بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Lecture -6 Neurophysioloy Dr. Noor
2nd stage 2021
………………………………………………………………………
Spinal cord reflexes
Objectives:
What is a reflex?
Classifications of reflexes?A reflex is an involuntary, stereotyped pattern of response brought about by a sensory stimulus.
Classification of Neural Reflexes
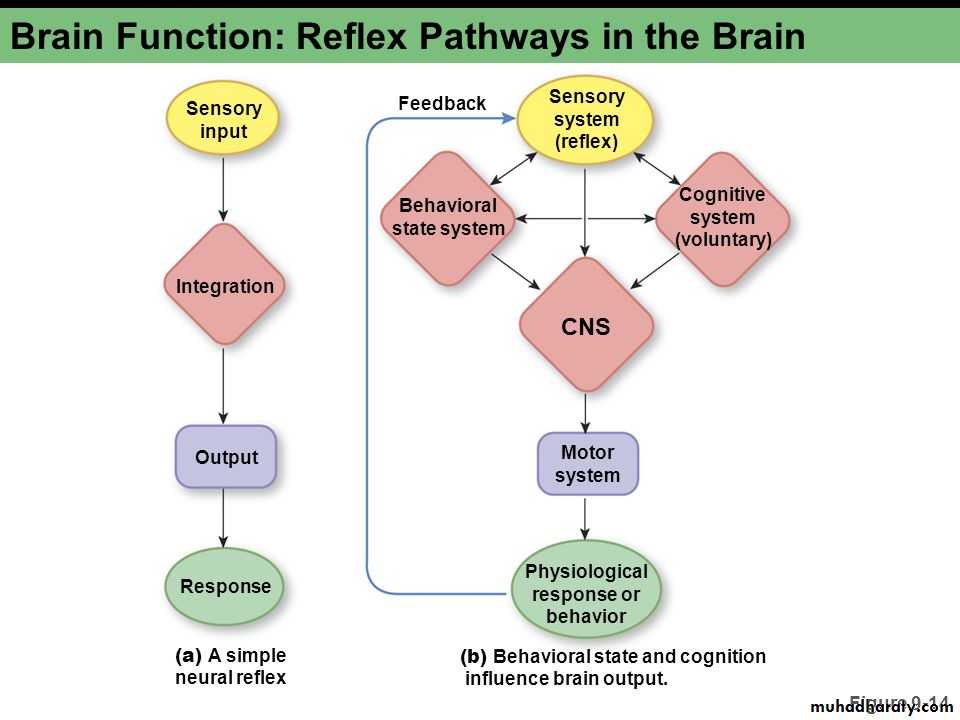
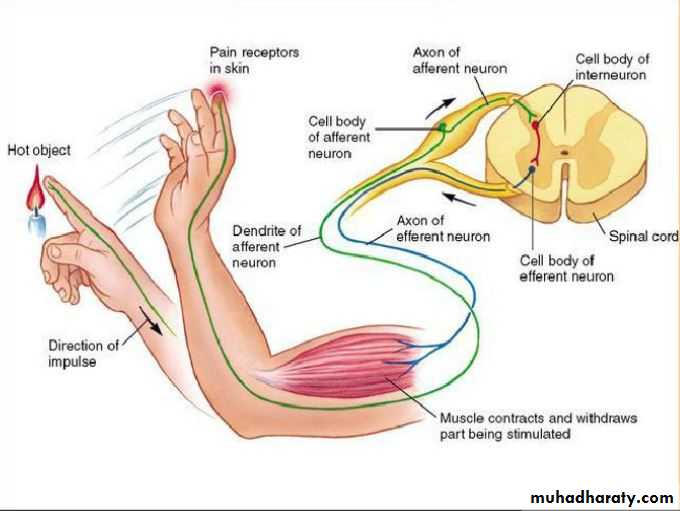
Reflex arc
Defines the pathway by which a reflex travels—from the stimulus to sensory neuron to motor neuron to reflex muscle movement.
Components of a reflex arc:
Afferent neuron: the peripheral endings of the afferent neurons are modified to form sensory receptors, which may be exteroceptors, interoceptors, or proprioceptors.
Interneuron : functions to modify the activities of afferent neurons.
Efferent neuron: motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord, or those associated with certain cranial nerves.
Effector : brings about the reaction; it may be a muscle, a gland, or a vessel.
Types of Reflex Arcs
There are two types of reflex arcs: the autonomic reflex arc, affecting inner organs, and the somatic reflex arc, affecting muscles. When a reflex arc consists of only two neurons, one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron, it is defined as monosynaptic.
Monosynaptic refers to the presence of a single chemical synapse. In the case of peripheral muscle reflexes (patellar reflex, achilles reflex), brief stimulation to the muscle spindle results in the contraction of the agonist or effector muscle.
