BASIC PRINCIPLES IN PLASTIC SURGERY(Surgical flaps)
Dr.YASIR NAIF QASSIM ,F.I.B.M.S(plastic & reconstructive)
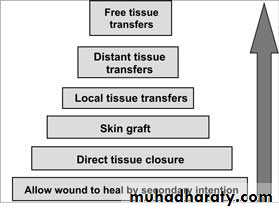
Reconstructive ladder
Surgical flaps:
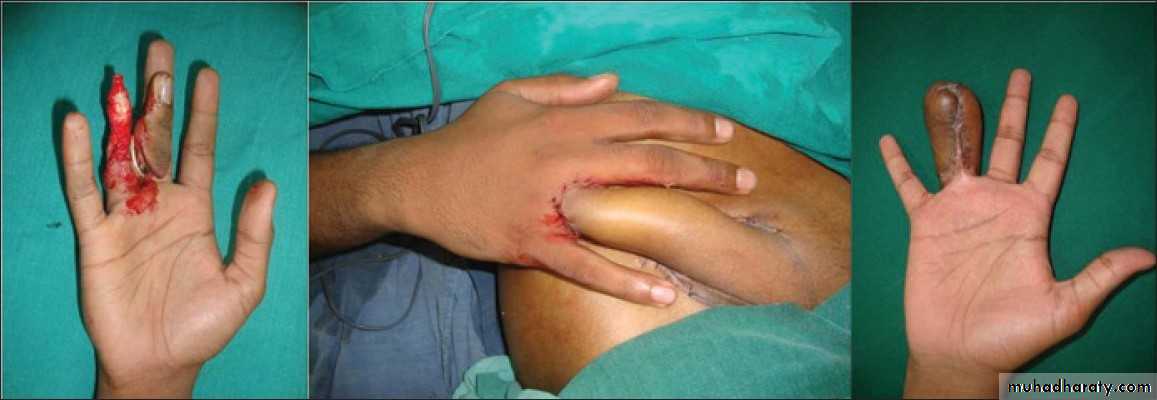
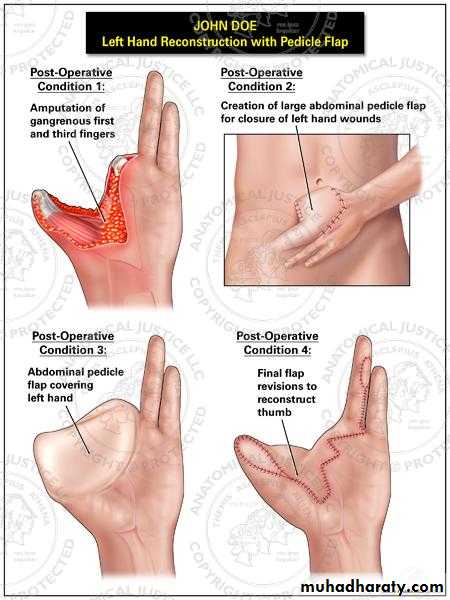
A flap is a segment or unit of tissue that has its own blood supply.Indications
1.Covering recipient beds that have poor vascularity(e.g. denuded bone,denuded cartilage,denuded tendon,…etc).2.Covering vital structures(exposed nerves,exposed major vessels…etc).
