White & Red Lesions of The Oral Mucosa
By:Dr. Ahmed Salih KhudhurBDS, MSc, PhD Newcastle University/ UK
دكتور احمد صالح خضر
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Department of:
HERE
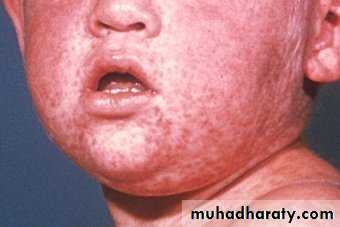
Measles or Rubeola
• Measles Koplik’s spots
•
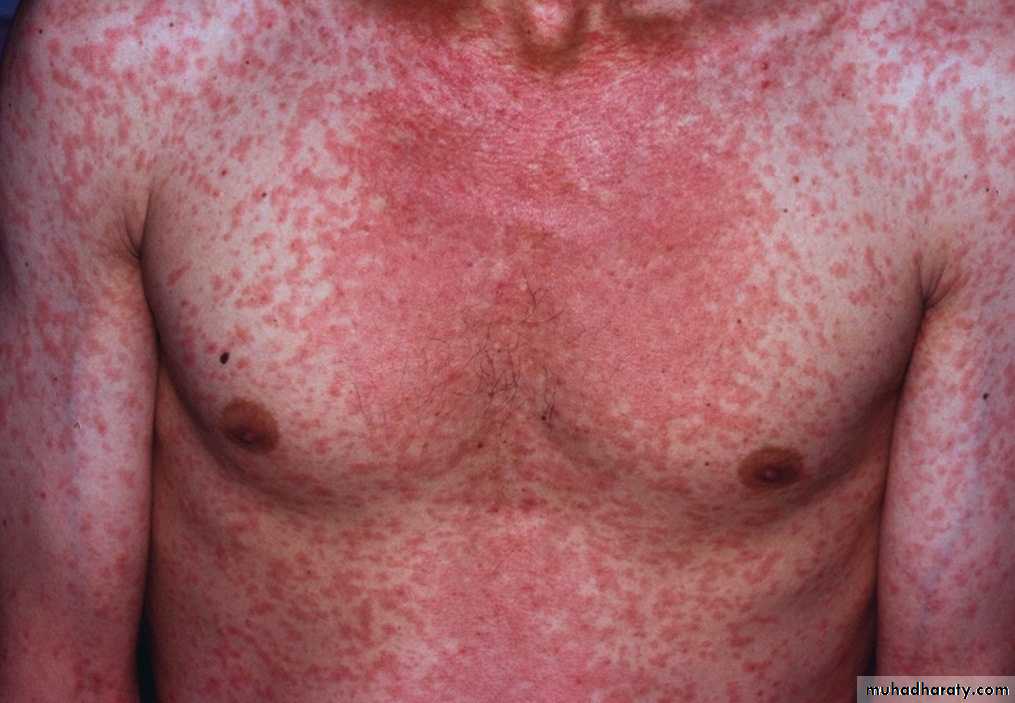
Measles or Rubeola
• Measles skin rash•
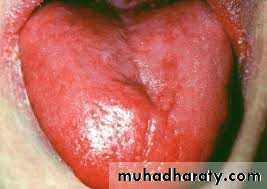
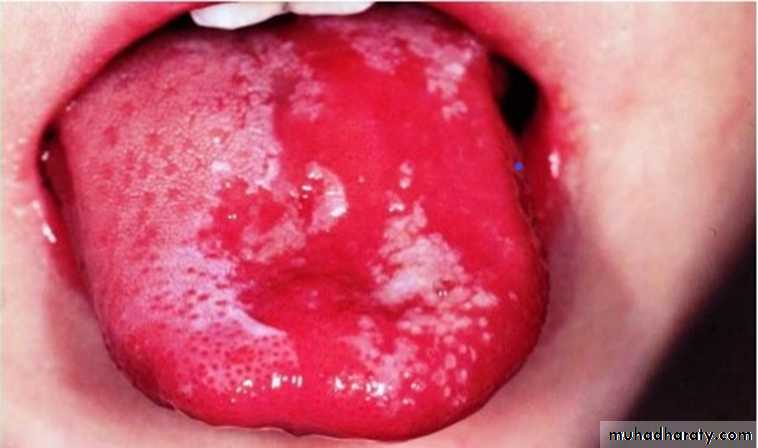
Anemia
• Anemia is associated with pallor of the oral mucosa and atrophic glossitis due to erythema• and atrophy of papillae in addition to other features of anemia
• _______________________________________________________________