By contrast, in polysynaptic reflex arcs, one or more interneurons connect afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) signals.For example, the withdrawal reflex (nociceptive or flexor withdrawal reflex) is a spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimuli. It causes the stimulation of sensory, association, and motor neurons.
What is the importance of reflex testing in a routine physical examination?
Allows the condition of the nervous system to be assessed. Pathology is indicated by exaggeration, distortion, or absence of reflexes normally present.Spinal Reflexes
Are reflexes that their centers are present in spinal cord .Classification of spinal cord reflexes:
Are classified into 3 types:Superficial spinal reflex:
Their receptors are present on body surface (skin), Examples:
Scratch reflex.
Flexor withdrawal reflex.
Abdominal reflex.
Planter reflex.
Cremasteric reflex.
Deep spinal reflexes:
Their receptors are present in deep structures like muscle, joints , bone, Examples: stretch reflex.
Visceral spinal reflexes:
Their receptors are present in visceral organs, Examples:
Micturition reflex.
Defecation reflex.
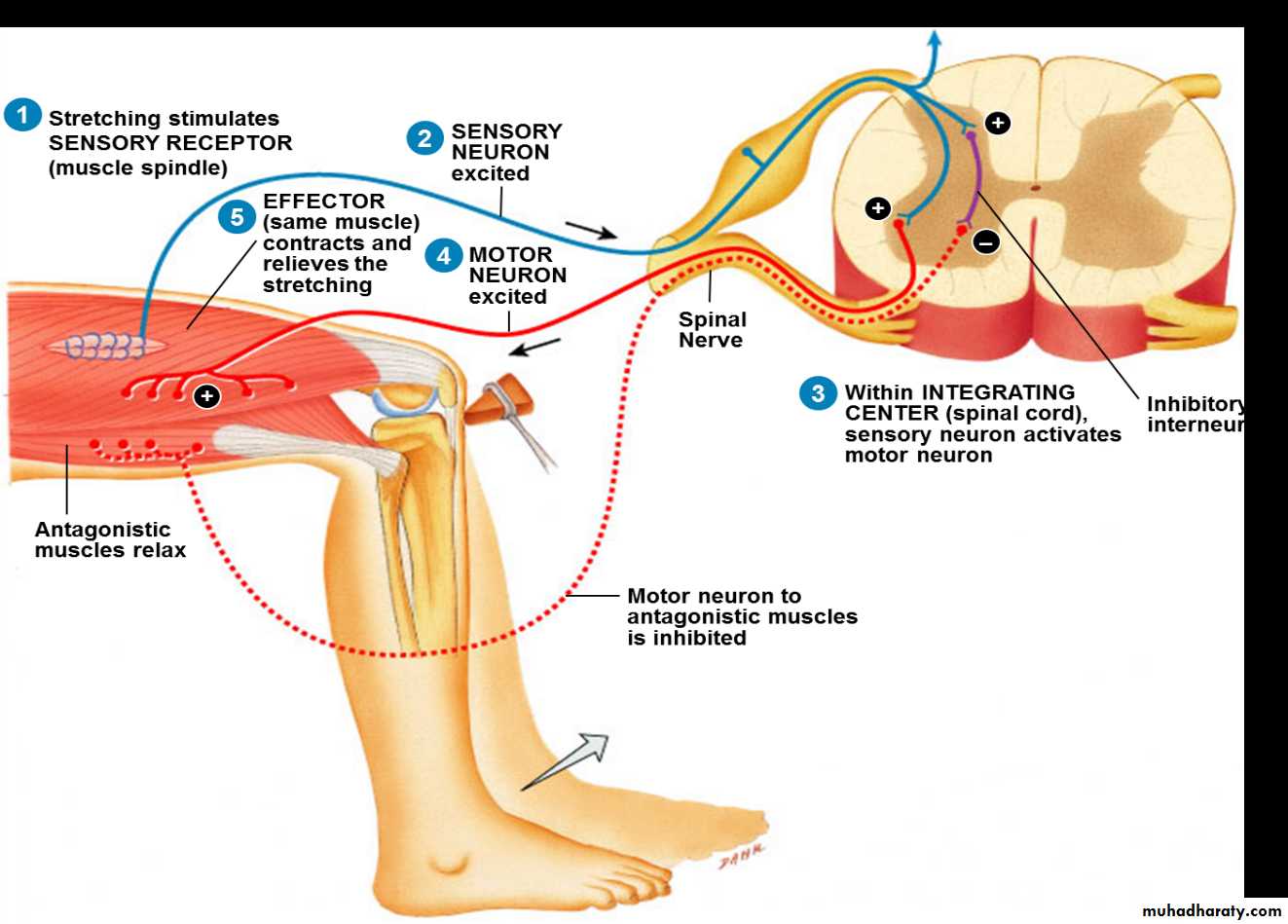
Stretch Reflex
The stretch reflex (myotatic reflex) is a muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle. This reflex has the shortest latency of all spinal reflexes. It is a monosynaptic reflex that provides automatic regulation of skeletal muscle length.
