Biochemistry
2nd stageDr.Lamees Majid Al-Janabi
Amino Acids: Disposal of Nitrogen
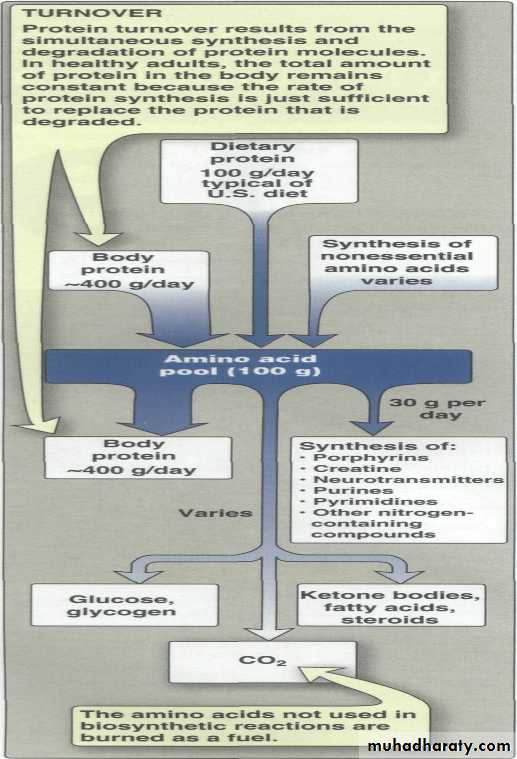
Unlike fats and carbohydrates, amino acids are not stored by the body, that is, no protein exists whose sole function is to maintain a supply of amino acids for future use. Therefore, amino acids must be obtained from the diet, synthesized de novo, or produced from normal protein degradation. Any amino acids in excess of the biosynthetic needs of the cell are rapidly degraded.
Overall Nitrogen Metabolism
Amino acid catabolism is part of the larger process of the metabolism of nitrogen-containing molecules. Nitrogen enters the body in a variety of compounds present in food, the most important being amino acids contained in dietary protein. Nitrogen leaves the body as urea, ammonia, and other products derived from amino acid metabolism.Catabolism of amino acids
free a.a s are derived from dietary proteins or from degradation of endogenous proteins are metabolized in identical ways .Their alpha amino nitrogen is first removed either by transamination or by oxidative & nonoxidative deamination . The resulting carbon skeleton is then degraded .
Removal of Nitrogen from Amino Acids
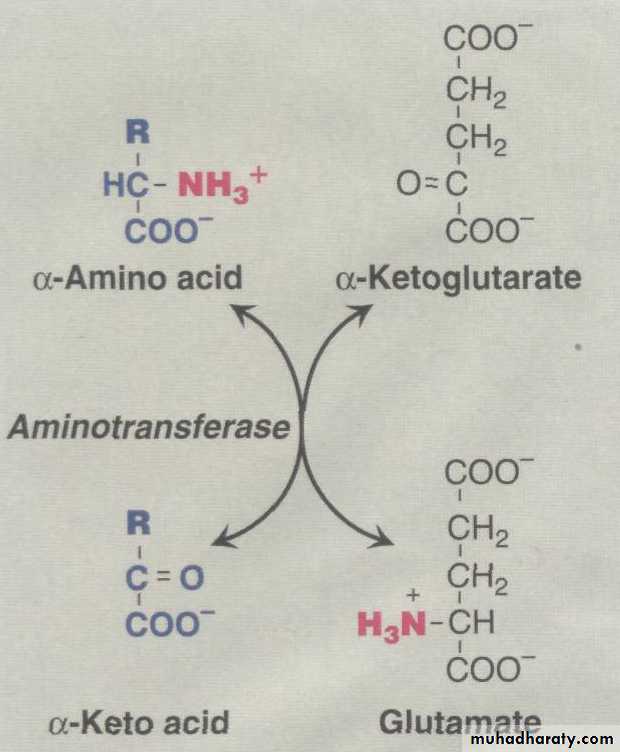
Transamination:The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the transfer of their α-amino group to α-ketoglutarate
Glutamate produced by transamination can be
oxidatively deaminated .used as an amino group donor in the synthesis of nonessential amino acids.
This transfer of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of enzymes called aminotransferases . These enzymes are found in the cytosol and mitochondria of cells throughout the body—especially those of the liver, kidney, intestine, and muscle.
All amino acids, with the exception of lysine and threonine, participate in transamination at some point in their catabolism.