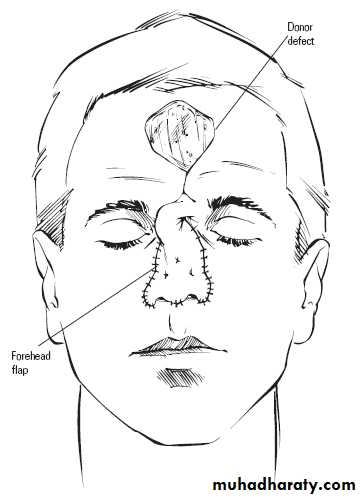
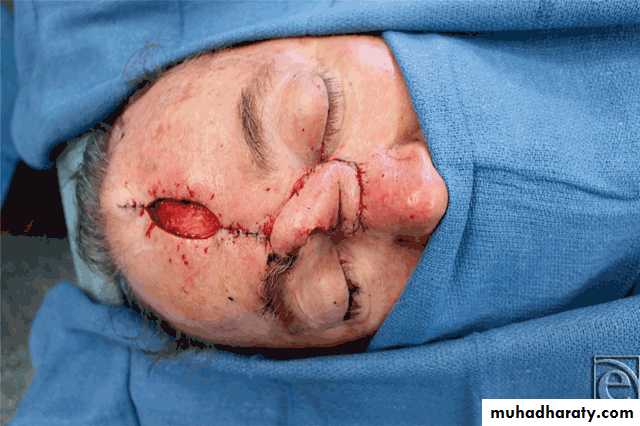
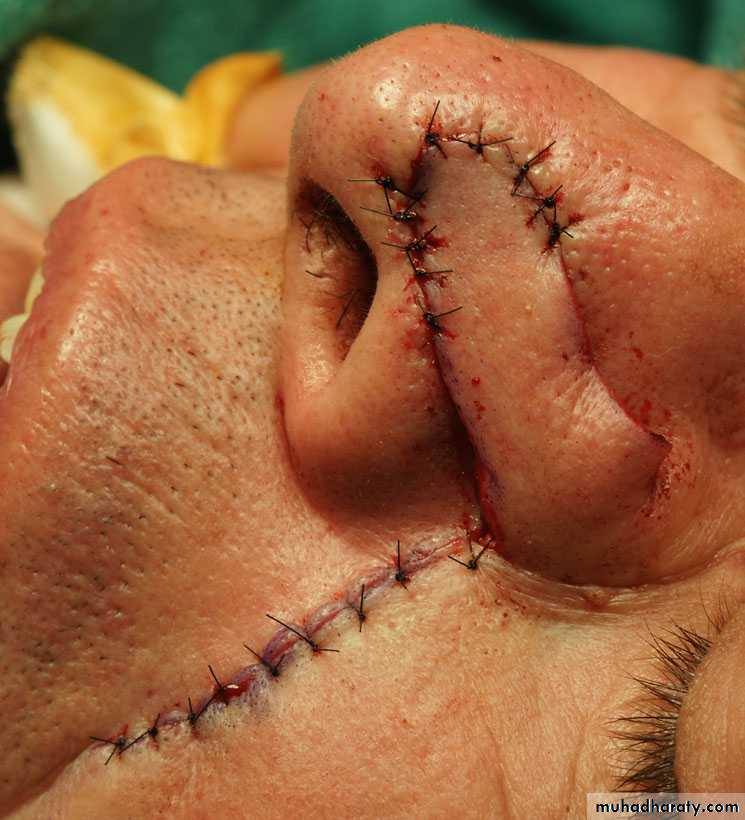
3.Reconstructing the full thickness defects of eyelids, lips, ears, nose, and cheeks.
4.Padding body prominences.
5.When it may be necessary to operate through the wound at a later date to repair underlying structures.
6.providing a functional motor unit using muscle flaps.
7.Providing sensation using sensate flap.
8.controlling infection in the recipient area(e.g.in chronic O.M.).
Classification
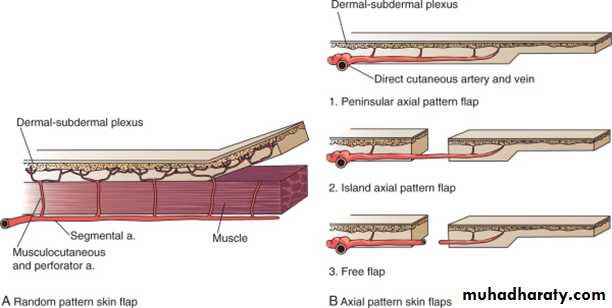
I-ACCORDING TO BLOOD SUPPLY
A.Random flaps.B.Axial flaps.
• 1.Peninsular axial flaps.
• 2.Island axial flaps.
3.Free flaps.
Random & Axial flaps
RandomAxial
II.ACCORDING TO LOCATION
1.Local flaps.2.Regional flaps.
3.Distant flaps.