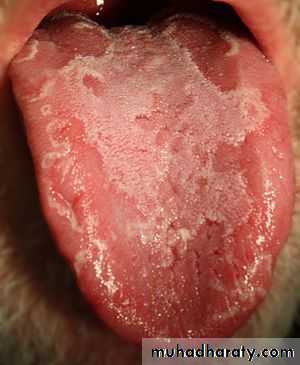
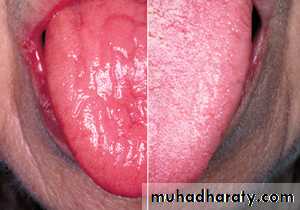
• Depapillation of the tongue:
• Localized:
• 1. Geographic tongue 2. Median rhomboid glossitis 3. Chronic atrophic candidiasis
• 4. Depapillation of elderly
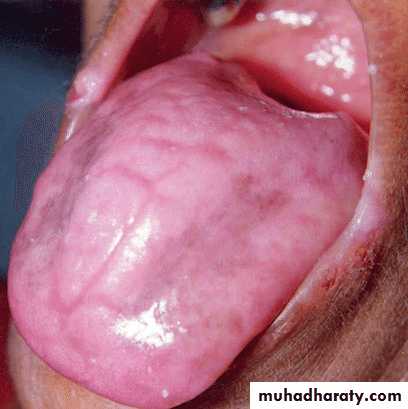
• Complete:
• 1. Anemia: Iron, B12, Foliate 2. Atrophic lichen planus 3. Discoid lupus erythematosus
• 4. Tertiary syphilis atrophic glossitis
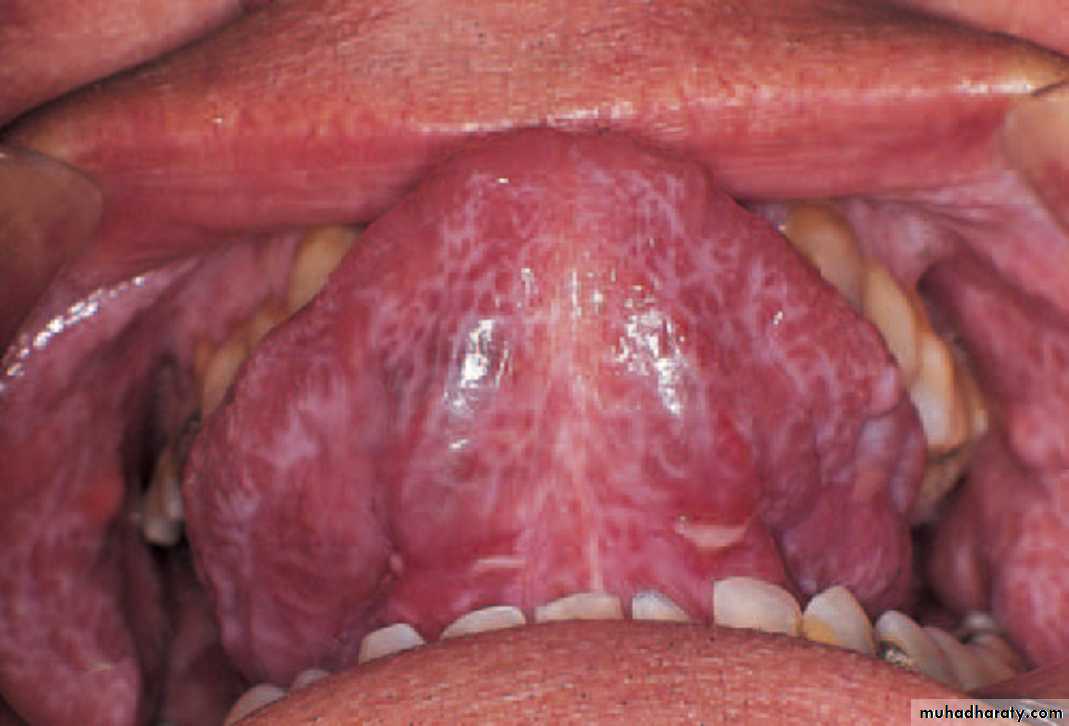
Depapillation of the tongue
• Localized atrophy of the tongue in geographic tongue
•
Depapillation of the tongue
• Complete atrophy of the tongue in anemia & plummer vinson syndrome (Paterson–Brown–Kelly syndrome)•
