Posterior abdominal wall
prof.Dr. Alaa Jamel
FACS, CABS. MRCSI .MBChB
The diaphragm
Nature and shape;It’s a large dome shape fibro muscular partition separate thorax from abdomen.
Upper surface convex
Lower surface concave
Its rt side higher than lf side because of rt lobe of liver
Origin of diaphragm;
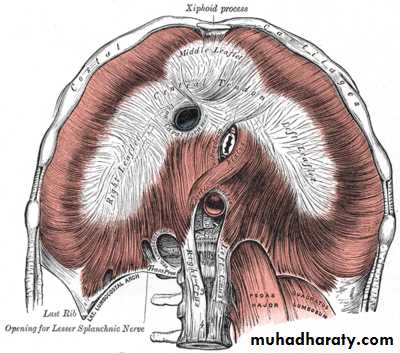
Peripheral part of dia. take origin from the circumference of the thoracic out let .origin divided to 3 parts;sternal origin ;from back of xiphoid process
Costal origin; from inner surface of lower 6 ribs and there costal cartilage.
Vertebral origin; by 2 muscular band called rt&lf crura and 5 tendinous arches called arcute ligaments(one median,2 medial,2 lateral)
Rt crus arise from front of upper 3 L.V
Lf crus arise from front of upper 2 L.VMedian arcute lig. it’s a tendinous arch connecting 2 crura in front of aorta.
Medial arcute ligs. connecting the RT crus with tip of trans. process of L1
Lat.arcute lig s connecting t. process of l1 with the last rib
Insertion of diaphragm;
All fiber converge to be inserted to central tendonNerve fiber;
Motor ; rt&lf phrenic nerves
Sensory ; phrenic sensory to the central part
Lower 6 thoracic nerve are sensory to the peripheral part.
Arterial supply;
1- phrenic branches of thoracic and abdominal aorta.2-precardiophrenic and musculo phrenic branch of internal mammary art.
3- lower 3 post. intercostal arteries.
;
1- it’s a major muscle of insp. On contraction it descend leading to increase in the vertical diameter of the thorax thus air is sucked
2- increase intra abdominal pressure useful in vomiting .labour, micturition
3- rt crus has a sphincter action on the lower end of esophagus.
4- it help in venous return of blood to the heart by
A- increase intra abdo.pre. b- decrease intra thoracic pre. C- widening the IVC opening.
Action of diaphragm
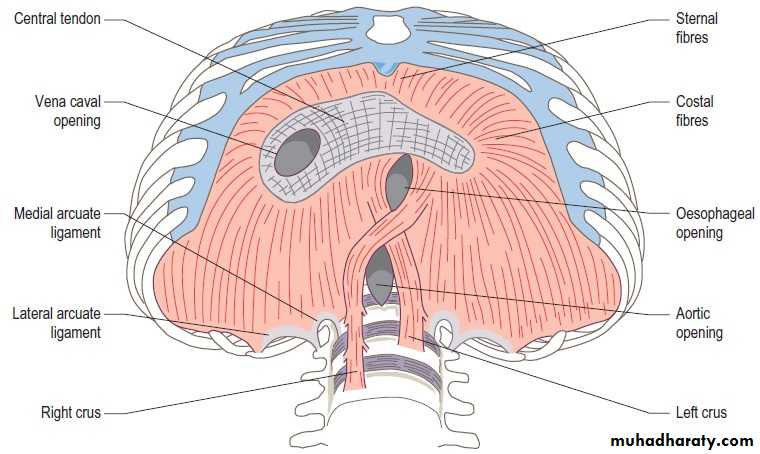
V.C. opening , oesophageal opening , aortic opening (voice of America).
V.C OPENING OESOPHAGEAL OP. AO.OPT8 t10 T12
1inch rt to m.plane 1 inch lf to m.p on m.p
Help in venous return * act as asphictor to lower oes. *Protect oa from contraction of diaph.
Pass
Ivc+rt phr. N+lymphatic from liver to mediall.n (Ivc. opening)
Oeso+ant and post vagal trunk+ oes.branch of lf gastric art.(oes.opening.
Aorta+ thoracic duct+ azygus vein+ lymphatic from thorax to the cisterna chyli.
Major foramina of the diaphragm
1- sup .epigastric art.
2- musculo phrenic art. pass between 7th and 8thrib3- lower 5 intercostal n
4- lf phrenic n
5- the greater and lasser splanchic ns.
6- subcostal n & v pass behind lat arcute ligament
7- sympathetic chain pass behind medial arcute ligament.
