Anatomy of skinByDr.Alaa NaifDec 07, 2020
Is the largest organ in the bodyFunction
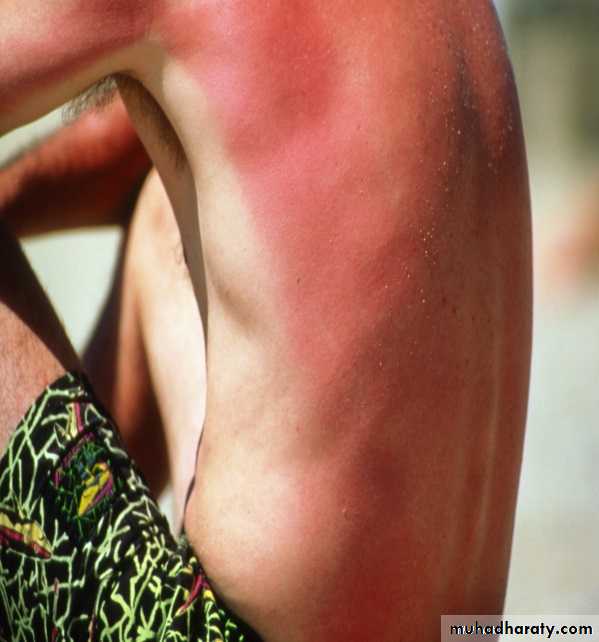
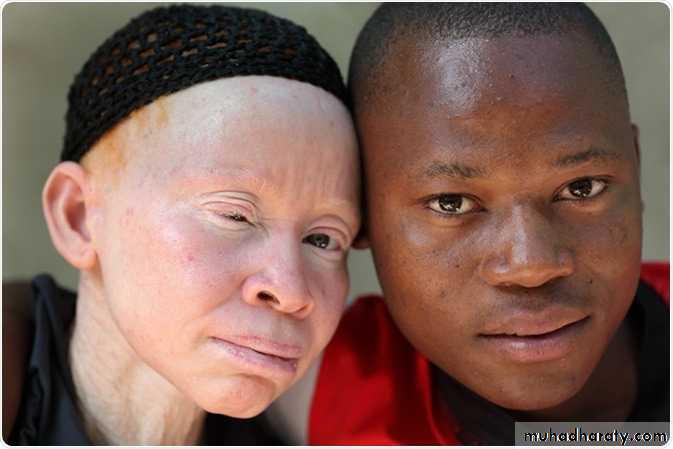
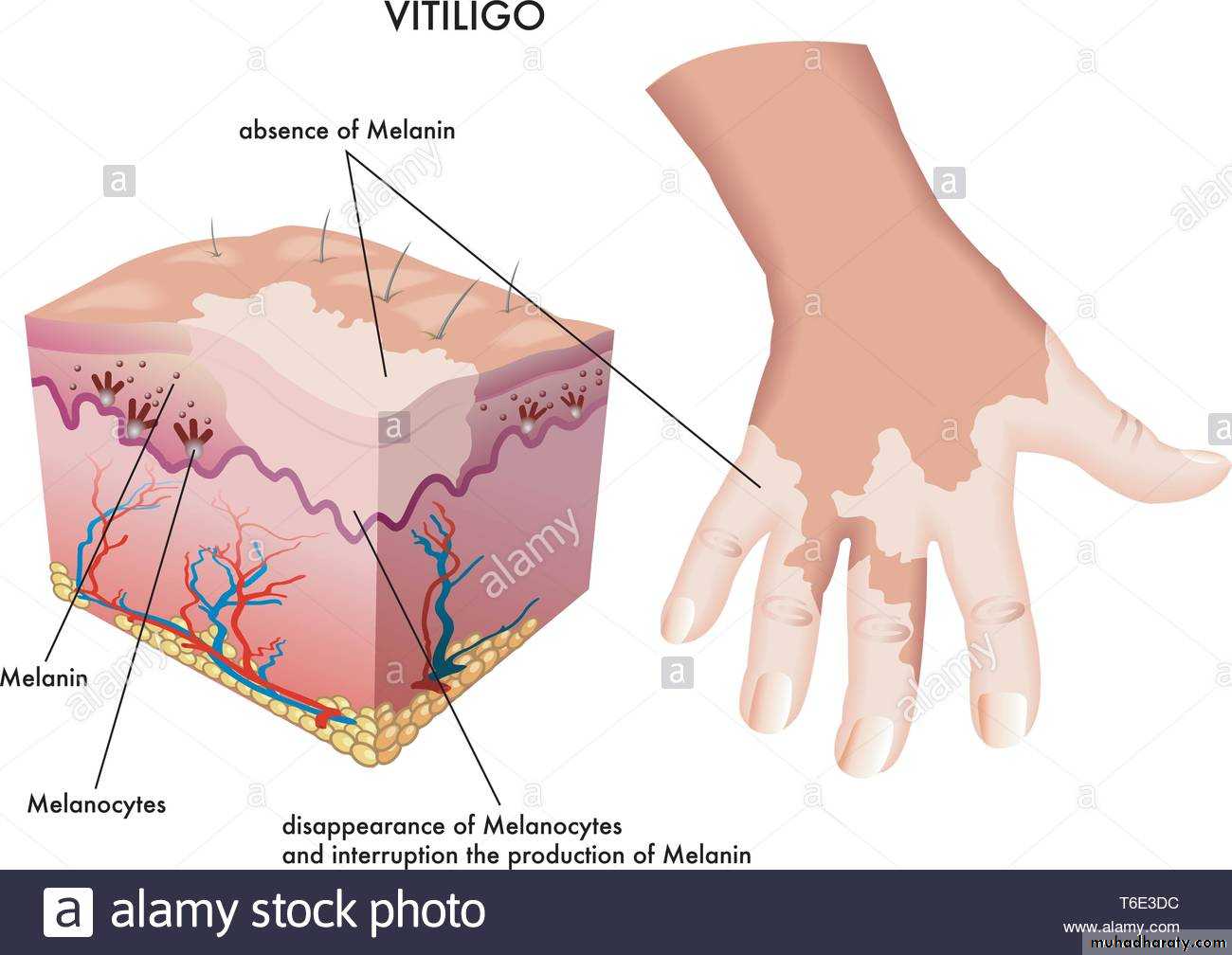
Photoprotection from skin cancer and sunburnAlbinism
(No melanin)are liable
to skin cancer and
sunburn
Barrier against microorganisms
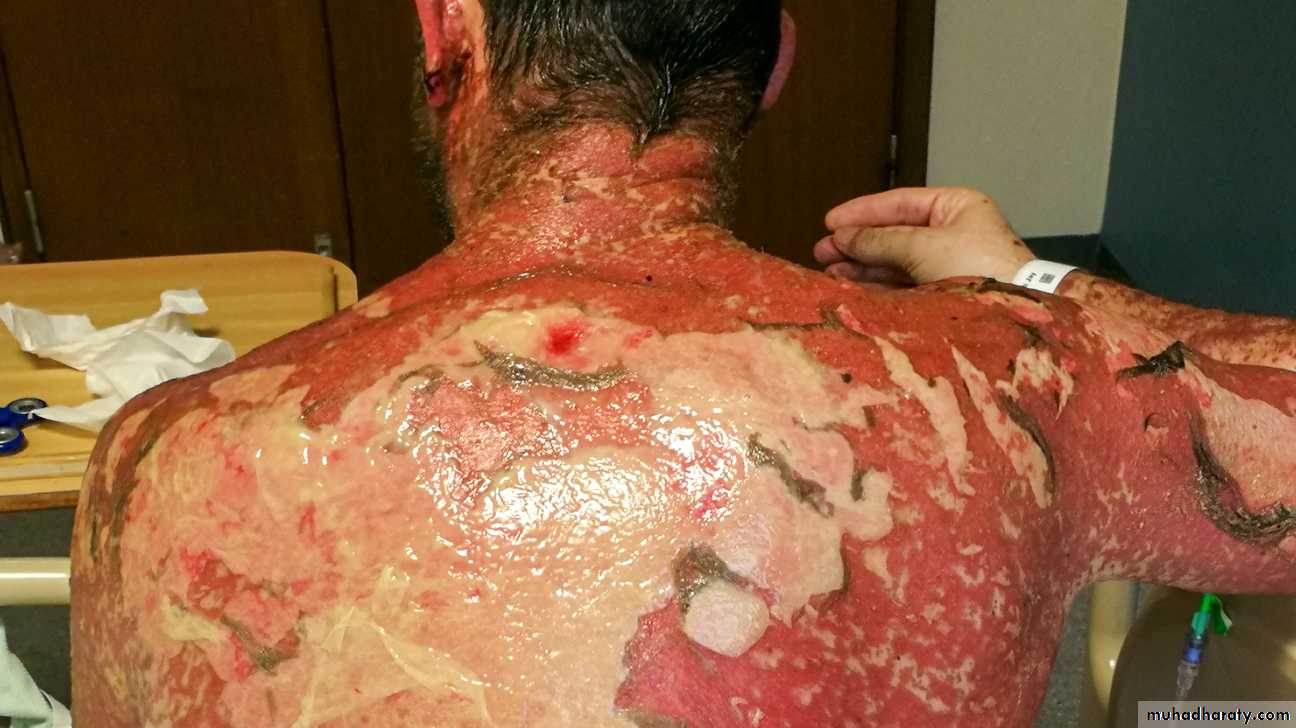
Steven Johnson syndrome
(sloughing of skin)
caused by drugs
liable to infection and
septicemia
Thermoregulation
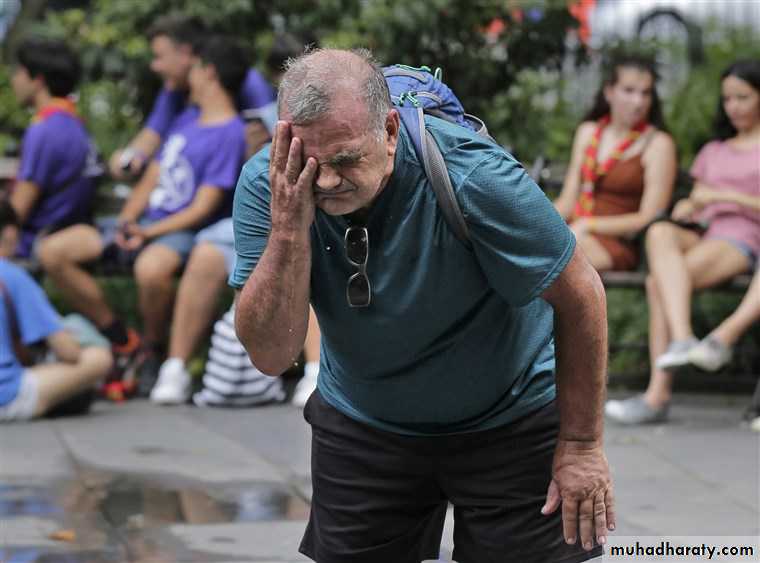
Ectodrmal dysplasia
(no sweat glands)Liable to heat stroke in hot weather
Vit D synthesis
Immunological protection
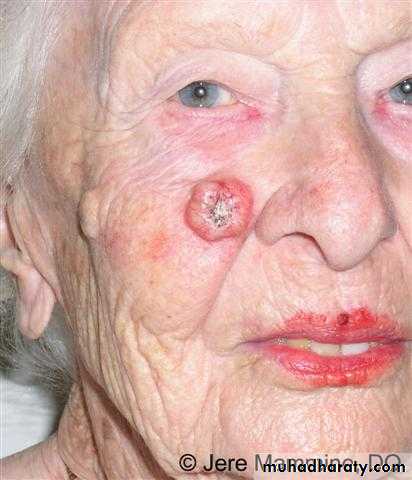
Renal transplant recipients
Liable to skin cancerBeauty organ
Sensory organ
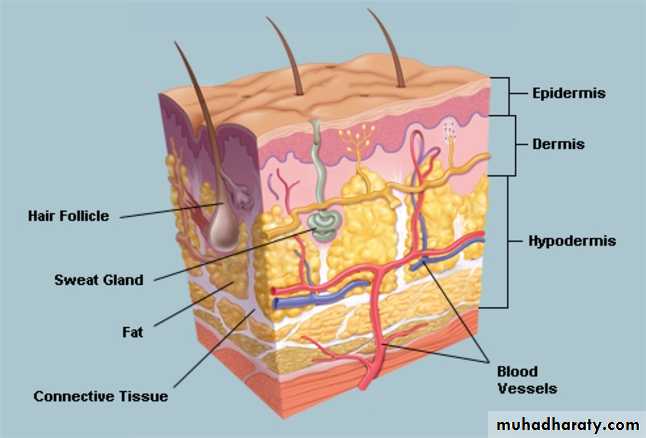
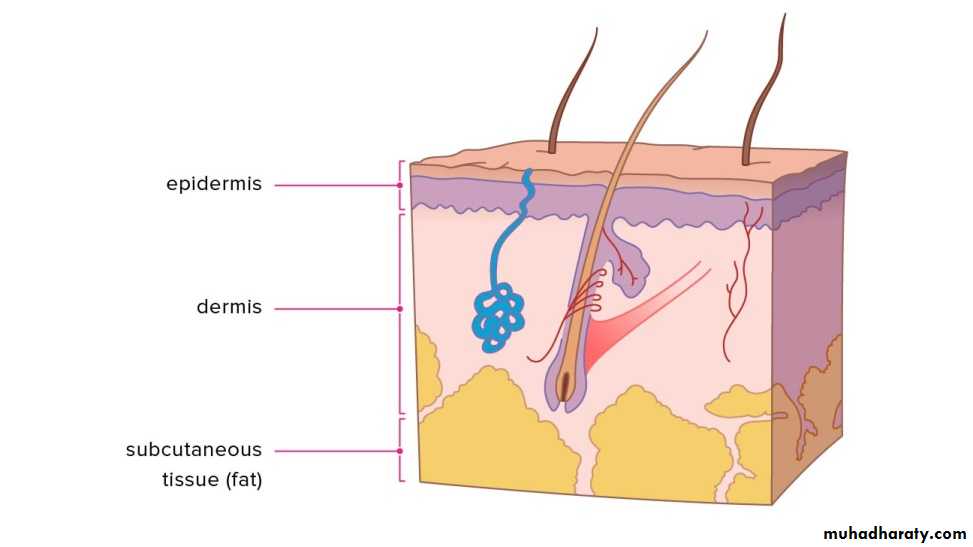
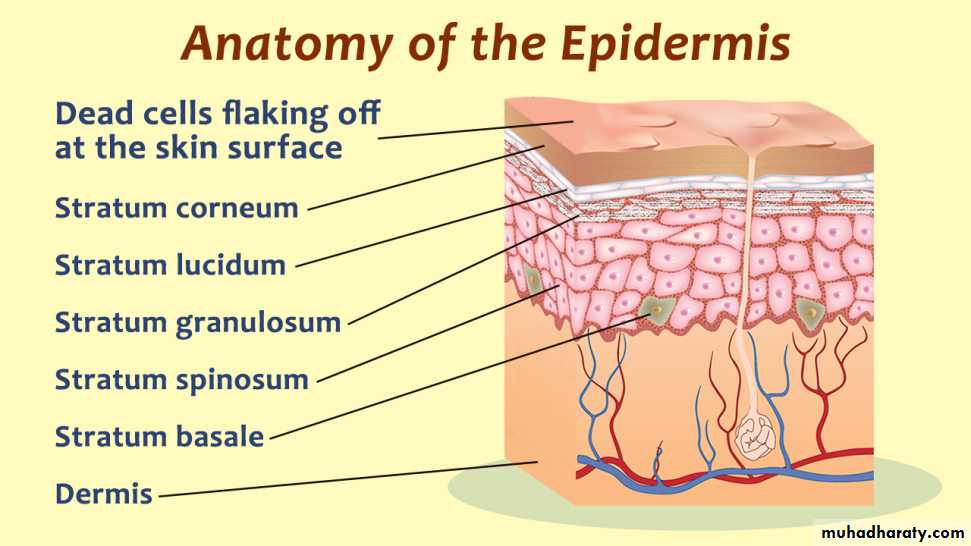
Skin is composed of three layers:
(1) Epidermis
(2) Dermis
(3) subcutaneous fat (panniculus)
There is considerable regional variation in the relative thickness of these layers
The epidermis is thickest on the palms and soles and thinnest on eyelids
The dermis is thickest on the backThe subcutaneous fat is thickest on the abdomen and buttocks
EpidermisComposed of:
(1) Keratinocytes
(2) Melanocytes(3) Langerhans cells
(4) Merkel cells
(5) Skin appendages
Keratinocytes
Ectodermal origin
Produce filamentous protein(keratin) that form a surface coat(stratum corneum) and is the structural protein of hair and nail
Mutation of this protein cause many diseases
Mutation of keratinEpidermolysis bullosa
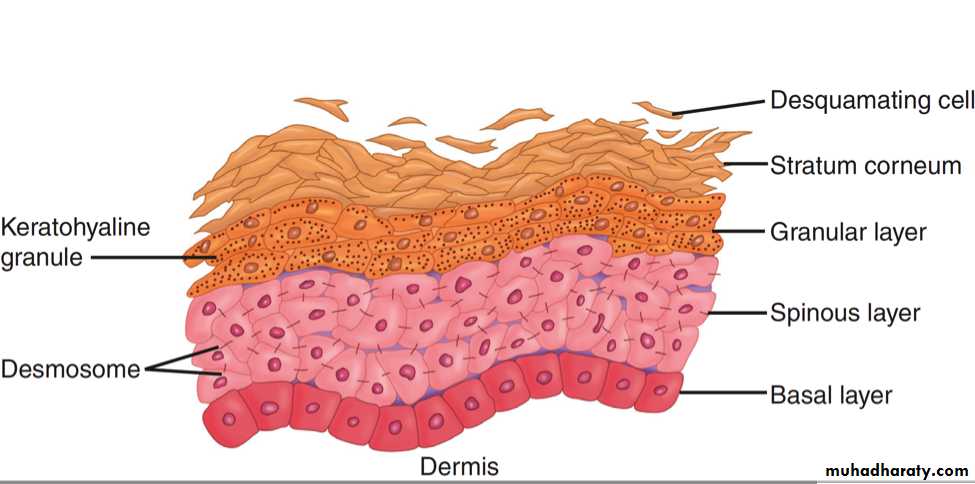
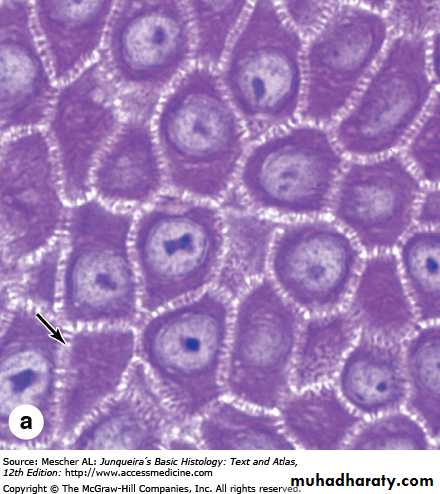
Keratinocytes are composed of many layers:
Basal layer(stratum basale)Stratum lucidum (on thick skin only)
Prickle layer(stratum spinosum)
Granular layer(stratum granulosum)
Horny layer(stratum corneum)
The horny layer is nonviable cells and does not have nuclei
Parakeratosis is when the horny layer keep their nuclei as in psoriasisHyperkeratosis is when the horny layer get thicker as in corn
Granular layer has keratohyalin granules
Stem cells provide a reservoir for regeneration of the epidermis located the deepest portions of the basal layer and hair bulgeKeratinocytes play an active role in the immune function and secrete a wide array of cytokines and inflammatory mediator
Keratinocytes are attached
to each other by bridges calleddesmosomes
Epidermal cell cycle
After the cells are produced by basal layer, they ascend and by reaching the surface they lose their nuclei and become corneocytes that are shed continuously as scales to be replace by new onesThis cycle take 4 week
This cycle is accelerated in ceratin diseases such as psoriasisMelanocytes
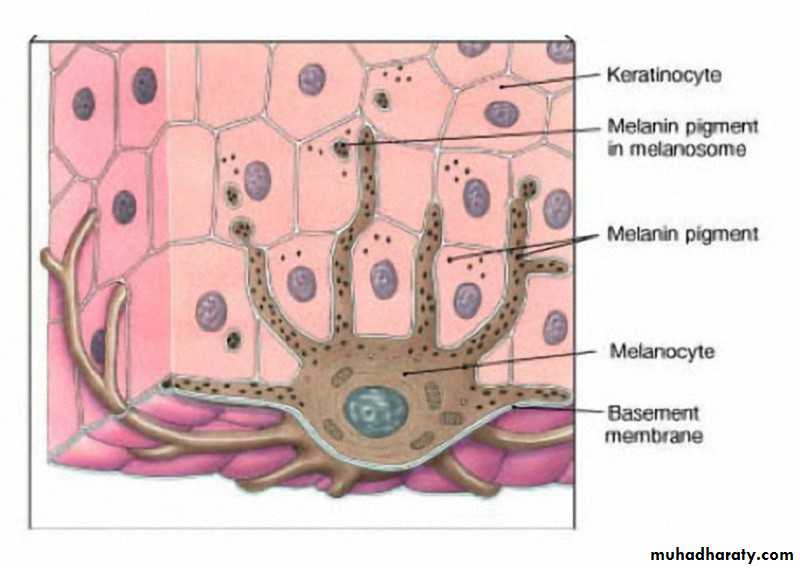
Are dendritic cell and derived from the neural crestReside in the basal layer at a frequency of about 1 in every 10 basal keratinocytes.
Face and genitalia and sun damaged skin has a higher density of melanocytesIncreased melanocytes
Decreased melanocytesRacial differences in skin color are not caused by differences in the number of melanocytes. It is caused by the number, size, and distribution of the melanosomes (pigment granules) within keratinocytes
Melanocytes in red-haired individuals produce more pheomelanin and in other skin type produce more eumelanin
Within keratinocytes, melanin typically forms a umbrella over the nucleus, functions principally as photoprotective
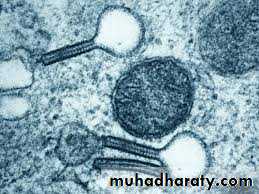
Langerhans Cells
Originte in bone marrow and found scattered among keratinocytes of the stratum spinosumCytoplasm contain Birbeck granules that appear as a tennis racquet
Responsible for the recognition, uptake, processing, and presentation of antigens to sensitized T lymphocytes (antigen presenting cells)
Merkel cell
Have neuroendocrine functionsFound in basal layer of epidermis
Skin appendagesApocrine glands
Eccrine glandsOpen into infundibulum of hair follicle
Open directly onto skin surface
Secretion is mediated by adrenergic innervation and androgen
Secretion is Mediated by cholinergic innervation
Found at axillae, areolae, anogenital region, external auditory canal and eyelids
Are found at all skin sites (mostly palms, soles and axilla)
Apocrine sweat is odorless until it reaches the skin surface, where it is altered by bacteria
(responsible for odor of body)
The play a role in cooling when it is hot (thermoreguation)
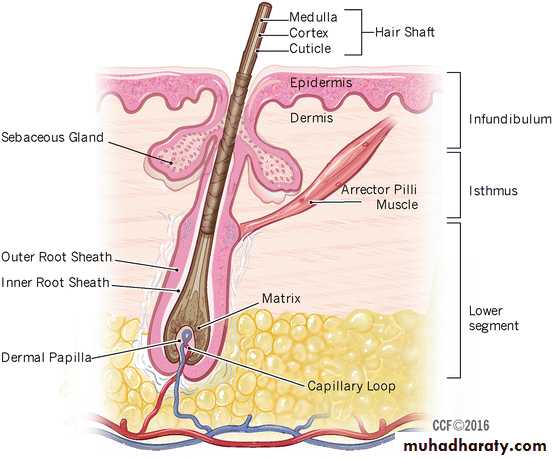
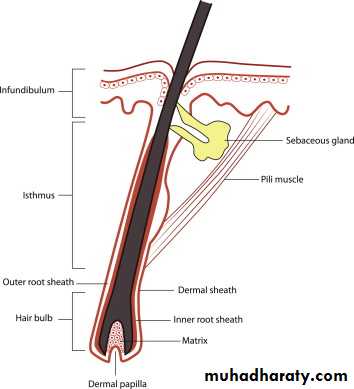
Hair Follicles
Infundibulum is the uppermost part, extend from the skin surface to opening of sebaceous glandThe isthmus is middle part, extend between opening of sebaceous gland and insertion of arrector pili muscle is isthmus
hair bulb is the lower part
The hair shaft is produced by matrix
(in hair bulb)Hair goes through three phases:
Anagen: growth phase last for three yearsCatagen: involution phase last or three weeks
Telogen: resting phase last for three months
Anagen length determine the length of hair
Sebaceous Glands
Sebaceous duct open into the infundibular portion of the hair follicle
They are distributed throughout all skin sites except the palms and soles
They are found in large numbers in face, scalp, upper chest, back and shoulder(seborreic areas)They are always associated with hair follicles, except :
Eyelids (meibomian glands)Buccal mucosa and the lip (Fordyce spots)
Penile mucosa (Tyson glands),
labia minora and Female areola (Montgomery tubercles)
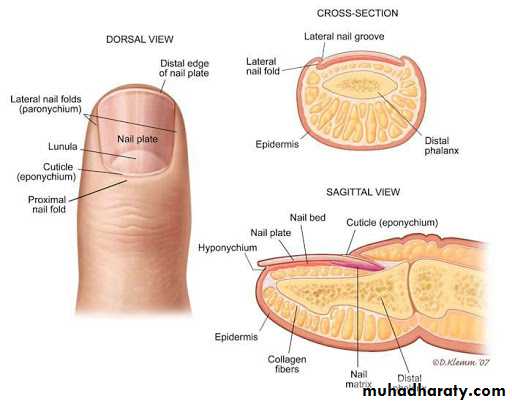
Nails
Is composed of thick keratinThe nail plate is produced by nail matrix
Parts of nail:
Nail plate
Nail bedNail matrix
Nail bed
Cuticle
Dermis
The constituents of the dermis are mesodermal in origin except for nervesSupport the epidermis structurally and nutritionally(source of the nutrition to the skin)
Dermis is comoposed of:Cells: fibroblast, mast cells, macrophages
Fibers: Collagen fibres type I and III constitute the bulk, other fibers are elastic and reticular
Ground substance: composed of glycosaminoglycan e.g. hyaluronic acid due to its high water binding capacity is responsible for hydration of skin