بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
28/2/2021IN THE NAME OF GOD THE MOST MERCIFULL
ObjectivesTo know the following..DPL
Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathogenesis
Clinical presentation
Diagnosis
Treatment
Complication and prognosis
Interstitial and infiltrativepulmonary diseases
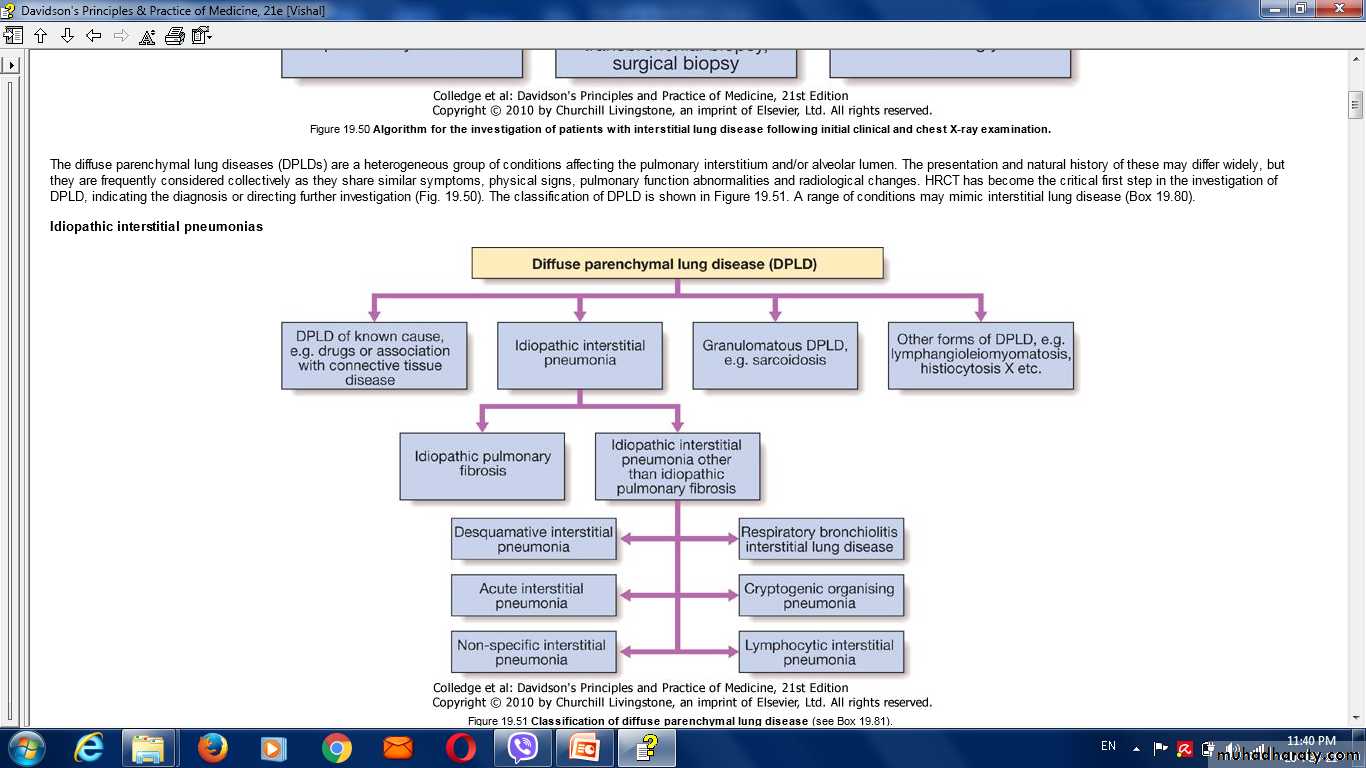
I-Diffuse parenchymal lung diseaseInterstitial and infiltrativepulmonary diseases
I-Diffuse parenchymal lung disease
II-Lung diseases due to systemic inflammatory disease.
