Oral Ulceration
By:Dr. Ahmed Salih KhudhurBDS, MSc, PhD Newcastle University/ UK
دكتور احمد صالح خضر
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Department of:
HERE
Introduction
•
How to Examine an Ulcer
•How to Examine an Ulcer
•How to Examine an Ulcer
While examining a patient with an oral ulcer, ask about the following:History of the ulcer:
1. According to the patient’s chief complain, is the ulcer painful?
2. According to the patient’s chief complain, does the patient know the duration? or was it noticed by another clinician who referred the patient to you?
3. Can the patient recall any possible cause?
4. Recurrent or not?
Past dental history?
Medical history?Family history?
Social history?How to Examine an Ulcer
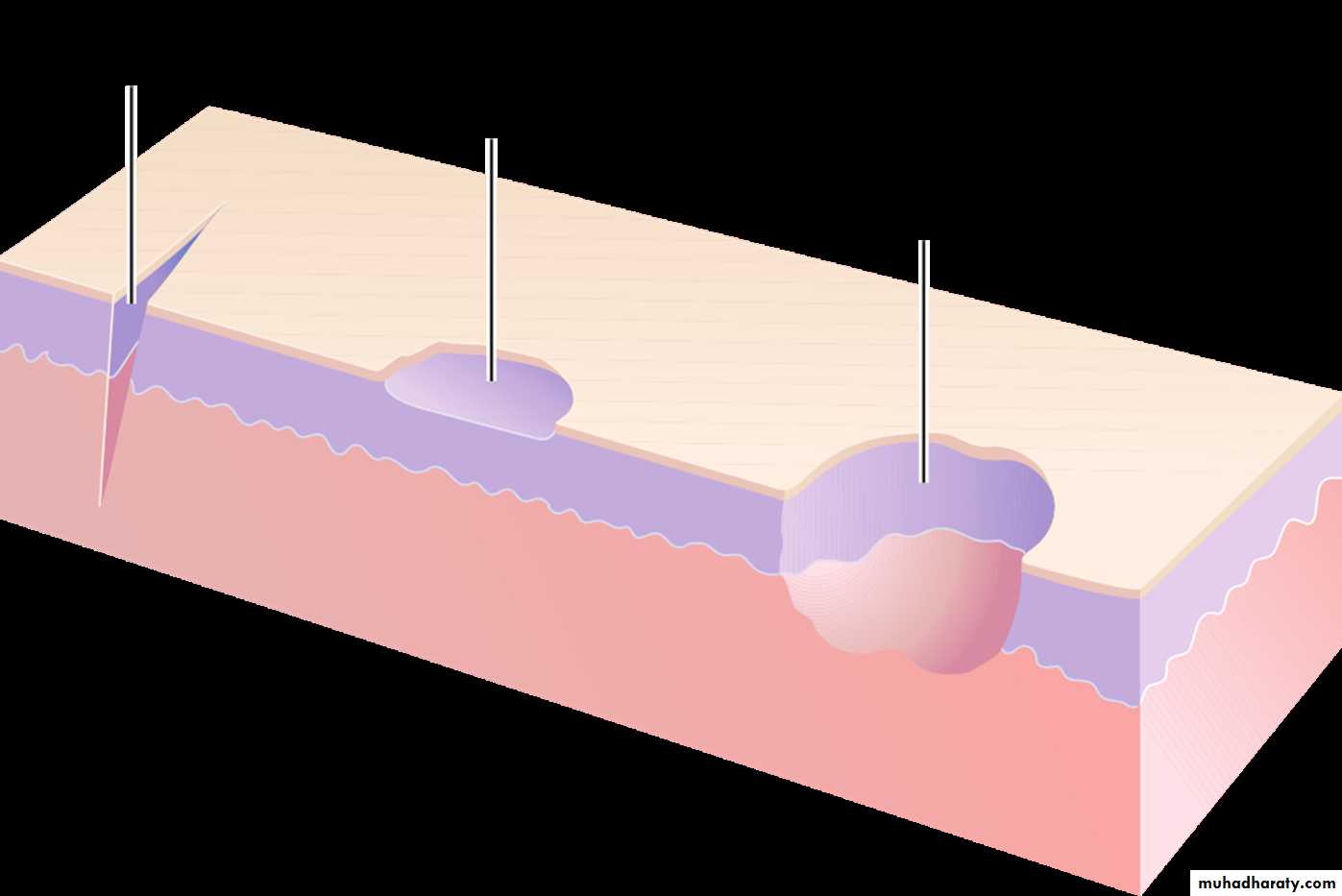
While examining a patient with an oral ulcer, inspect the following:Location (position)
Number
Size and shape
Color
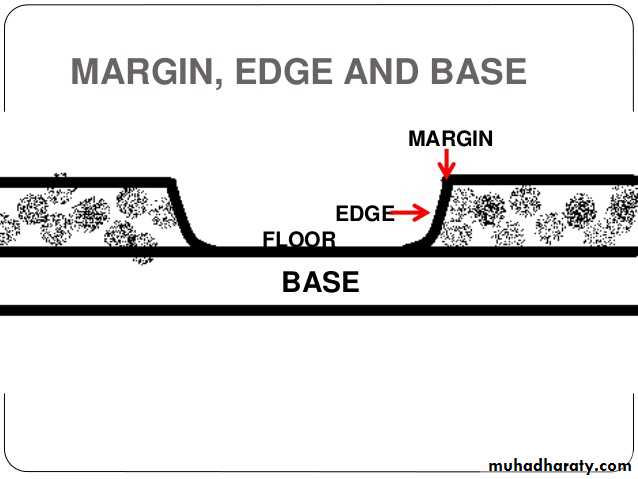
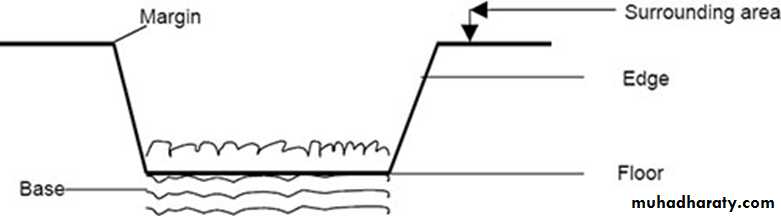
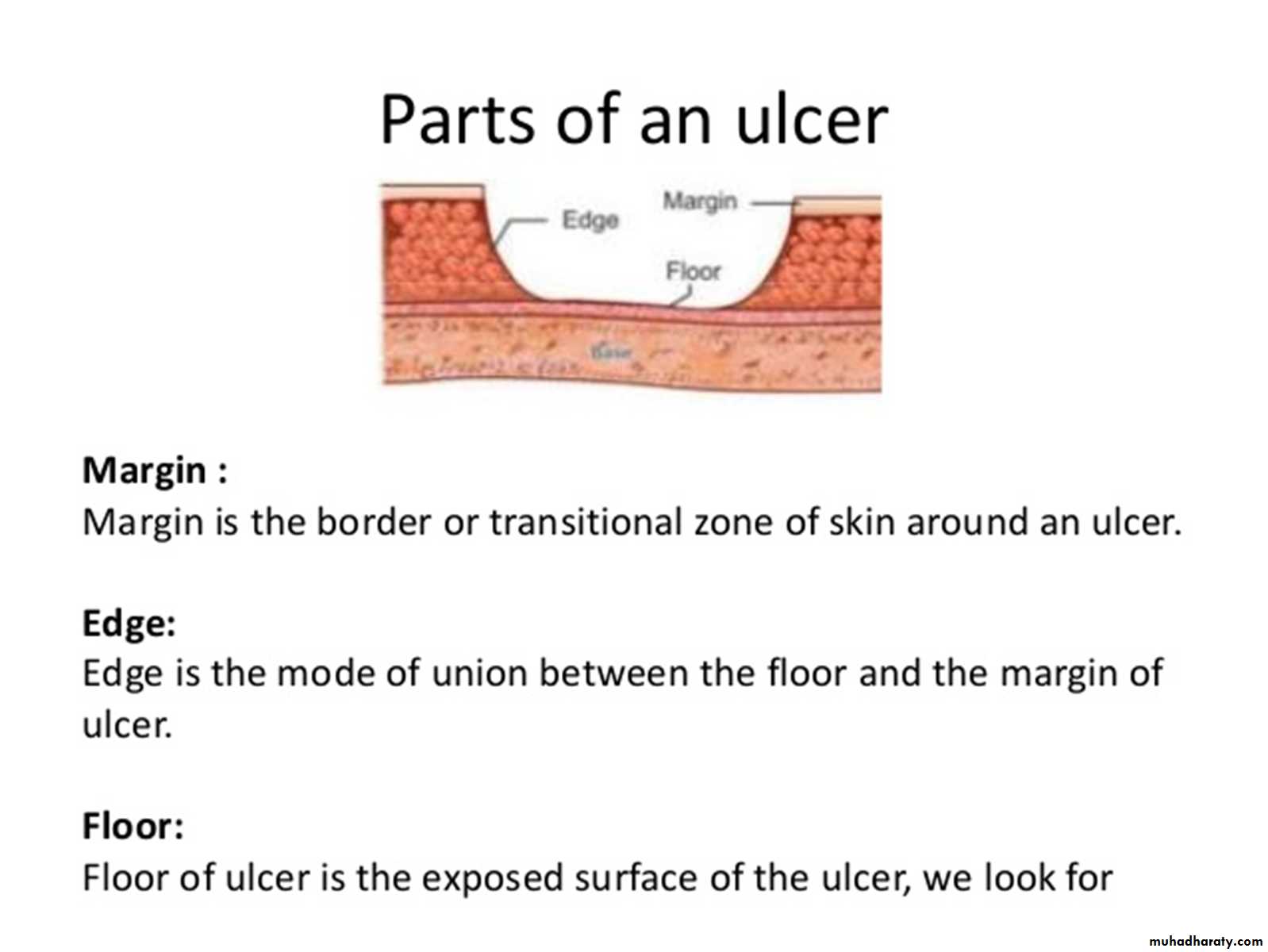
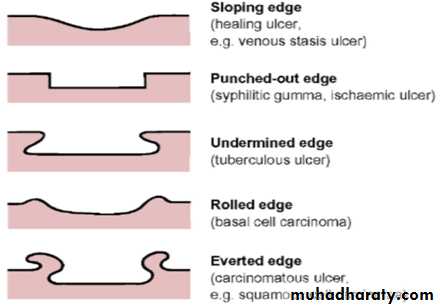
Edge and floor
Surrounding area
Tender to palpation?
Base: Relation to the underlying structures? (Loose, Firm or Fixed/ Indurated)
