Anatomy of Nose and Paranasal Sinus
The Nose
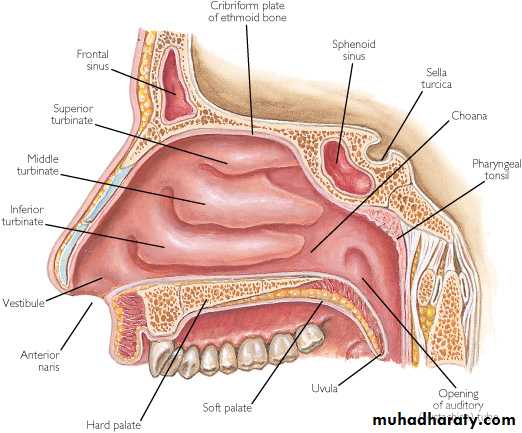
The nose consists of the external nose and the nasal cavity,Both are divided by a septum into right and left halves.
External Nose
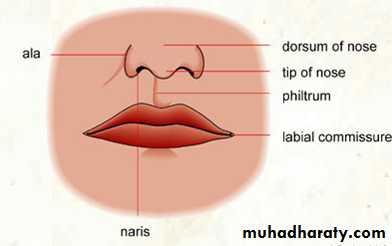
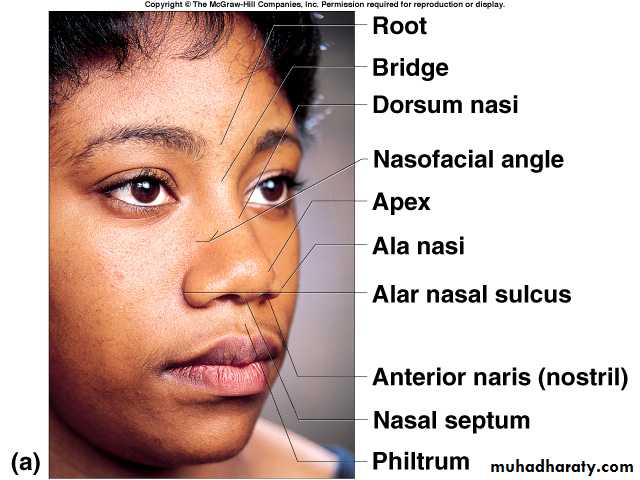
The external nose has two elliptical orifices called the naris (nostrils), which are separated from each other by the nasal septum.The lateral margin, the ala nasi, is rounded and mobile.
External Nose
External Nose
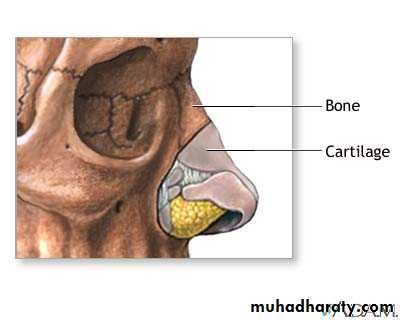
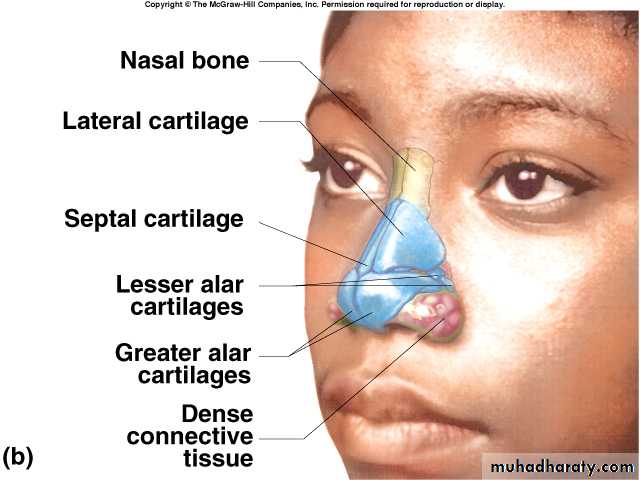
The framework of the external nose is made up above by the nasal bones, the frontal processes of the maxillae, and the nasal part of the frontal bone.Below, the framework is formed of plates of hyaline cartilage
External Nose
Blood Supply of the External Nose
The skin of the external nose is supplied by branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary arteries.The skin of the ala and the lower part of the septum are supplied by branches from the facial artery.
