5th stage Dr.Khalid Ali Orthopaedics
Fractures and Dislocations about the Elbow in the adult PatientDislocation of Elbow joint
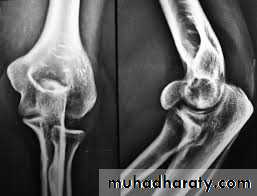
Elbow dislocation more common in adult >children.
Fall on outstretched hand elbow in extension.
90% posteriorly or posteriolateraly.
C.F.;
The patient supports his arm with the elbow slightly flexed.
Pain, swollen elbow.
The bony landmarks (olecranon and epicondyles are abnormally placed).
Neurovascular exam.
X-ray;
To establish the diagnosis and exclude associated fractures.
Treatment
M.U.A.Pulls on the forearm while the elbow is slightly flexed. with one hand, sidewayes displacement is corrected ,then the elbow is further flexed while the olecranon process is pushed foreward with the thumbs.
Test stability.
X-ray.
Neurovascular exam.
Collar & cuff or slab 3Ws.
Complications
Early
Associated fractures; coronoid process of the ulna,medialepicondyle,radial head,olecranon process.
Side-swip injuries; a car drivers elbow protruded through the window, is struck by another vehicle. the result is foreword dislocation with fracture of any or all bones around the elbow, soft tissue damage is usually severe, often associated with damage to the major vessels.
Vascular injury.
Nerve injury.
Late
Stiffness-prolong immobilization.
Heterotopic ossification (myositis ossificans).
Recurrent dislocation.
Osteoarthritis.
Unreduced dislocation.
Bicondylar T &Y fractures
C.F.high-energy injuries which are associated with vascular and nerve damage.
Radiology
Type A: an extra-articular supracondylar #.Type B: An intra articular unicondylar #.
Type C: Bicondylar # with varying degree of comminution.
Treatment
ORIF.Elbow replacement.
Complications
Early: neurovascular injuries.
Late: stiffness, heterotopic ossification.
Capitellum fracture
Mechanism of injury
The patient is usually elderly or middle-aged and presents following a fall onto an outstretched extremity or following direct trauma to the elbow.
C.F.
Pain, swelling, and tenderness that are localized to the lateral elbow are evident on physical examination. Any attempt at flexion or extension motion is resisted, and the pain is accentuated with forearm rotation.X-ray ,C.T.
Treatment: ORIF
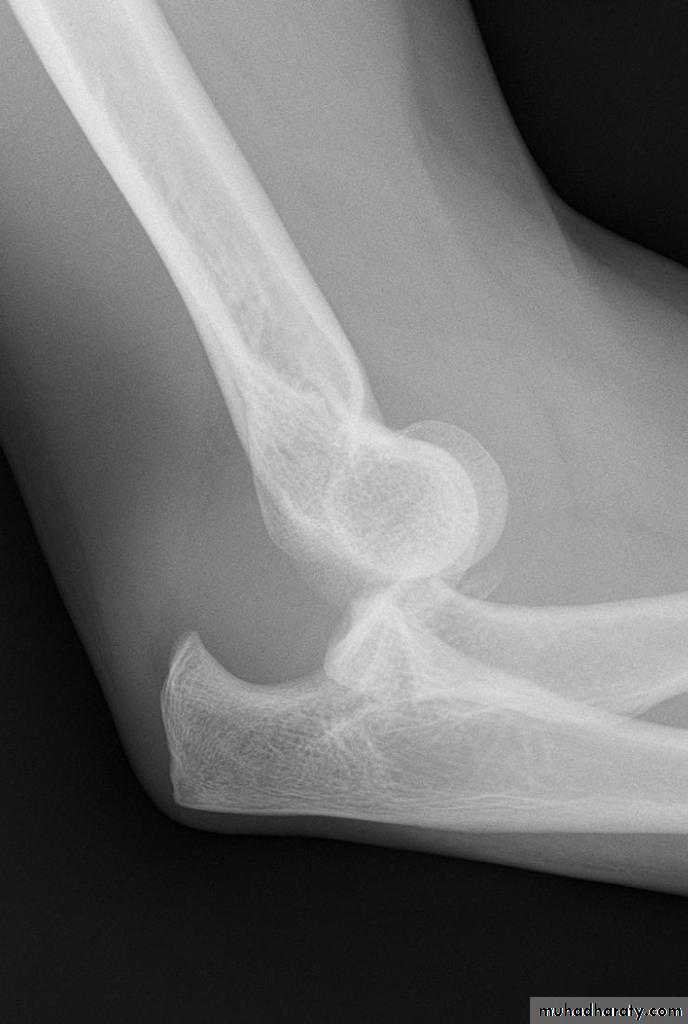
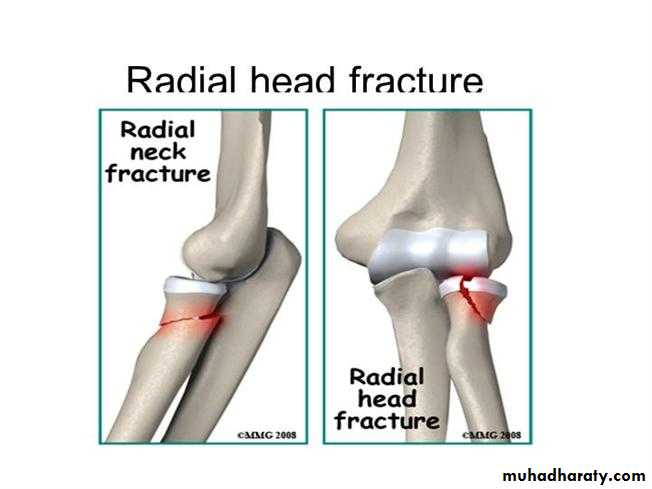
Fractured head of radiusMOI; a fall on the outstretched hand with the elbow extended and the forearm pronated cause impaction of the radial head against the capitulum.