8- inf. Hemiazygos v pierce the lf crus.
Minor foramina of the diaphragm
it triangle between the vertebra and costal origin .its wider in lf side ,abdominal content may herniate through this gap in to the thoracic (hernia of bockdalek)Sternocostal triangle
triangle between sternal and costal origins may produce (congenital parasternal hernia.
Vertebro costal triangle;
Upper surface;
Central tendon related to the pericardium & heartRt side related to the rt pleura and base of rt lung
Lf surface related to the lf pleura and lf base of lung.
Relation of diaphragm
Lower surface
Rt side related to the * rt lobe of the liver*rt kidney & rt suprarenal gland
Lf side related to the
* lf lobe of the liver * lf kidney & lf suprarenal gland *stomach & spleen
Hiccough ; due to spasmodic contraction of diaph.
Irritation of diaphragm cause pain to epsi lateral shoulder pain ---phrenic n ( sensory)and supra clvicular n.( sensory to shoulder) have same root(c3-c4).Injury of one phrenic n cause paradoxical movement of diaph. Insp. normal downward abnormal upward.
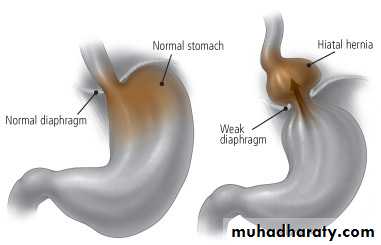
Acquired hiatus hernia; widening of oesoph. opening of diaph---herniate stomach to the thorax.
Applied anatomy
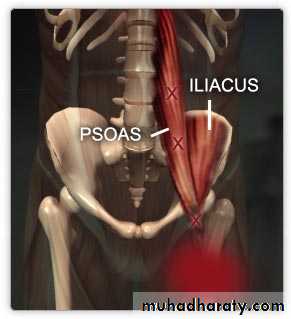
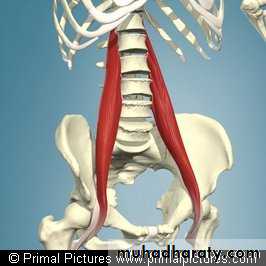
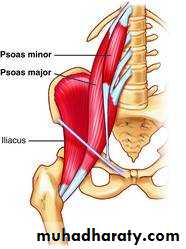
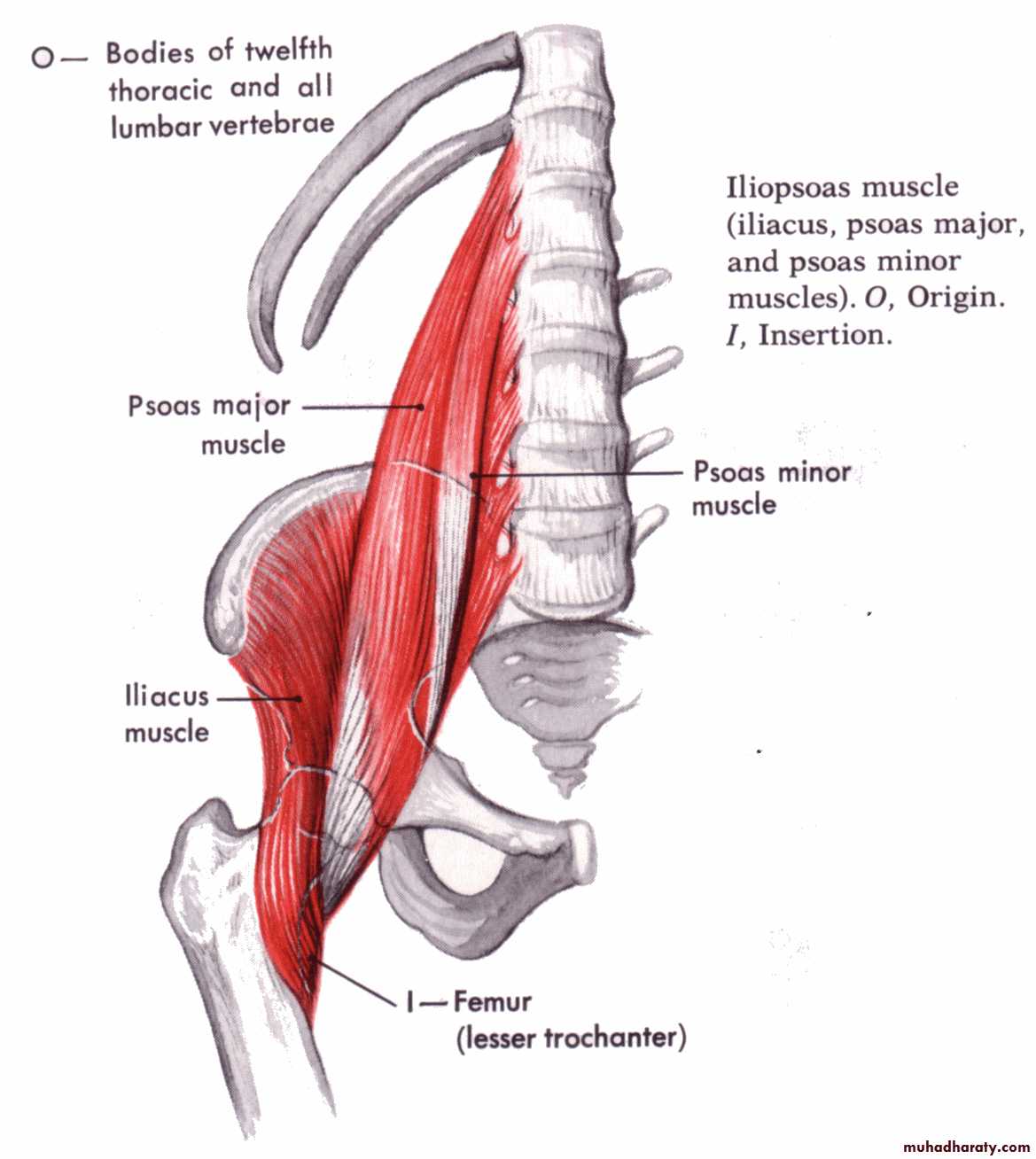
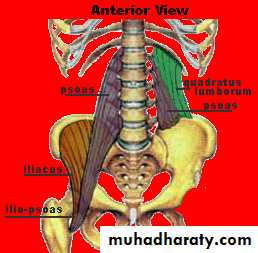
PSOAS MUSCLE
Its long fusiform m. lying on either side of v. coloumn and along the side of pelvic brim.
Origin ;1-ant.surface of 5 L.transv.process2-from the 4 tendentious arch
Course; it leave the abdomen behind lateral part of ing. ligament closely relate to the iliacus m.
Insertion; together with iliacus producing ilio psoase tendon inserted to the ant.and med. aspect of lesser trochanter of femur.
Psoas major muscle
Nerve supply; ventral rami of L 1,2,3
action1- powerful flexion of thigh and rotated medially