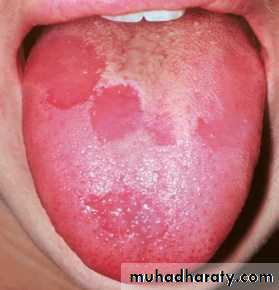
Vitamin A deficiency
• It's characterized by :• Night blindness
• Dry conjunctiva
• Corneal ulceration and xerophthalmia
• Keratinizing metaplasia of the non- keratinized epithelial cells which usually results in
• white lesion such as leukoplakia of the oral mucosa, and dryness of the skin
• Also it is characterized by defective formation of the enamel, dentin & pulp
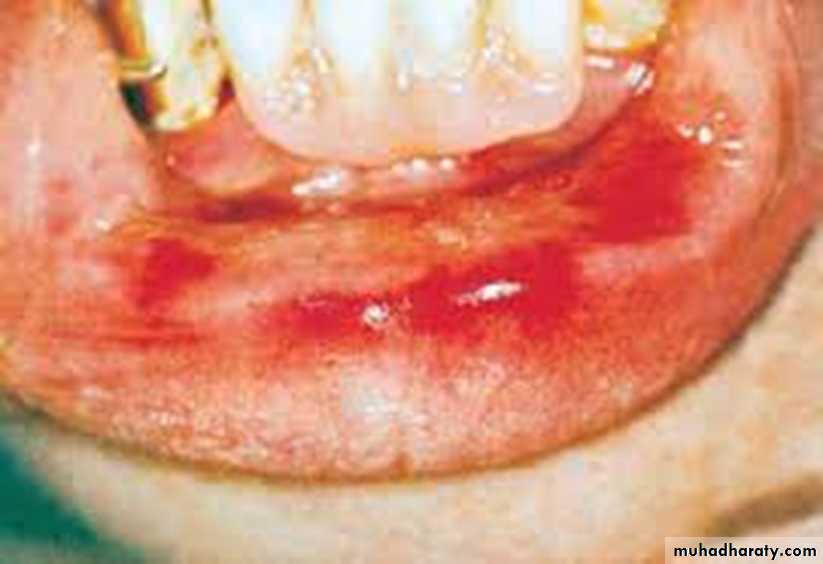
Drugs-Chemical burn (Aspirin burn)
• Drugs-Chemical burn
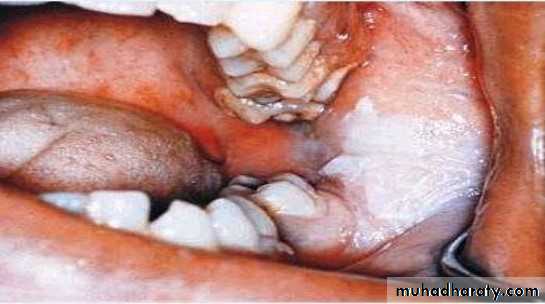
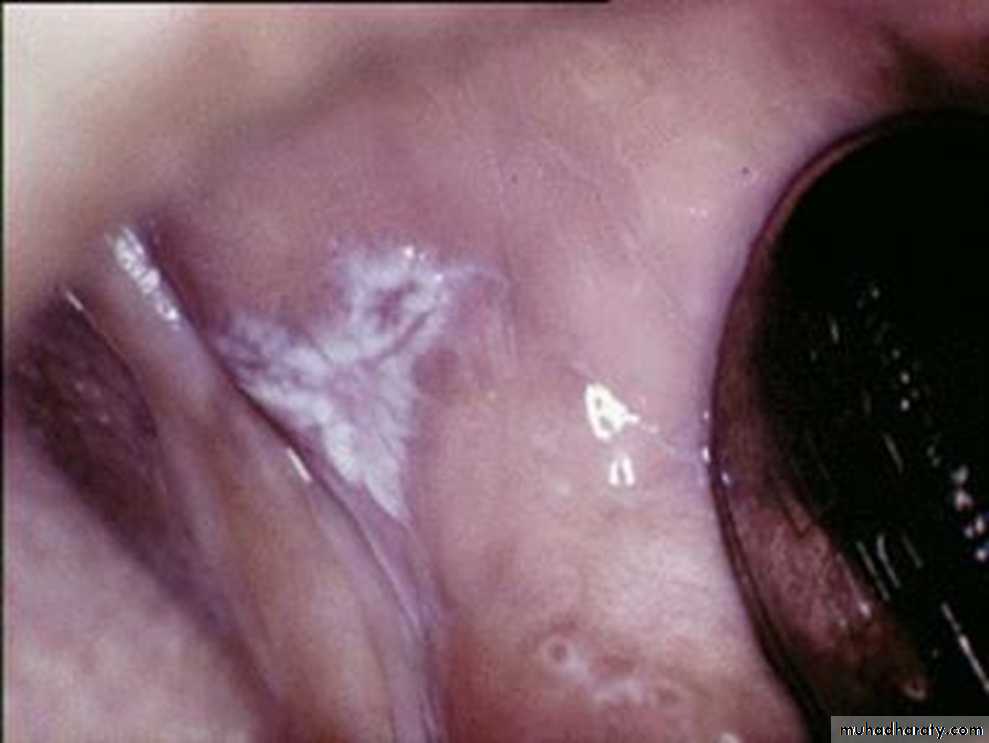
Drug reactions- Lichenoid drug reaction