III-Pulmonary eosinophilia and vasculitides
IV-Lung diseases due to irradiation and drugs
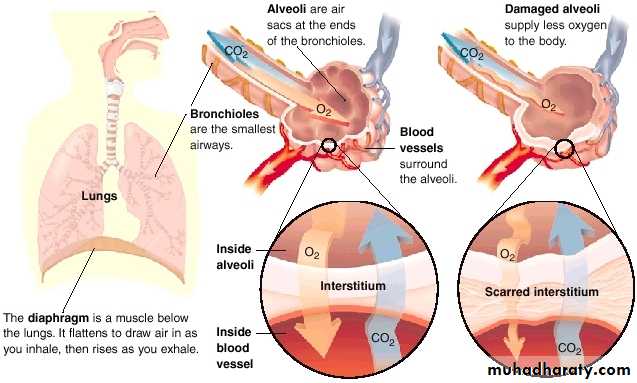
Effect of Damaged Interstitium
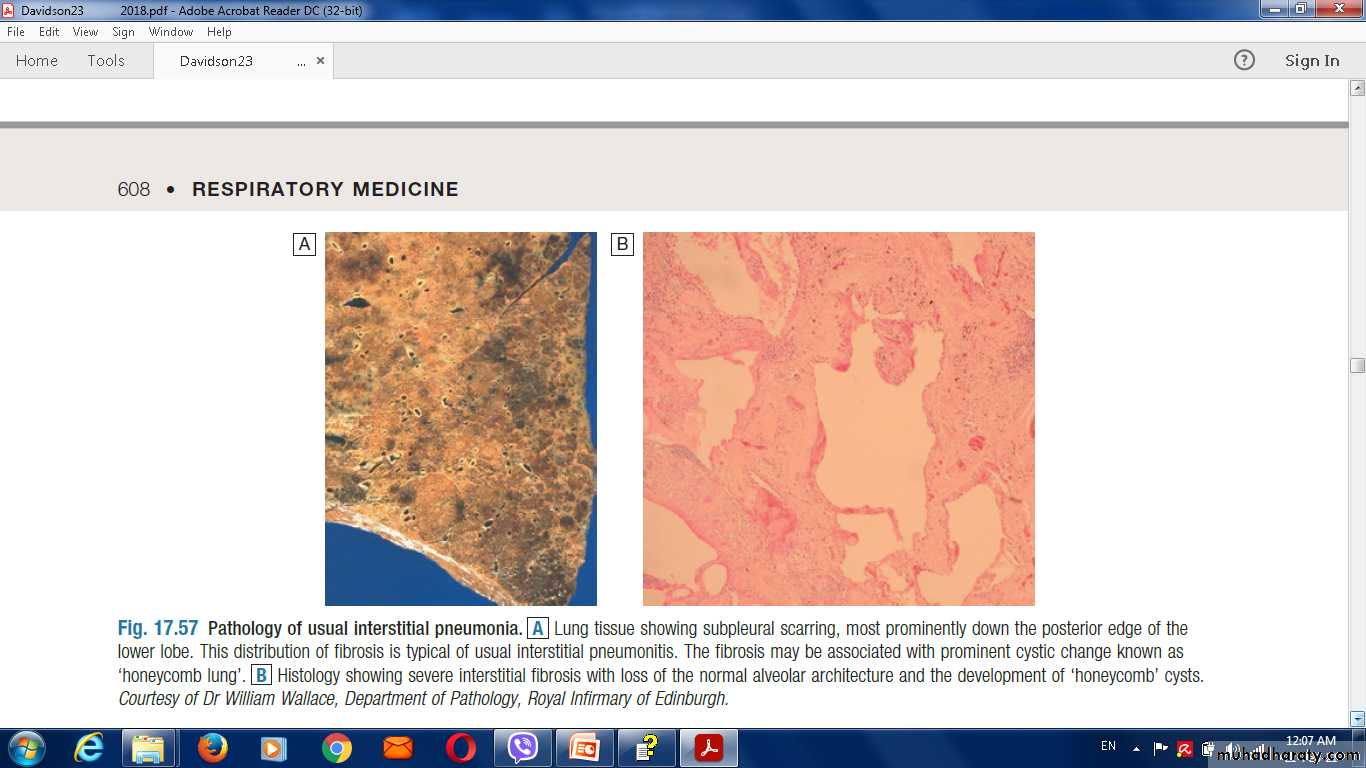
Pathology of usual interstitial pneumonia
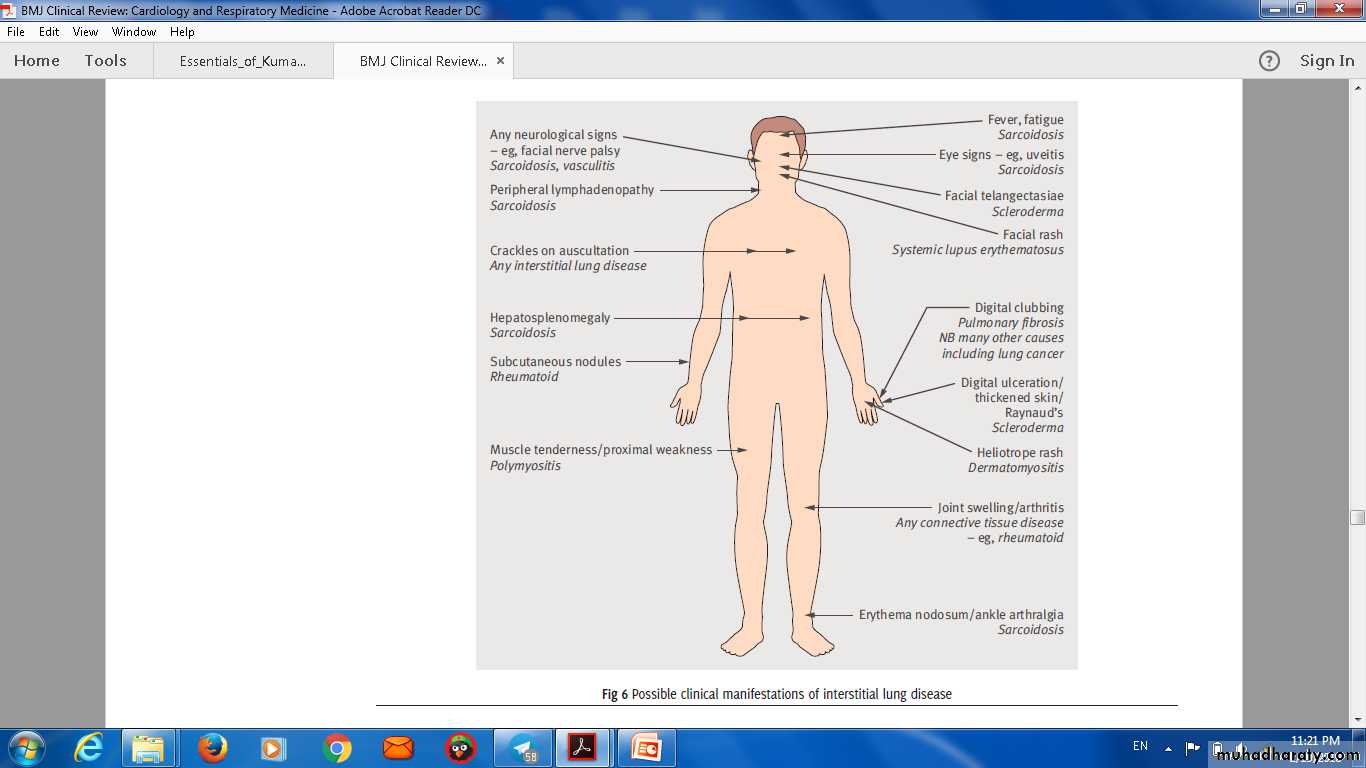
Possible clinical manifestations of interstitial lung disease
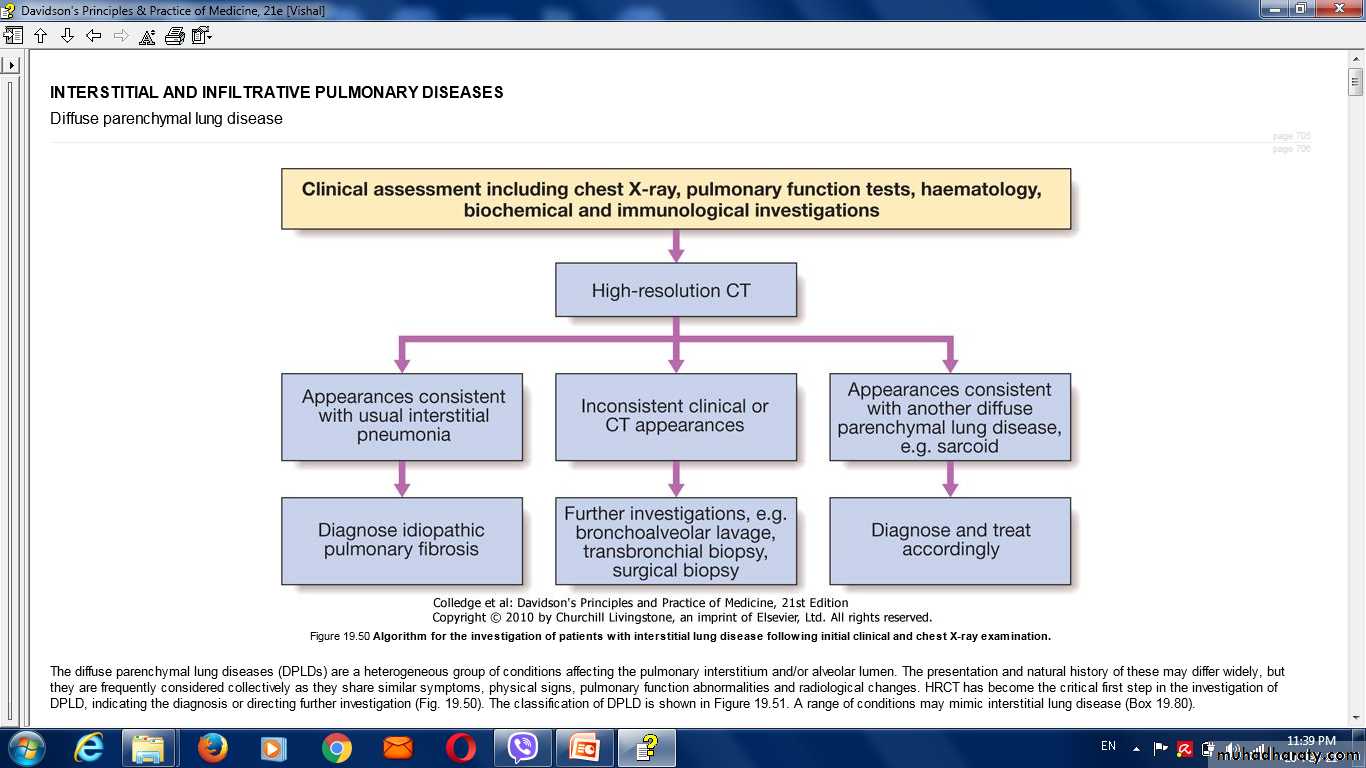
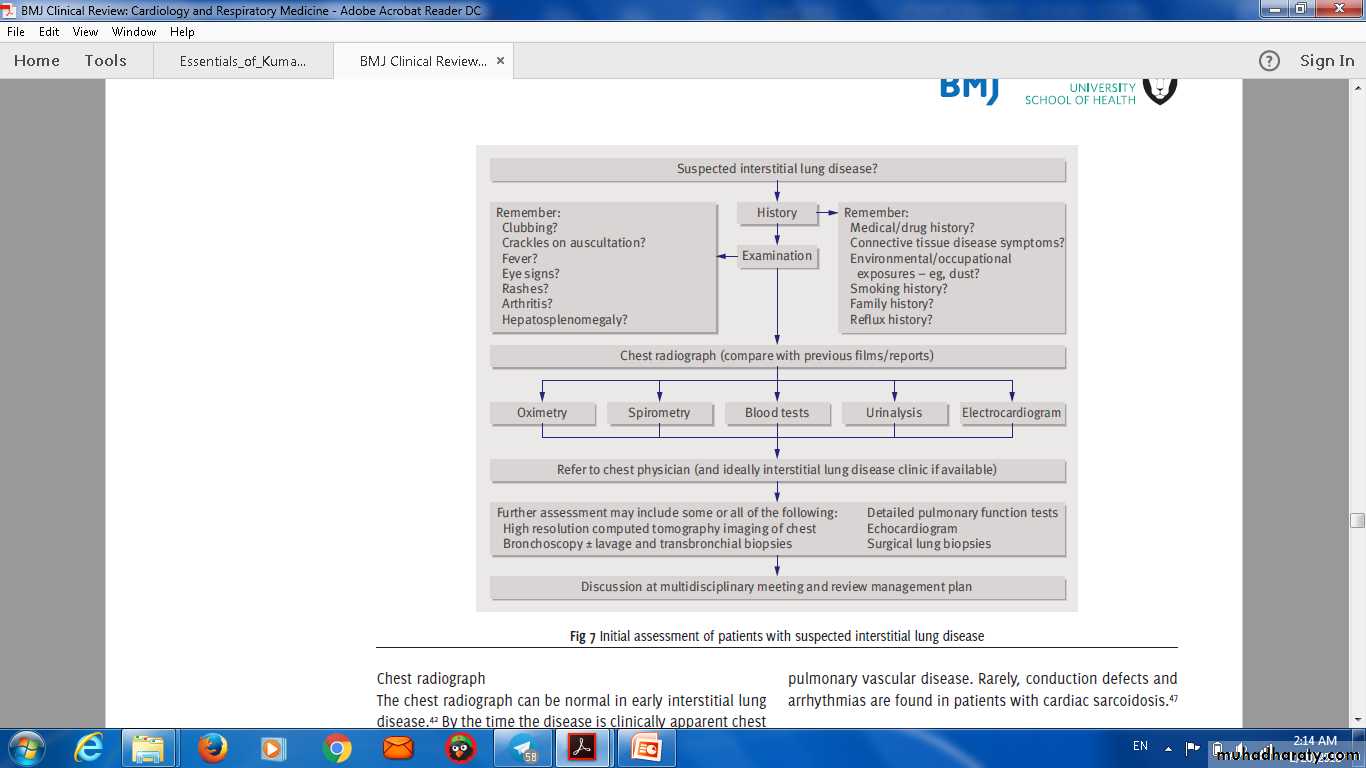
Approach in ILD
Differential diagnosis of DPLD
• 1-Infection :• viral pneumonia.
• pneumocystis jirovecii
• mycoplasma pneumoniae.
• tuberculosis
2. Malignancy :
Leukaemia and lymphoma.
Lymphangitic carcinomatosis.
Multiple metastases.
Bronchoalveolar carcinoma.
3. Pulmonary oedema.
4. Aspiration pneumonitis.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Progressive fibrosing interstitial pneumonia in the adults of unknown aetiology with histological & radiological pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia.DDx:
Lung fibrosis secondary to drugsOccupational exposure
Connective tissue diseases.
Clinical presentation:
Uncommon before the age of 50 years.Progressive insidious breathlessness with dry cough.
Bilateral fine basal end-inspiratory crackles & digital clubbing.
Patients can develop exacerbations during the chronic course of the disease with severe SOB, reduced gas transfer & new ground-glass changes or consolidations on
chest CT.
Investigations:
A/ CXR: bilateral lower lobe and subpleural reticular shadowing but can be normal in early or limited disease.B/ High-Resolution CT of the chest (HRCT):
C/ Pulmonary function test: restrictive defect with reduced lung volumes and gas transfer.