CF; tenderness over radial head. pain on pronation&supination.
X-RAY:
TI undisplaced vertical split.T2 Displaced single fragment.
T3 comminution.
Treatment;
T1 splint.
T2 ORIF.
T3 excision or reconstruction (replacement).
Complications;
Joint stiffness.Myositis ossificans.
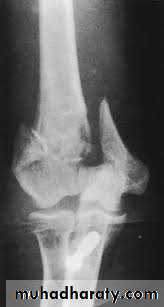
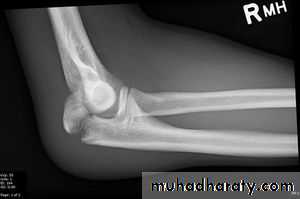
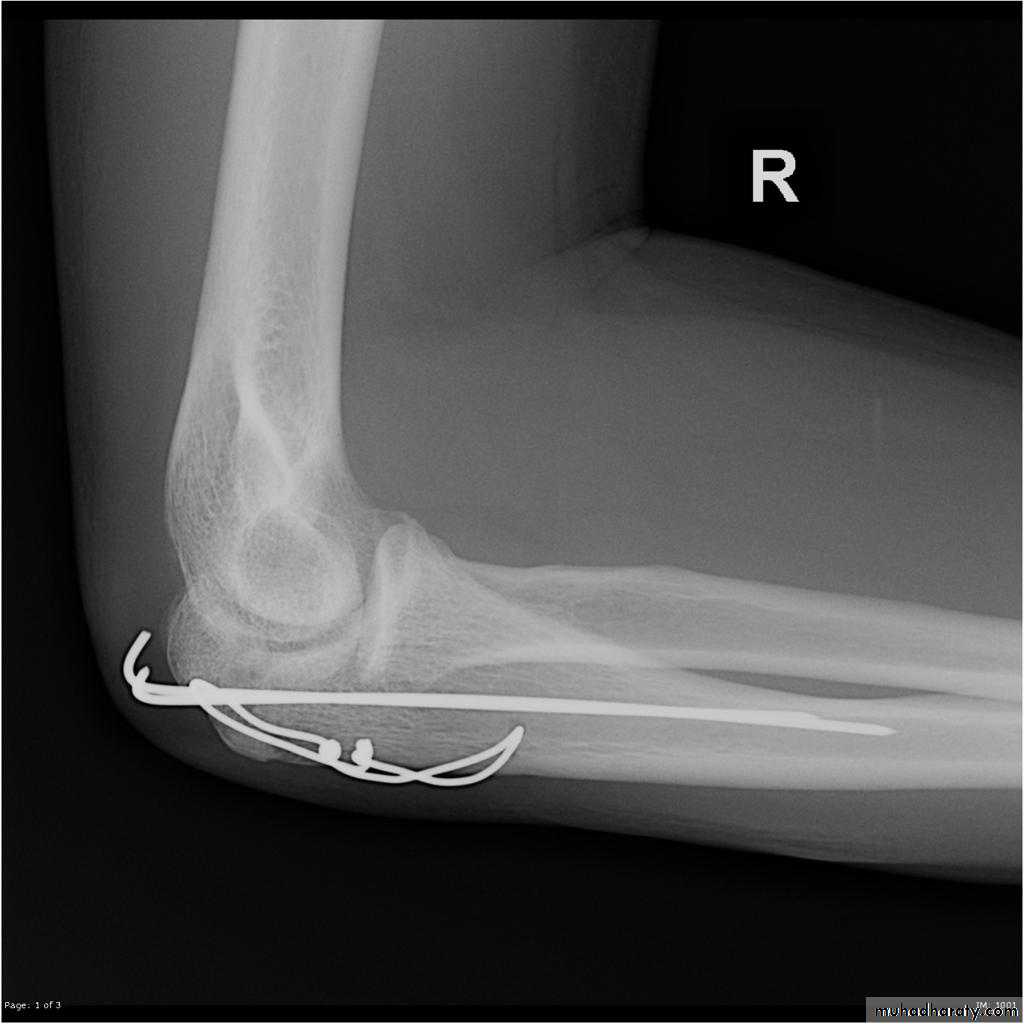
Olecranon Fractures
MOI
Type 1 - direct blow or a fall on the elbow = comminuted #.
Type 2 - Traction when the patient falls onto the hand while the triceps muscle is contracted = transverse #
CF;
Type1-bruise over the elbow, triceps is intact and the elbow can be extended against gravity.Type-2- palpable gap the patient is unable to extend the elbow against gravity.
X-RAY; check the position of the radial head.
Treatment;Type1 splint.
Type2 displaced ORIF. (K wire & tension band wiring).
Complication;
Stiffness.Non union.
Ulnar N.palsy .
Osteoarthritis.