•Lichenoid reaction to captopril. White striae across red lesions covering the ventral surface
of the tongue and buccal mucosa
Drug reactions- Lichenoid drug reaction
Lichenoid reaction to gold salts used for treatment forrheumatoid arthritis.
There is an extensive ulceration of the dorsal surface of
the tongue with atrophy and keratosis
Drug reactions-Stomatitis venenata or contact stomatitis-allergic stomatitis- stomatitis medicamentosa• Treatment:
• In mild cases remove the cause and relief pain• In severe cases topical corticosteroid is used
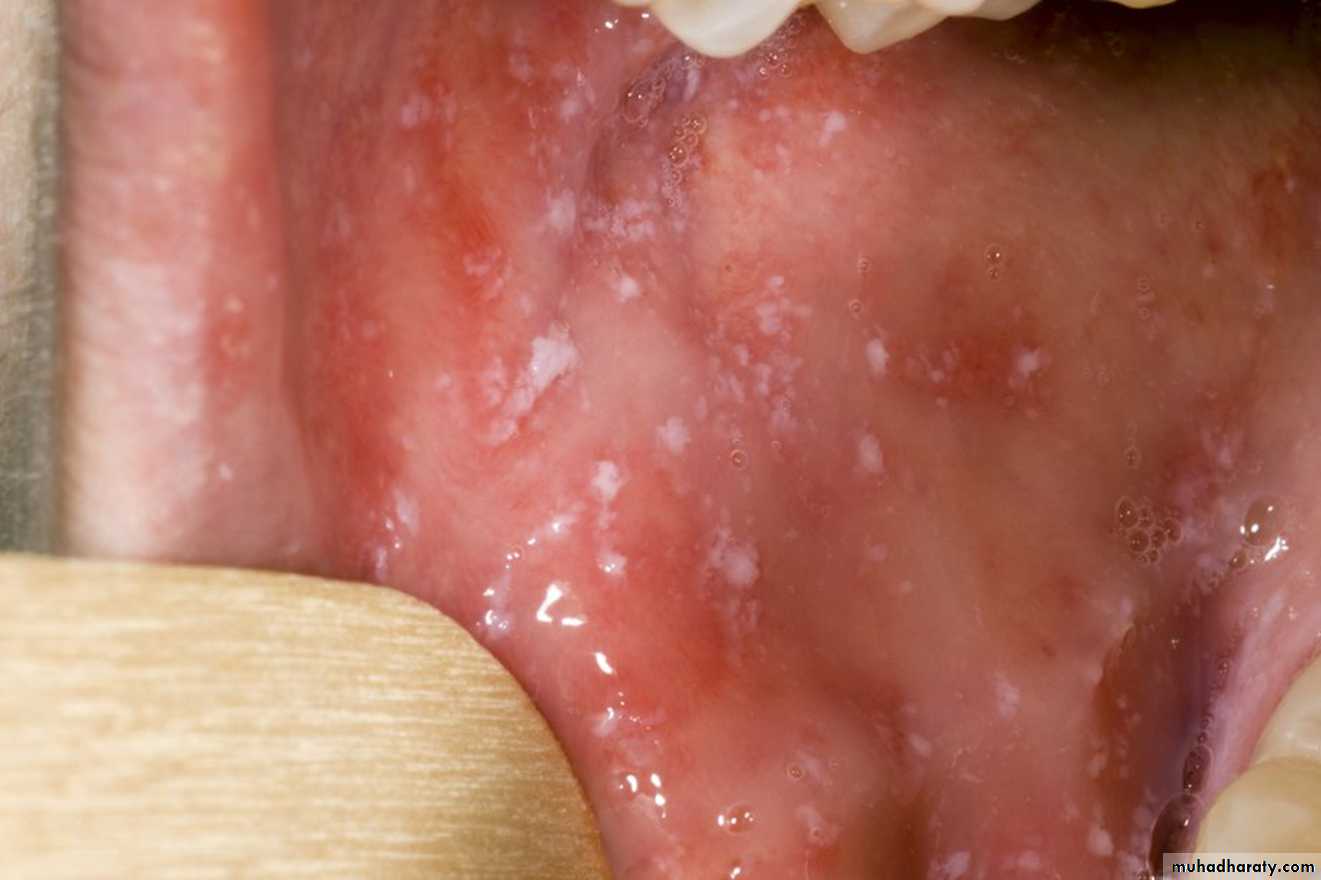
Lichen planus
• Common sites of OLP include:• Buccal mucosa which is the most common site, and the lesion may spread to the
