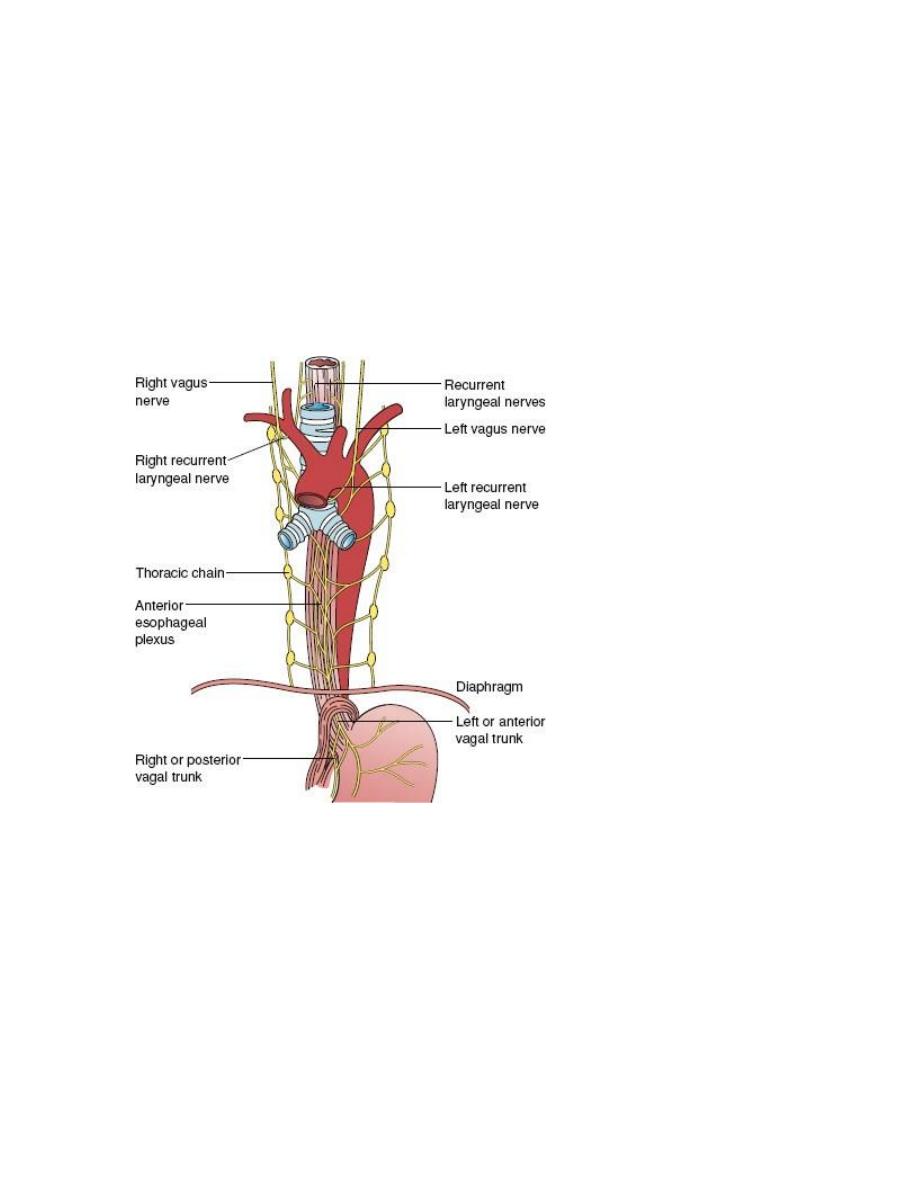
The esophagus
Objactives
1. what are the symptoms of the esophagueal diseases?
2. what are the types of dysphagia?
3. patient had a history of CVA present with inability to swallow the
bolus of food, what is the type of dysphagia
?
Evaluation of oesophageal diseases
Symptoms:-
The clinical history is extremely important in the diagnosis of oesophageal dis. Heart
burn ,dysphagia,and odynophagia virtually always indicate a primary disorder.
a. heart burn (pyrosis):- is the feeling of substernal burning ,often radiating to the
neck, caused by reflex of acidic (or rarely alkaline) material into the oesophagus ,
it is highly specific for gastro esophageal reflux disease. produce retrosternal
chest pain radiating to the neck, back or to the side of the chest, exaggerated by
bending down and relieved by drinking soda, antacid and diagnosed by (Bernstein
test), introduction of hyperosmotic solution or diluted hydrochloric acid (0.1N)
into the esophagus.
b. Dysphagia:- difficulties in swallowing may arise from problem in transferring
the food bolus from the oropharynx to the upper oesophagus or from impaired

transport of the bolus through the body of the esophagus.(esophageal
dysphagia),it may occur by obstruction of passage of food bolus from the mouth
also.
c. Aphagia complete obstruction which is medical emergency.
d. Non cardiac chest pain: it is a must to exclude cardiac cause before consideration
of esophageal disease as a cause of non cardiac chest pain.it may be caused by
GERD which relieved by PPI ingestion , diffuse esophageal spasm(DES) which
relieved by smooth muscle relaxant , esophageal hypersensitivity syndrome which
is relieved by antidepressant drugs many patients may have psychiatric
abnormalities, and peri esophageal content may be a cause also.
e. Odynophagia: painful swelling.
f. Regurgitation effortless appearance of esophageal or gastric contents in the
mouth.it may result in chronic cough, laryngitis, and laryngeal aspiration. Water
brash is reflux salivary hyper secretion that occur in response to peptic esophagitis
must be differentiated from GERD.
g. Upper GIT bleeding
h. Weight loss
Causes of dysphagia in general
Oesophagitis:-
Reflux oesophagitis
Infective oesophagitis
Peptic oesophagitis
Erosive oesophagitis
Causes of oropharyngeal dysphagia:
Oropharyngeal mechanical dysphagia:
1. Wall defect-
Congenital as cleft palate and lips
Or post surgery.