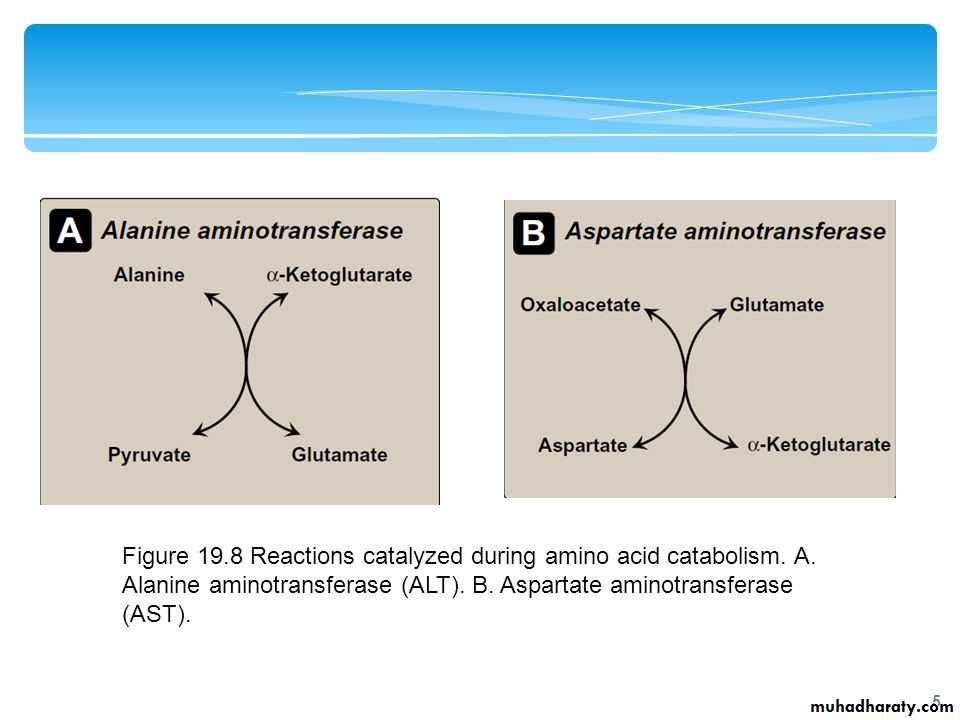
The two most important aminotransferase reactions are catalyzed by alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase AST:
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): Formerly called glutamate-pyruvate transaminase(GPT), ALT is present in many tissues.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): AST formerly called glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase(GOT)
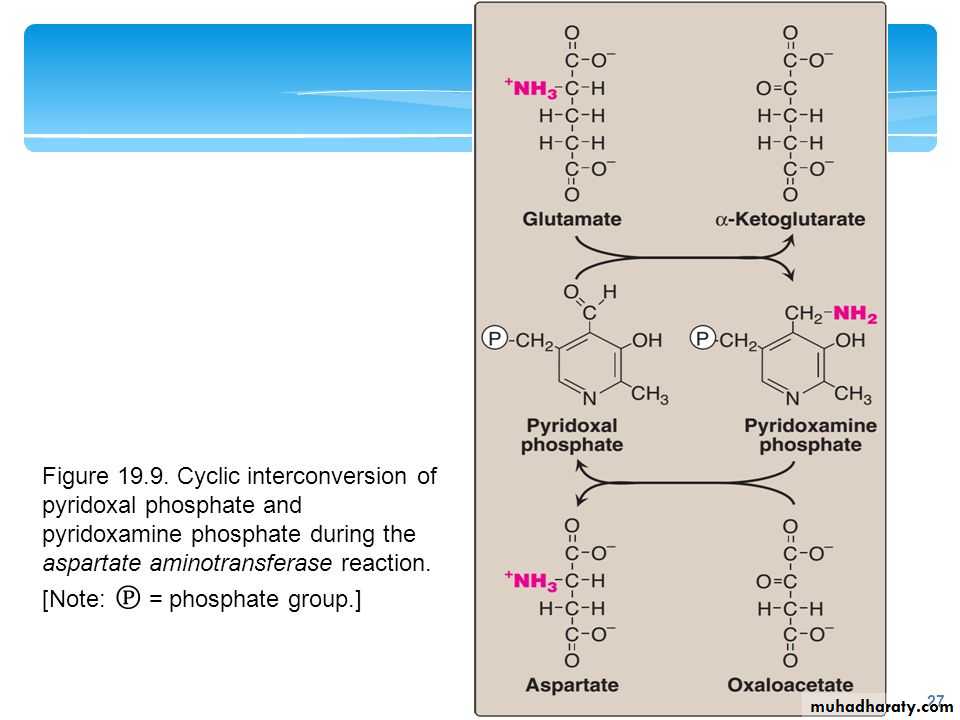
all transaminases have pyridoxal phosphate as coenzyme.
Since the reactions are freely reversible , they can serve to form a.as from the corresponding keto - acid. So transaminases reactions are central to both the degradation and the synthesis of a.as .Since these reactions involve the Interconversion of amino acid with pyruvate or alpha ketoglutarate, they function as a bridge between the metabolism of amino acids & CHO.
Diagnostic value of plasma aminotransferases:
The presence of elevated plasma levels of aminotransferases indicates damage to cells rich in these enzymes.Liver disease: Plasma AST and ALT are elevated in nearly all liver diseases, but are particularly high in conditions that cause extensive cell necrosis, such as severe viral hepatitis, toxic injury, and prolonged circulatory collapse.
Nonhepatic disease: Aminotransferases may be elevated in nonhepatic disease, such as myocardial infarction and muscle disorders. However, these disorders can usually be distinguished clinically from liver disease.