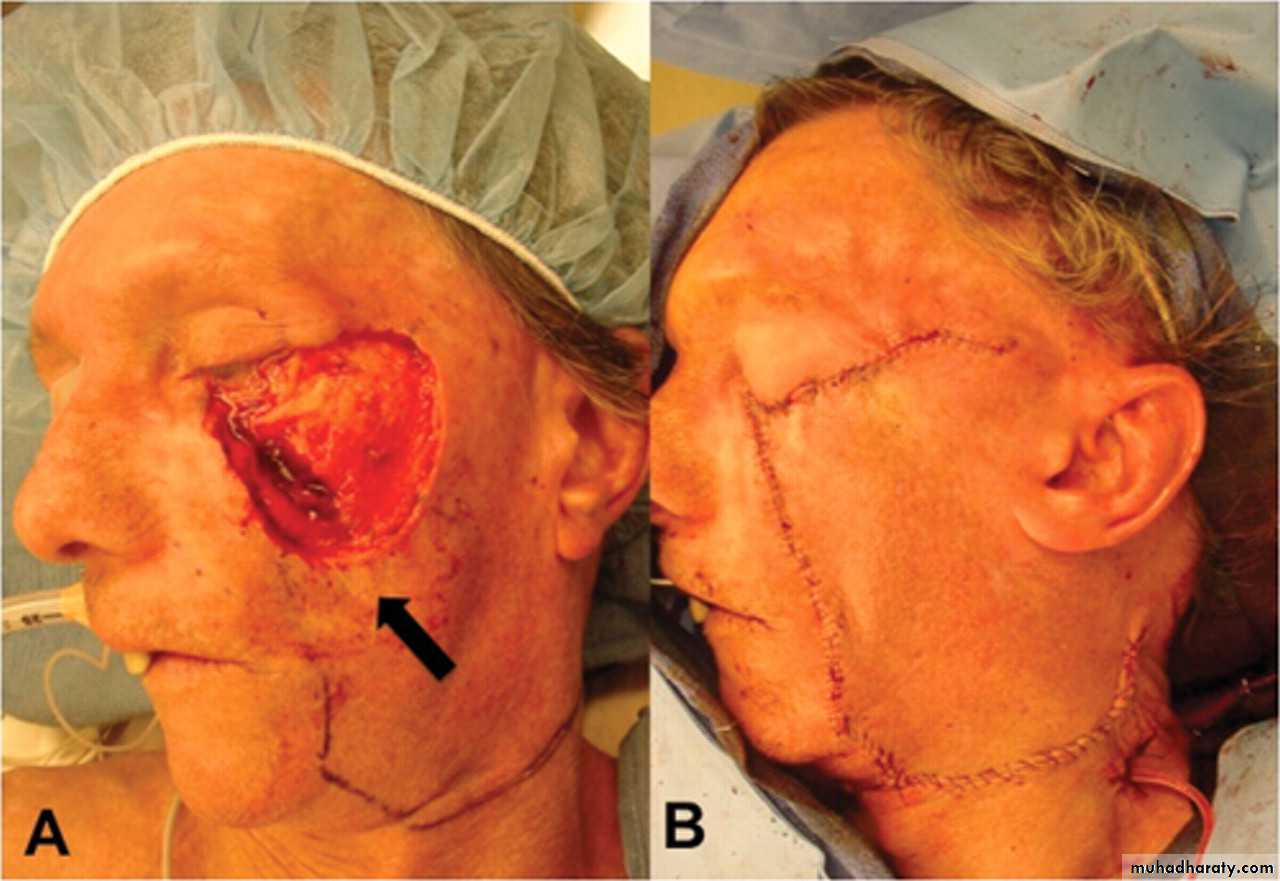
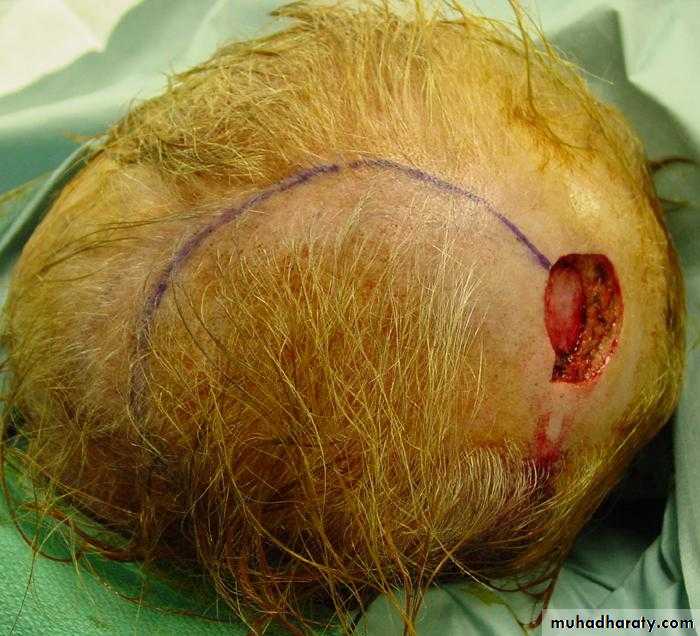
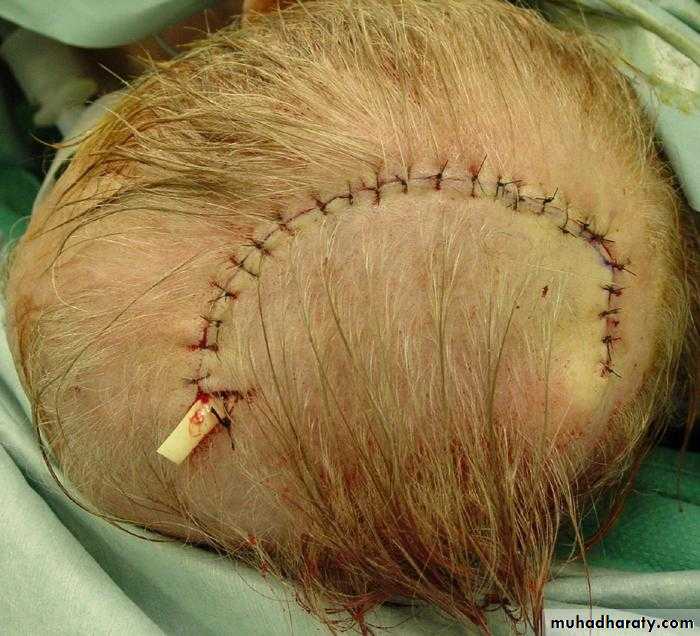
Local flaps
Regional flaps
Distant flaps
• III.ACCORDING TO THE WAY OF MOVEMENT
