LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF CANCER:
The laboratory diagnosis of cancer becomes more complex, more advanced and more specialized, it
is broadly divided in to :
1-morphological methods .
2-moleculr diagnosis or cytogentics .
The morphological methods include:
1- histopathological and cytological diagnosis .
2- immunohistochemistry.
3- flow cytometry.
4- and tumor markers.
The cytogentics diagnosis include:
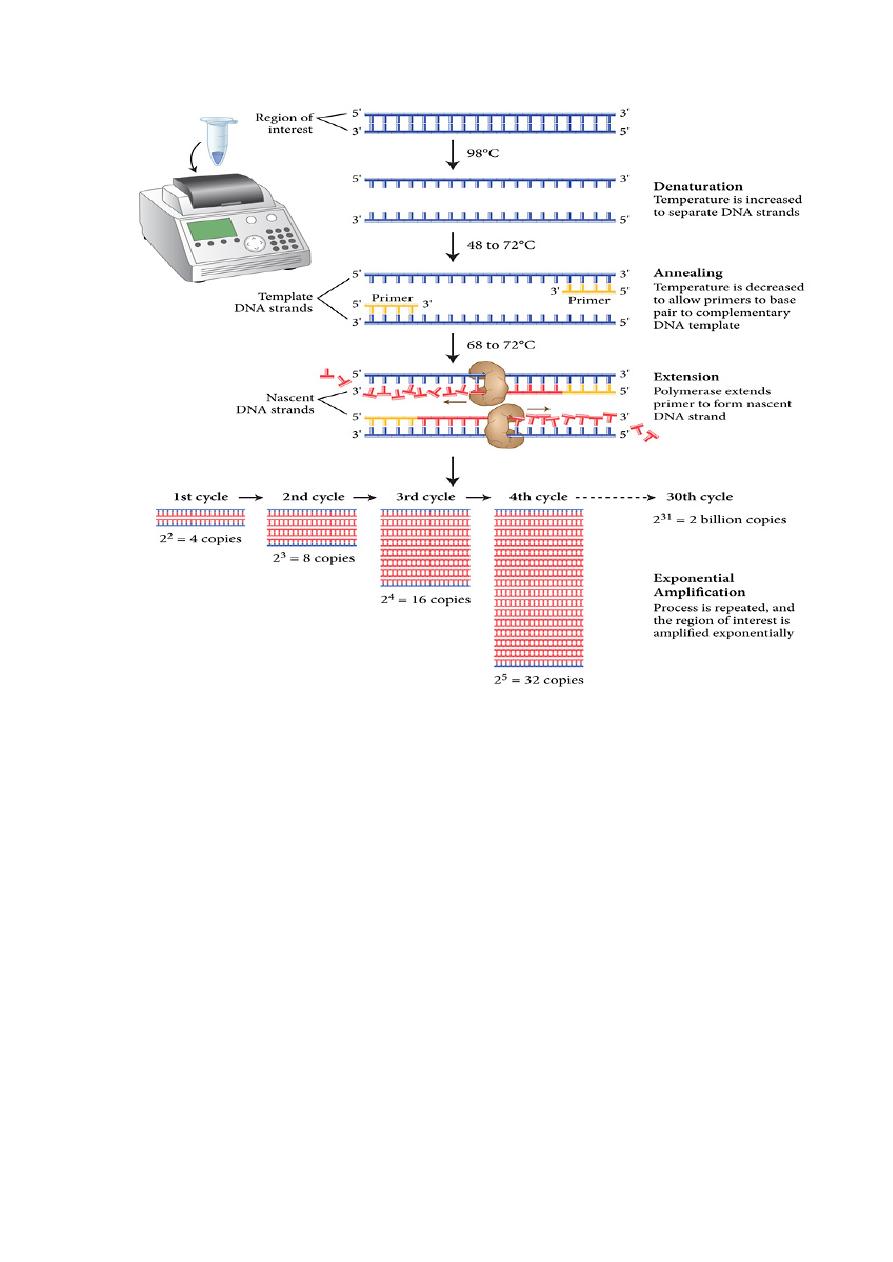
1- PCR .