Regional lymph nodes
If necessary and to exclude a disease/ condition (differential diagnosis) or to confirm the diagnosis, you may send the patient for investigations such as:
# Biopsy # Microbiological & Immunological tests # Haematological tests
# Imaging (MRI, CT scan, CBCT, PET scan…) # Further investigations…..
PET scan: positron emission tomography
Classification of Oral Ulceration
Ulcers divided clinicallyPersistent Recurrent
Which is a useful first step in differential diagnosisMost oral ulcers heal after a few days to 2 weeks (maximum duration) depending on their size and location, more rapidly on the floor of mouth or buccal mucosa (non-keratinized mucosa) than on the palate or gingivae (Keratinized mucosa).
Recurrent oral ulcers recur singly or in groups at the same or different sites.
It is important to distinguish recurrent oral ulceration which has a few causes, from recurrent aphthous ulceration (RAU/RAS) which is a specific ulcer (condition).Classification of Oral Ulceration
Ulcers can be According to NumberPrimary Secondary Single Multiple
• Other classification according to etiology:• Traumatic
• 2. Infective
Acute infection such as: Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis & Noma
Chronic infection such as: Tuberculosis, Syphilis, Histoplasmosis
Viral infections such as: Herpes viruses
• 3. Miscellaneous causes ( RAS/RAU, Behçet’s disease, IBD, Cyc. N, EM, SJS/TEN, Oral mucositis, Pemphigus & MMP, Oral cancer, ulcers associated with oral & systemic diseases
Classification of Oral Ulceration
• Important causes of oral mucosal ulcers• Vesicular-bullous diseases
• Ulceration without preceding vesiculation• Infectious
• Primary herpetic stomatitis
• Herpes labialis
• Herpes zoster and chickenpox
• Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
• Herpangina
• Measles
• Glandular fever
• Tuberculosis
• Syphilis
• Non-infectious
• Pemphigus vulgaris
• Mucous membrane pemphigoid
• Linear IgA disease
• Dermatitis herpetiformis
• Bullous erythema multiforme
• Traumatic
• Aphthous stomatitis
• Behçet’s disease
• HIV-associated mucosal ulcers
• Lichen planus
• Lupus erythematosus
• Eosinophilic ulceration
• Wegener’s granulomatosis
• Some mucosal drug reactions
• Carcinoma
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021