
TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
(THA)
Fifth Year Orthopedic Lecture
Dr. Omar I. Mahmood

INTRODUCTION
•
Hip replacement .. known as “Arthroplasty
”
.
…
is a reconstructive surgery involves
replacement of hip joint by a prosthesis to restore motion , function and relieve pain.
• Hip replacement surgery can be either :
•
Total HIP arthroplasty
: replacing both the acetabulum and the femoral head.
•
Hemiarthroplasty
: replacing only femoral head
HISTORY
• 1940 Austin Moore performs first metallic hip replacement surgery
(hemiarthroplasty)
• 1960s Sir John Charnley introduces concept of low friction arthroplasty
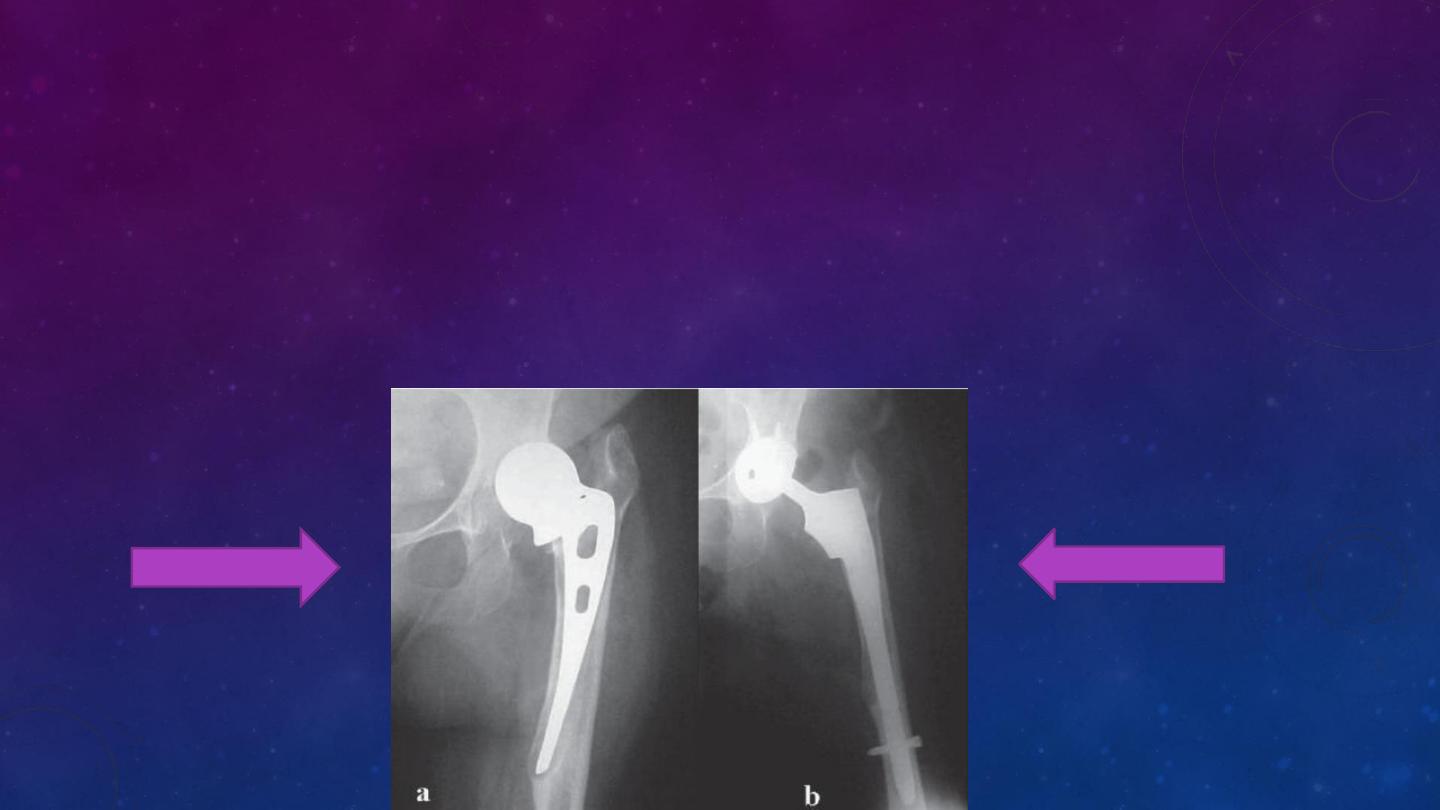
Austin moore charnley TH design

INDICATIONS
1. patients with sever pain and irreversibly damaged joints
• Severe Hip osteoarthritis
• Rheumatoid arthritis
2. femoral neck fracture in elderly patients above 70s
3. Failure of previous reconstructive surgery ( osteotomy, femoral neck fracture complication – non union)
4. avascular necrosis of femoral head
5. Congenital hip diseases … DDH at 40 – 50 years old
6. Pathologic fractures of femoral neck from metastatic cancer
7. joint instability.