2-flexion of pelvis over the thigh
3-one psoas produce lat. flexion of v. column toward it side
Medialy;
*bodies of L.V and lumber vessels
*sympathetic chain
*ext. iliac vessels
*ivc
*aorta ¶ aortic l.n
*obtr.n,--lumbosacral trunk---ilio lumber art.
Relation;
Laterally; 2muscles and 4 nerves
1- quadr.m 2- iliacus m3- 4-iliohypo gastric and ilio inguinal n
5-6-lat.cutanous n. of the thigh and femoral n*medial border of quad.lumborum m.
*lumber arteries*lumber transvers process
*lumber plexus(embeded in post part of m.)
capsule of hip joint (in the thigh
Post .relation;
Boundries between
a- medial border of paoas major.
b-body of L5 vertebra.
c- the ala of sacrum.
Lumbosacral triangle;
;
Its fascial sheath enveloping the psoas major m
Above its thickened to form medial arcute lig.
Medially its attach to the L.V
Laterally; it blend with the fascia covering quad. lumborum & iliacus m
Applied anatomy; psoas abscess ;
It’s a tuberculose abscess of lumber spread to the psoas sheath and descend to reach the front of thigh just below ing .lig.
Psoas fascia (sheath)
It’s a long slender m. lying in front of psoas major m.in 60% of people.
Origin ;from side of T12 and L1 v.and the disc in between.Insertion; by long tendon into the ilio pubic eminence of hip bone
Nerve supply; branch from L1.nerve.
Action; weak flexor of the trunk
Psoas minor muscle
Its quadrilateral m lying post lat. To psoas major.
Origin ;ilio lumber lig. and inner lip of iliac crestInsertion ;TIP of transverse process of upper 4 L.V& medial half of lower border of last rib.
Nerve supply; branch from t12&upper 4 L. nerve.
Action; 1- lat. Flexion of vert..coloumn
2-muscle of inspiration by fixing the last rib during contraction of diaph.
Quadrotus lumborum muscle
anteriorly its cover by thoroco lumber fascia.it crossed by the fallowing structures
1- subcostal n2- iliohypogastric nerve
3- ilioinguianal nerve.