D/ABG :Hypoxemia & hypocapnia initially presents with exercise but later on at rest as the disease progressed.E/ Bronchoscopy & lung biopsy: only indicated in uncertain cases that cannot be diagnosed based on other tests.
F/ Immunology: antinuclear antibody (ANA) or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide 2 (anti-CCP2) may be mildly positive.
Management:
Managment of IPF• Disease-modifying therapy:
• 2-Oral N‑acetylcysteine3- Proton Pump inhibitors.
Treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflex (relieving cough).
4. Stop smoking.
5. Annual pneumococcal vaccines.
6. Pulmonary rehabilitation program & domiciliary O2 therapy in severe cases.
7. Lung transplantation (in severe cases).
In acute exacerbations, the treatment mainly supportive (antibiotics, glucocorticoids, immunosuppression & respiratory support).
Prognosis
Prognosis is poor with 3-years survival is the expected outcome. However, cases with minimal disease can live longer.Progression of the disease results in central cyanosis with pulmonary hypertension & right side heart failure.
Predictors of poor prognosis ???
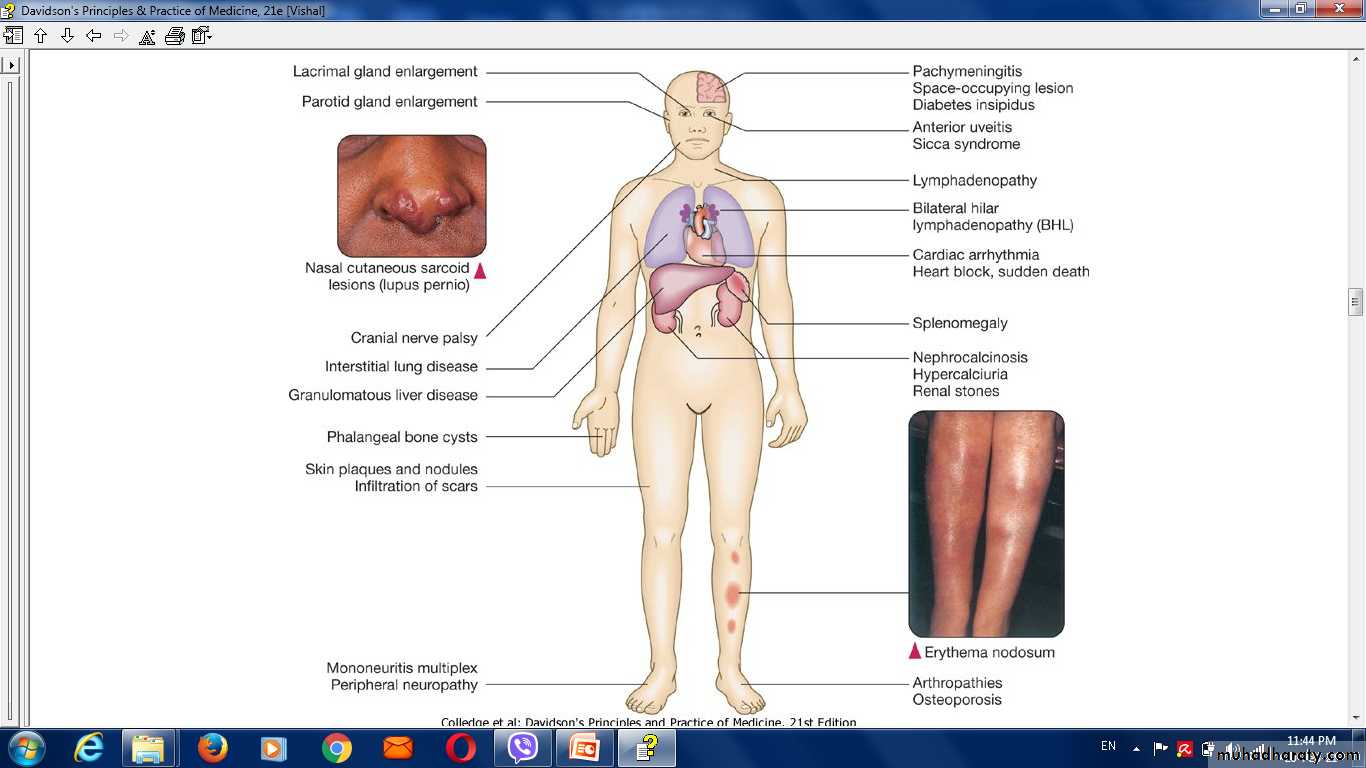
SarcoidosisSarcoidosis is a multisystem granulomatous disorder of unknown
aetiology that is characterised by the presence of non-caseating
granulomas.