IMPLANTS
prosthetic implant used in hip replacement consist of different part.
1.
The acetabular cup
• Cemented .. Cement act as grout between bone and stem
• Uncemented ( press fit ) .. Biological fixation .. use friction, shape and surface coating to stimulate bone to bond to the
implant
2.
The femoral component
• Cemented .. use acrylic bone cement to form a mantle between the stem and the bone for initial and long term stability
• Uncemented ( press fit )… use friction, shape and surface coating to stimulate bone to bond to the implant.
3.
The articular interface .. Bearing surface
• Metal -Polyethylene : (cobalt-chrome) femoral head on polyethylene acetabular liner
• Metal – metal : (cobalt-chrome) femoral head and acetabular liner
• Ceramic – ceramic … ceramic femoral head and liner
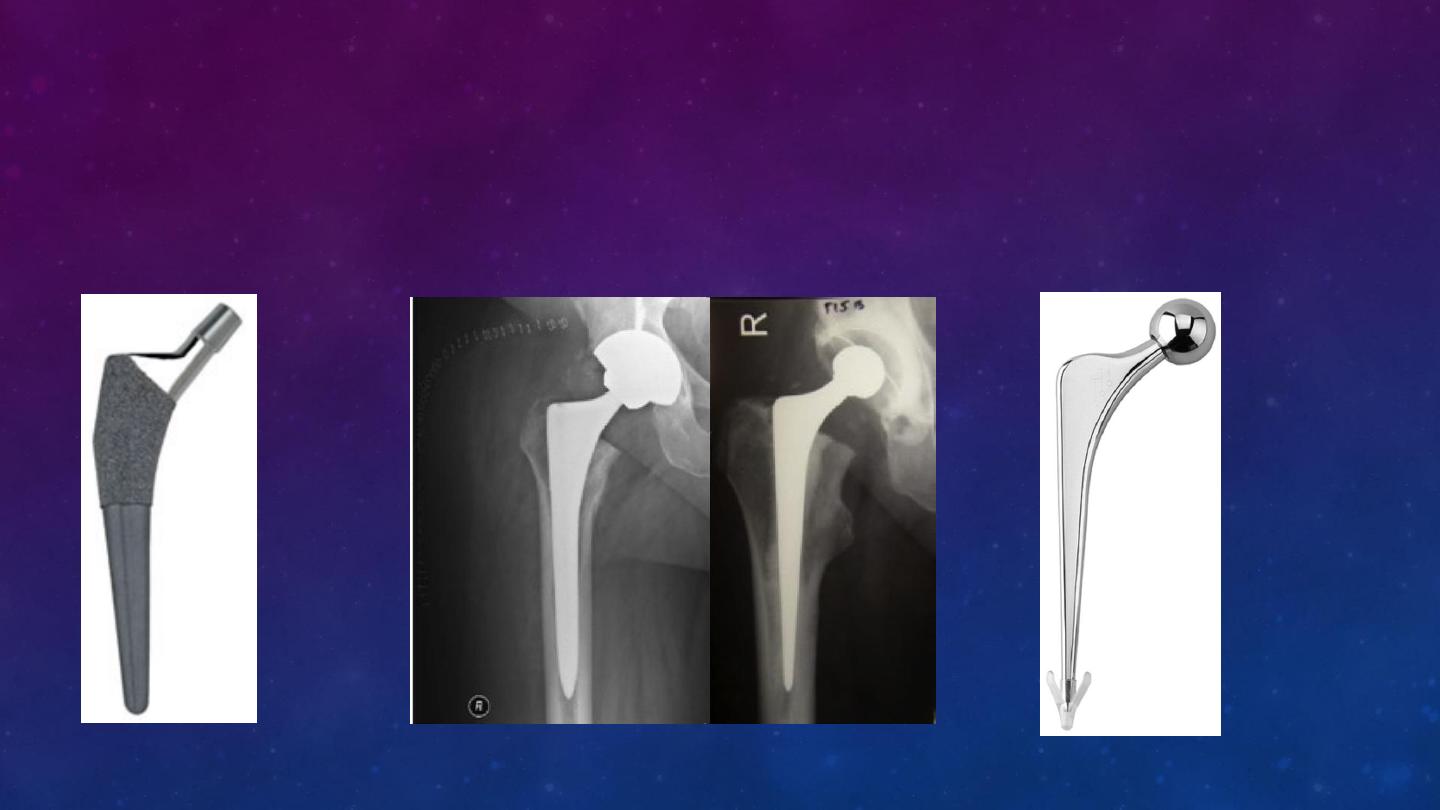
FEMORAL STEM
Uncemented ( press fit )
Cemented

BEARING SURFACE

APPROACHES
1.
Posterior (Moore)
:- The posterior (Moore or Southern) approach accesses the joint and capsule
through the back, taking piriformis muscle and the short external rotators off the femur.
1.
Lateral (Hardinge )
:- The approach requires elevation of the hip abductors (gluteus medius and gluteus
minimus) to access the joint
2.
Antero-lateral (Watson-Jones)
:- develops the interval between the tensor fasciae latae and the
gluteus medius.
1.
Anterior (Smith-Petersen):-
The anterior approach uses an interval between the sartorius muscle and
tensor fascia latae.

POST OPERATIVE CARE
Appropriate position After Hip Arthroplasty to prevent dislocation
a) Patient is usually positioned supine in bed
b) The affected extremity is held in slight abduction by either abduction splint or pillow or Buck’s
extension traction to prevent dislocation of the prosthesis.
c) Avoid acute flexion of the hip.
d) patient must not adduct or flex the operated hip

PATIENTS EDUCATION
1. wear elastic stockings after discharge until full activities are resumed.
2. avoid excessive hip adduction, flexion and rotation for 6 weeks after hip arthroplasty
3. Avoid sitting low chair or toilet …. avoid flexing hip > 90º
4. Keep knees apart :- do not cross leg.
5. Limit sitting to 30 minutes at a time – to minimize hip flexion
6. Avoid internal rotation of the hip.

COMPLICATIONS
• Vein thrombosis
• Pulmonary embolism
• Dislocation
• Infection
• Osteolytis
• Metal sensitivity
• Metal toxicity
• Sciatic or femoral Nerve palsy
• Chronic pain
•
length inequality