• commissures
• Tongue, the 2nd most common affected site, on which the lesions found on the dorsum
• and lateral sides
• Gingivae and lips are occasionally affected
• Then comes the floor of the mouth and palate
• Though OLP may be asymptomatic, however, it may present with the following
• symptoms:
• Roughness
• Burning sensation
• Metallic taste
• Difficulty in eating and drinking
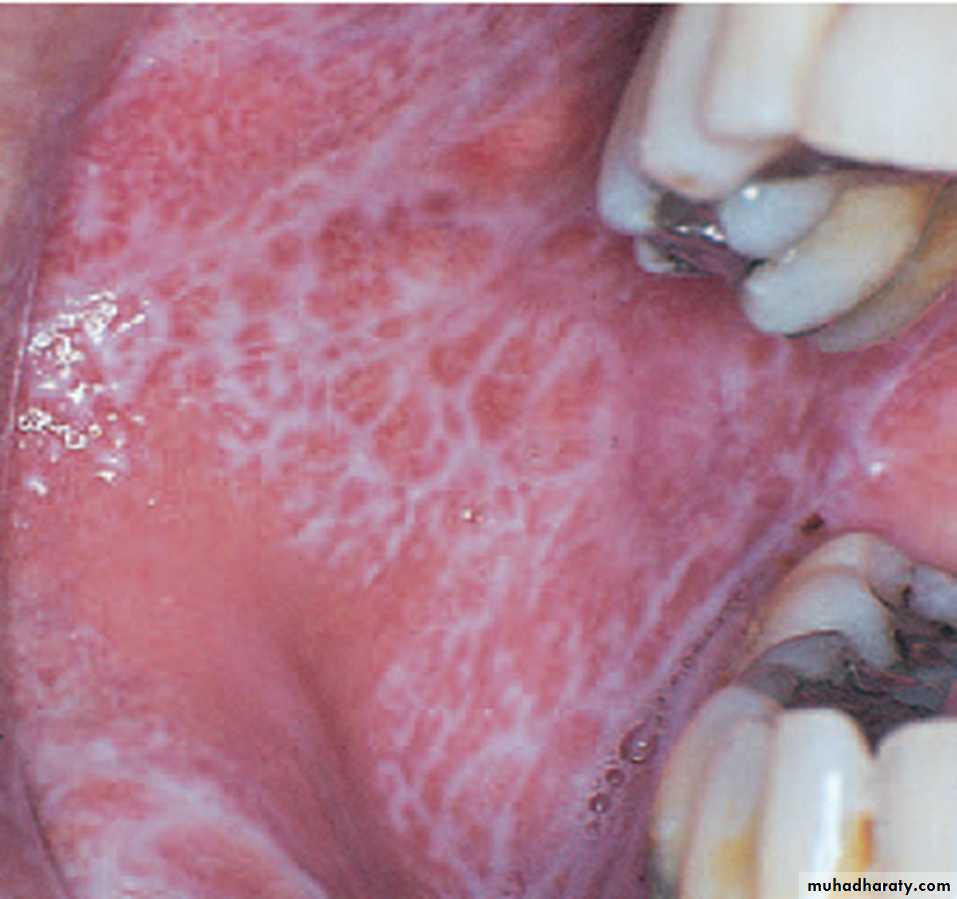
Lichen planus
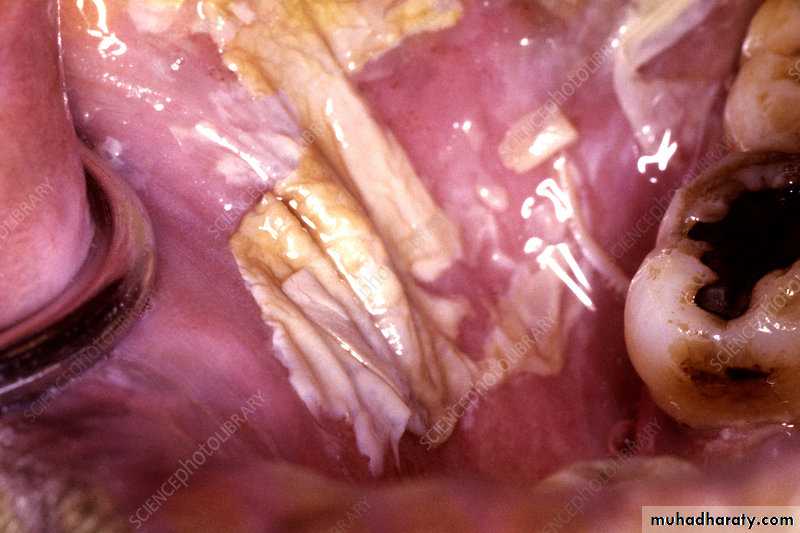
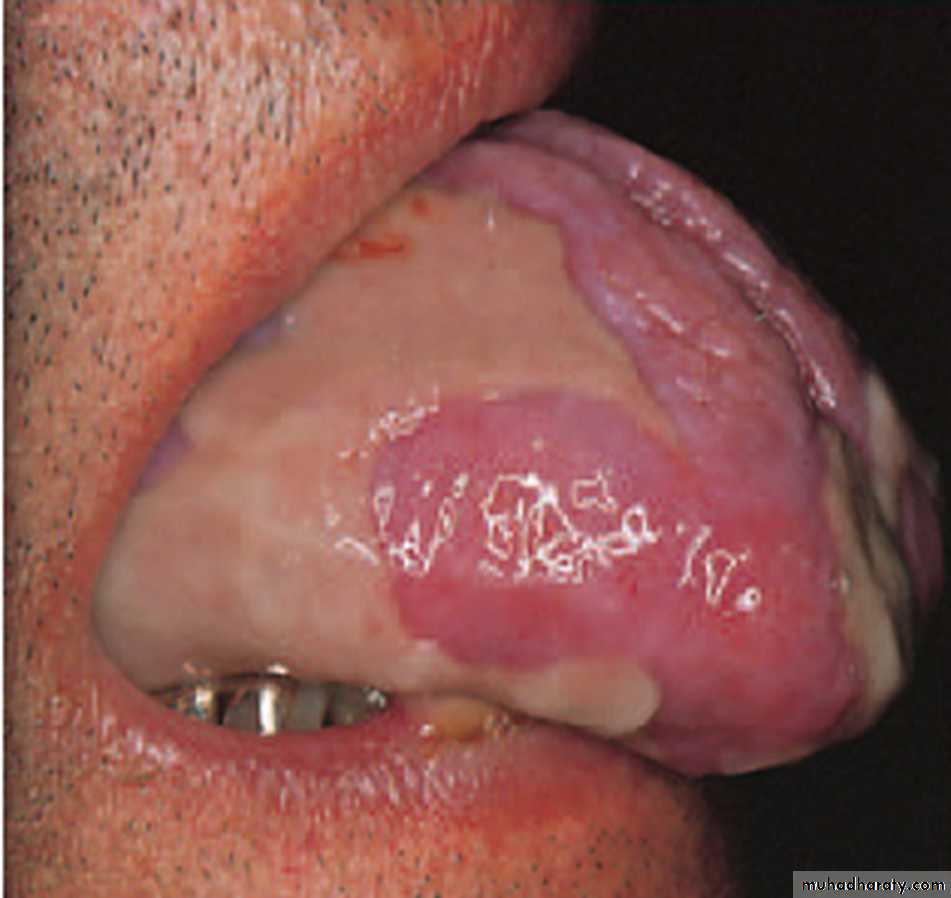
Reticular OLP (Striate form)
The most common type and site of OLP.
Lacy network of white striae on the buccal mucosa,the lesions are usually symmetrical