2- FISH.
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY:
Immunohistochemistry or IHC refers to the process of detecting antigens (e.g.,
proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding
specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots
"immuno," in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo," meaning
tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry)
This involves the detection of cell products or surface markers by monoclonal
antibodies. The binding of antibodies can be detected by fluorescent labels or
chemical reactions that result in the generation of a colored product.
This technique is useful in:
1. Categorization of undifferentiated malignant tumors e.g., cytokeratin in
carcinoma and desmin in tumors of muscle.
2. Classification and categorization of leukaemias and lymphomas; B and T cell
lymphomas can be identified.
3. Determination of the site of origin of metastasis using antibodies against tissue
specific antigens. e.g., thyroglobulin and PSA (prostatic specific antigen) in
thyroid and prostatic neoplasms respectively.
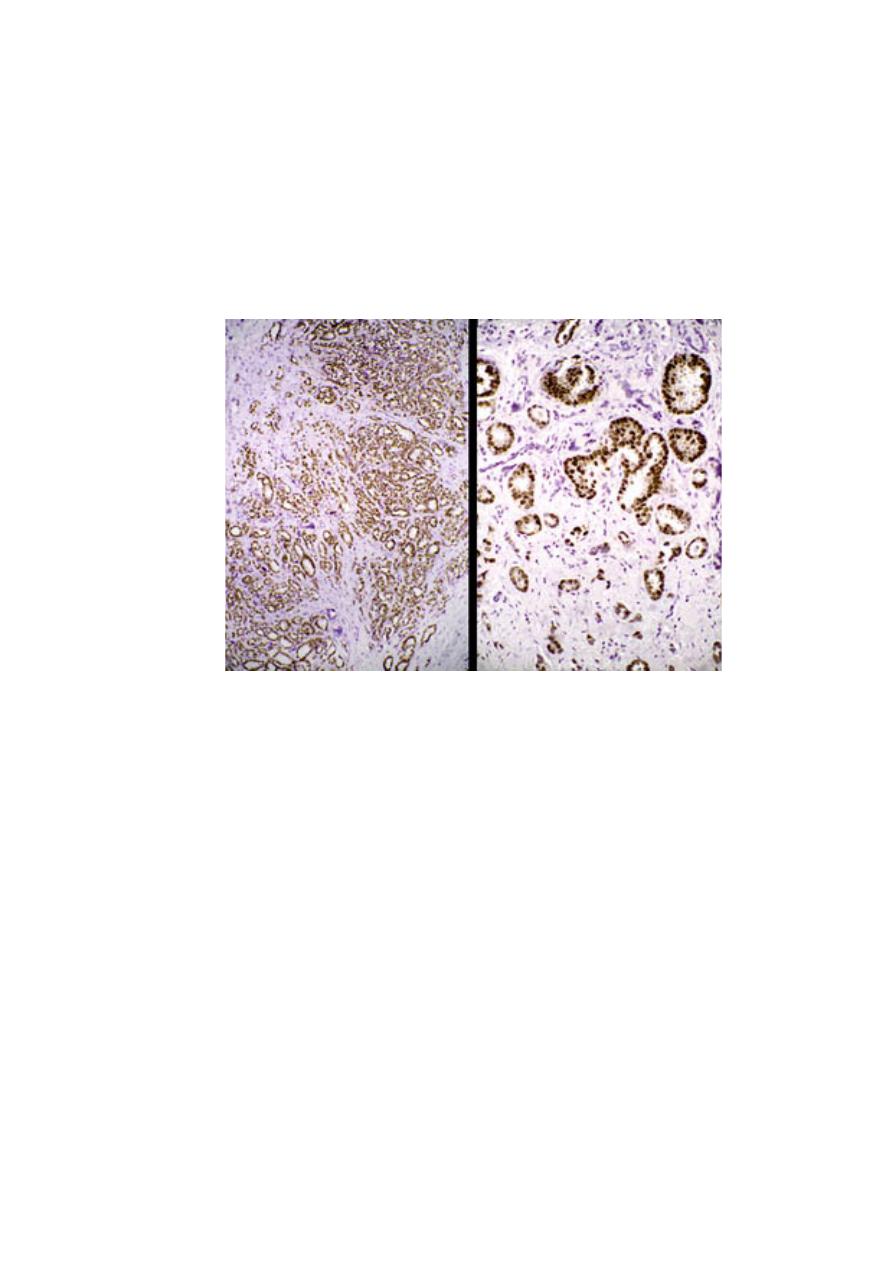
4. Detection of molecules that have therapeutic or prognostic significance e.g.,
estrogen and progestrone receptors in breast cancer. Products of certain cancer
suppressor genes (e.g., p53) and oncogenes (e.g., c-erb B2) can also be
detected. Over-expression of the latter in breast cancer is associated with poor
prognosis.