More common in northern Europe.
Clinical features:
• Asymptomatic:• Respiratory and constitutional symptoms
• Erythema nodosum and arthralgia
• Ocular symptoms
• Skin sarcoid (including lupus pernio)
• Superficial lymphadenopathy
• Other , e.g. hypercalcaemia, diabetes insipidus, cranial nerve palsies, cardiac arrhythmias, nephrocalcinosis
Löfgren’s syndrome
Investigations:
• Blood tests: lymphopenia,• mild impairment of LFT,
• hypercalcaemia,
Hypercalciuria.
2. CXR: bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, pulmonary infiltrates & fibrosis.
3. Bronchoscopy:
Management:
Most patients recover spontaneously.Treatment includes NSAIDs,
steroids
immunosuppressive therapy in advanced cases.
Pulmonary eosinophilia and vasculitides
Pulmonary eosinophilia and vasculitidesPulmonary eosinophilia refers to the association of radiographic (usually pneumonic) abnormalities and peripheral blood eosinophilia.
• Acute eosinophilic pneumonia
• Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia
• Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia
• Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
• Goodpasture’s syndrome
Pulmonary eosinophilia and vasculitides
Pulmonary eosinophilia
Extrinsic (cause known)
Helminthes: e.g. Ascaris, ...
Drugs: nitrofurantoin,etc.
Fungi: e.g. Aspergillus fumigatus.
Intrinsic (cause unknown)
Cryptogenic eosinophilic pneumonia
Churg-Strauss syndrome .
etc.
Lung diseases due to irradiationand drugs
Lung diseases due to drugsNon-eosinophilic alveolitis
Pleural effusion
Asthma
• Pharmacological mechanisms (β-blockers, cholinergic agonists, aspirin and NSAIDs)
• Idiosyncratic reactions (tamoxifen, dipyridamole)
Non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema (ARDS)
Association of pulmonary haemorrhage and glomerulonephritis
IgG antibodies bind to the glomerular or alveolar basement membranes.
Goodpasture's syndrome.
Wegener's granulomatosis
Rare vasculitic and granulomatous condition .
Respiratory symptoms include cough, haemoptysis and chest pain.
Diseases due to radiotherapy
Acute radiation pneumonitis is typically seen within 6-12 weeks and presents with cough and dyspnoea.Chronic interstitial fibrosis may present several months later with symptoms of exertional dyspnoea and cough.
Interstitial lung disease in old age
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:.Chronic aspiration pneumonitis:
Asbestosis: symptoms appear in old age.
Drug-induced interstitial lung disease:
Lung diseases due to systemic inflammatory disease
Lung diseases due to systemicinflammatory disease1- Respiratory involvement in connective tissue disorders.
2-Acute respiratory distress syndrom .
