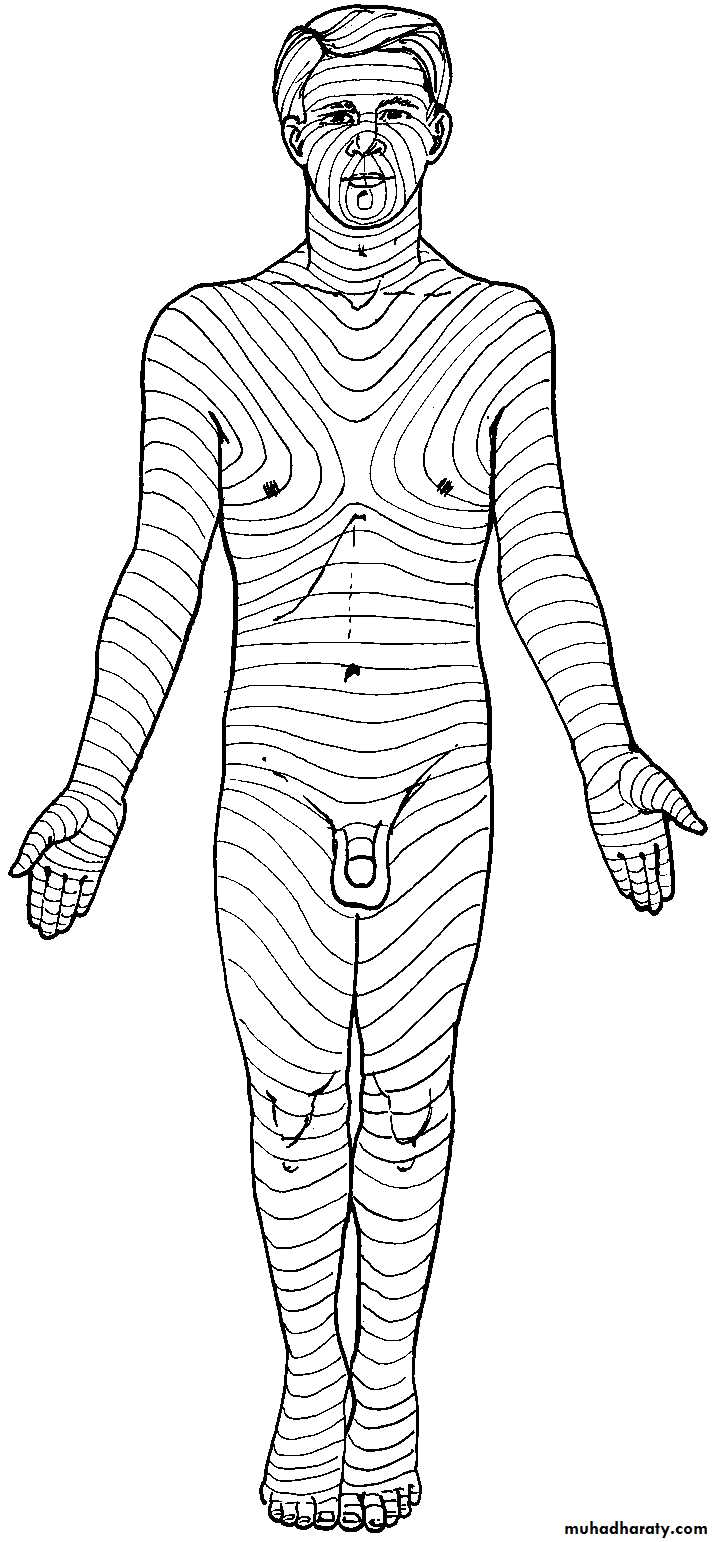
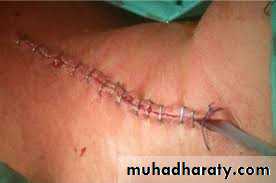
Surgical incisions
prof.Dr. Alaa jamel
CABS FACS. MRCSI MBCHB
2020-2021
General principles
To select appropriate incision should be :-1- near by the suspected target ( i.e grid iron in appendecectomy )
2-extensiblty for exposure so in explorative laparotomy do midline incision
3-rapidity such as top emergency or critical cases
4- less complication , (hernia , infection
-Security avoid injury to vessels or nerve or 5- avoid important structure (nerve,
6- cosmetic skin creases
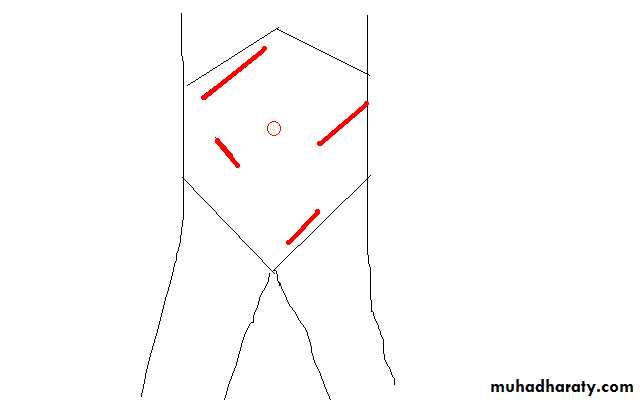
Abdominal incisions
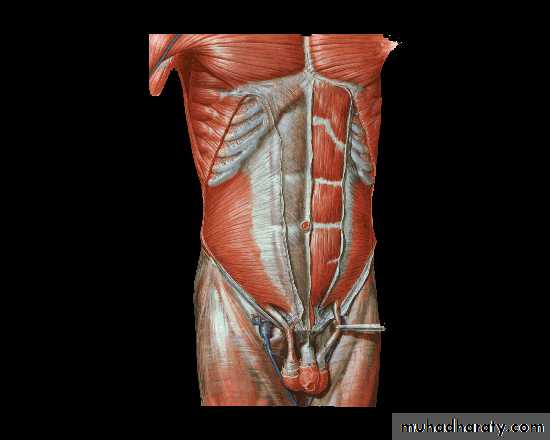
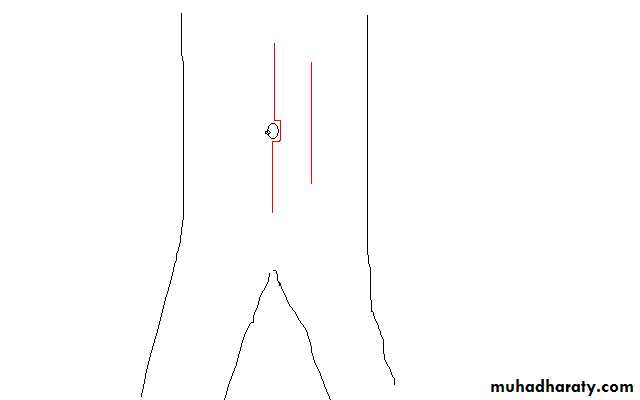
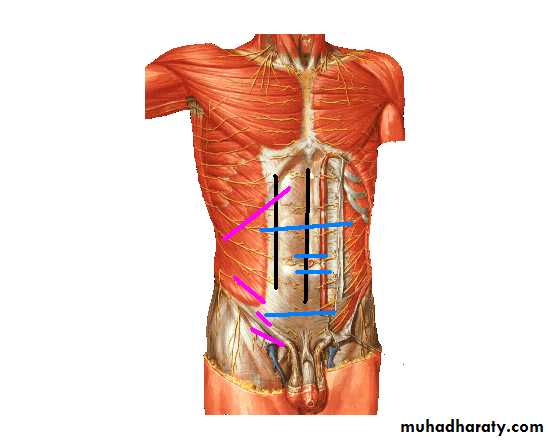
I -Vertical1- Medline incision
Through linea alba
, Advantages : avascular field , opened readily & closed easily
Enlarged quickly , dose not damage muscles Usually used in explorative laparotomy
Disadvantage :- high post op hernia specially in lower abdomen
2-paramedian IncisionThrough rectus sheath 2.5 cm from midline
can extended to thorax ( thoracoabdominal incision ) & to flank
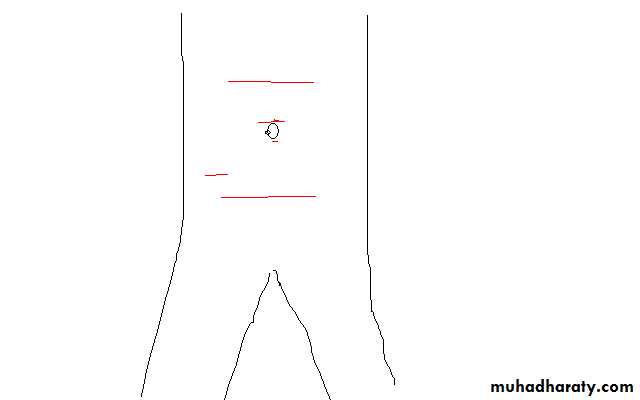
II - transverse incision
1-Upper abdomen used in children , cholicystectomy , or any upper abdominal pathology
2-Supraumbelical & infraublical :- used in paraumblical hernia , first incision of laparoscopy
3- Pfannenstiel ´s incision :- in gynecological & pelvis operation s
4- Lance :- is more or less transvers or oblique , its cosmotic incision for appendicectomyIII- oblique incisions
1-Kocher(sub costal) at Rt for gallbladder & liver operationWhile Lt for spleen op
2-Grid iron is incision which cruses on line between umbilical & sup. Iliac spine at Mc Berny point lat. to rectus sheath on ext. & int. & transv . abdominal muscles usually splitting of muscle , used in apendecectomy , its good incision less post op hernia
3- Retherford Morriss is extended grid iron up or down with muscle cutting , used in complicated apendecectomy
4- Lumber Moressian sub costal at lumber area used in renal & uretric surgery