Immunohistochemical stain of estrogen receptors in CA breast
FLOW CYTOMETRY
Flow cytometry is a technology that is used to analyse the physical and chemical
characteristics of particles in a fluid as it passes through at least one laser, cell
component are fluorescently labelled and then excited by the laser to emit light at
varying wavelength, the main application in tumor are:
1- measure the DNA content of tumor cells. Aneuploidy correlate with poor
prognosis in early stage breast cancer, colorectal, prostatic, urinary bladder and lung
cancers.
2- Identification of cell surface antigens by flow cytometry is widely used in the
classification of leukemias and lymphomas.

TUMOR MARKERS:
These are tumor derived or associated antigens, enzymes, cytoplasmic proteins and
hormones that can be detected in blood or other body fluids. They are not primary
methods of diagnosis but are useful adjuncts. They are also of value in monitoring
therapy and in early detection of relapse. Two widely used markers are:
1-
PSA:
used to screen for prostatic adenocarcinoma, is one of the most
frequently used tumor markers in clinical practice. Prostatic carcinoma can be
suspected when elevated levels of PSA are found in the blood, although PSA
levels often are elevated in cancer, PSA levels also may be elevated in benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Furthermore, there is no PSA level that ensures that a
patient does not have prostate cancer. Thus, the PSA test suffers from both low
sensitivity and low specificity. The PSA assay is extremely valuable, however,
for detecting residual disease or recurrence following treatment for prostate
cancer.
2-
Carcinoembryonic antigen.
This is normally produced by fetal gut, liver,
and pancreas. It may be elaborated by cancers of the colon, pancreas, stomach,
lung and breast. Less consistent elevations may be seen in some non-neoplastic
conditions e.g., alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis and ulcerative colitis. This antigen
is of value in detecting tumor burden in colorectal cancer and in detecting
recurrences after surgery.

Cytogenetics:
This study include karyotype analysis and abnormal genetics alteration in specific
tumors example of this application are:
1-polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
2-FISH (filter in situ hybridization )
An increasing number of molecular techniques are being used for the diagnosis of tumors and for
predicting their behavior, so these methods used for:
1-
Diagnosis of malignancy
: Many hematopoietic neoplasms, as well as a few solid tumors, are
defined by particular translocations, so the diagnosis can be made by detection of such
translocations
.
2-
Prognosis and behavior.
Sequencing of cancer genomes is now routine in some centers,
allowing for the identification of point mutations in cancer genes such as TP53 that predict a
poor outcome in many different types of cancer.
3-
Detection of minimal residual disease:
Another emerging use of molecular techniques is for
detection of minimal residual disease after treatment
.
4-
Diagnosis of hereditary predisposition to cancer:
Germ line mutation of several tumor
suppressor genes, such as BRCA1, increases a patient’s risk for developing certain types of
cancer. Thus, detection of these mutated alleles may allow the patient and the physician to
devise an aggressive screening protocol, as well as an opportunity for prophylactic surgery.
5-
Therapeutic decision-making :
Therapies that directly target specific mutations are
increasingly being developed, for example melanomas with the BRAF mutation respond
well to BRAF inhibitors, whereas melanomas without this mutation show no response.