
WOUND
CLOSURE

WOUNDS
-----------
Are breaks in tissue continuity.
-caused by trauma(physical, chemical, and
biological).
-They are of different
*types,
acute
and
chronic
*different
shapes
and
sizes
, and
*vary in their ways of healing.
Rapid closure and rapid repair of wound
is
mandatory to
*
assist and enhance
wound healing process,
*
reduced
morbidity and complications, and
*
even reduce
mortality especially in extensive
wounds and multiply injured patients.

There are five methods for wound
closure
:
1. Direct closure (Primary and
delayed)
2. Direct closure assisted by
undermining of margins.
3. Leaving the wound to heal by
secondary intention.
4. Skin grafts.
5. Skin flaps.
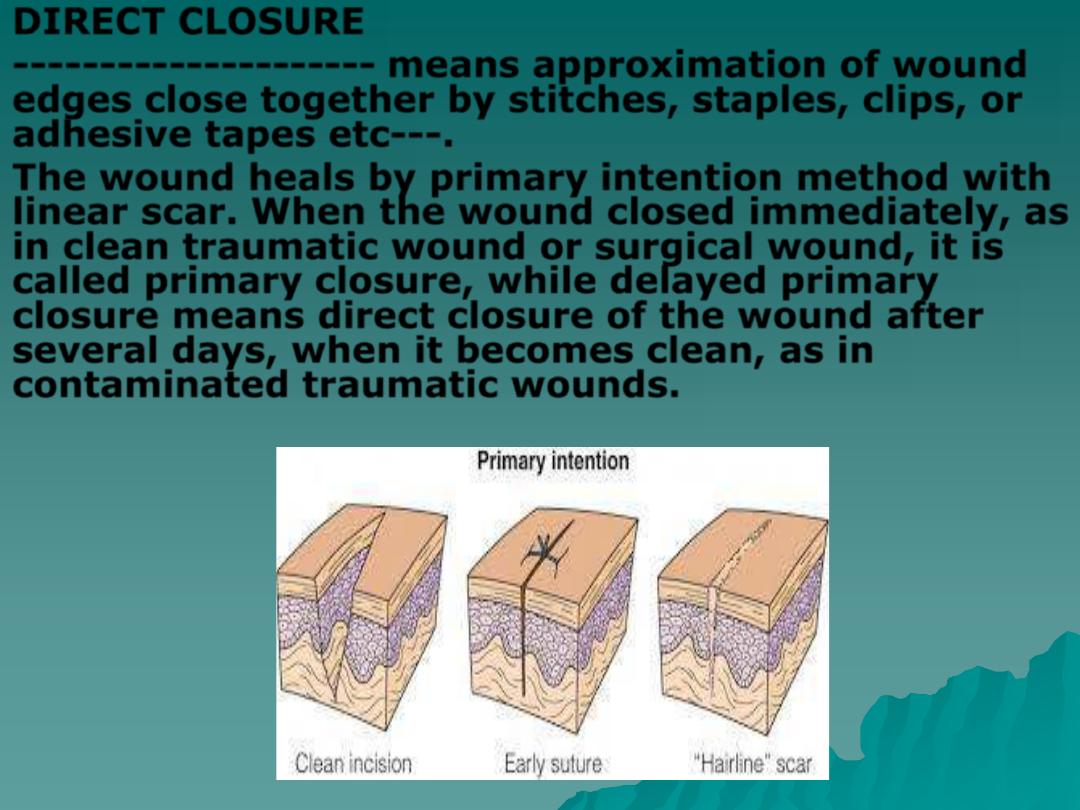
DIRECT CLOSURE
---------------------
means approximation of wound
edges close together by stitches, staples, clips, or
adhesive tapes etc---.
The wound heals by primary intention method with
linear scar. When the wound closed immediately, as
in clean traumatic wound or surgical wound, it is
called primary closure, while delayed primary
closure means direct closure of the wound after
several days, when it becomes clean, as in
contaminated traumatic wounds.

DIRECT CLOSURE ASSISSTED BY
UNDERMINING OF MARGINS
When the wound edges are so far that
can not be approximated together
without tension, we could make use of
skin elasticity and ability for
stretching and relaxation.
Undermining of the adjacent skin will
help in direct closure of the wound.
This undermining done at avascular
plane of tissue as blunt dissection for
a distance equal to one half of the
width of the wound.

GRAFT
--------------
Is apiece of tissue
transferred from one site(
donor site
)
to another(
recipient site
), with
complete separation from its
circulation at donor site and it built
new circulation at recipient site.
*Any tissue could be transferred as a
graft, like skin, mucus membrane,
bone, cartilage, tendon, nerve, fat. The
aim of graft is to bypass a gap of
tissue i.e. wound closure.