Respiratory involvement in connective tissue disorders
Pulmonary complications of connective tissue disease are common, affecting the
airways,
the alveoli,
the pulmonary vasculature.
the diaphragm
chest wall muscles,
the chest wall itself.
pulmonary disease may precede the appearance of the connective tissue disorder
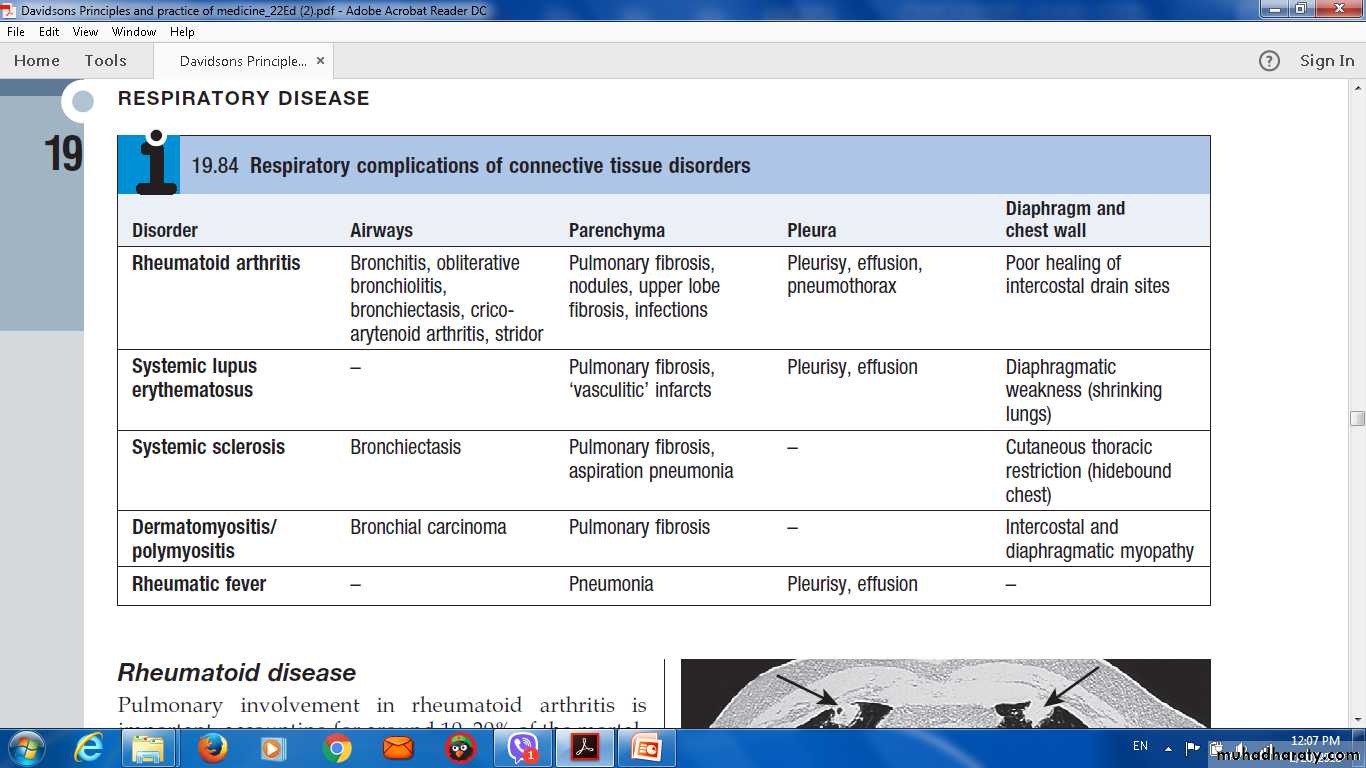
Respiratory complications of connective tissue disordersRheumatoid arthritis
Bronchitis, obliterative bronchiolitis, bronchiectasis, crico-arytenoid arthritis, stridorPulmonary fibrosis, nodules, upper lobe fibrosis, infections
Pleurisy, effusion, pneumothorax
Poor healing of intercostal drain sites
Systemic lupus erythematosus
-
Pulmonary fibrosis, 'vasculitic' infarcts
Pleurisy, effusion
Diaphragmatic weakness (shrinking lungs)
Rheumatic fever
Pneumonia
Pleurisy, effusion
Rare interstitial lung diseases
Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosisAlveolar proteinosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (histiocytosis X)
Neurofibromatosis
Alveolar microlithiasis
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis