UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Restorative dentistry for children..
By:
الأستاذ المساعد: عمر حسين اللويزي
• Department of
• Orthodontics
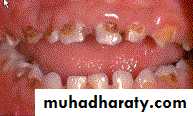
The basic principles in the selection of primary teeth for restoration
• Child's age.• Amount of tooth structure remain
• Exfoliation time.
• General health of the child.
• Present of draining
• fistula or history of swelling.
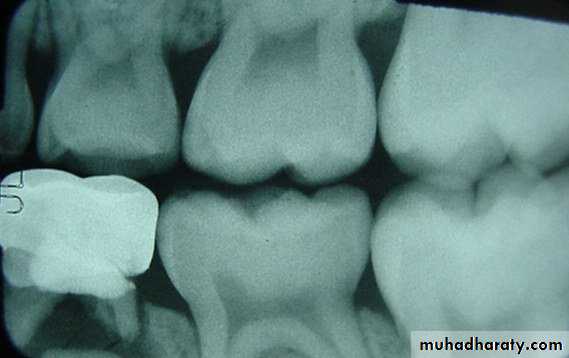
• Radiographic examination.
• Degree of tooth mobility.
• Child's oral condition
• and degree of parent education
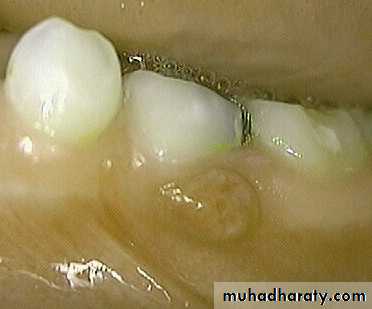
Restorable?
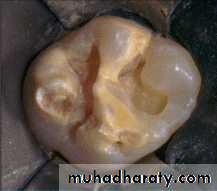
Conventional cavity preparation in primary teeth
Incipient Class Ichild under 2 years of age
small cavity preparation made without
the aid of the rubber dam or local anestheticobjective is to restore the tooth to arrest decay and to prevent further tooth destruction without a lengthily or involved dental appointment
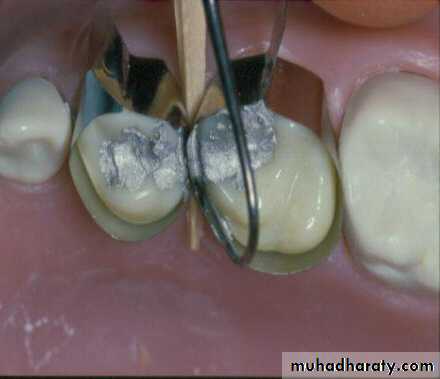
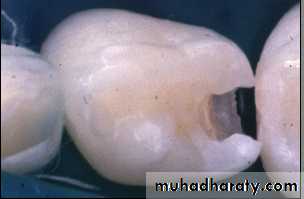
Basic principles in the preparation of cavities in the primary teeth :( Class I + Class II)
• .5 - 1 mm into dentin
• primary molars - 1.25 to 1.5mm
Intercuspal width - 1/3rd
Rounded internal line angles
B-L walls slightly undercut
M-D walls flare at marginal ridges
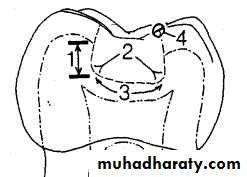
Internal Form of a Class I Prep
• depth .5 - 1mm into dentin• angle of floor and walls is rounded
• slightly rounded pulpal floor
• Avoids pulp
• sharp cavo-surface angle
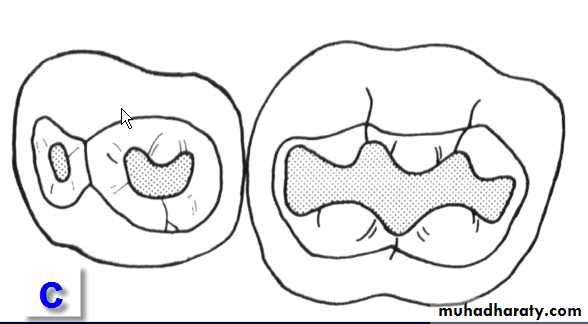
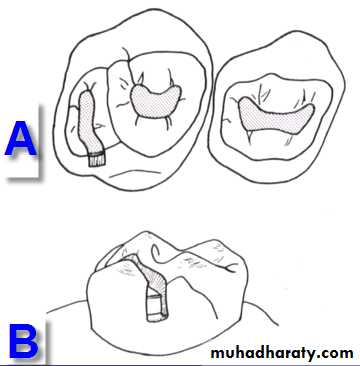
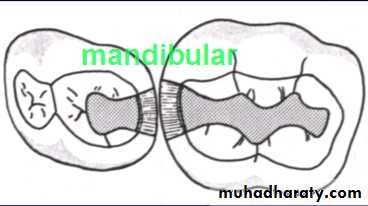
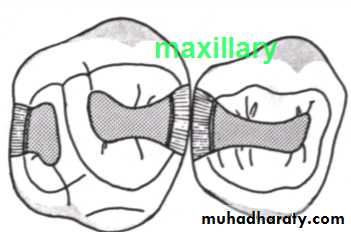
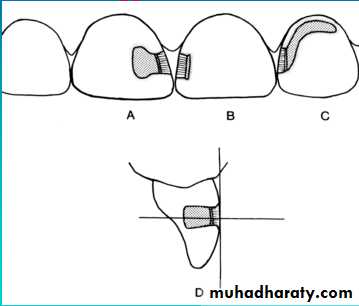
Class I Cavity Preparations
A Maxillary right first and second molars (occlusal view)B Maxillary second primary
molar (lingual view)C Mandibular right first and
second primary molars
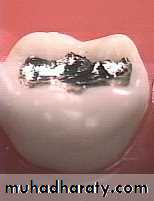
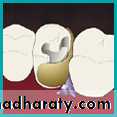
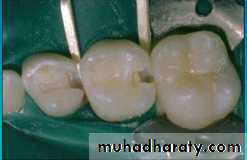
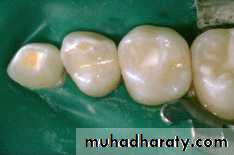
Class II Amalgam Preps
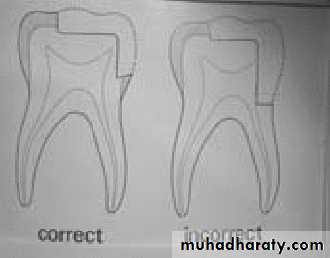
• self cleaning arealeave 90 degree cavosurface margins
isthmus width 1/3
Proximal box in an occlusal gingival direction is parallel to the long axis of the tooth
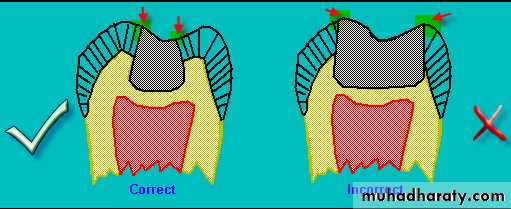
Class II Amalgam Preps
B-L walls of box should
converge occlusally
axiopulpal line angle should be slightly rounded or beveled
Gingival floor should be beneaththe contact, at, or just beneath the gingival tissue
Axial wall should follow
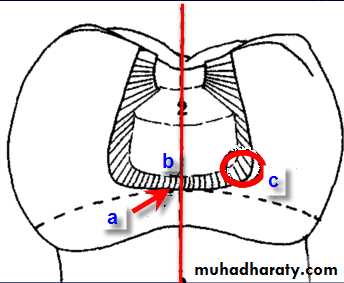
the contour of the toothClass II Amalgam Preps
• a) gingival floor position• b) box is perpendicular to long axis
• c) rounded angles
• d) Rounded axiopulpal line angle
• e) wide Contact area
• f) No bevel at gingival margins
Questions
What will happen if we:touch the adjacent tooth during prep of class II for the primary tooth
Use pins for the retention in primary teeth
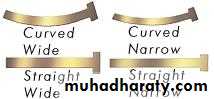
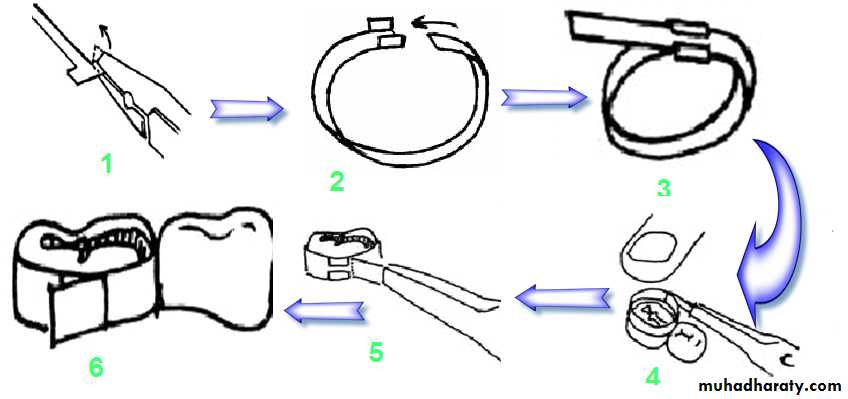
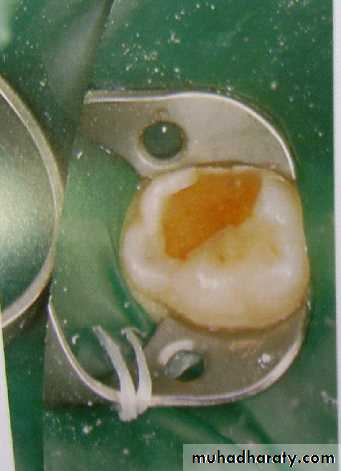
Types of matrix bands used in pediatric dentistry
• T-band: allows for multiple matrices.• Sectional matrices:
• allow for multiple matrix placements.
