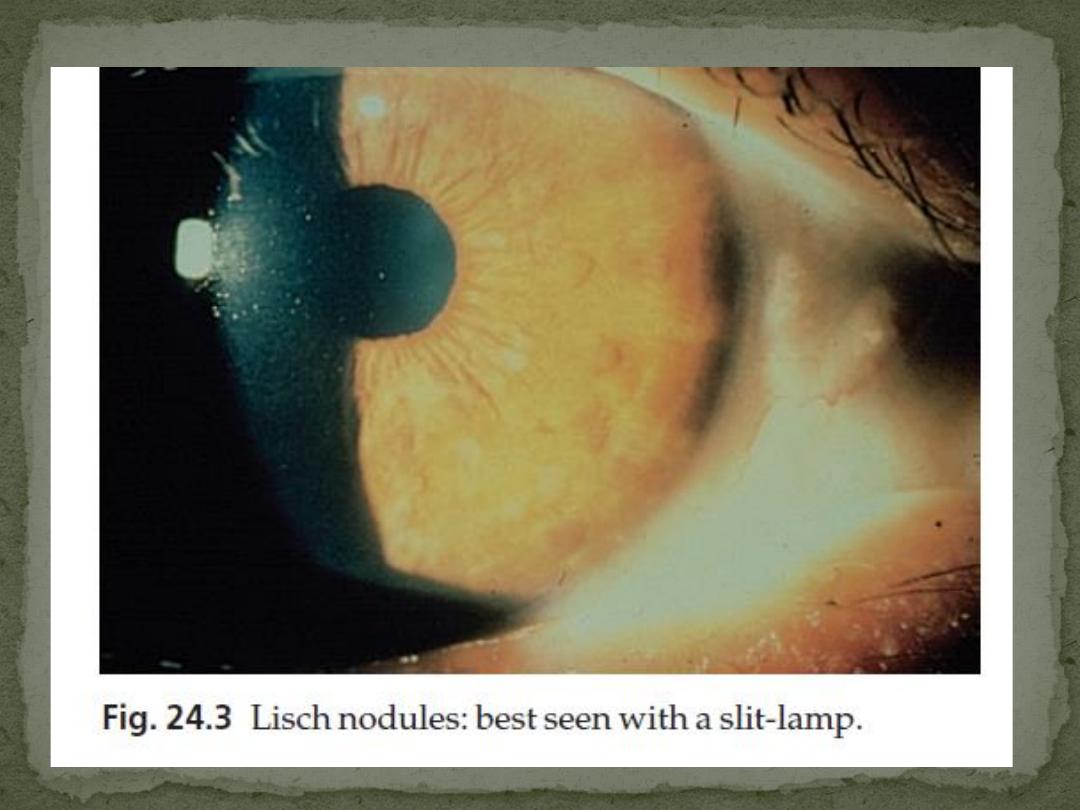

Nearly all NF1 patients meet the criteria for diagnosis
by the age of 8 years, and all do so by 20 years.
The usual order of appearance of the clinical features
is:
1.
café au lait macules
2.
axillary freckling
3.
Lisch nodules
4.
neurofibromas.

A segmental form of NF1 is caused by a post-zygotic
mutation.
Isolated neurofibromas are not uncommon in
individuals without neurofibromatosis and are of little
consequence unless they are painful.

1.
A neurofibroma will occasionally change into a
neurofibrosarcoma.
2.
Kyphoscoliosis
3.
Learning impairment
4.
Epilepsy,
5.
Renal artery stenosis
6.
an association with phaeochromocytoma

Ugly or painful lesions, and any suspected of
undergoing malignant change, should be removed.
The chance of a child of an affected adult developing
the disorder is 1 in 2
blood pressure checked regularly.

Cause
also autosomal dominant on chromosome 22q12.21
This gene also normally functions as a tumour
suppressor gene, the product of which is known as
Merlin.

l Bilateral acoustic neuromas;
l Few, if any, cutaneous manifestations;
l No Lisch nodules;
l Other tumours of the central nervous system may
occur, especially meningiomas and gliomas.

All NF2 patients and their families should have access
to genetic testing as presymptomatic diagnosis
improves clinical management.

uncommon condition, with a prevalence about 1 in
12000 in children under 10 years
autosomal dominant trait
Fertility is reduced, so transmission through more
than two generations is rare.

Inactivating mutations at two different loci can,
independently, cause clinically identical tuberous
sclerosis.
Both genes are tumour suppressors.
1.
(TSC1 on chromosome 9q34)
2.
(TSC2 on 16p13.3)
TSC2 gene mutations are responsible for 80–90% of
cases.

The skin changes include the following.
1. Ash leaf macules
Small oval white patches
occur in 80% of those affected
may be the only manifestation at birth.
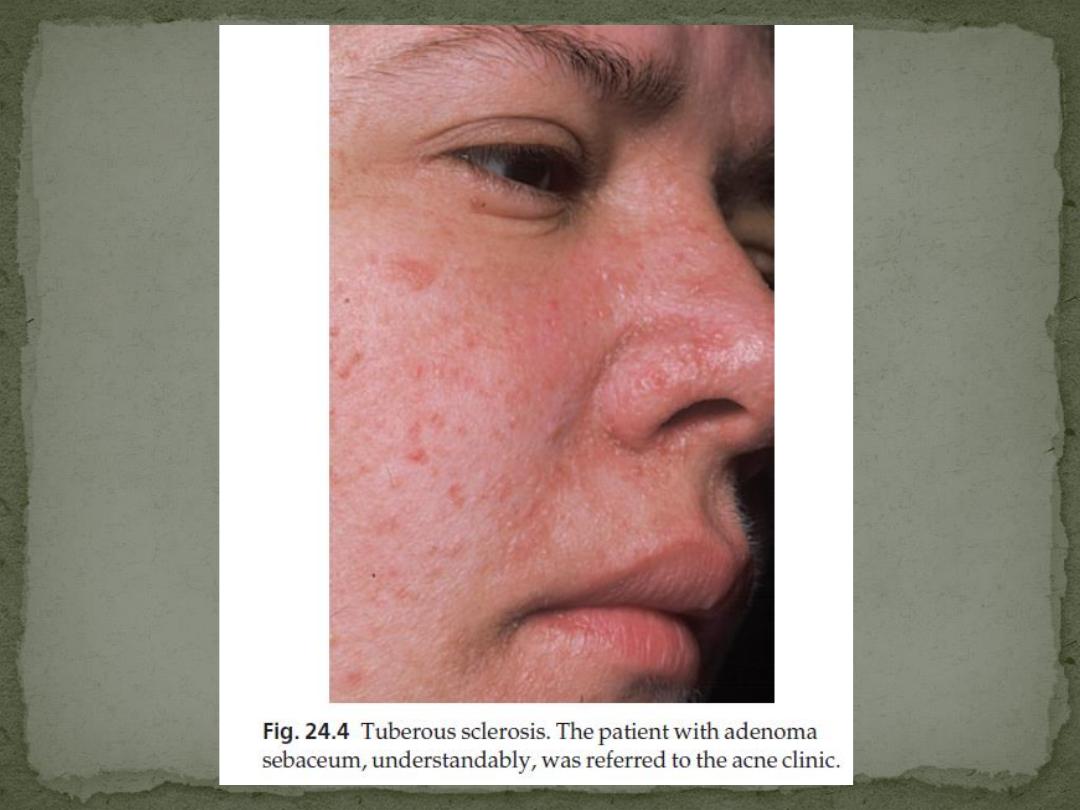
2. Angiofibromas (known as adenoma sebaceum)
occur in 85% of those affected
develop at puberty as pink or yellowish acne-like
papules on the face, often around the nose.

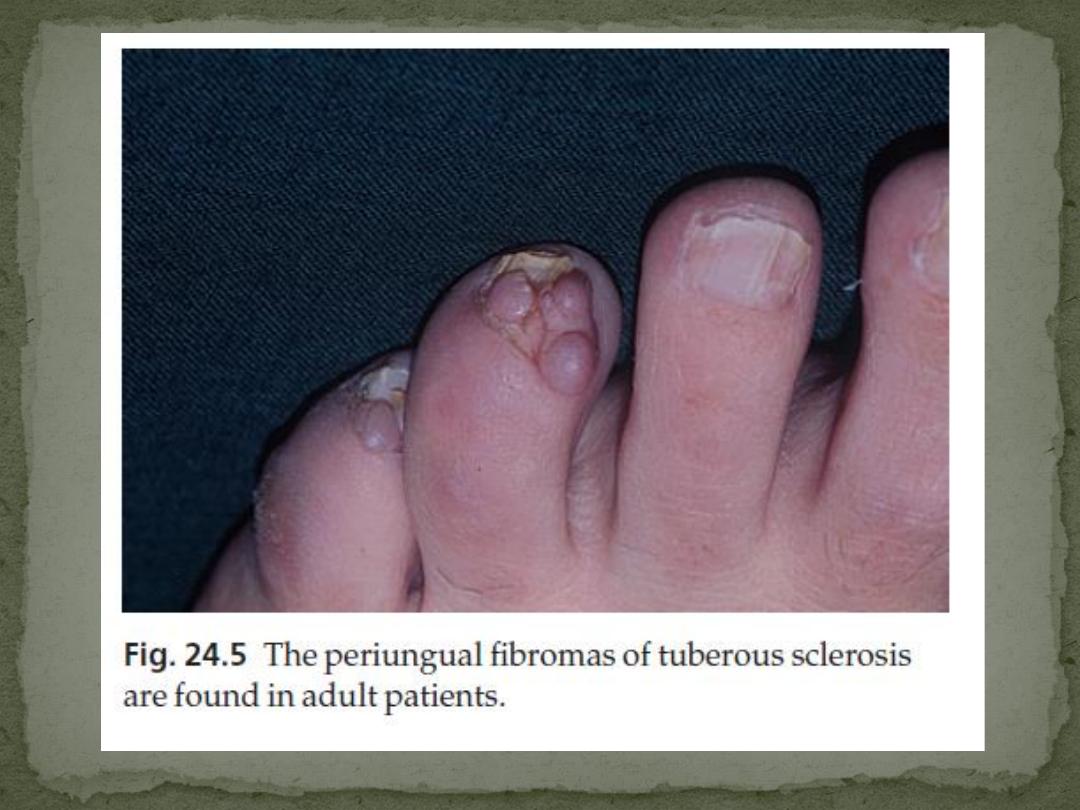
3. Periungual fibromas
occur in 50% of patients
develop in adult life as small pink sausage-like lesions
emerging from the nail folds.
4. Connective tissue naevi (‘shagreen patches’)
Are seen in 40% of patients.
Cobblestone, somewhat yellow plaques often arise in
the skin over the base of the spine.

may include:
1.
Epilepsy (in 75% of patients)
2.
Mental retardation (in 50% of patients)
3.
Ocular signs, including retinal phakomas and
pigmentary abnormalities (in 50% of patients)
4.
Hyperplastic gums
5.
gliomas along the lateral walls of the lateral
ventricles (80% of cases) and calcification of the
basal ganglia
6.
Renal and heart tumours.

Any baby with unexplained epilepsy should be
examined with a Wood’s light (p. 38) to look for ash
leaf macules.
Skull X-rays and computed tomography scans of CNS
and kidneys.
The lesions of adenoma sebaceum (a misnomer, as
histologically they are angiofibromas) may be
mistaken for acne.

Genetic counselling
Facial angiofibromas may improve cosmetically after
electrodessication, dermabrasion or destruction by
laser but tend to recur

heterogeneous group of autosomal recessive
disorders, characterized by the defective
repair of DNA after its damage by ultraviolet
radiation.
rare, affecting about 5 per million in Europe.

There are many variants but all follow the same
pattern.
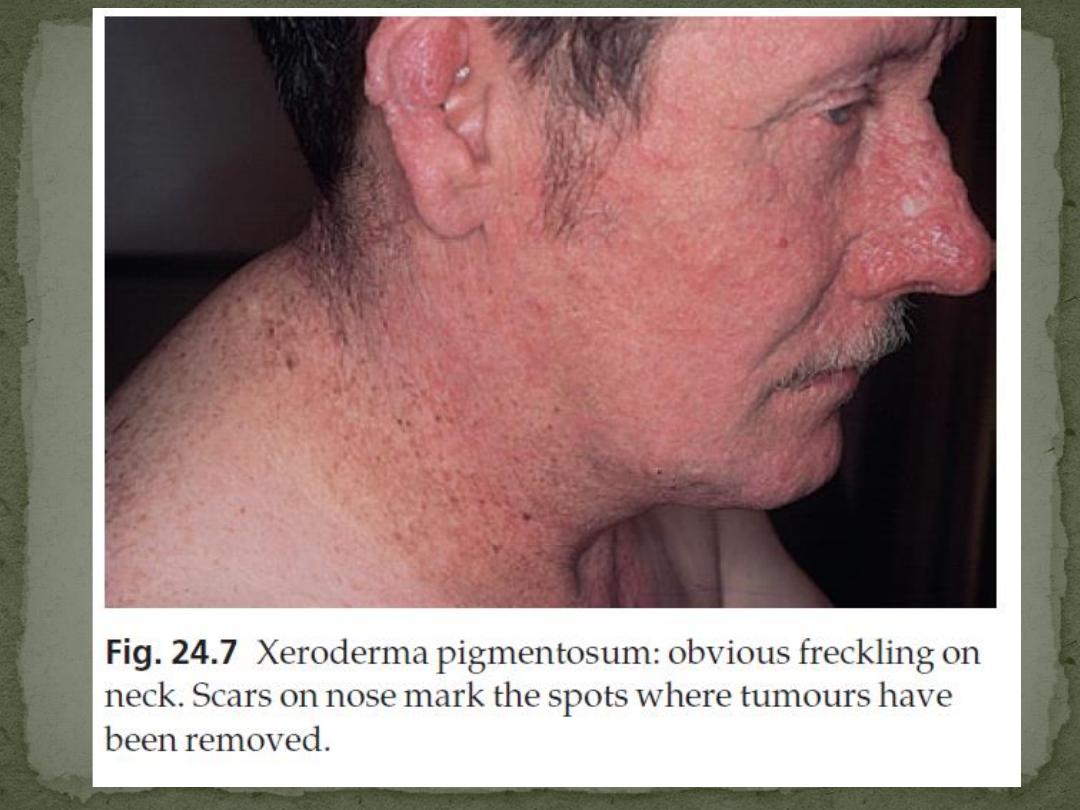
1. The skin is normal at birth.
2. Multiple freckles, roughness and keratoses on exposed
skin appear between the ages of 6 months and 2
years
3. Photosensitivity increases thereafter.
4. The atrophic facial skin shows telangiectases and
small angiomas.

5. Many tumours develop on light-damaged skin: BCC,
SCC, MM
Many patients die before the age of 20 years.
6. Eye problems are common and include photophobia,
conjunctivitis and ectropion.
7. The condition may be associated with microcephaly,
mental deficiency, dwarfism, deafness and ataxia (De
Sanctis–Cacchione syndrome).
Strict avoidance of sunlight, the use of protective
clothing, widebrimmed hats and of reflectant
sunscreens and dark glasses.
If possible, patients should not go out by day.
Early and complete removal of all tumours is essential.
Radiotherapy should be avoided