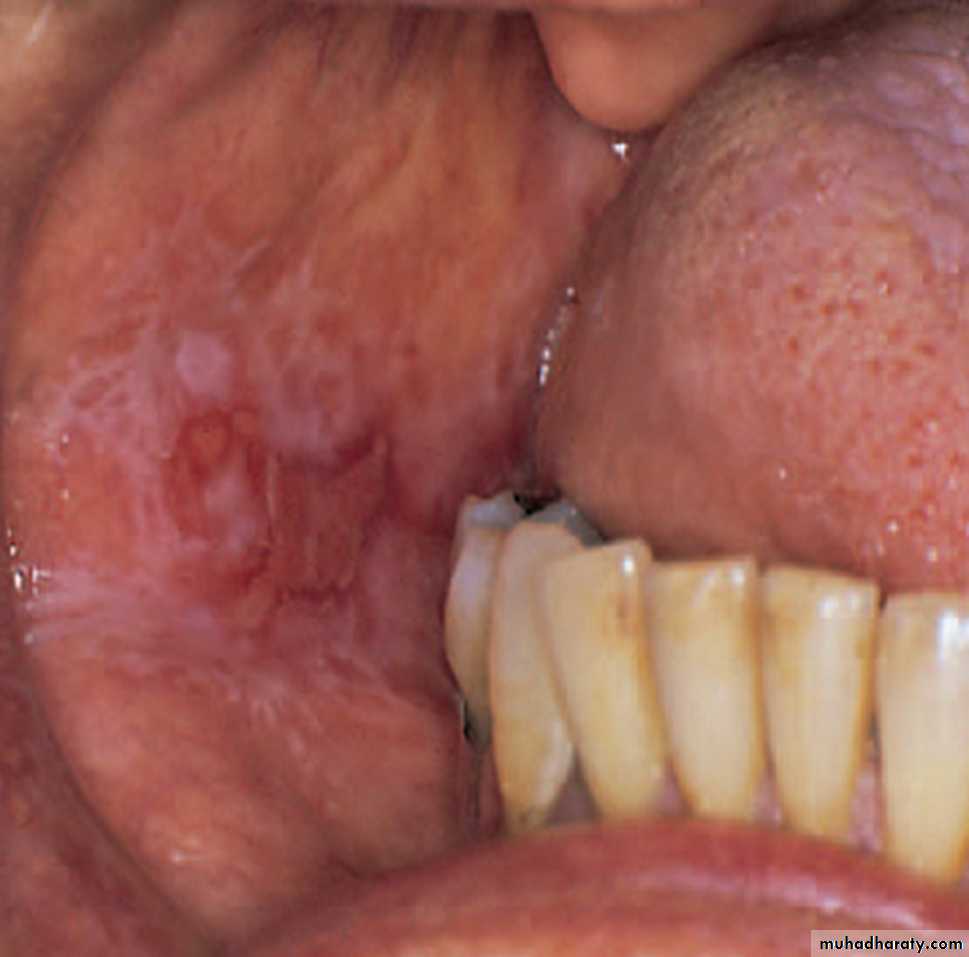
Lichen planus
Atrophic OLPShallow irregular zones of erythematous atrophied
Epithelia surrounded by poorly defined striaeLichen planus
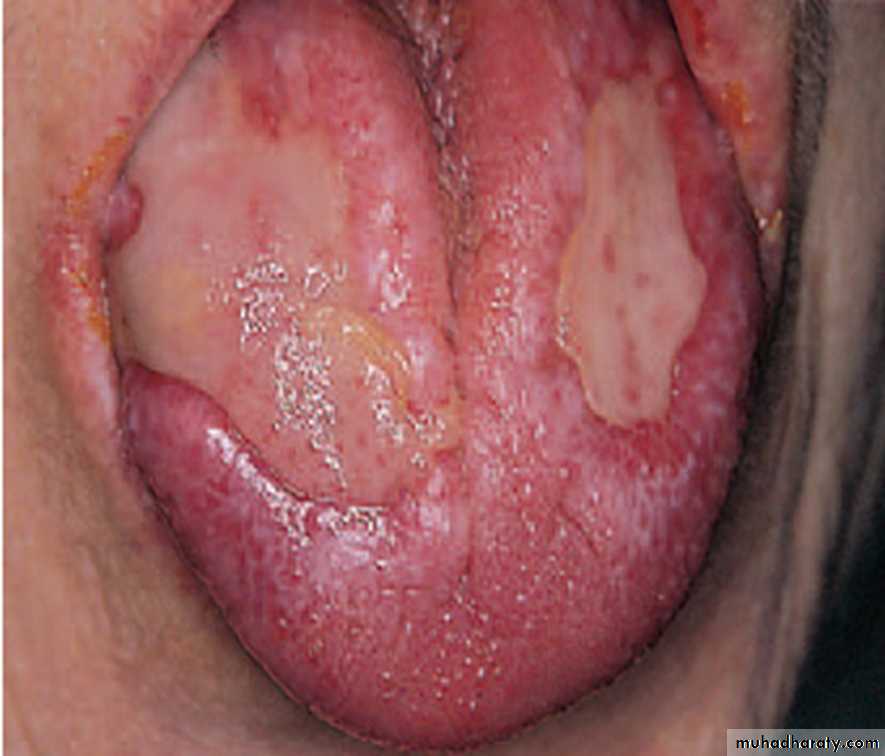
Severe erosive OLPThick layers of yellowish fibrin covers extensive ulcers
on the dorsum of the tongue
Lichen planus
Erosive OLP: Two extensive areas of shallow ulcerations on the dorsum of the tonguecovered with fibrin layers
Lichen planus
Plaque like OLPLichen planus
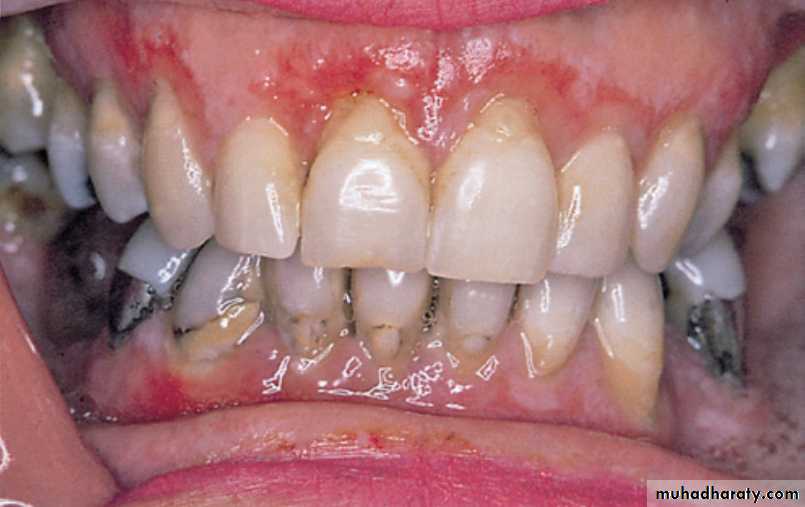
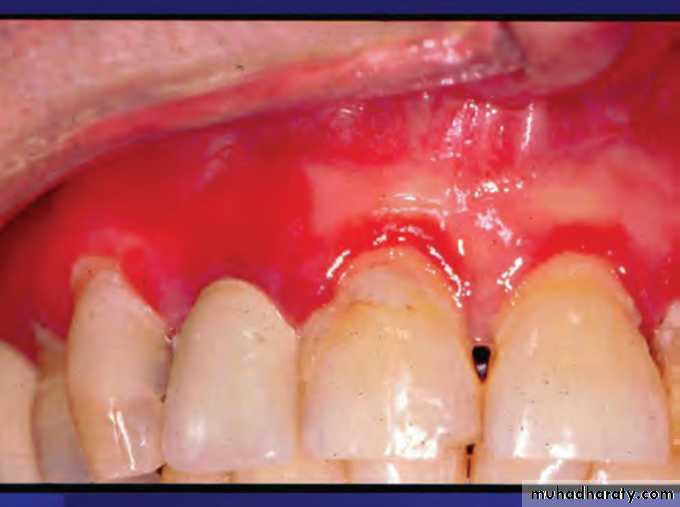
Desquamative gingivitis lichen planusDifferential diagnosis: mucous membrane pemphigoid.