Nerve Supply of the External Nose
The infratrochlear and external nasal branches of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V) and the infraorbital branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V).Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity has
a floor,
a roof,
a lateral wall,
a medial or septal wall.
The Floor of Nasal Cavity
Palatine process maxillaHorizontal plate palatine bone
The Roof of Nasal Cavity
NarrowIt is formed
anteriorly beneath the bridge of the nose by the nasal and frontal bones,
in the middle by the cribriform plate of the ethmoid,
posteriorly by the downward sloping body of the sphenoid
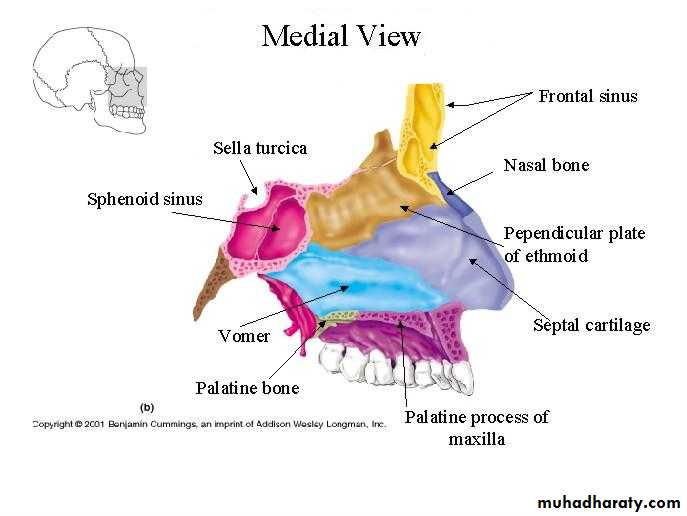
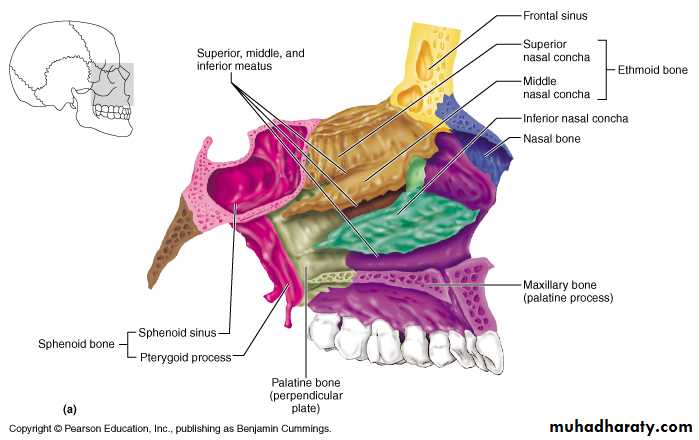
The Medial Wall of Nasal Cavity
The Nasal SeptumDivides the nasal cavity into right and left halves
It has osseous and cartilaginous parts
Nasal septum consists of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone (superior), the vomer (inferior) and septial cartilage (anterior)
Perpendicular Plate (ethmoid)
Septal CartilageVomer
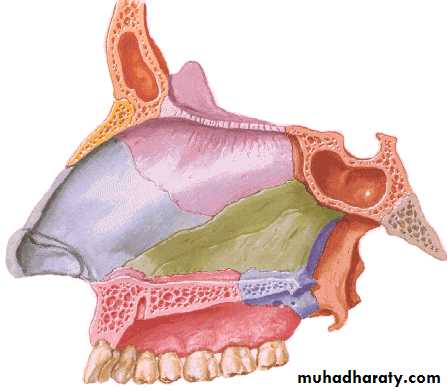
The Lateral Walls of Nasal Cavity
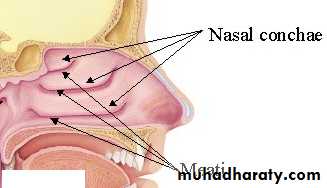
Marked by 3 projections:Superior concha
Middle concha
Inferior concha
The space below each concha is called a meatus.
The Lateral Walls of Nasal Cavity
The Lateral Walls of Nasal Cavity
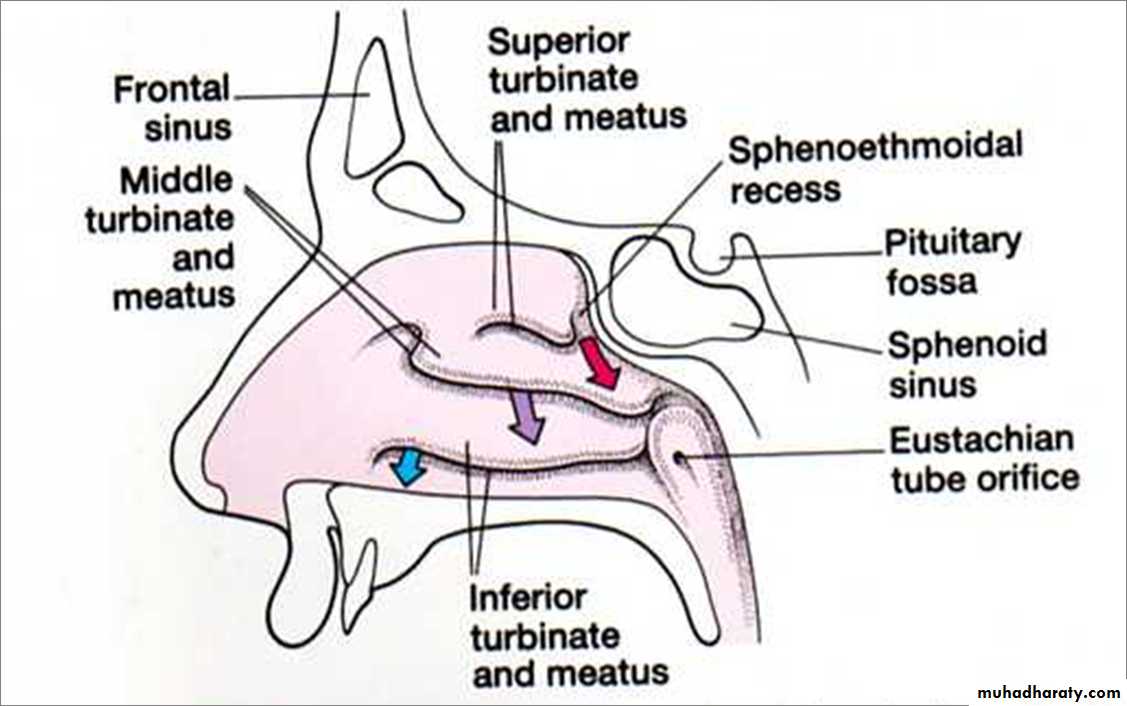
• Inferior meatus: nasolacrimal duct• Middle meatus:
• Maxillary sinus
• Frontal sinus
• Anterior ethmoid sinuses
• Superior meatus: posterior ethmoid sinuses
• Sphenoethmoidal recess: sphenoid sinus
Openings Into the Nasal Cavity
Nasolacrimal Canal drains into Inferior Meatus
Sphenoid sinus opens into sphenoethmoidal recess
Posterior ethmoidal air cells open into superior meatus
Anterior & middle ethmoid air cells, maxillary and frontal sinuses open into middle meatusBlood Supply to the Nasal Cavity
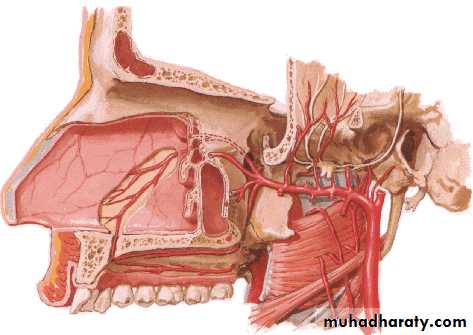
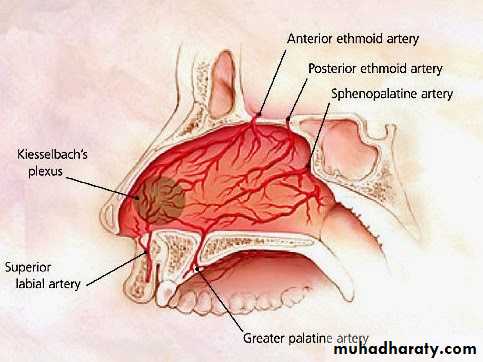
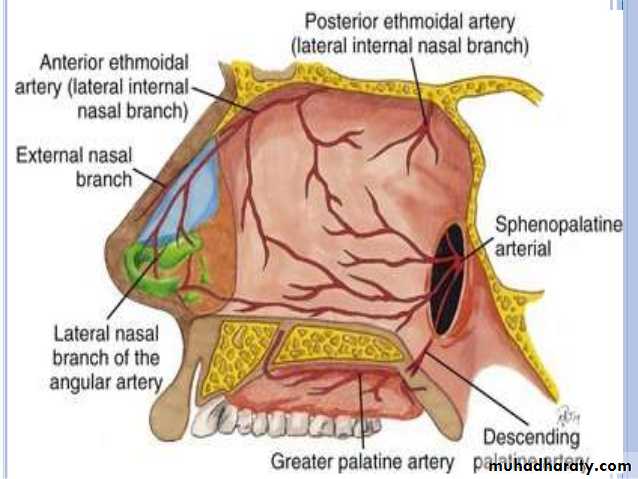
Sphenopalatine a.