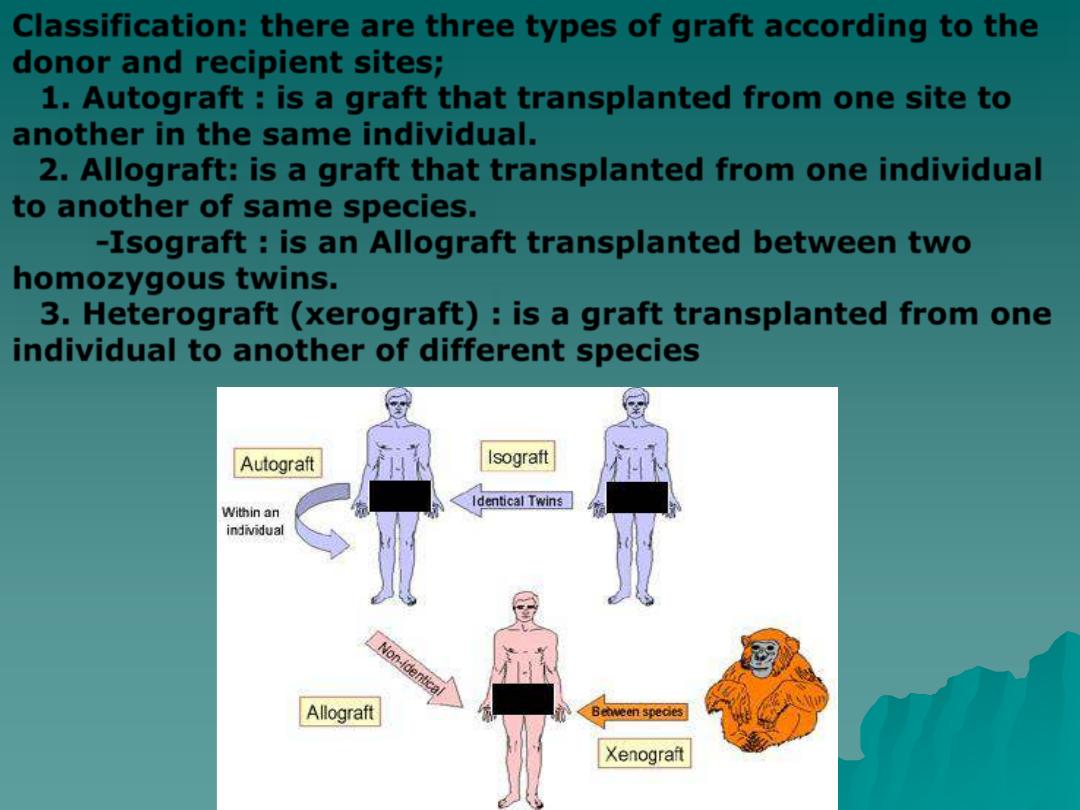
Classification: there are three types of graft according to the
donor and recipient sites;
1.
Autograft
: is a graft that transplanted from one site to
another in the same individual.
2.
Allograft
: is a graft that transplanted from one individual
to another of same species.
-
Isograft
: is an Allograft transplanted between two
homozygous twins.
3.
Heterograft (xerograft)
: is a graft transplanted from one
individual to another of different species
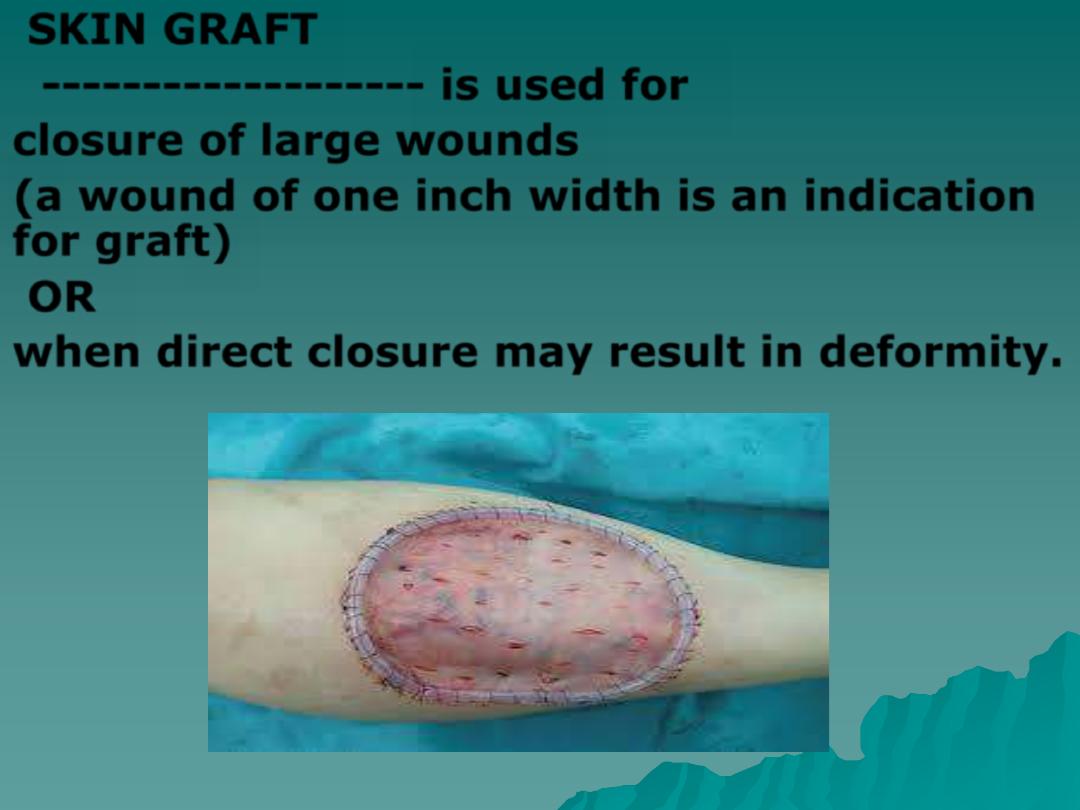
SKIN GRAFT
------------------- is used for
closure of large wounds
(
a wound of one inch width is an indication
for graft
)
OR
when direct closure may result in deformity.
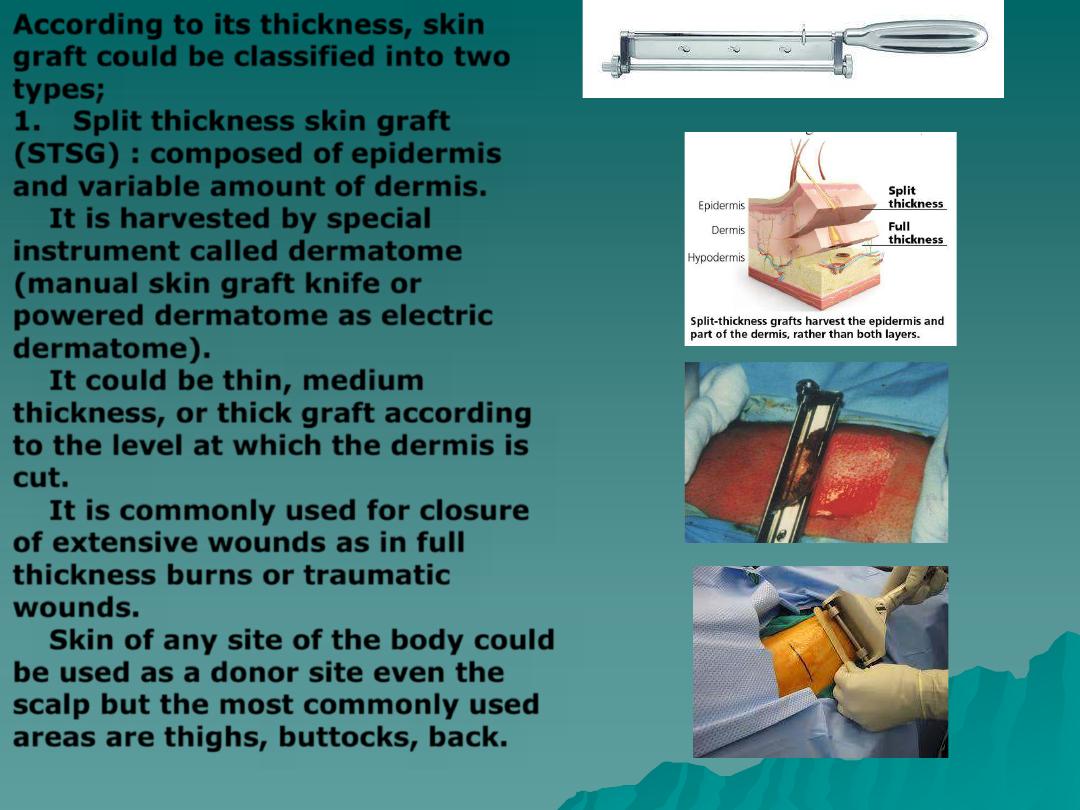
According to its thickness, skin
graft could be classified into two
types;
1.
Split thickness skin graft
(STSG)
: composed of
epidermis
and variable amount of dermis.
It is harvested by special
instrument called
dermatome
(manual skin graft knife or
powered dermatome as electric
dermatome).
It could be
thin, medium
thickness, or thick
graft according
to the level at which the dermis is
cut.
It is commonly used for closure
of extensive wounds as in full
thickness burns or traumatic
wounds.
Skin of any site of the body could
be used as a donor site even the
scalp but the most commonly used
areas are thighs, buttocks, back.
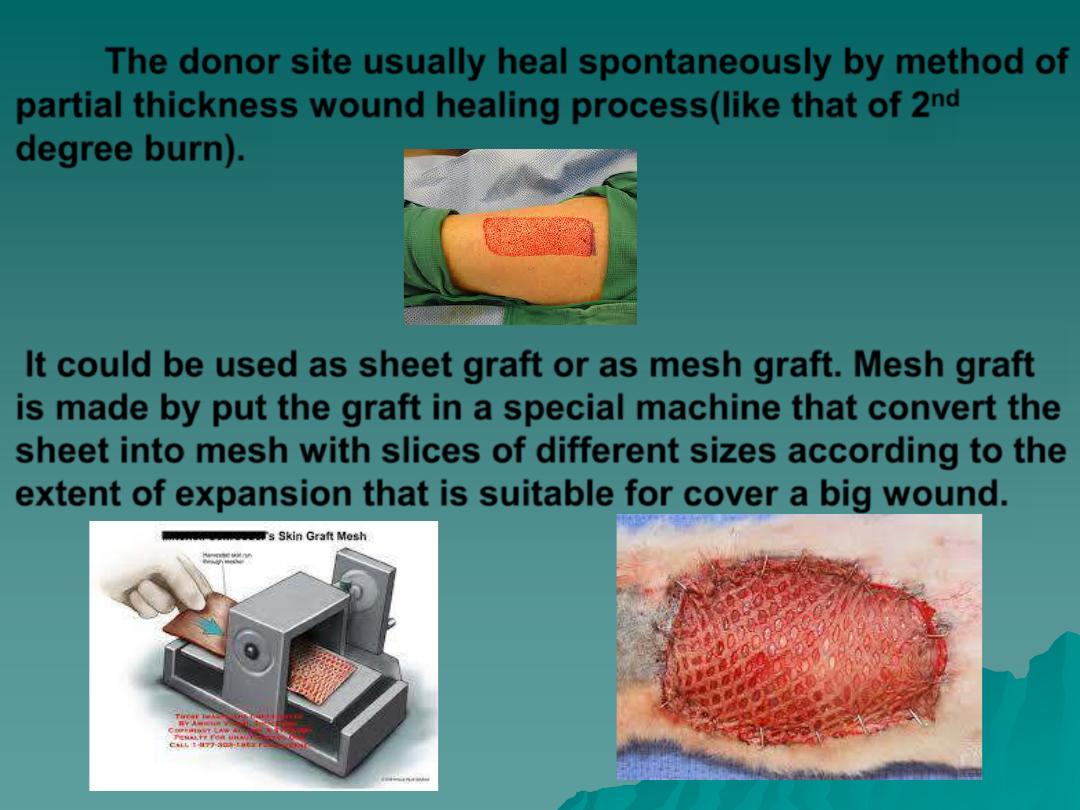
The donor site usually heal spontaneously by method of
partial thickness wound healing process(like that of 2
nd
degree burn).
It could be used as sheet graft or as mesh graft. Mesh graft
is made by put the graft in a special machine that convert the
sheet into mesh with slices of different sizes according to the
extent of expansion that is suitable for cover a big wound.
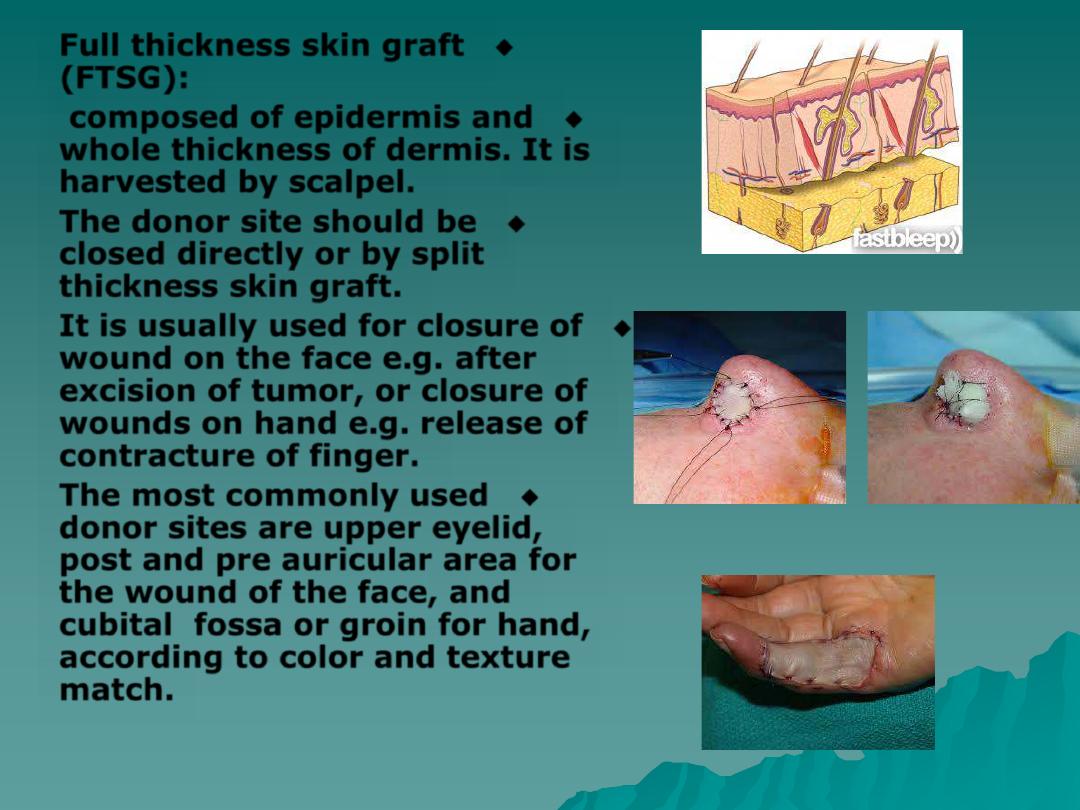
◆
Full thickness skin graft
(FTSG):
◆
composed of epidermis and
whole thickness of dermis. It is
harvested by scalpel.
◆
The donor site should be
closed directly or by split
thickness skin graft.
◆
It is usually used for closure of
wound on the face e.g. after
excision of tumor, or closure of
wounds on hand e.g. release of
contracture of finger.
◆
The most commonly used
donor sites are upper eyelid,
post and pre auricular area for
the wound of the face, and
cubital fossa or groin for hand,
according to color and texture
match.

SKIN GRAFT “take”
Vascularisation of graft is called “take”.
As the skin graft is transplanted from one site to another
with complete separation from its circulation at
donor site
, it
need to build a new circulation at the
recipient site
.
This needs about 72 hours( the graft takes its nutrient from
recipient site by diffusion and plasma imbibitions through the
vascular network of the graft during this period).
There three main REQUIREMENTS for skin graft “take”;
1.
Good circulation at recipient site
: dermis,
periostium, pericranium, perichondirium, perineurium,
paratenon, dura matter, pleura, peritoneum, muscle, healthy
granulation tissue, and fat are good recipient sites, while bare
bone, bare cartilage, bare nerve, bare tendon, wound covered
with poorly grown granulation tissues, and irradiated area are
of absent or very poor circulation and are bad recipient sites.

2.
Clean wounds
: The wound should be free
from infection. Infection cause failure of graft as it
result in graft necrosis or produce pus that impede
Vascularisation of graft.
3.
Good contact between the graft and
the recipient site
:
there are two main factors
that may interfere with contact;
a.
Presence of fluid
between the graft &
recipient site
like blood as hematoma, serous fluid
as seroma, or pus.
b.
Absence of optimal tension
either in
excessive tension
that result in tenting of graft over
concave shape wound, or
loose graft
with folding
that result in facing of its inner surfaces together.
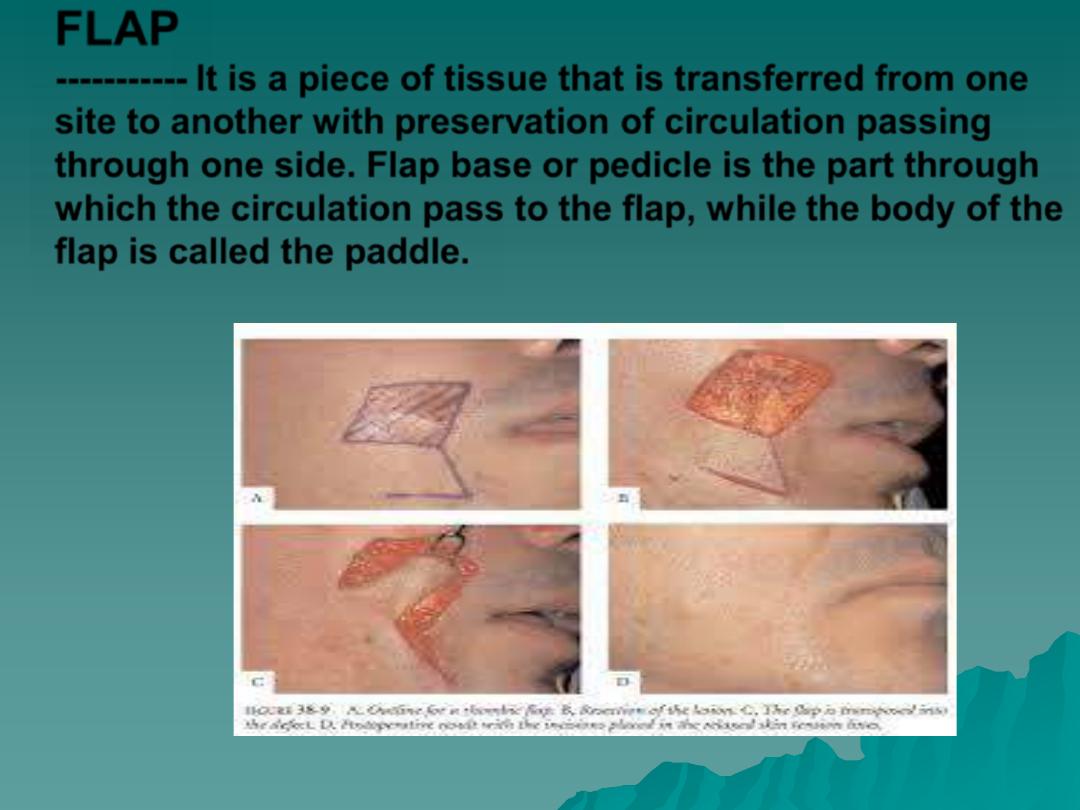
FLAP
----------- It is a piece of tissue that is transferred from one
site to another with preservation of circulation passing
through one side. Flap base or pedicle is the part through
which the circulation pass to the flap, while the body of the
flap is called the paddle.
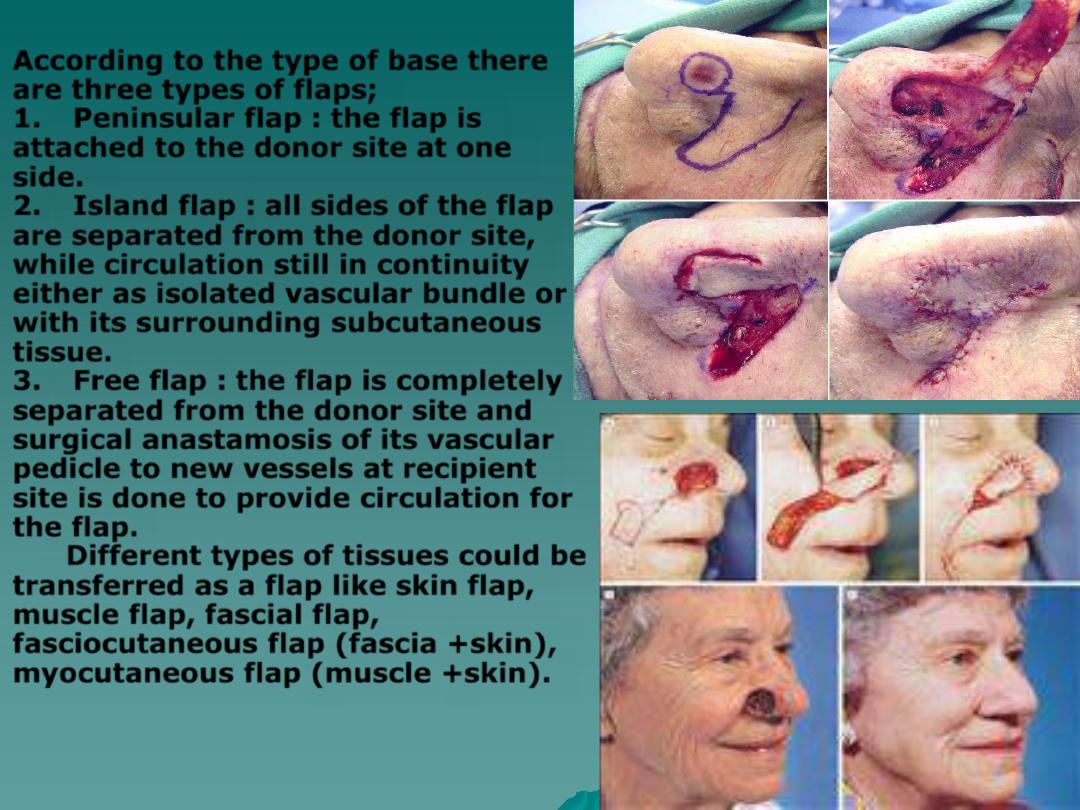
◆
According to the type of base there
are three types of flaps;
1.
Peninsular flap
: the flap is
attached to the donor site at one
side.
2.
Island flap
: all sides of the flap
are separated from the donor site,
while circulation still in continuity
either as isolated vascular bundle or
with its surrounding subcutaneous
tissue.
3.
Free flap
: the flap is completely
separated from the donor site and
surgical anastamosis of its vascular
pedicle to new vessels at recipient
site is done to provide circulation for
the flap.
Different types of tissues could be
transferred as a flap like skin flap,
muscle flap, fascial flap,
fasciocutaneous flap (fascia +skin),
myocutaneous flap (muscle +skin).
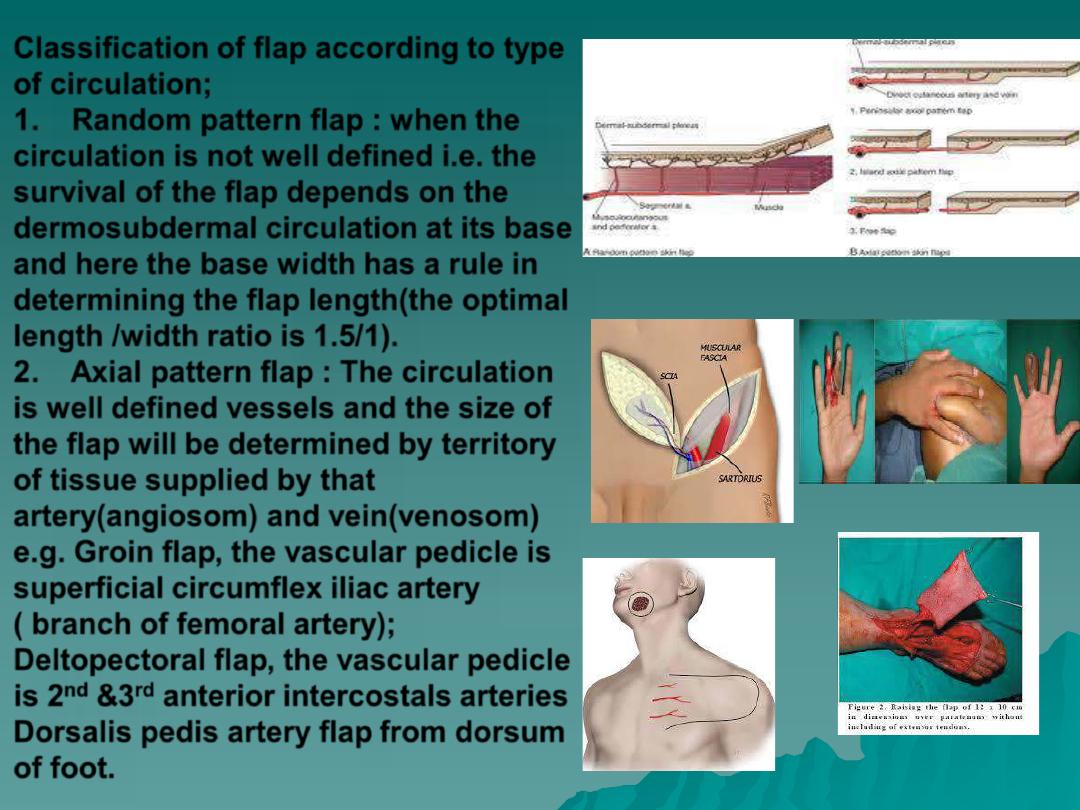
Classification of flap according to type
of circulation;
1.
Random pattern flap
: when the
circulation is not well defined i.e. the
survival of the flap depends on the
dermosubdermal circulation at its base
and here the base width has a rule in
determining the flap length(the optimal
length /width ratio is 1.5/1).
2.
Axial pattern flap
: The circulation
is well defined vessels and the size of
the flap will be determined by territory
of tissue supplied by that
artery(angiosom) and vein(venosom)
e.g.
Groin flap
, the vascular pedicle is
superficial circumflex iliac artery
( branch of femoral artery);
Deltopectoral flap
, the vascular pedicle
is 2
nd
&3
rd
anterior intercostals arteries
Dorsalis pedis artery flap
from dorsum
of foot.
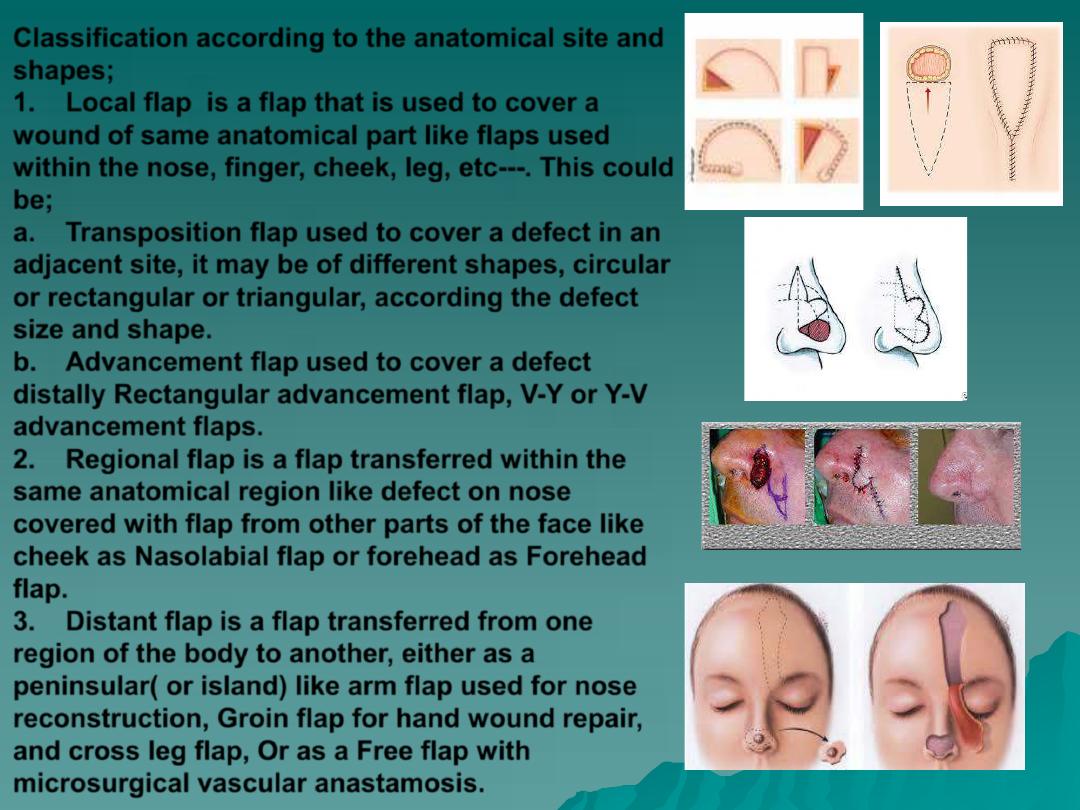
Classification according to the anatomical site and
shapes;
1.