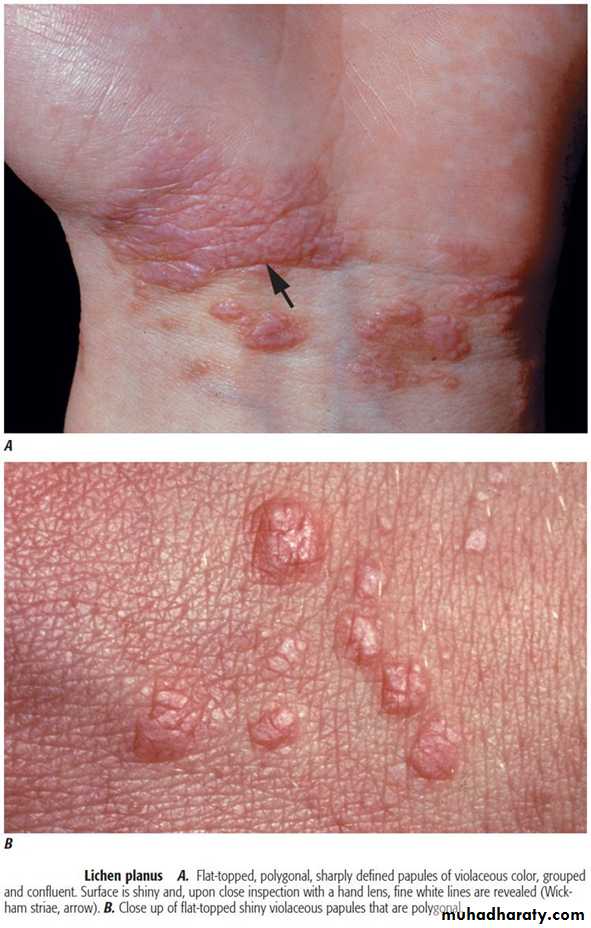
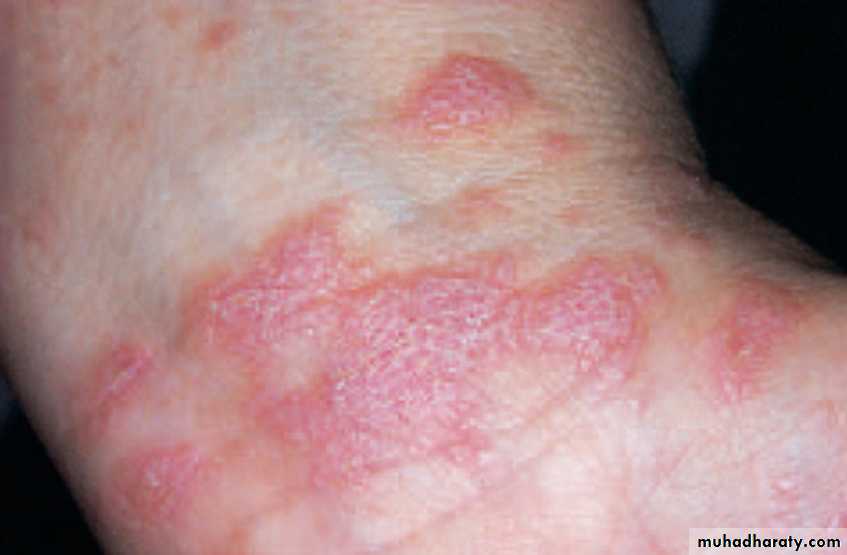
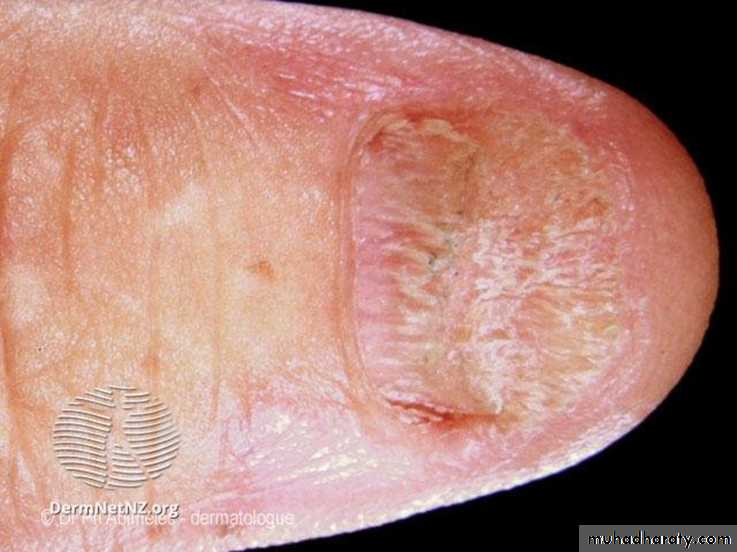
Lichen planus-Skin lesions and nail lesions
Purplish papules and Wickham's striaeLichen