Maxillary a.Netter, Frank H., Atlas of Human Anatomy. Ciba-Geigy Corporation, Summit, N.J. 1993. Plate 35.
Blood supply of the septum
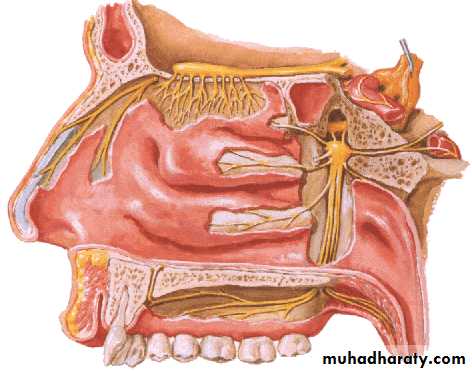
Nerve Supply of the Nasal Cavity
The olfactory nerves from the olfactory mucous membrane ascend through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone to the olfactory bulbs .The nerves of ordinary sensation are branches of the ophthalmic division (V1) and the maxillary division (V2) of the trigeminal nerve.
Nerve Supply of the Nasal Cavity
CN I – Olfactory Nerves (SVA)
Anterior ethmoidal branch of V1Posterior nasal branches of V2
Cut nasopalatine branch of V2 to septumLymph Drainage of the Nasal Cavity
The lymph vessels draining the vestibule end in the submandibular nodes.The remainder of the nasal cavity is drained by vessels that pass to the upper deep cervical nodes.
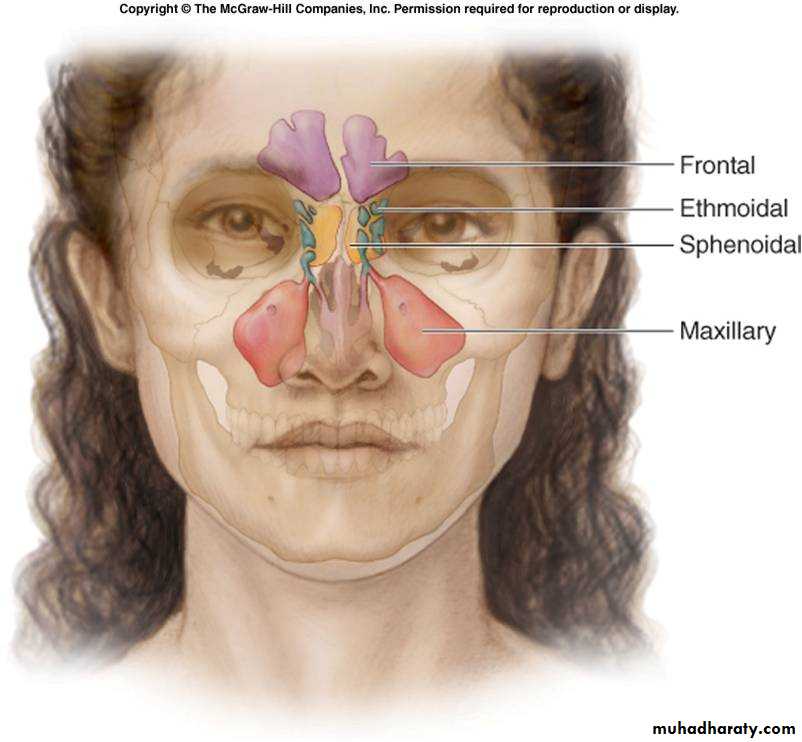
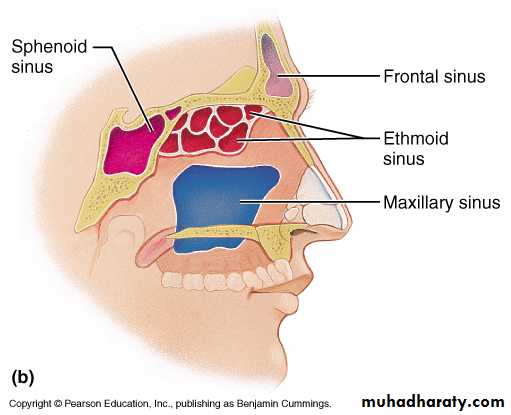
The Paranasal Sinuses
The Paranasal Sinuses
The paranasal sinuses are cavities found in the interior of the maxilla, frontal, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones .They are lined with mucoperiosteum and filled with air.