2.intrinsic causes :
a. inflammatory-infectious, bullous diseases ,caustic, chemical or thermal.
b. webs
c. stricture.
tumours
.
3. extrinsic compression:
Thyroid, vertebral osteophytes, Zenker's diverticulum, abscess or mass
.
Oropharyngeal motor dysphagia
It may occur in conscious or un conscious patients
a. Neurological disorders: - brain stem lesion, mass lesion, pseudo bulbar pulsy,
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, poliomyelitis .
b. Neuromuscular junction diseases as myasthenia gravis ,eaton-lambert syndrome,
aminoglycoside drugs and others or botulism .
c. Muscular disorder:- myopathies, polymyositis or hypothyroidism
d. Motility disorders: - upper esophageal sphincter dysfunctions.
e. Cranial nerve diseases.
Causes of esophageal dysphagia
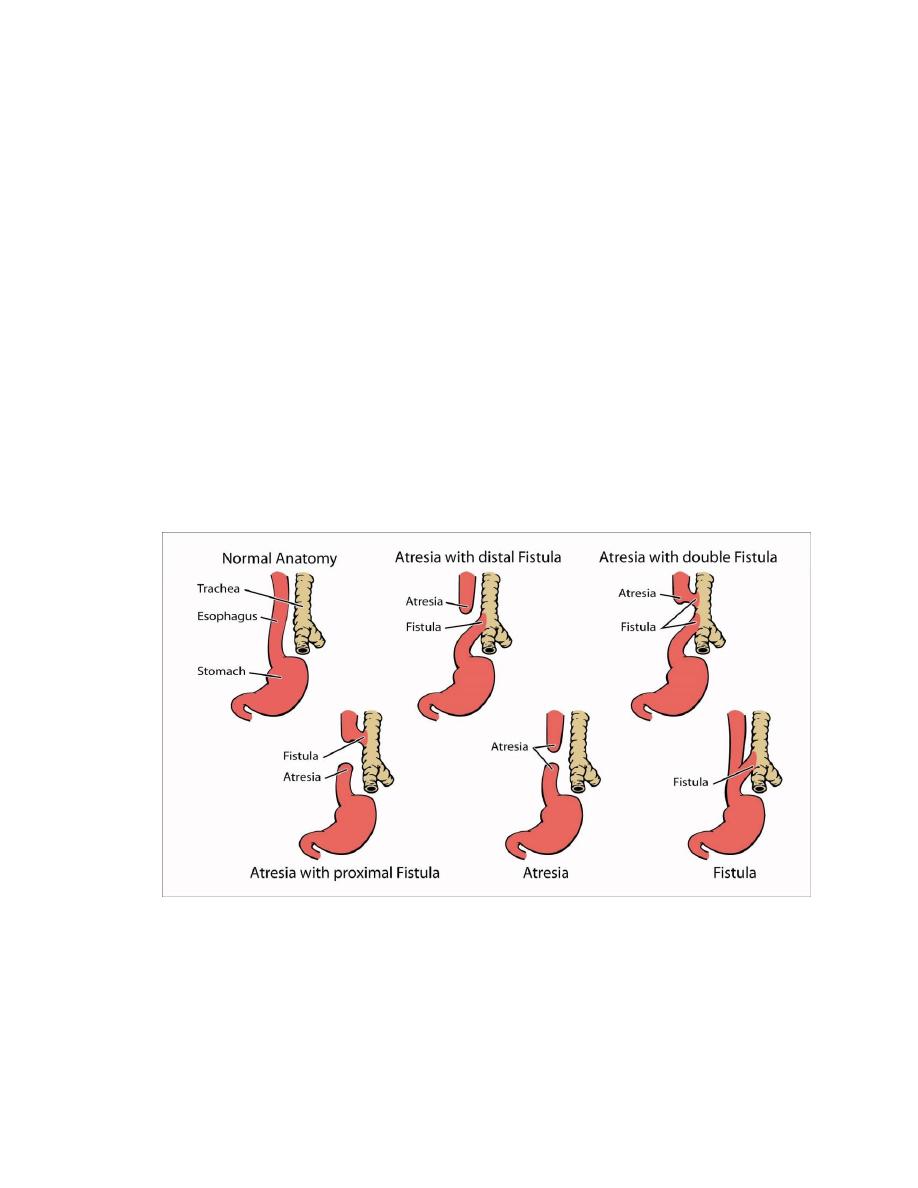
1.Congenital as tracheoesophageal fistula
2.Intrinsic narrowing
a. Inflammatory- infection.
b. webs, ring,
c. benign strictures
d. tumours
3.extrinsic compression
a. vascular compression(aberrant right subclavian artery, right sided aorta, left atrial
enlargement or aortic aneurysm)
b. post mediastinal mass.
c. post vagotomy hematoma or fibrosis
Causes clues
Mechanical obstruction solid foods worse than liquids
--Schatizki ring intermittent dysphagia; not progressive
--peptic stricture chronic heart burn; progressive dysphagia
--oesophageal CA progressive dysphagia; age more than 50 years
Motility disorders
--achalasia progressive dysphagia
--diffuse oesophageal spasm intermittent not progressive may have chest
pain
--scleroderma chronic heart burn; rhaynaud phenomenon.
Other causes:-
Chronic alcoholism
DM
Extrinsic compression (mediastinal tumor).
Psychiatric ex:-globus hystericus
Referances:
