Temporomandibular joint disorders-I
Dr. Mohammed AmjedBDS, MSc, PhD
28.1.2021
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
1
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
2Objectives of this lecture
• Revision of the anatomy of the TMJ
• Diagnosis of TMJ disease
• Surgical Approach
• TMJ disorders
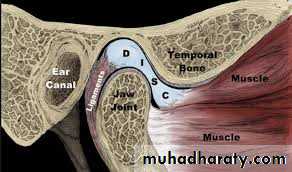
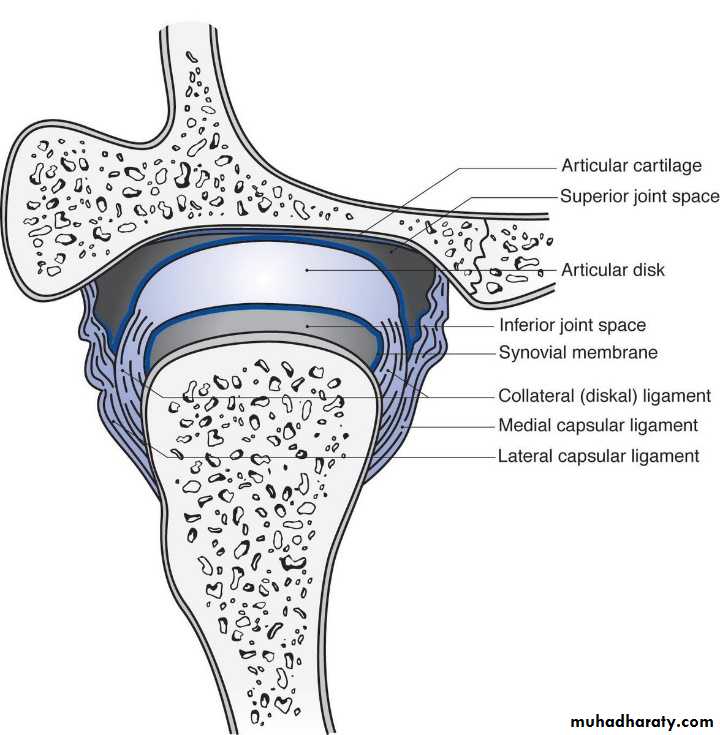
Components of the TMJ
• Bony articular components [condylar head, glenoid fossa]• Intra-articular disc
• Capsule of the joint
• Ligaments of the joint
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
3
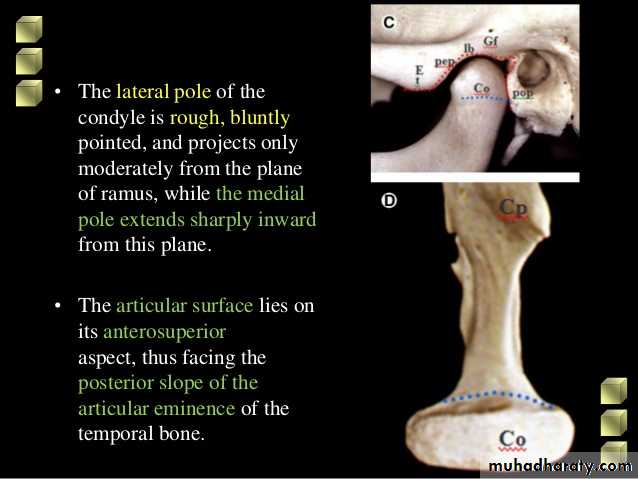
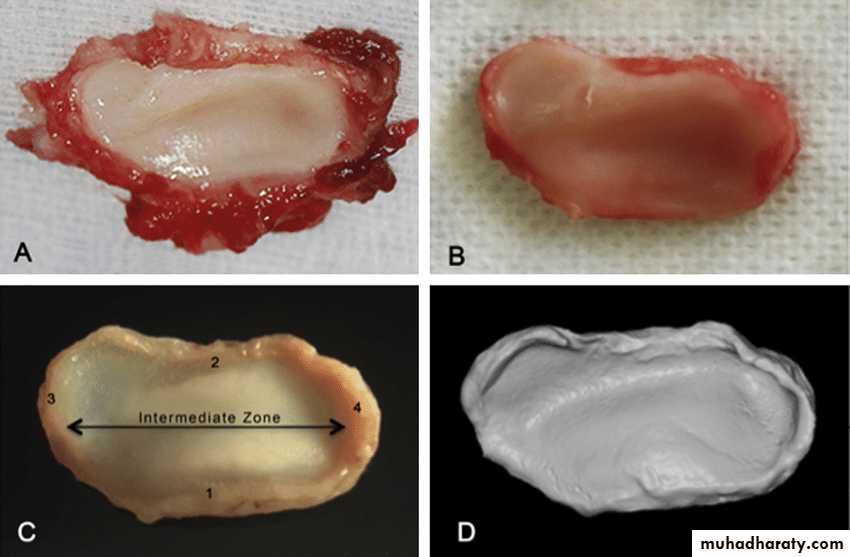
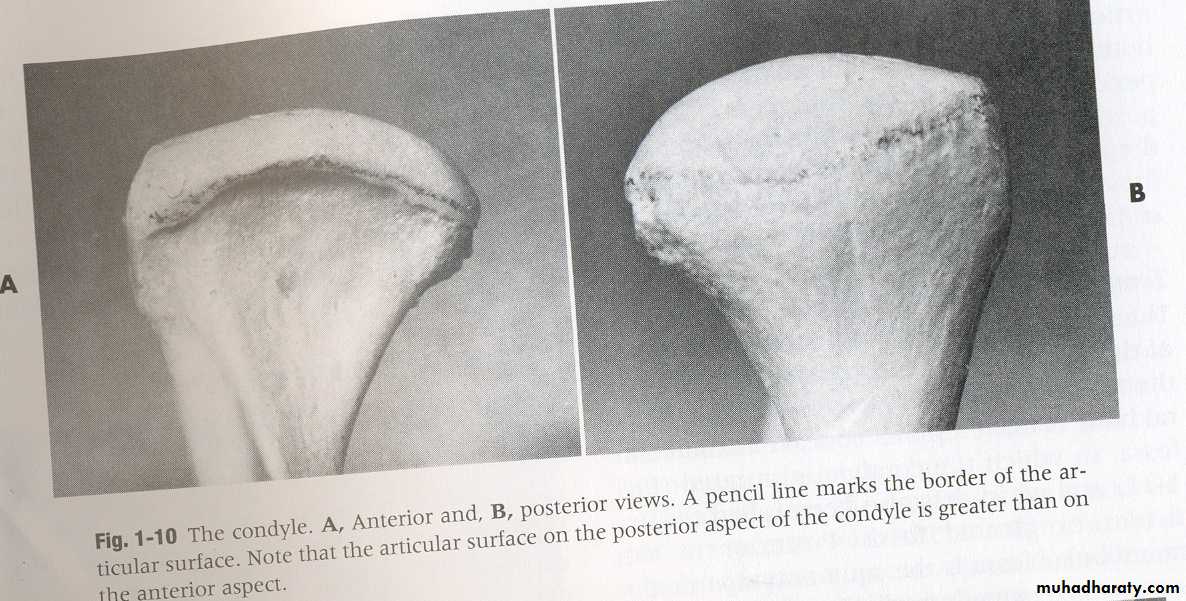
The mandibular condyle:
Its mediolateral dimension (around 20 mm) is larger than the anteroposterior dimension (8–10 mm).The mandibular (glenoid) fossa
The mandibular fossa is a hollow on the inferior surface of the squamous temporal bone. The fossa is bounded anteriorly by a ridge of bone, the articular eminence, which forms the anterior margin of the joint.
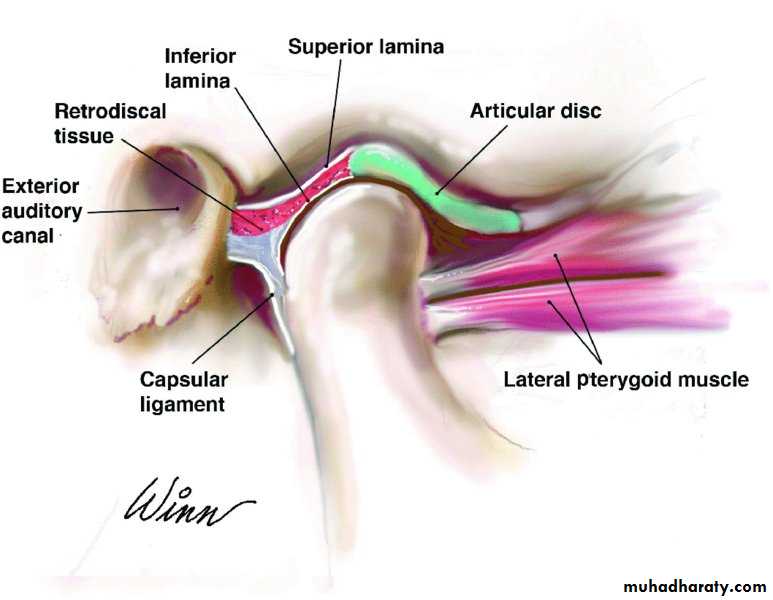
Interarticular disc
The interarticular disc is a biconcave sheet of avascular dense fibrous tissue that divides the joint into a superior (1.2 ml) and inferior joint space (0.9 ml). At its anterior margin, it blends with fibers of the lateralpterygoid muscle. Posteriorly, it attaches to looser connective tissue (bilaminar zone) containing nerves and lined with synovial membrane.
Components of the TMJ
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
4
The main functions of the disc are:
• Absorb shock2. Establish joint stability while translatory movements of the condyle occur
3. Help in lubrication of the jointComponents of the TMJ
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
5
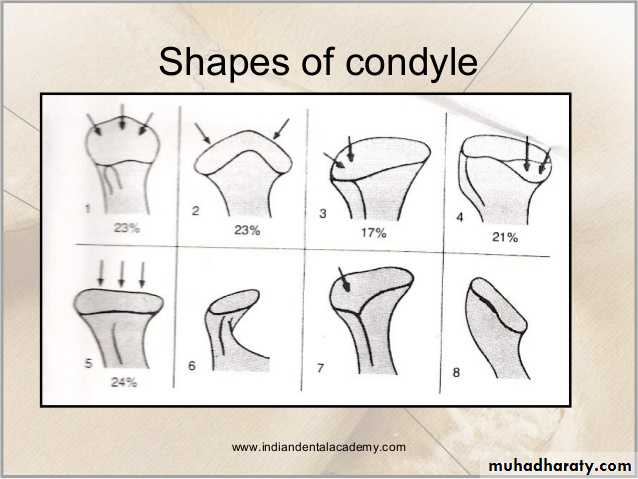
Shape of condyle varies considerably. Variations in shape may cause difficulty with radiographic interpretation
Superior aspect maybe flattened, rounded or markedly convex
Mediolateral contour is usually slightly convex
Shape of condyle
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 20216
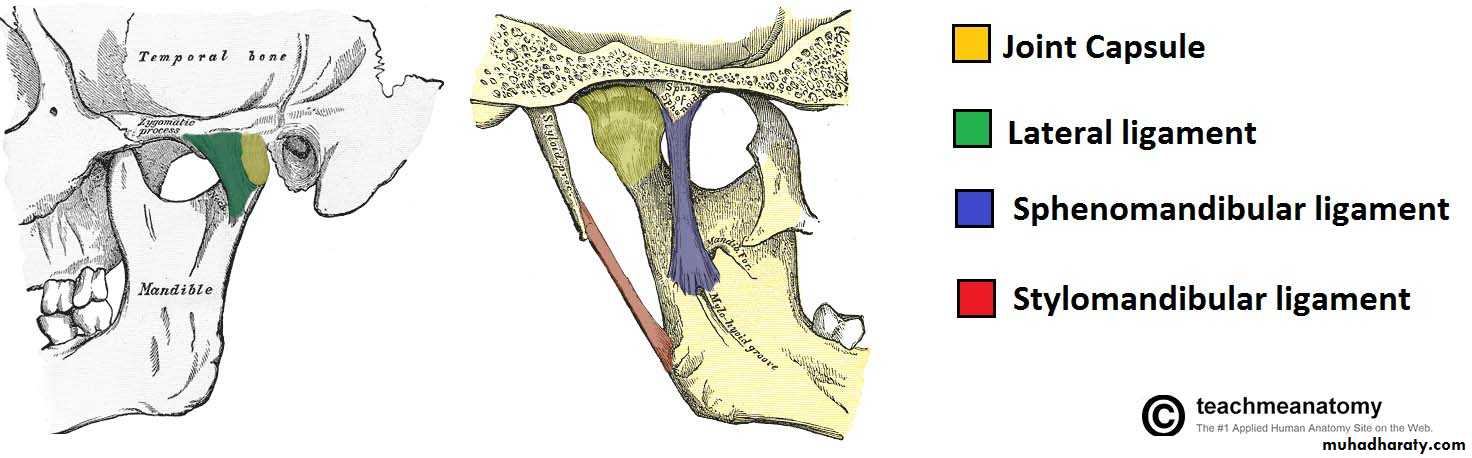
Capsule
The TMJ has a fibrous capsule attached to the rim of the mandibular fossa and the neck of the condyle. The disc attaches to it medially and laterally. The lateral aspects of the capsule are thickened by the lateral (temporomandibular) ligament. The medial wall formed the synovial membrane that secret the synovial fluidLigaments
The lateral ligament lies lateral to the TMJ and runs from the root of the zygoma to the posterior aspect of the condylar neck. It limits anteroposterior joint movement and limit external lateral movement. The sphenomandibular and stylomandibular ligaments are also part of the joint complex and probably also serve to limit movement.
Components of the TMJ
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
7
Joint movement
The joint has a combination of rotatory movement [hinge movement] of the condyle in the lower joint space and anterior translation of the condyle in upper compartment , with sliding of the disc forwards along the articular eminenceDr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
8
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
9Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
10Diagnosis of TMJ disease
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
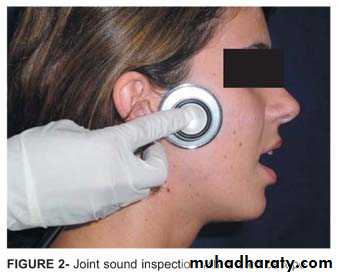
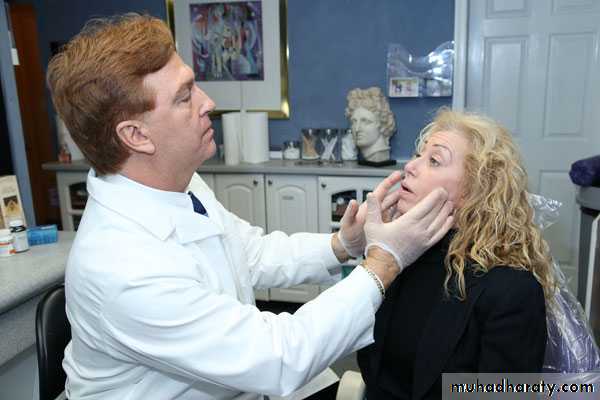
11Examination of TMJ
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
12Radiography is not normally indicated: Most clinical problems related to the TMJ are caused by muscular parafunction (e.g. bruxism) or internal disc derangements.
Neither is likely to be associated with any relevant bony abnormalities.
RadiologyInvestigations
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
13
Bony abnormality, could be seen in rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthrosis
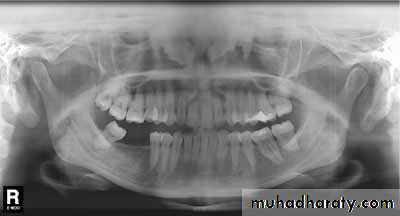
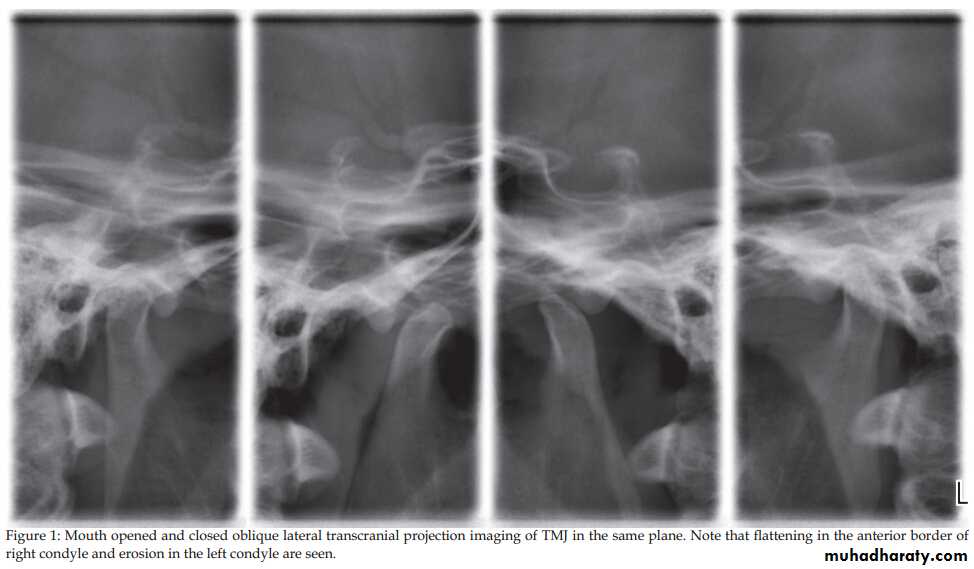
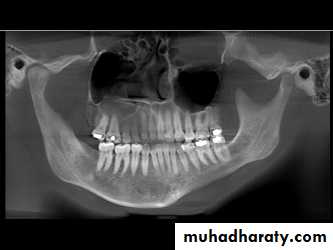
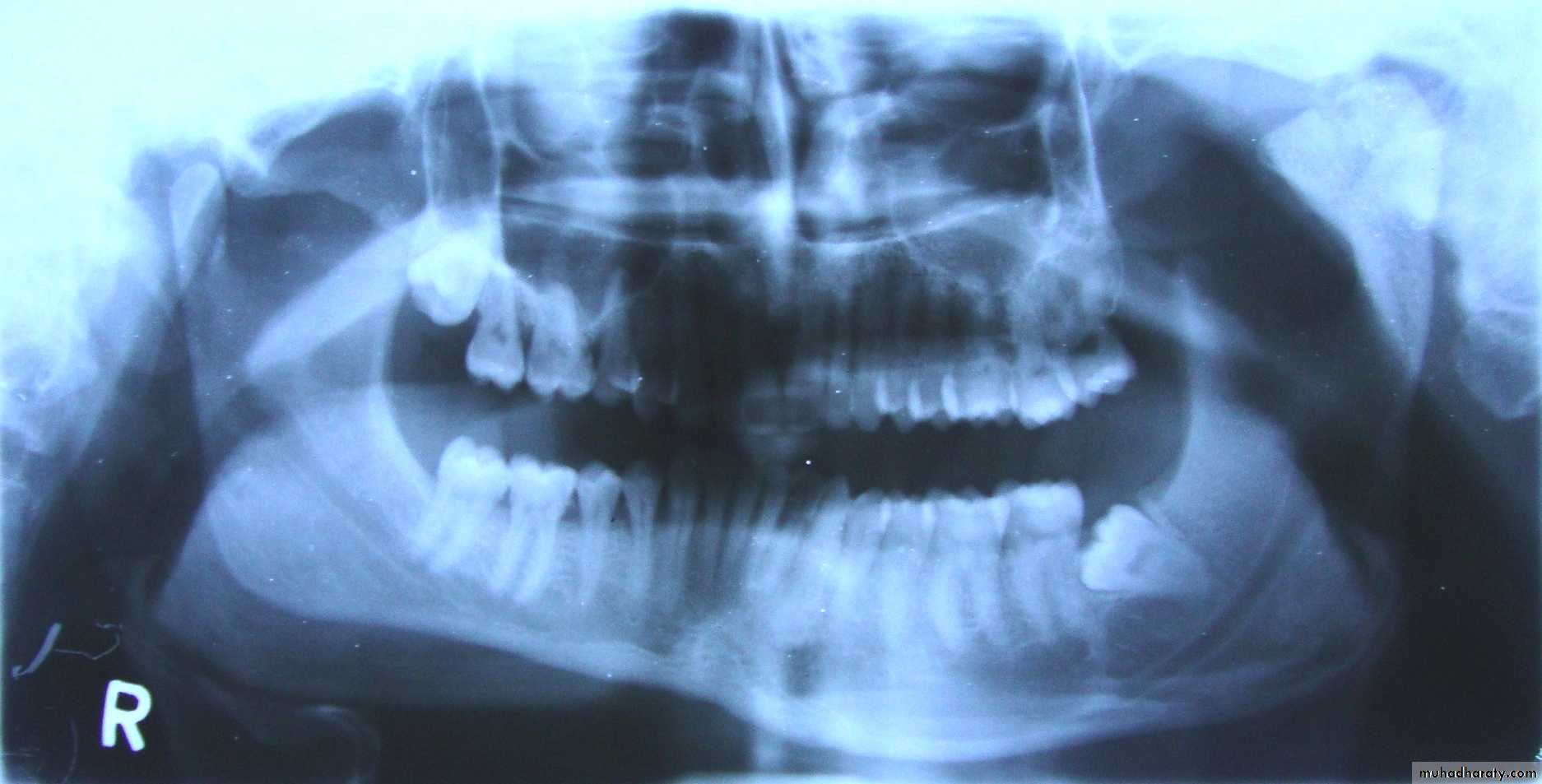
1. OPG & Transcranial oblique lateral view.
Radiology
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
14
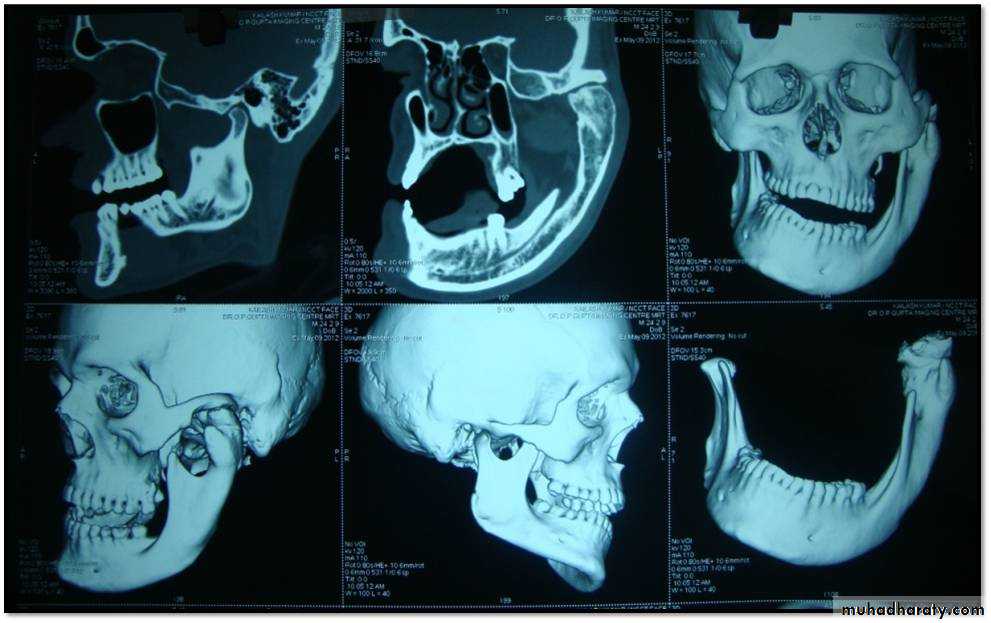
2. Cone-beam computed tomography images (CBCT)
It is usually indicated if bony changes are anticipated like in degenerative joint diseasesRadiology
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202115
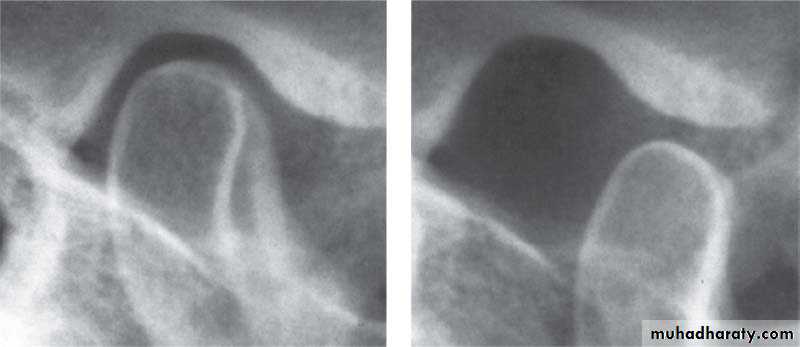
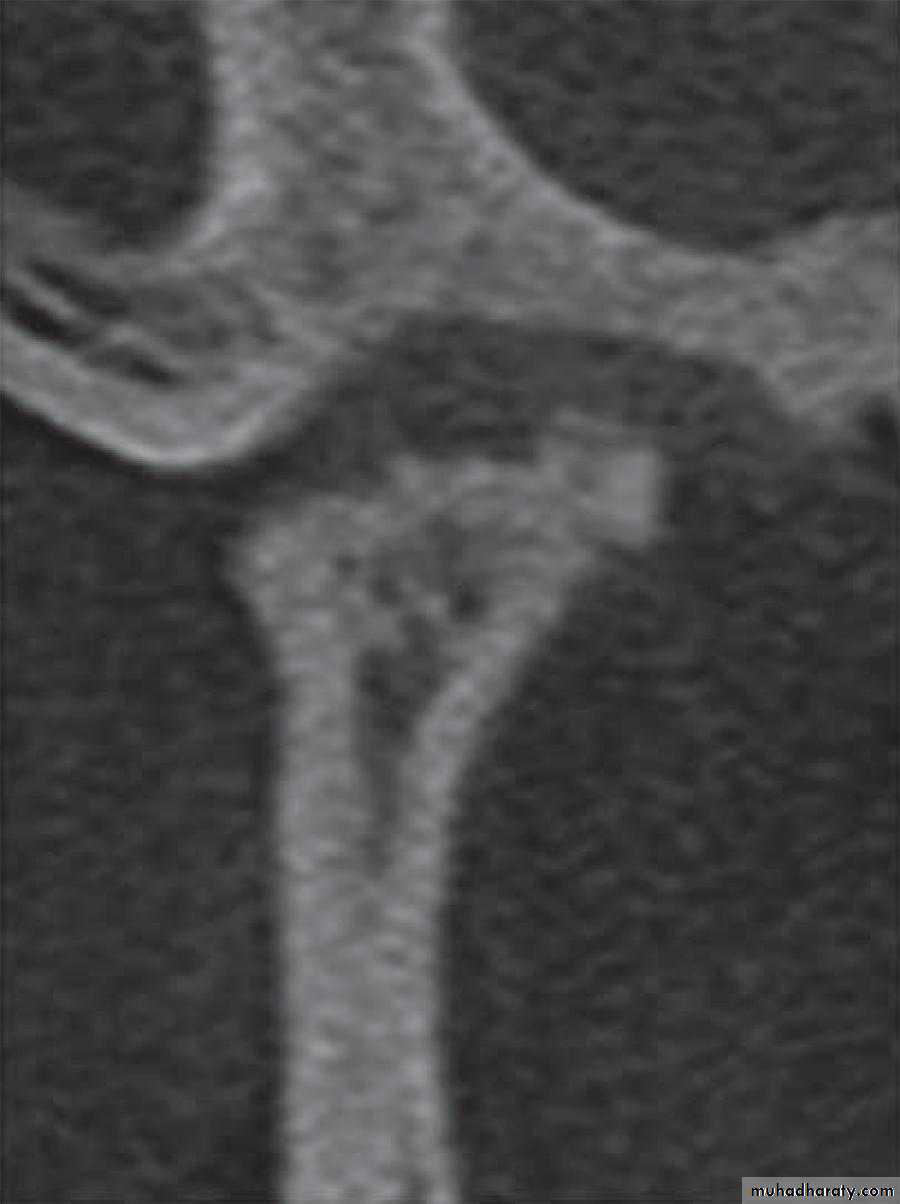
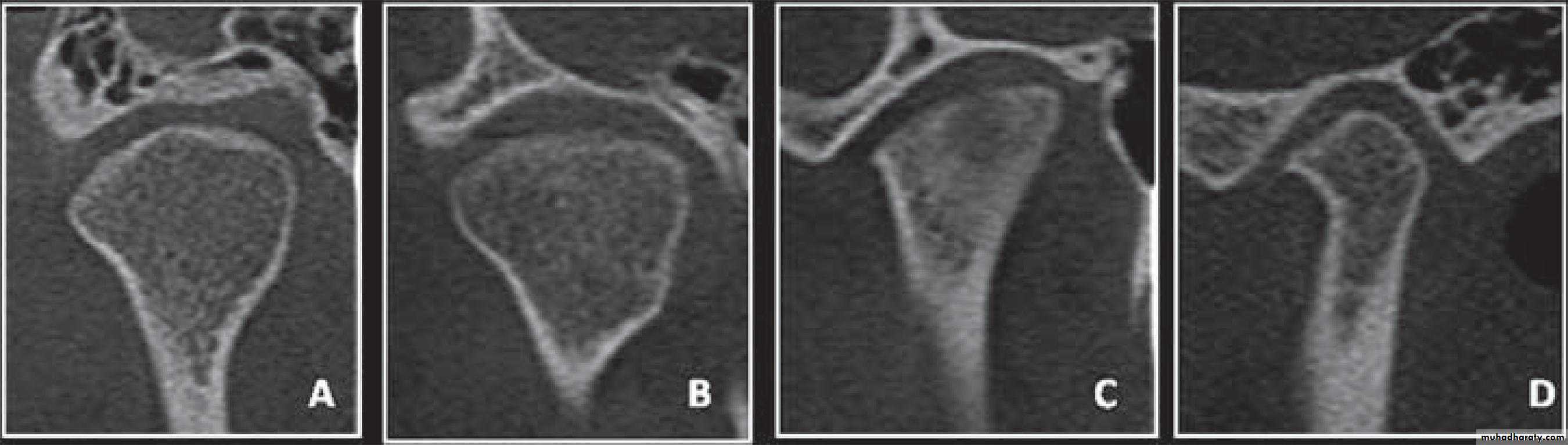
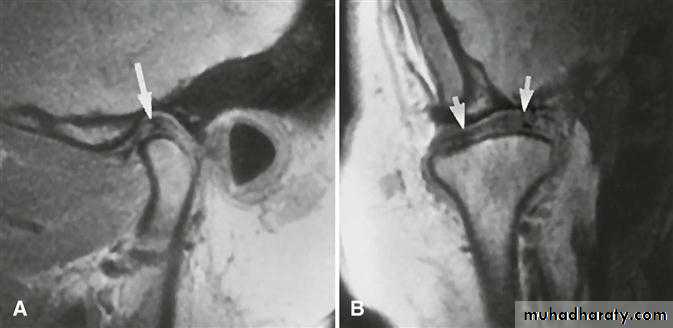
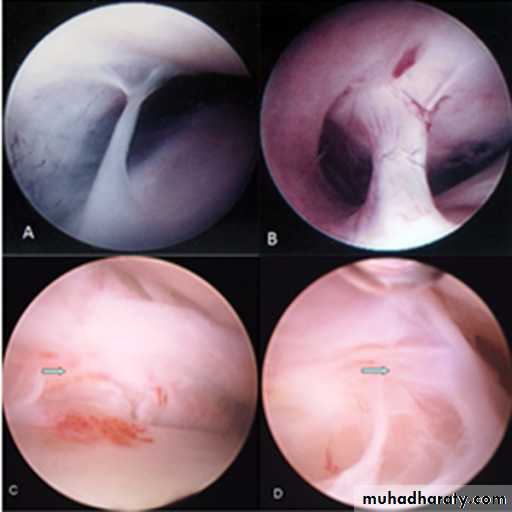
Cone-beam computed tomography images of temporomandibular joint showing morphological variation of the mandibular condyle. A- Normal (coronal view); B- Flattening (coronal view); C- Erosion (coronal view); and, D- Osteophyte (sagittal view)
Radiology
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
16
A clinical diagnosis of suspected internal derangement might lead to a requirement for imaging of the disc. This is done by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Previously, TMJ arthrography is used widely
Radiology
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202117
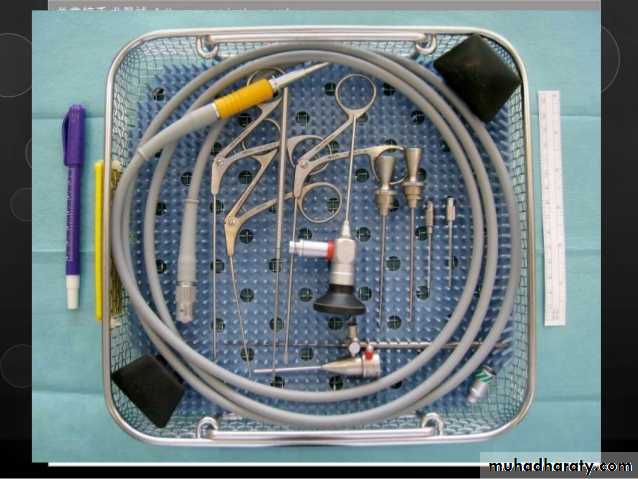
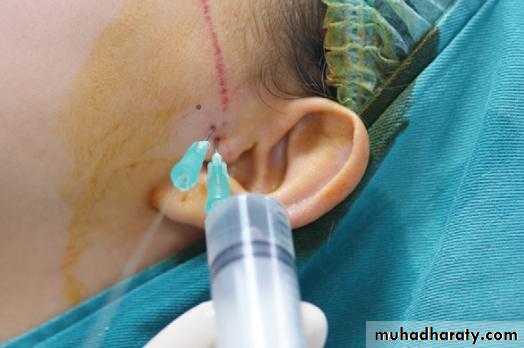
Arthroscopy
• Arthroscopy allows visual examination of the upper joint space and an opportunity for minor surgical treatment. A small arthroscope can be used to facilitate lavage and division of joint adhesions.• The lower joint space is difficult to access without risk of damage to the articular disc.
• Arthroscopy is undertaken under local anaesthesia; however, if lengthy arthroscopic surgery is to be undertaken, then a conscious sedation technique would be appropriate or even general anaesthesia.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
18Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
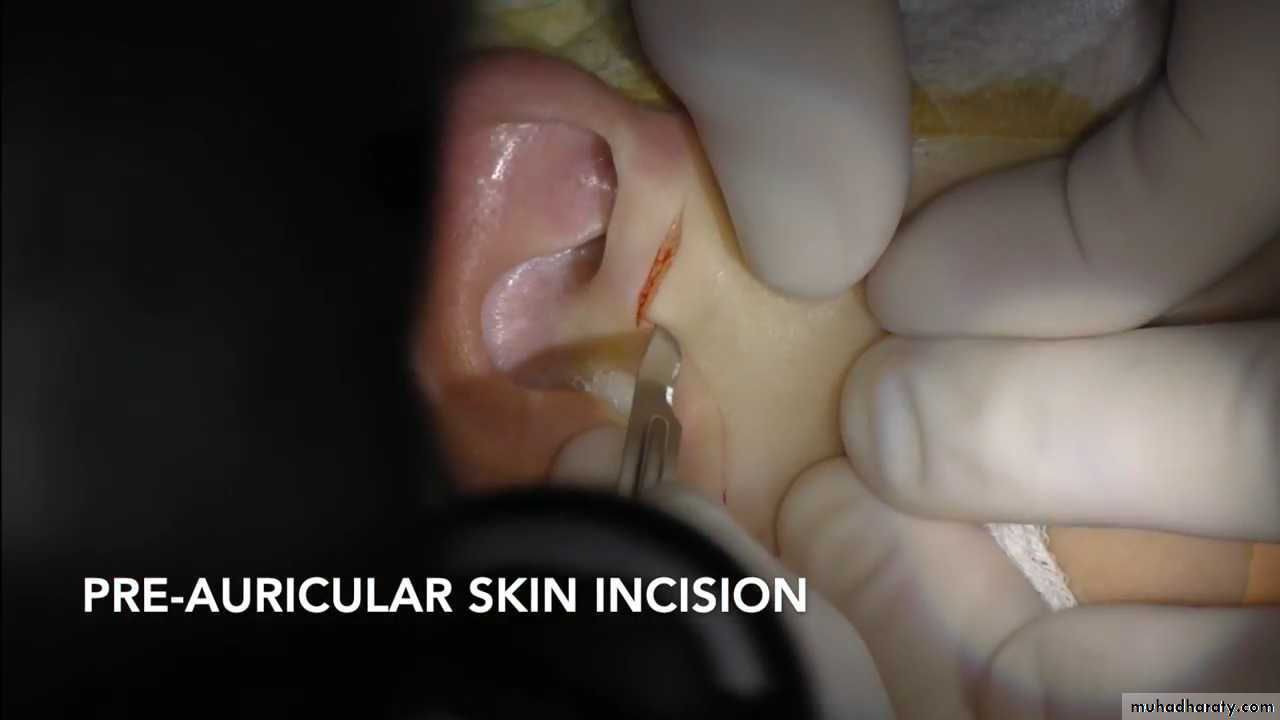
19SURGICAL APPROACH
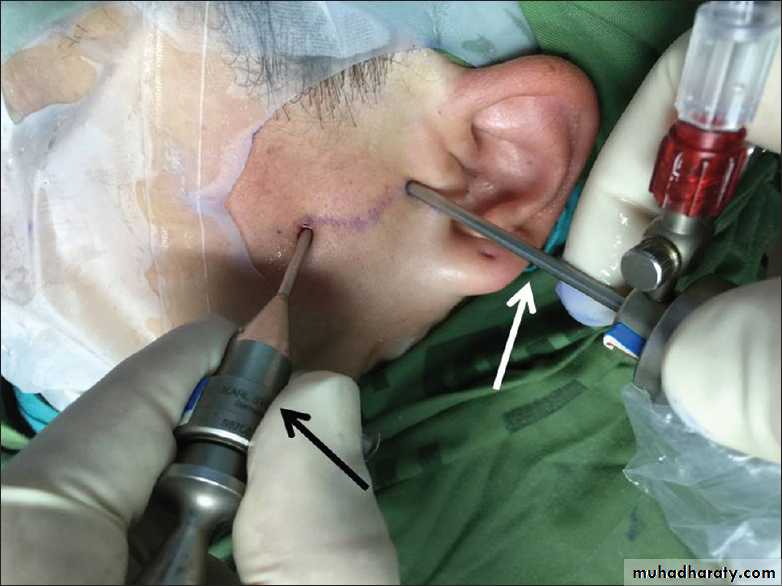
Common approaches1. Pre-auricular
2. Submandibular
3. Post-auricular
4. Intra-oral
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
20
TMJ disorders
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
21
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
22CONDYLE HYPERPLASIA
MYOFUNCTIONAL PAIN DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME (MPDS)
INTERNAL DERANGEMENT
DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE (ARTHROSIS, OSTEOARTHRITIS)
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
DISLOCATION
ANKYLOSIS
NEOPLASIA
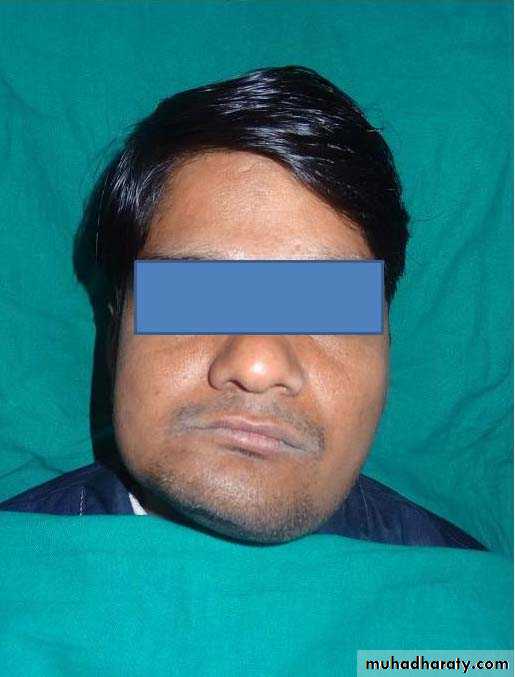
Condyle Hyperplasia
It is a unilateral or bilateral increase in the condyle growth due to local or systemic causes.Features
• Limited mouth opening with occasion pain
in the TMJ.
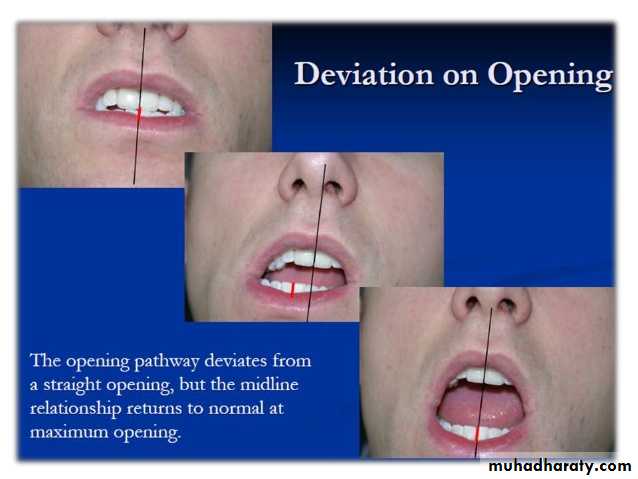
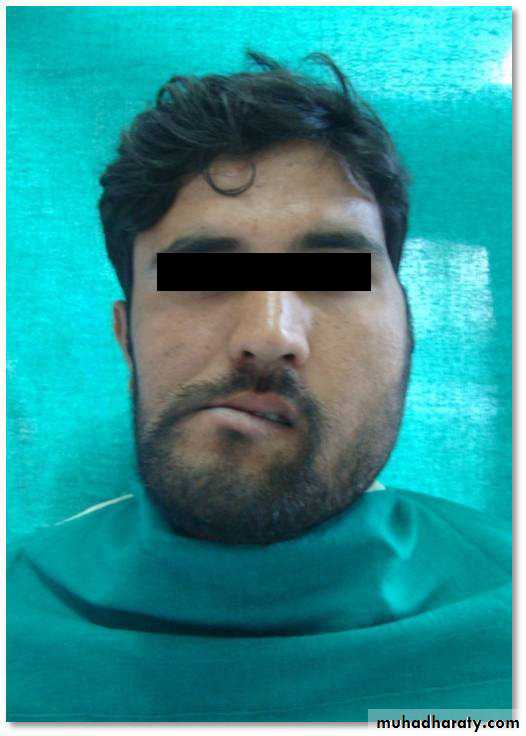
• Deviation of mandible to the unaffected side with facial asymmetry.
• Open bite on affected side with maxillary cant
• Treated by orthognathic surgery, without any permanent facial deformities, if done at an early age.
• Condylectomy or condyloplasty may also be done in some mild cases.
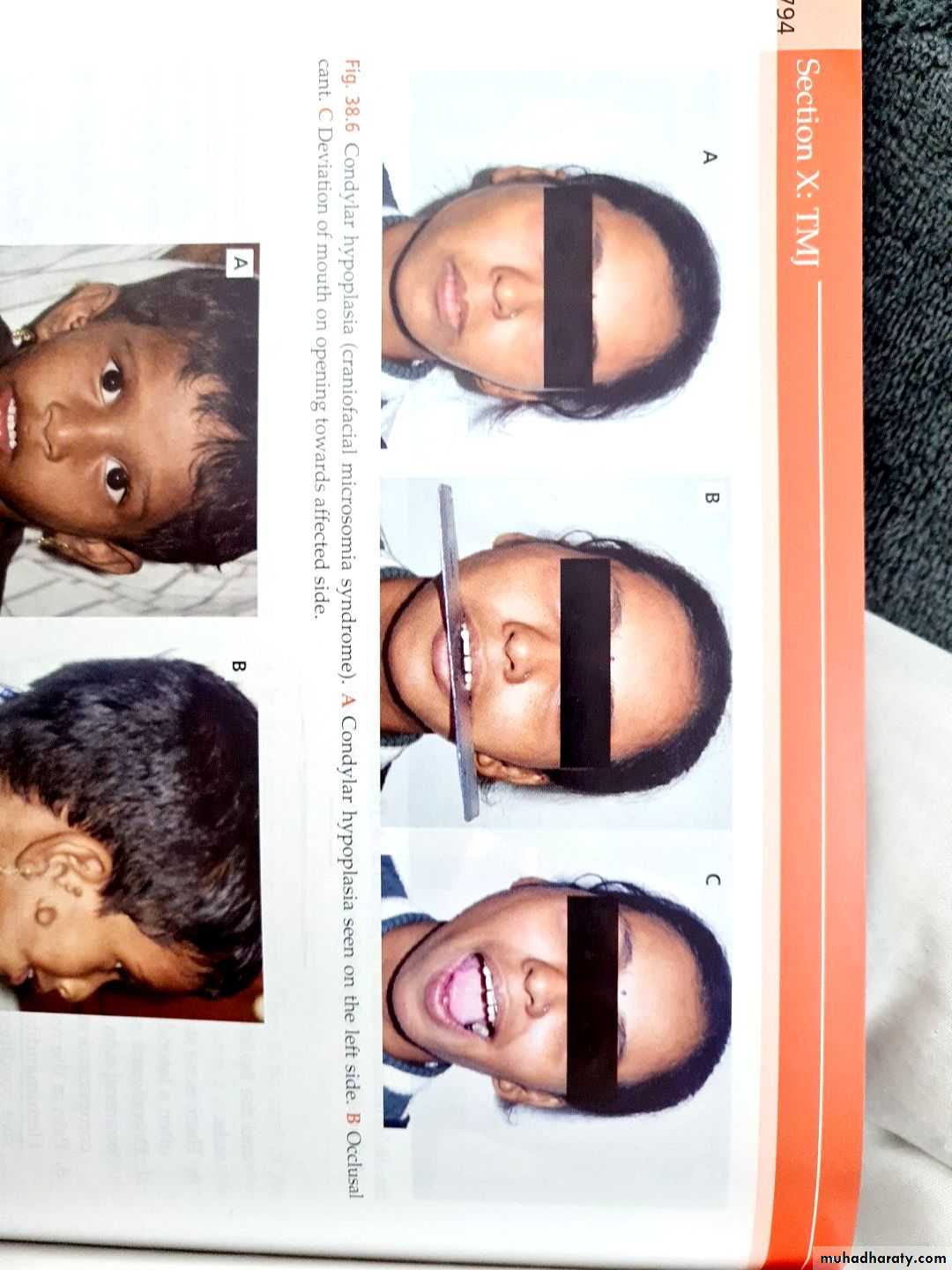
2. Condyle Hypoplasia
It is a unilateral or bilateral decrease in the condyle growth due to local or systemic causes
Features
• Limited mouth opening with occlusion
deviation toward the affected side and facial deformity is seen
• Treated by
- Graft surgeries with or without cosmetic improvement.
- Distraction osteogenesis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
23
Developmental
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
24Condyle Hyperplasia
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
25
Condyle Hyperplasia
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
26Condyle Hyperplasia
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
27Condyle Hyperplasia
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
28Condyle Hypoplasia
• It is [pain+ jaw movement irregularity+ muscle spasm]
• The most common TMJ disorder• It does not have definite clinical entity
• No organic lesion has been detected clinically
Clinical features
Symptoms are a combination of:
# joint pain could associated with headache, referred to neck and shoulder
# limitation ( on start or end of the day)
# deviation of jaw opening specially at awakening
# joint sounds (clicking usually bilateral, without concomitant pain )
# pain on palpation of the TMJ
# pain on palpation of the associated muscles
# Emotional factors: due to secretion of catecholamine
Etiology
psychological factors and/or occlusal derangement
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
29
MYOFASCIAL PAIN DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME(MPDS)
Radiology
There is no abnormality visible.
Management
[Symptomatic first & then etiologic]
The treatment of MPDS varies from giving comfort to the patient to giving intra-articular injection.
• Reassurance and explanation to patients.
• Jaw rest and soft diet.
• Medications:
- Analgesics/anti-inflammatory drugs.- Muscle relaxants (relaxon= chlorzoxazone 250 mg + 300 mg paracetamol. 1X3 or 1X4).
- Anxiolytic like diazepam.
• Occlusal splints to interfere with parafunction may offer some help.
• Physiotherapy. Hot or cold application.
( hot & Ultrasound) which alters blood flow and metabolic activity. Cold which reduce pain by decreases nerve conductivity
• Intra-articular injections: Injection of steroid can be given in acute pain and inflammation but it should not be done as a regular practice. These injection should be given to those patients whom all other measures fail.
MYOFASCIAL PAIN DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME(MPDS)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
30
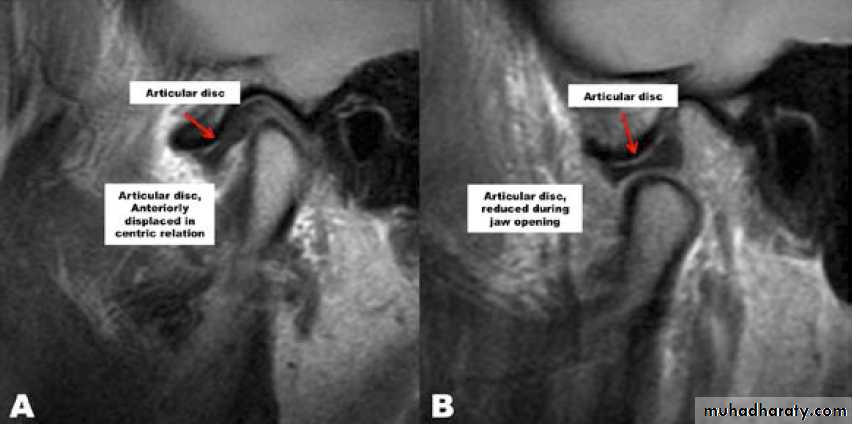
Internal derangement
- The articular disc normally sits above the anterior aspect of the condylar head.- A disc may be anterior to this ‘normal’ position in asymptomatic individuals, suggesting that an anterior disc position is a normal variant. Thus, an internal derangement is best thought of as an abnormality in position that interferes with function and that may be associated with other symptoms.
• An anterior disc ‘displacement’ during closure of the jaw is the most common internal derangement, but anteromedial, medial, and anterolateral displacements are all seen.
• It is progressive from simple clicking to osteoarthritis.
• It is closely related to MFPDS & it is difficult to differentiate between them.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202131
Internal derangement
Either microtrauma or macrotraumaMicrotrauma like bruxism, clenching
Macrotrauma like long dental procedure & overextension of jaw on yawingTrauma lead to elongation of the capsul and discal ligaments and thinning of the articular disc
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
32
Changes in the joint usually occur as a result of trauma.
Disc displacement with reduction
Reduction means that a displaced disc ‘reduces’ into a normal position on opening but reverts to an abnormal position on closing (reciprocal click).Clinical features
• Clicking on opening (after about 10 mm).
• Clicking on closing.
• Transient jaw deviation during opening/closing.
Radiology
No abnormalities are apparent on plain radiographs. MR imaging shows the displaced disc in a closed/ rest position ( nothing is indicative, but real time MRI) is helpful.
Internal derangement
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
33
Internal derangement
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202134
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
35
Management
It is non surgical management.1. Consider no treatment other than reassurance and explanation. a clicking joint may be considered as normal. It should be emphasized that treatment should only be considered where the abnormality is affecting the patient’s quality of life.
2. Occlusal splints ( anterior repositioning) to interfere with parafunction may offer some help. And recapture the disc to its normal position.
Internal derangement
Disc displacement with reduction
3. Supporative therapy : decrease loading, NSAID to control pain, physiotherapy like heat application.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
36
Disc displacement without reduction
If there is no reduction, a displaced disc remains in a displaced position regardless of the stage of opening.This interferes with movement and may cause pain
Clinical features
• limitation in mouth opening.
• In unilateral cases, lasting deviation on opening. If with reduction Deviation to affected side after 10 mm, but if without reduction is deviated from the beginning.
• No click.
• Pain may be present in front of the ear.
• Normal lateral movement toward the same side and restricted toward the other side.
Internal derangement
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
37
Radiology
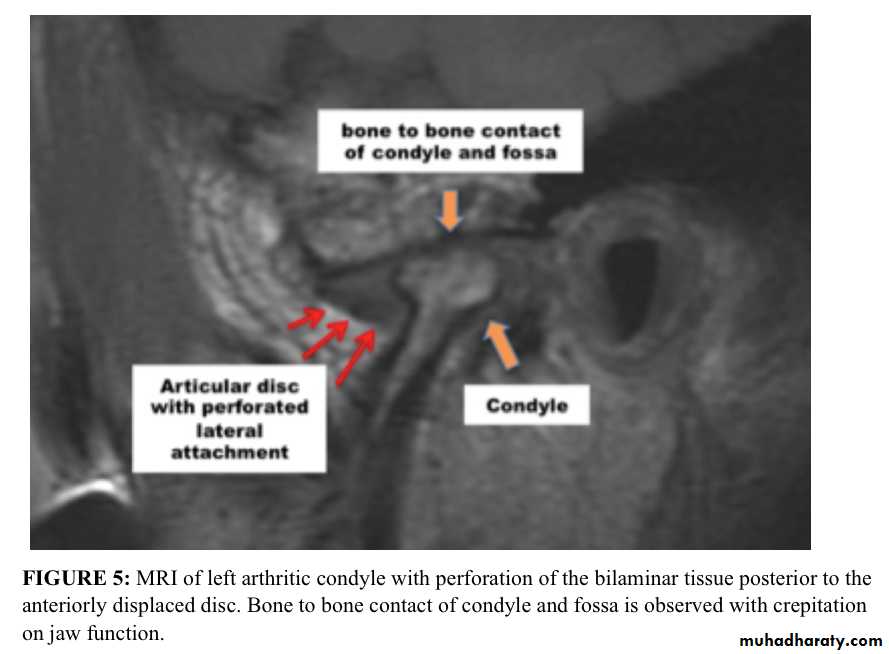
Plain films usually show nothing. In long- standing cases, there may be signs of osteoarthrosis.
MRI shows an abnormal disc position in all movements.
In long standing cases, perforation of the disc may be seen and joint space adhesions inferred.
Internal derangement
Disc displacement without reduction
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
38
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
39Management
• Explanation of the condition and reassurance.• Muscle relaxants and physiotherapy.
• Manipulation under anaesthetic
• TMJ surgery.
Internal derangement
Disc displacement without reduction
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
40
Surgical treatment of internal derangement
# Surgery is only indicated where non-surgical methods have failed and symptoms are severe. The goal is to return the disc to normal functional relationship with the condyle.
# A range of surgical treatments may be used, depending often on the surgeon managing the case.
• Arthrocentesis
• Arthroscopy
• ‘Open’ surgery may also be used
• Meniscoplasty
• Menisectomy
• Disc replacement
Internal derangement
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
41
Arthrocentesis involves lavage of the upper joint space, using hydraulic pressure and manipulation to release adhesions.
Arthroscopy: eliminate joint adhesions. Joint can be mobilized which itself may improve disc mobility. Arthroscopy can be used to release adhesions directly, to perform joint space lavage and to introduce steroids.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
42Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
43Open procedures
# Meniscoplasty Is a procedure to reposition the disc.
The capsule is opened, the disc visualized, repositioned and sutured in place.# Arthrotomy or arthroplasty: Retrodiscal tissue my be tightened by plication.
# Menisectomy In which the disc is removed if it cannot be repositioned because of deformity or degeneration. It may have been replaced with an alloplastic material in the past but is more likely to be replaced now with an autogenous tissue such as temporalis muscle or auricular cartilage.Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
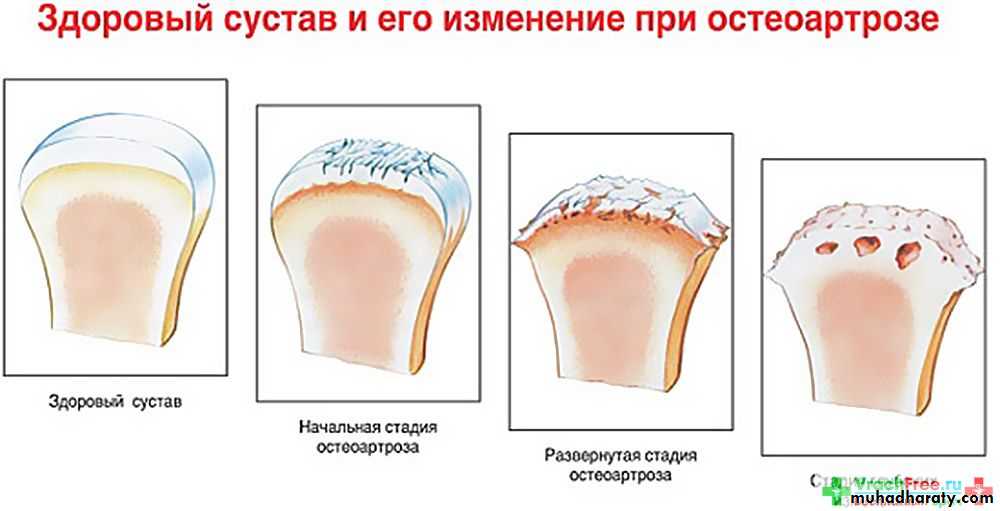
44# Osteoarthrosis is a non-inflammatory degenerative disorder of joints which affects the articular surface of the joint and is accompanied by remodeling of underlying bone
# [there is joint deterioration with bony proliferation]
- The deterioration leads to loss of articular cartilage and bone erosions.
- The proliferation manifests as new bone formation at the joint periphery and subchondrally.
Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202145
It has an unknown etiology
But the Suggested etiological factors• When intensity of stress increases the functional capacity of the joint ( like trauma and parafunction of the joint)
2. When the functional capacity of the joint has reduced so that even normal stress causes degenerative changes in the joint ( like in case of rheumatoid arthritis)
3. internal derangements
4. Aging may not a factor
Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
46
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
47
intensity of stress
functional capacityWhat is the relationship between osteoarthritis and TMJ disc displacement?
Disc displacement may be a sign, as well as a cause, of TMJ osteoarthritis.Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202148
Clinical features
• Usually affect pt in 5th decade of life.• Pain localized to the TMJ region.
• Limitation of opening, worse with prolonged function.
• Crepitus.
• Tender on palpation of TMJ.
Usually one joint is affected, but it could be bilateral.
May be lead to palpable mass on the pr-auricular area because of osteophyte reaction.
Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
49
Radiology
By OPG OR Ct-Scan
It not seen in early changes
1. Erosions of the articular surfaces of the condyle (flattening) and, less commonly seen, of the mandibular fossa.
2. Sclerosis of the bone and marginal
bony proliferation (‘lipping’ or osteophytes).3. Narrowing of the radiographic joint space.
4. Bony proliferations may break away and be seen as loose bodies in the joint space.5. Subcondyle pseudocyst.
Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
50Cone-beam computed tomography images of temporomandibular joint showing morphological variation of the mandibular condyle. A- Normal (coronal view); B- Flattening (coronal view); C- Erosion (coronal view); and, D- Osteophyte (sagittal view)
Radiology
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
51
5. Perforation of the disk or its posterior attachments problems.
By MRIDegenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
52
Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202153
Management
• Explanation and reassurance. And eliminate the cause.• Anti-inflammatory drugs.
• Physiotherapy.
• Restore deficiencies in the posterior occlusion to reduce loading on TMJs.
• Intra-articular steroid injections (advanced disease).
Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthrosis, Osteoarthritis)
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
54
Surgical
Surgery (advanced disease; final option) to smooth irregular condylar head where there are osteophytes or irregularities.
• Arthroplasty is done.
• High condyle shaving or condylectomy with or without TMJ prosthesis.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
55Summary
To be continued
DJD
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
DISLOCATION
ANKYLOSIS
NEOPLASIA
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
56THE END