Post. Its cover by middle layer of thoroco lumber fascia.
Relation;
It’s a strong sheath of deep fascia which cover and envelops most of the deep muscles of the back and bind them to the vertebral column.
Extend ;from sacrum to the neck.
Layers; in the lumber region differentiate to 3 region;
1- anterior layer; it cover ant, surface of quad. lumborium m. and attach to the ant aspect of trans. Process OF L.V
Thorocolumber fascia;
Middle layer; it cover post layer of quad.lum.m. and attach to trans. process of L.V
Post layer; it cover the post .surface of erector spinae (sacrospinalis m.)and its attach medially to the spines of the lumber vertebra.N.B;1- post layer is the strongest and extend from the sacrum to the neck.
2-In the lat. border of guad.lum.,the ant and middle layer fuse together and this fusion give origin to 3 m.
1- TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINS
2- INTERNAL OBLIQUE M3- LATISSIMUS DORSSI M.
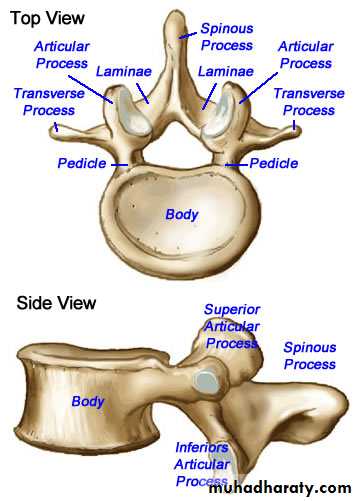
CHARACTERISTIC;
The body; large in size ,kidney shape has no costal facetsThe vertebral foramen; small in size and triangular in out line
The transverse process; flat and elongated
The sup. Articular facet ; concave and directed medially.
LUMBAR VERTEBRAE
The inf articular facet; convex and directed laterally.
The spine is quadrilateral and project directly backwards.N.B;
the 5th L.V differ from the rest in having a thick strong T. Process which is attach to the pedicle.
;
1- ant.& post. longitudinal ligaments
2- rt & lf crus of diaph.
3- psoas major and minor m
4-lumber inter vertebral disc.
Stactures attached to the body of vertebra
;
1- psaos major and quadratous lumb.m
2- lat& medial arcute lig.of diaph.
3- ilio lumber lig.(to L5 only)
4- lumber fascia and sacrospinalia m.
Structure attach to transverse process
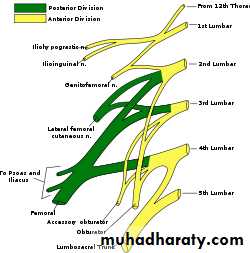
Lumber plexus;
Site; in the post part of psoas major m.
Formation; from ant. Rami of upper 4 lumber nerves (L1,2,3,4).EACH OF which divided to ant,and post.divisions.
Branches;
Large branches;
1- femoral n.(post division of L2,3,4
2-obturator nerve (ant. divisions of L2,3,4)
Nerves of post. abdominal wall
Small branches;
1- iliohypogastric n L12- ilioinguainal L1
3- gentofemoral L1,2
4- lat.cutanouse nerve of the thigh(post.division of L2,3).
*accessory obturator n is frequantly present and arises from ventral divisions of L3&L4
Obturator n.+accessory obturator n+ lumbosacral trunk ____from medial border of psoas m.
Iliohypogastric n+ ilioinguinal n+ lat cutanouse n.of thigh+femoral n._____from lat.border of psoas major.Gentofemoral n. emorge from ant. Surface of psoas major
EXIT OF THE BRANCHES FROM THE PSOAS MAJOR MUSCLE
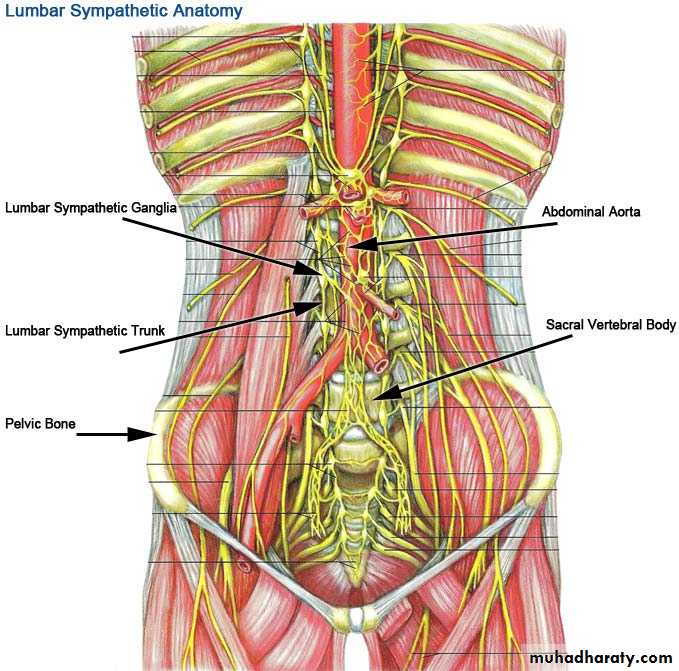
It enter the abdomen by passing behind medial arcute lig. of diaphragm.