A.Pivotal flaps:1-Rotational flaps.
2-Traspositional flaps.
3-Interpolational flaps.
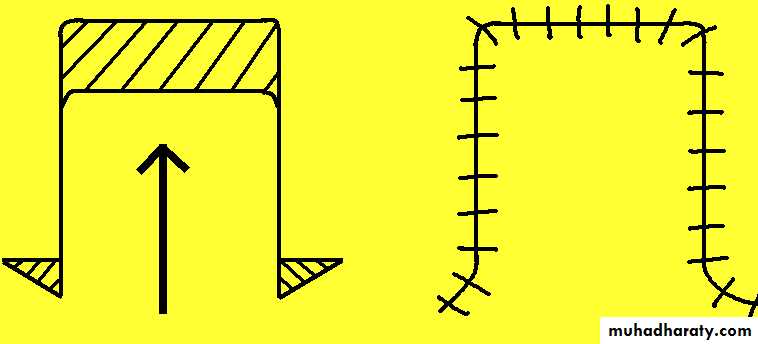
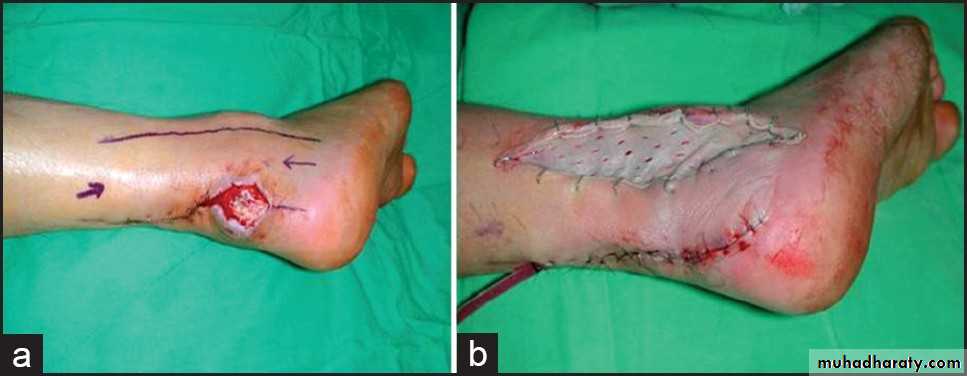
B.Advancement flaps.