Local flap
is a flap that is used to cover a
wound of same anatomical part like flaps used
within the nose, finger, cheek, leg, etc---. This could
be;
a.
Transposition flap
used to cover a defect in an
adjacent site, it may be of different shapes, circular
or rectangular or triangular, according the defect
size and shape.
b.
Advancement flap
used to cover a defect
distally Rectangular advancement flap, V-Y or Y-V
advancement flaps.
2.
Regional flap
is a flap transferred within the
same anatomical region like defect on nose
covered with flap from other parts of the face like
cheek as Nasolabial flap or forehead as Forehead
flap.
3.
Distant flap
is a flap transferred from one
region of the body to another, either as a
peninsular( or island) like arm flap used for nose
reconstruction, Groin flap for hand wound repair,
and cross leg flap, Or as a Free flap with
microsurgical vascular anastamosis.
Indications for use of flaps;
1.
Cover of wounds that are not suitable for graft
“
take
”
like exposed bone or cartilage or irradiated
wounds.
2.
Provide a good cover that facilitate another surgery
e.g. bone graft or tendon repair or graft.
3.
Reconstruction of anatomical loss as built of lost
part of lip, nose, eyelids, ears, scalp, etc---.
4.
Functional replacement Temporalis and masseter
muscles transfer used for animation of face in
facial(CN7) palsy.
5.
Treatment of infection muscle flap are used for
covering an exposed bone with osteomyelitis.
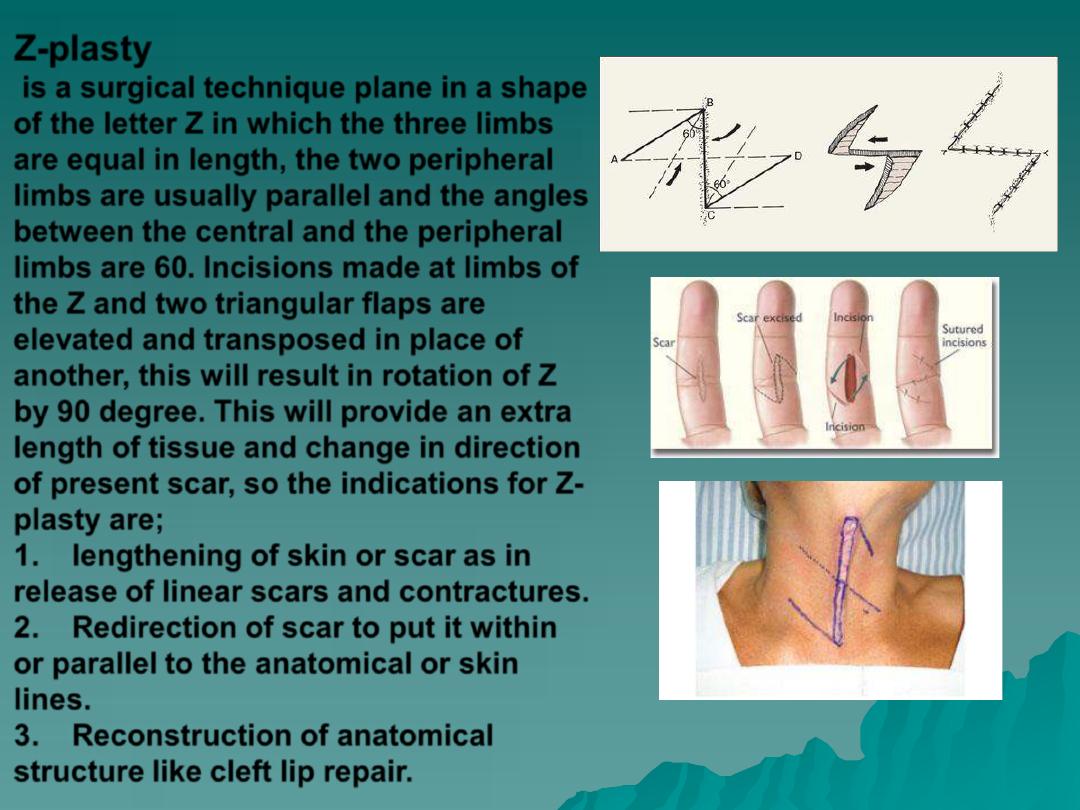
Z-plasty
is a surgical technique plane in a shape
of the letter Z in which the three limbs
are equal in length, the two peripheral
limbs are usually parallel and the angles
between the central and the peripheral
limbs are 60. Incisions made at limbs of
the Z and two triangular flaps are
elevated and transposed in place of
another, this will result in rotation of Z
by 90 degree. This will provide an extra
length of tissue and change in direction
of present scar, so the indications for Z-
plasty are;
1.
lengthening of skin or scar
as in
release of linear scars and contractures.
2.
Redirection of scar
to put it within
or parallel to the anatomical or skin
lines.
3.
Reconstruction of anatomical
structure
like cleft lip repair.