There are 2 chain rt one behind ivc lf one on the lf side of aorta.
It leave the abdomen by passing behind common iliac vessels
Each chain contain 4 ganglia
Lumbar part of sympathetic chain
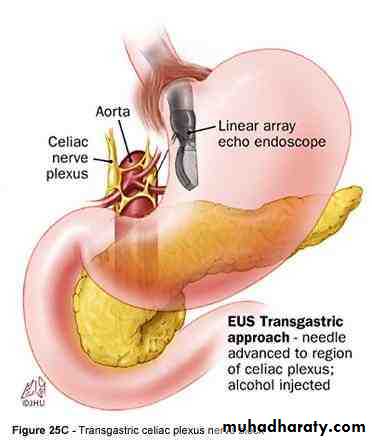
1- the coeliac plexus
2-aortic plexus (intermesentric plexus3- sup.hypogastric plexus
4- inf.hypogastric plexus
Autonomic plexuses of abdomen
It’s a plexus of autonomic nerve fiber
Site ;infront of abdominal oarta & crura of diaphragm around the coeliac trunk.Plexus end lateraly in a number of nodule called coeliac ganglion.
Coaliac ganglia;
site on each side of coeliac trunk
Size ;is the largest ganglion on the body
Coeliac plexus ;
Coeliac plexus ; situated around coeliac trunk
Formed of sympathetic postganglionic fiber and parasympathatic preganglion from both vagi.Site ; its surround the abdominal aorta between the origin of sup and inf mesenteric art, continue above with coeliac plexus and inf with hypo gastric plexus.
Formed of;
Sympathetic fiber ; from coeliac plexus &1st and 2nd lumber splanchnic nerve
Parasympathetic fiber; from pelvic splanchnic nerve of both sides(S.2,3,4)
Aortic plexus (intermesentric)
SITE; just below the bifurcation of abdominal aorta infront of L5 it continuous above with the aortic plexus and below divided to rt & lf which join with rt and lf hypo gastric plexus
Formation; 1- sympathetic fiber a- aortic plexus
B- 3rd &4th lumber splanchic nerve of both sides
Parasympathatic from pelvic splanchic nerve of both side (S 2,3,4)
SUP.HYPOGASTRIC PLEXUS
SITE;there are 2 plexuses rt &lf lying in the extrapertoneal tissue of the pelvis on each side of the rectum and base of urinary bladder (or cervix of uterus)
Formation; formed of
A- sympathetic fiber; from 1- sup.hypogastric plexus
2- the upper 2 sacral sympathetic ganglia.
B- parasympathetic fiber from pelvic splanchic nerve (S2,3,4)
INFERIOR HYPOGASTRIC PLEXUS
According to their relation to the abdominal aorta they are classified to the
1- preaortic l.n which are a- coeliac l.n
B- sup&inf. mesentric l.n .
Group a receive lymph from gastric ,hepatic, & pancreatico splenic l,n while group b received lymph from mesentric l.n ,coeliac l.n,pararectal l.n along side of the rectum.
All these l.n send lymph (efferent) through intesinal lymph trunk to the cysterna chyli.
Abdominal lymph nodes
2- rt& lf aortic groups ;(on the rt & lf sides of the abdominal aorta drain lymph from kidney ,ureter ,fallopian tubes ,upper part of body of uterus send lymph( efferent) to the lumber lymph trunk which open to cisterna chyli.
3- retroaortic lymph node (behind abdominal aorta),have no particular area of drainage.
Its aspindle shaped lymph sac about 2 inch long.
Site; infront of upper 2 lumber vertebrae between abdominal aorta (to the lf) and azygous vein (to the rt) over laped by the rt crus of diaphragm.It received intestinal l.trunk &rt&lf lumber l.trunk(which drain the lower limb &all the abdomin except the upper surfice of the liver.
Upper end forming the thoracic duct.
The cisterna chyli