They communicate with the nasal cavity through relatively small apertures.
Drainage of Mucus and Function of Paranasal Sinuses
The mucus produced by the mucous membrane is moved into the nose by cilliary action of the columnar cells.Drainage of the mucus is also achieved by the siphon action created during the blowing of the nose.
Functions:
Resonators of the voice
They also reduce the skulls weight
Help warm and moisten inhaled air
Act as shock absorbers in trauma
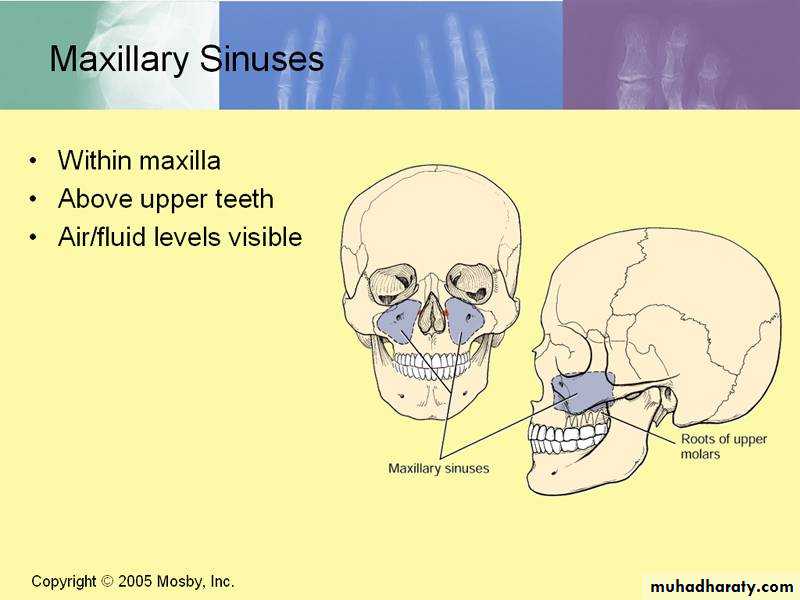
Maxillary Sinus
Pyramidal in shapePaired & symmetric
Located within the body of the maxilla behind the skin of the cheek.
The roof is formed by the floor of the orbit, and the floor is related to the roots of the 2nd premolars and 1st molar teeth.
The maxillary sinus opens into the middle meatus of the nose
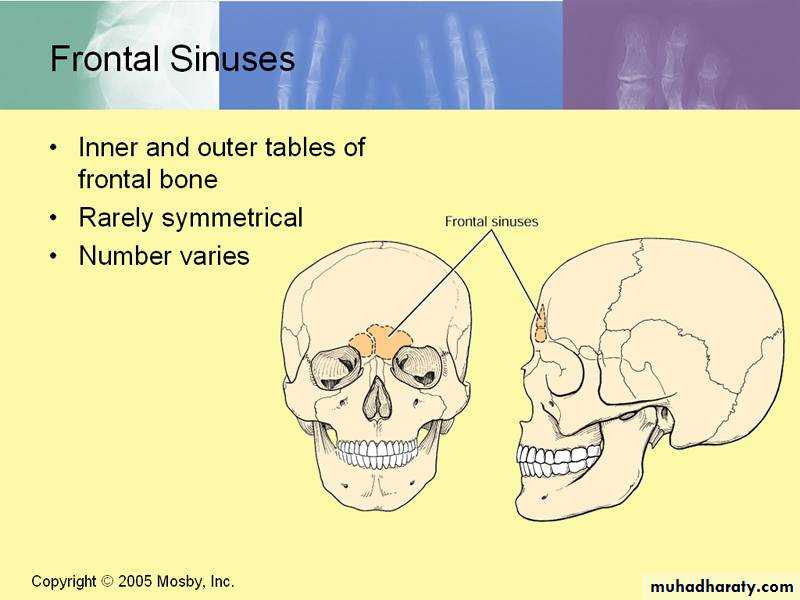
Frontal Sinuses
Rarely symmetricalContained within the frontal bone .