planus-Skin lesions and nail lesions
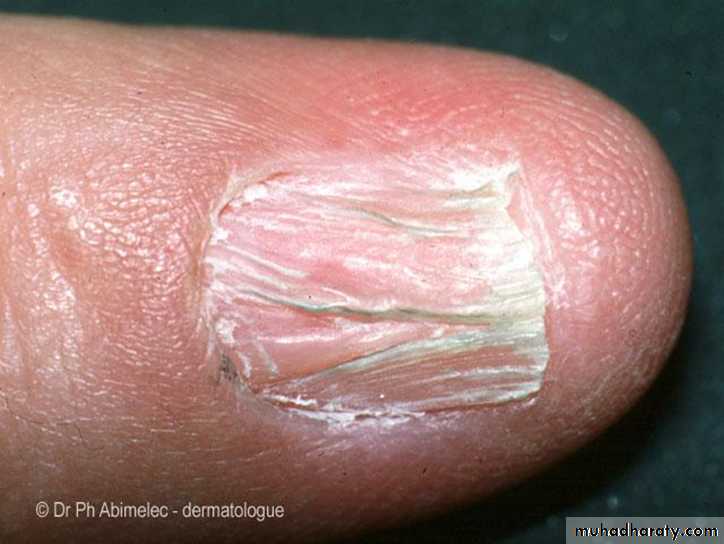
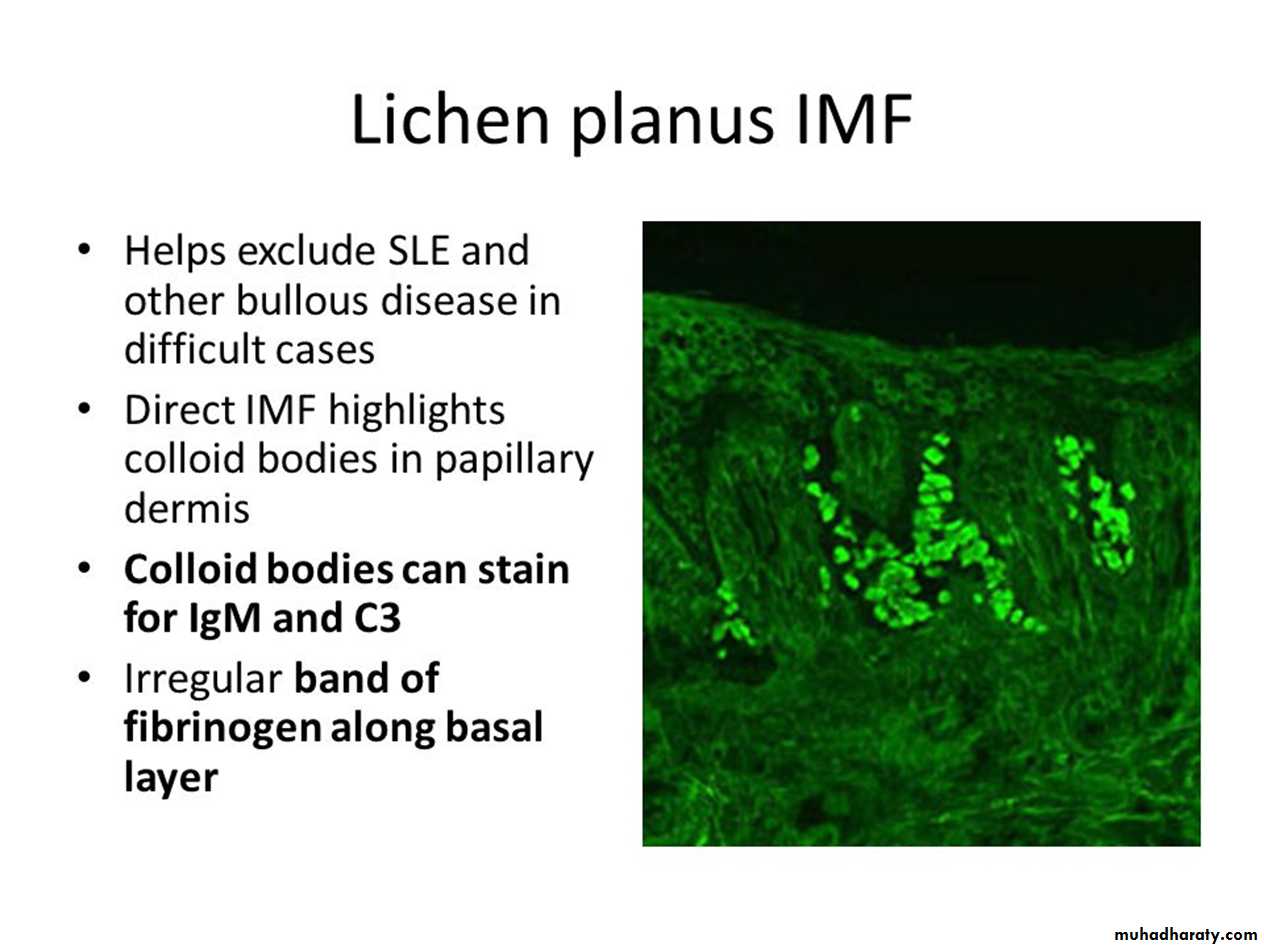
LP Nail lesionsLichen planus-Diagnosis
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021