5-Inguainal incision used for inguinal hernia
Thoracic incisions
1-Thoracostomy(chest tube )In pnemothorax at 5nd ICS ant. axillary line
2-Mediastenial vertical incision used for cardiac op
3-Intercostals at 5th ICS & 8th ICS
4-Thoracoabdominal extended to Rt or Lt paramedian used for oesophagial op
Breast incisions
1- Circumareolar incision : - around areola , used in lumpectomy , gynecomastia2- Mastectomy incisions :- there is many types of incisions (Steward for simple Mastectomy , Orr , Grey for radical (Halisid ) op …. )
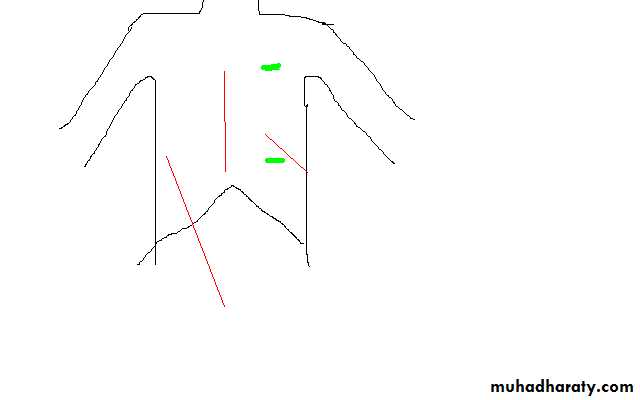
Neck & face incisions
1-Coller incision transverse incision at lower neck 2.5 cm above suprastrnal notch for thyroid & parathyroid surgery2- Neck dissection for radical neck LN dissections
• Mac Fee incision (2 horizontal incisions 1st from mastoid to hyoid , 2nd above clavicle 2cm
3-Periauricular for parotidectomy
Other face incisions should be with skin creases for good cosmotics
Complications of incisional wound
Early1-Wound infection & seroma
open stitch and evacuation of pus or serous fluid , daily dressing
2-skin allergy from plaster, dressing or content of wound discharge
3- stitch abscess ( Rx :- removal of infected stitch)
4-Wound dehiscence
if partial can use plastering and delay removal of stitches
if major should reoperation and close it again with use tension suture
5-non or bad healing due to bad technique (over lap , everted , enverted ) or poor immunity(DM ,uremic …) or early removal
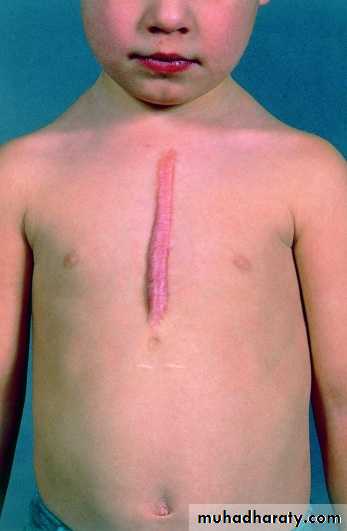
Late :-1-Incisional Hernia 2-Hypertrophic scar or kiloid 3- Chronic Pain ( specially if nerve entrapment 4-Hyper- or hypopegmentation
This complication due to :-
--Pt causes ( poor immunity , post op. cough ,near by source of infection like colostomy --Surgeon causes ( use inappropriate stitches , poor handling …) --Nurses causes ( poor and inappropriate dressing --Operation causes ( poor sterilization )keloid
Suture materials
Classification according to :-Absorbtion :-
1- Absorbable like plain or chromic catgut
2-delay Absorbable ( PDS , vicryl ,
3- Non absorbable ( silk , nylon ,metalic clips)
Biological or synthetic
--Biological like
. cutgut from sheep intestine
. silk from silkwarm larva, cotton
--Synthetic vicryl , nylon , PDS , metalic clip
Monofelement or polyfelement (braided or twisted )Monofelement like nylon , catgut , metalic clippolyfelement ( braided or twisted like silk ,vicryl
Suture Packaging
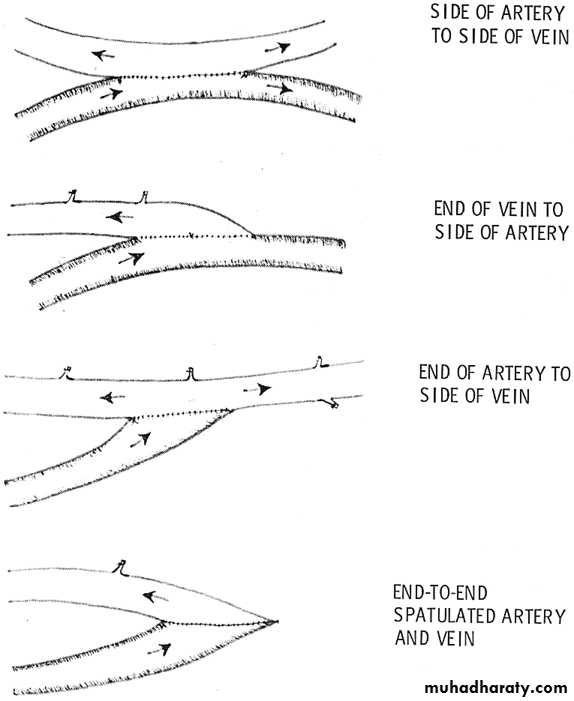
Methods of anastomosis
End to endEnd to side
Side to side
Removal of suture
Early as possible , depend on
Site :- face &neck 3-5 days , while in abdomen 7-8d , In joint more
Facter influence healing
A) general :- Ca , DM , Malnutrition , jaundice , septecaemia . steroid , Vit. C deficiency , uremiaB) local :- poor blood supply (tension , atherosclerosis , ).infection , poor
alignment, foreign body , local X ray
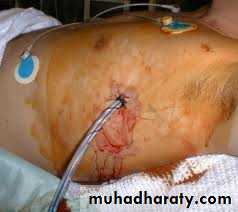
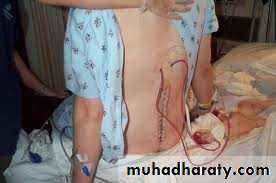
surgical drain
A surgical drain is a tube used to remove
pus, blood or other fluids from a wound.
Indications:
1. To help eliminate dead space
2. To evacuate existing accumulation of fluid or gas, To remove pus, blood,serous exudates, chyle or bile , urine ….
3. To prevent the potential accumulation of fluid or gas
4. To form a controlled fistula e.g. after common bile duct exploration
Classification:
• either Open or Closed Systems:- Open
- Closed
• according mechanisim of action
- Active. or Passive
-one way or two ways
-internal or external drain
open drain ( wick in abscesse , currigate , pinross ) need regular changes packs until become less wetting to be removed
closed drain (the drain connect to closed bag for drainage , removed after become very little amount or cease function ),
e.g simple tube drain( for post operative ) , foleys catheter ( for urine ) , T tube ( for bile ), NG tube ( for stomach decompression )
curregate
pinroseMechanism of action
-- Passive drainMost of drains depend on gravity siphon phenomenon ,
-- some use valve for one way direction as in chest tube use underwater seal because plural cavity pressure less than atmospherec pressure ,
--Active drain
some operation use redivac drain (continuous –ve pressure
Simple drain
Radivac drainComplications and Failure of Drains
1-Infection due to• Ascending bacterial invasion
• Foreign body reaction
• Poor postoperative management
2-Discomfort / Pain
• Thoracic Tubes – diameter too large
• Stiff tubing
3- Inefficient Drainage
• Exiting in non-dependent locale (passive drains)
• Kinked tube
• Obstructed
• Poor drain selection – diameter too small to remove viscous fluid
4-Incision dehiscence / hernia Poor placement
5- Premature Removal Accumulation of fluid
•
Removal of drain
• Generally, drains should be removed once the drainage has stopped or becomes less than 25 ml/day.
Nasogastric Tubes
Naso-gastric tube; pases through the nostrils (sometimes through oral cavity!) to the stomach, to the doudenumIndications:
-- Aspiration: to provide samples of gastric contents for lab analysis;--to keep stomach free of gastric contents and air; during & post operation
--Feeding
-- Lavage: in cases of poisoning or overdose
- Medication
-- Contrast study introduced into tube for Upper GIT
Complications of NG tube
• Epistaxis• Erosions in the nasal cavity, and nasopharynx
• More dangerous complications include:
-Esophageal penetration.
-Aspiration.
Foley Urethral Catheterization
Folye’s is classified according to:
-The number of lumens:1 way for aspiration and drain.
2 way one for the balloon inflation and the other for drain or aspiration.
3 way one for irrigation (infusion),one for the balloon inflation, and the third for drain
Indications
DiagnosticTo collect uncontaminated urine specimen
Study anatomy of the urinary tract (cystography )
Urine output monitoring
Therapeutic
Acute urinary retention
Chronic obstruction causing hydronephrosis
Intermittent bladder decompression for neurogenic bladder
Chronically bed-ridden patients for hygiene
Contraindications
-Urethral injury
-Trauma patients with blood at meatus or
Complications:
Inability to locate the urethra.
Vaginal catheterization.
Urethral stricture.
UTI
Inability to deflate