Pivotal rotational flaps:
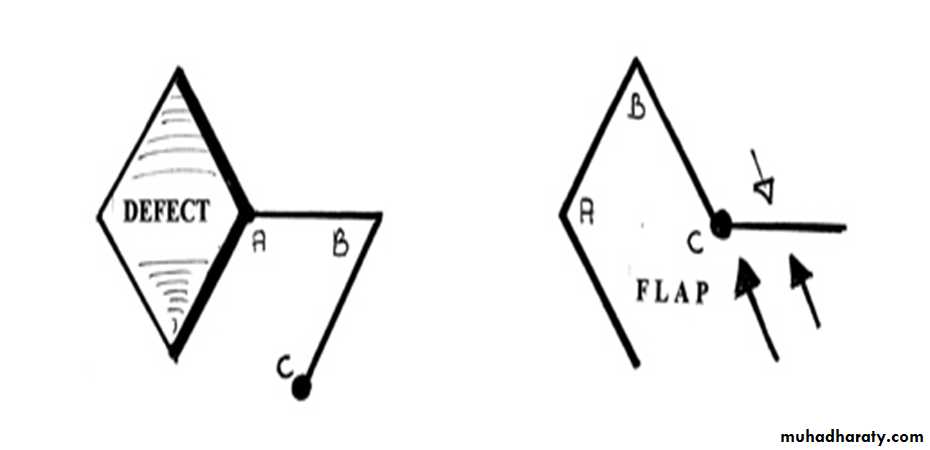
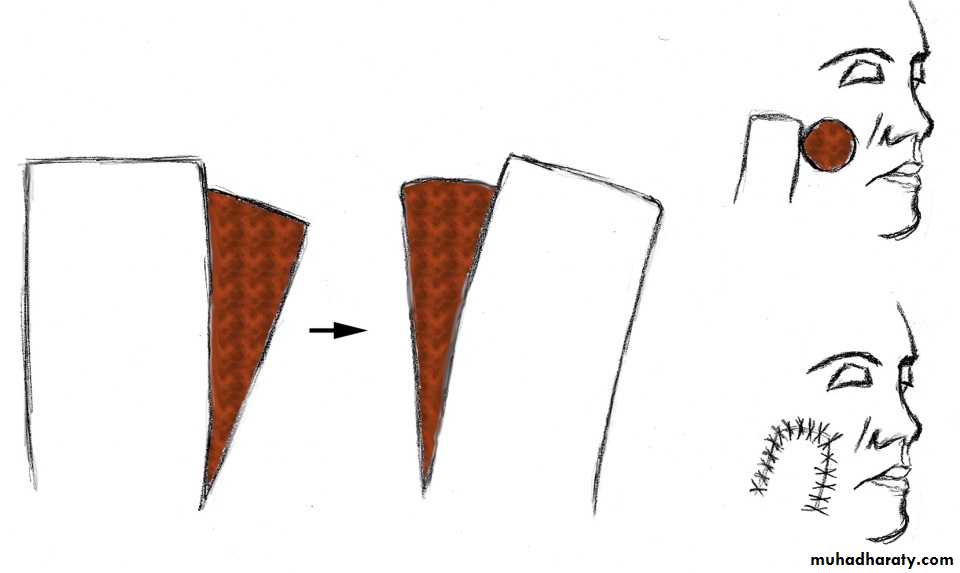
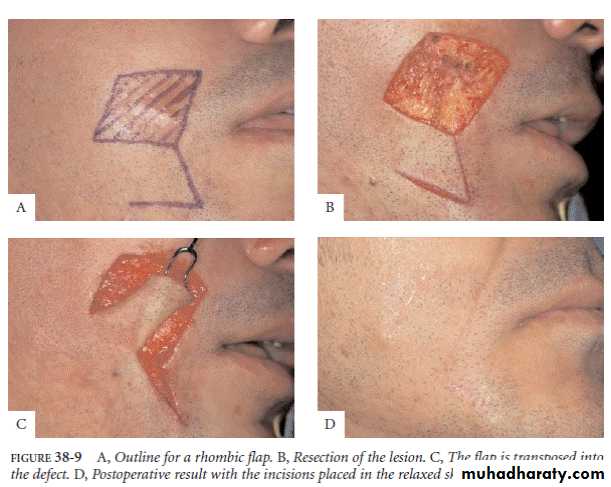
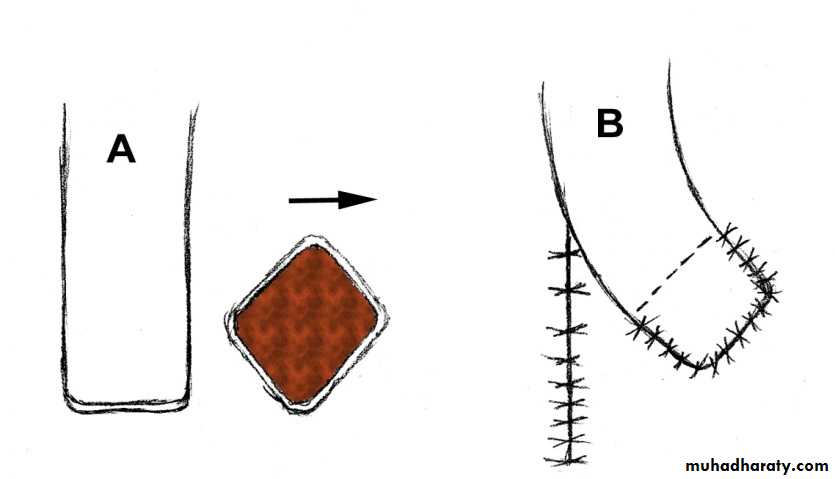
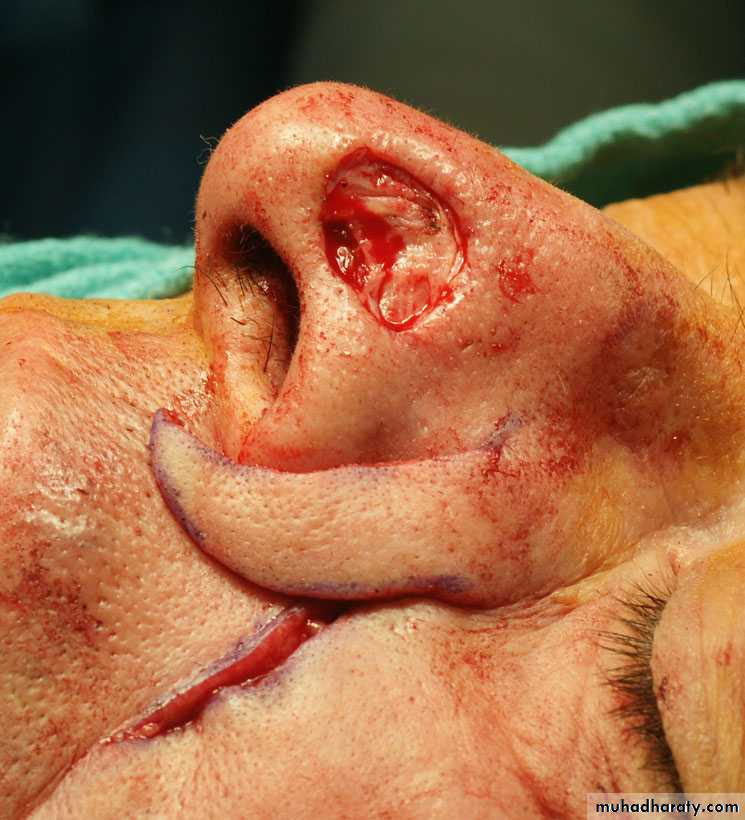
Pivotal transpositional flaps:
Pivotal interpolated flaps:
Advancement flap(Single-pedicle)
Advancement flap(bipedicle)
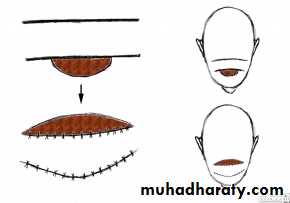
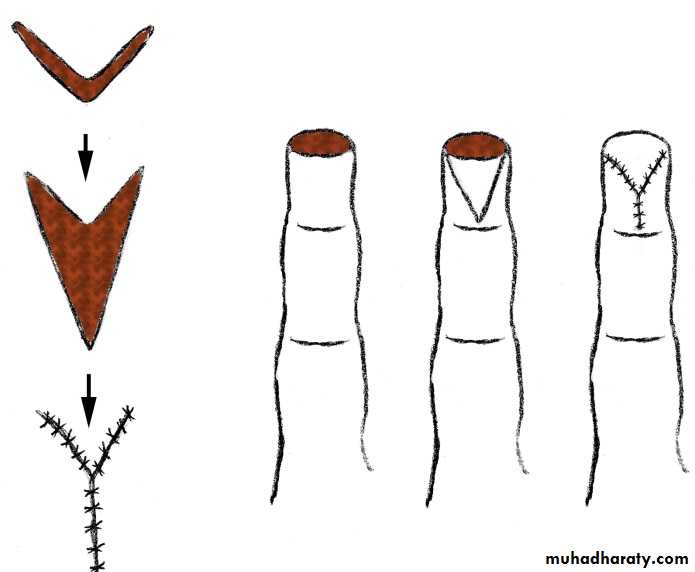
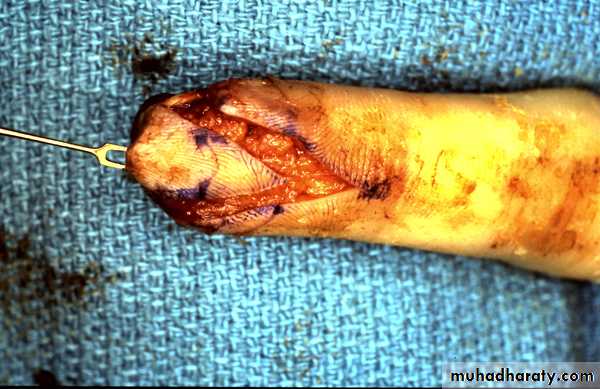
V-Y advancement flap
• IV.ACCORDING TO TISSUE CONTAINED(COMPOSITION):