• easy to use, not circumferential.
• must be held in place by wedge.
• Tofflemire matrix:
• does not fit primary teeth contour well
• difficult to place as multiple matrices.
• Spot welded matrix:
• allow for multiple matrix placements.
• a spot welder is required at chair side.
T band
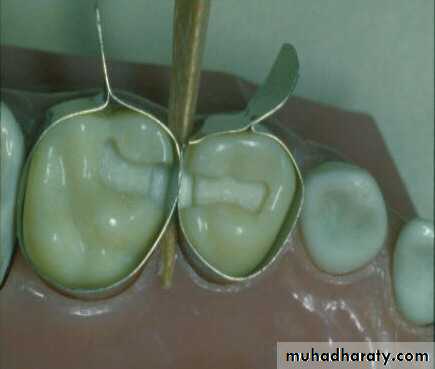
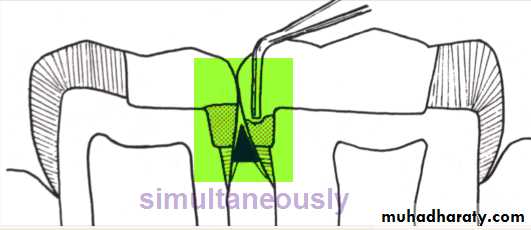
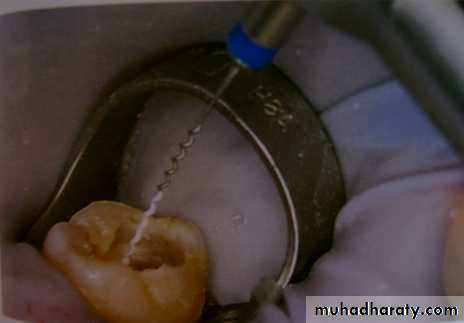
Back to back restoration technique of Class II’s
It is desirable to restore adjacent class II’s lesion simultaneouslyTime
Patient management
Esthetic composite resin or glass ionomer restoration for posterior teeth:
Can be used in:
lesions on distal of 2nd primary molars adjacent to permanent first molarHypoplastic tooth
Modification:
No undercutThe margins are beveled
Class III Cavity - Incisors
Avoid weakening the incisal edgeThe modification is not mandatory
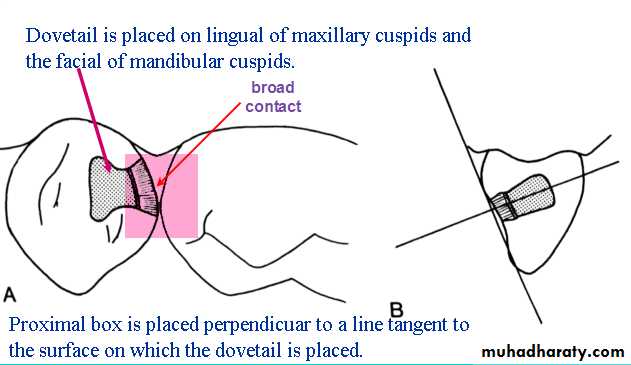
Class III Cavity (modified) Cuspids
Why the dove tail is mandatory here?Do we have to
use wedge?Can we use amalgam?
of restorative dentistry as we approach the 21st century should be to delay and prevent placement of initial restorations.
The goal
Rubber dam
Save time
Aids in management of the child patientControl saliva
Provides protection
Rubber dam helps the dentist in educating parents