When a muscle lengthens, the muscle spindle is stretched and its nerve activity increases. This increases alpha motor neuron activity, causing the muscle fibers to contract and thus resist the stretching. A secondary set of neurons also causes the opposing muscle to relax. The reflex functions to maintain the muscle at a constant length.
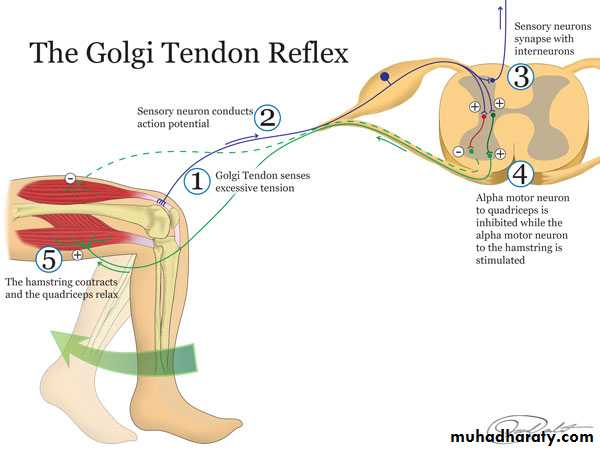
Golgi Tendon Reflex
The Golgi tendon reflex is a normal component of the reflex arc of the peripheral nervous system. The tendon reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle tension by causing muscle relaxation before muscle force becomes so great that tendons might be torn. The sensory receptors for this reflex are called Golgi tendon receptors, and lie within a tendon near its junction with a muscle. In contrast to muscle spindles, which are sensitive to changes in muscle length, tendon organs detect and respond to changes in muscle tension that are caused by a passive stretch or muscular contraction.Crossed Extensor Reflex
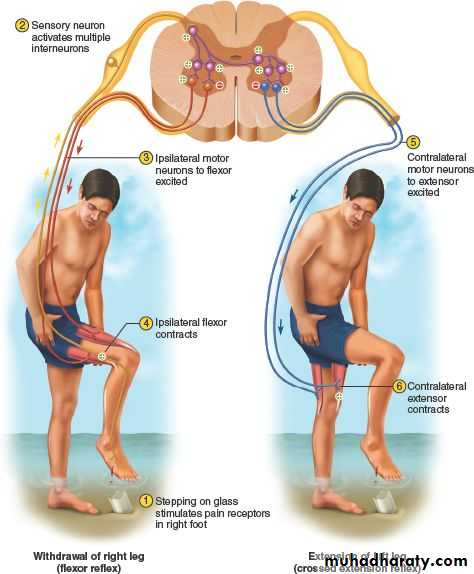
The crossed extensor reflex is a withdrawal reflex. The reflex occurs when the flexors in the withdrawing limb contract and the extensors relax, while in the other limb, the opposite occurs. An example of this is when a person steps on a nail, the leg that is stepping on the nail pulls away, while the other leg takes the weight of the whole body. The crossed extensor reflex is contralateral, meaning the reflex occurs on the opposite side of the body from the stimulus. To produce this reflex, branches of the afferent nerve fibers cross from the stimulated side of the body to the contralateral side of the spinal cord. There, they synapse with interneurons, which in turn, excite or inhibit alpha motor neurons to the muscles of the contralateral limb.Withdrawal Reflex
The withdrawal reflex (nociceptive or flexor withdrawal reflex) is a spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimuli. It is polysynaptic, and causes the stimulation of sensory, association, and motor neurons.When a person touches a hot object and withdraws his hand from it without thinking about it, the heat stimulates temperature and danger receptors in the skin, triggering a sensory impulse that travels to the central nervous system. The sensory neuron then synapses with interneurons that connect to motor neurons. Some of these send motor impulses to the flexors to allow withdrawal.
Some motor neurons send inhibitory impulses to the extensors so flexion is not inhibited—this is referred to as reciprocal innervation. Although this is a reflex, there are two interesting aspects to it:
The body can be trained to override that reflex.
An unconscious body (or even drunk or drugged bodies) will not exhibit the reflex.
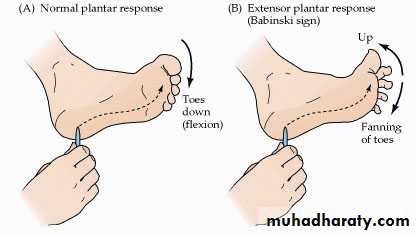
Plantar reflex:
Induced by stroking or scratching the sole of the foot.In a normal adult, this results in plantar flexion and adduction of the toes.
When the pyramidal tract is interrupted, stroking the sole of the foot results in a dorsiflexion of the great toe and fanning of the other toes - Babinski’s sign.
Abdominal reflex:
Contraction of the abdominal muscles when the skin on one side of the abdominal wall is stroked with a blunt point.Thank you