• Skin flap (skin+superficial fascia).• Fascia flap e.g. Serratus fascia flap
• Fasciocutaneous (skin +superficial fascia+deep investing
• fascia)
• Muscle flap e.g.temporalis muscle flap.
• Bone flap e.g. Fibula flap
• Myocutaneous flap(skin+fascia+muscle).
• Osseomyocutaneous(skin+fascia+muscle+bone).
•
FLAP MONITORING
• 1. Clinical evaluation is the best method of assessment.• 2.Doppler studies.
• 3.Fluorescein dye study.
• 4.Sensors for O2, pH, temperature.
Factors leading to flap necrosis
• 1.Haematoma collection beneath the flap.• 2.Tight suturing.
• 3.Tight dressing.
• 4.Kinking of flap pedicle.
• 5.Cool ambient.
• 6.Nicotine,caffeine & other vasoconstrictive
• agents.
• 7.Technical errors.
•
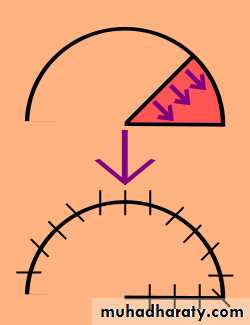
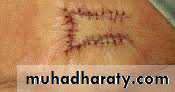
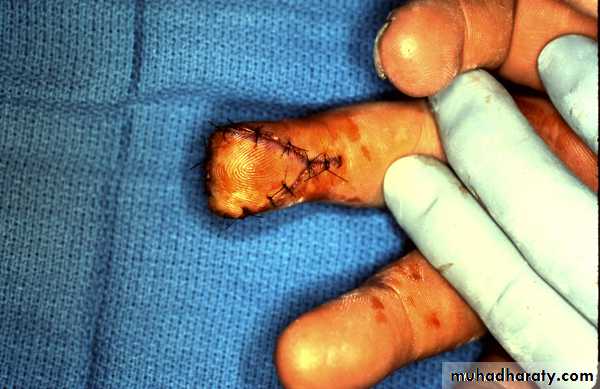
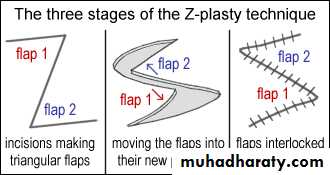
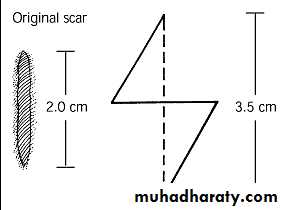
Z-PLASTY
• Is a technique in which two triangular flaps are transposed and interdigitated with each other to revise and redirect existing scars or to provide additional length in the setting of scar contracture.
•