Separated from each other by a bony septum.
Each sinus is roughly triangular
Extending upward above the medial end of the eyebrow and backward into the medial part of the roof of the orbit.
Opens into the middle meatus
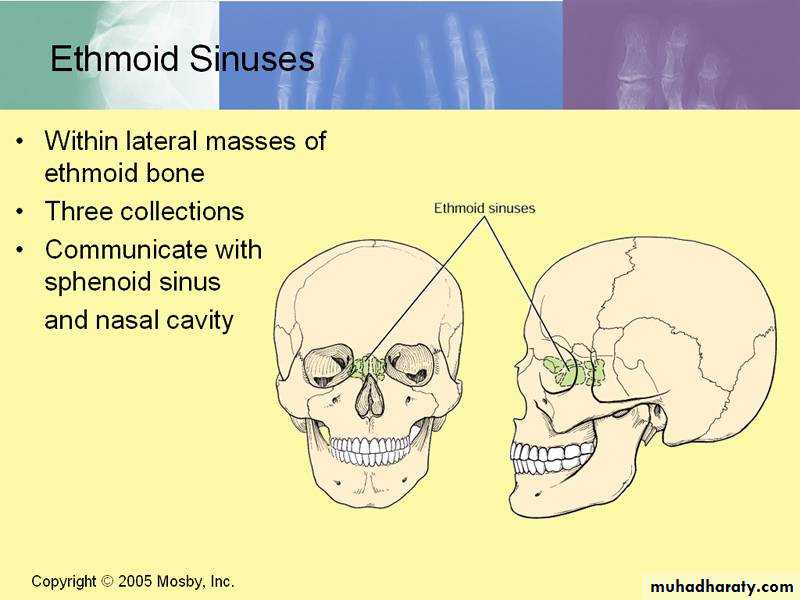
Ethmoid Sinuses
They are anterior, middle, and posteriorThey are contained within the ethmoid bone, between the nose and the orbit
Anterior & middle
Drains into middle nasal meatus
Posterior
Drain into superior nasal meatus
Separated from the orbit by a thin plate of bone so that infection can readily spread from the sinuses into the orbit
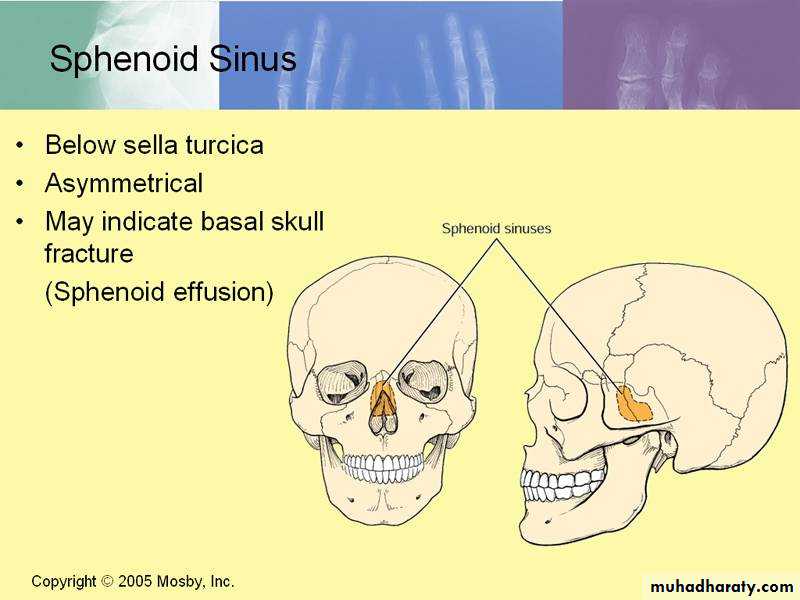
Sphenoidal Sinuses
Lie within the body of the sphenoid boneBelow sella turcica
Opens into the sphenoethmoidal recess above the superior concha