White & Red Lesions of The Oral Mucosa
By:Dr. Ahmed Salih KhudhurBDS, MSc, PhD Newcastle University/ UK
دكتور احمد صالح خضر
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Department of:
HERE
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF)
OSF is a high-risk, precancerous condition characterized by chronic, progressive scarring of the oral & oropharynx mucosa
It is seen primarily in the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Taiwan, southern China, Polynesia, and Micronesia. Cases among Asian communities out of Asia, also have been reported
It’s a slowly progressive chronic fibrotic disease. In the earliest stages there may be a burning sensation and scattered small vesicles, followed by fibro-elastic changes and inflammation of the mucosa with epithelial atrophy and scarring leading to a progressive stiffness of the oral mucosa, trismus & inability to open the mouth, eat & swallow, or speak
Lesions may also appear as leukoplakia or erythroplakia patch
Etiology:
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF)Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Pallor and fibrosis of the soft palate in a betel quid chewer. The uvula has retained its normal color
•
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF)
Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Gutkha user with limited mouth opening and pale palatal mucosa•
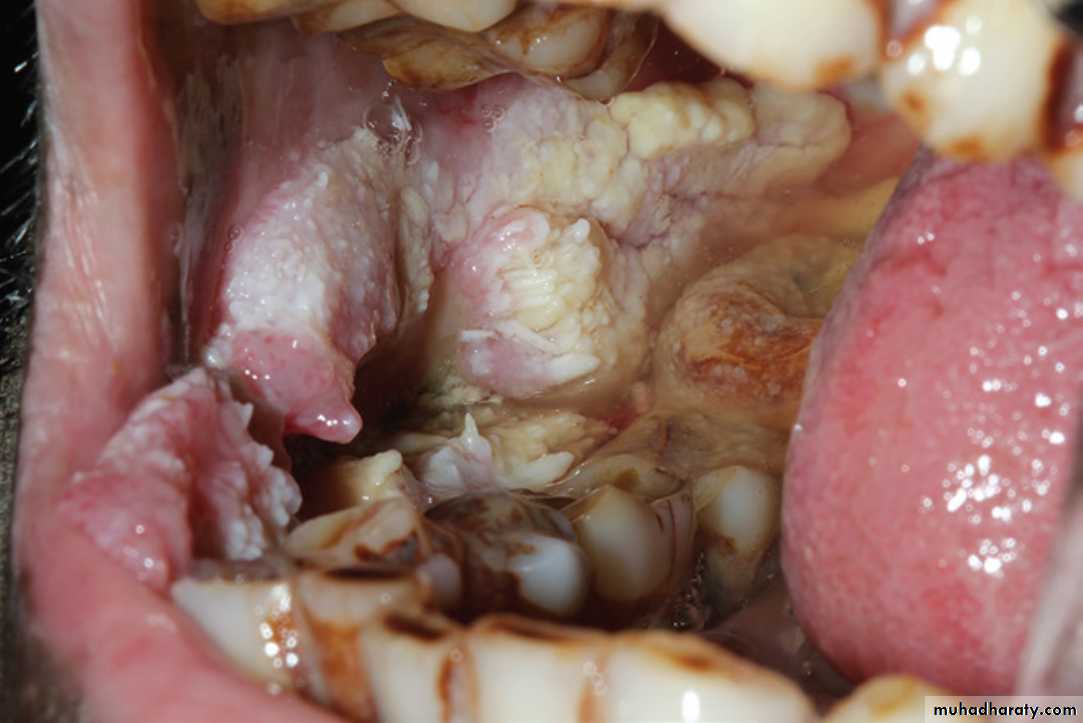
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF)
Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Same Gutkha user patient showing pallor of the left buccal mucosa.•
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF)
Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Same Gutkha user patient after years developed Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Extensive mass involving the right buccal mucosa and right lower labial mucosa•
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF)
Diagnosis: History & clinical examination. BiopsyTreatment:
Lupus Erythematosus
It's a chronic immunologically mediated inflammatory disorder of the skin, connective tissue (CT) and specific internal organsIt occurs in 3 clinical forms that represent the severity and distribution of involvement:
*The mildest form is called Discoid LE, it's chronic lesions confined to the sun exposed skin of the face scalp & ears, as well as oral mucosa*The intermediate form is called acute cutaneous LE, it’s widely spread & affects the head, neck, upper trunk & extensor surfaces of the arms
*The severe form is called systemic LE, in addition to the skin, it involves many organs such as kidneys, heart, lungs & bone marrow
Skin lesions of LE
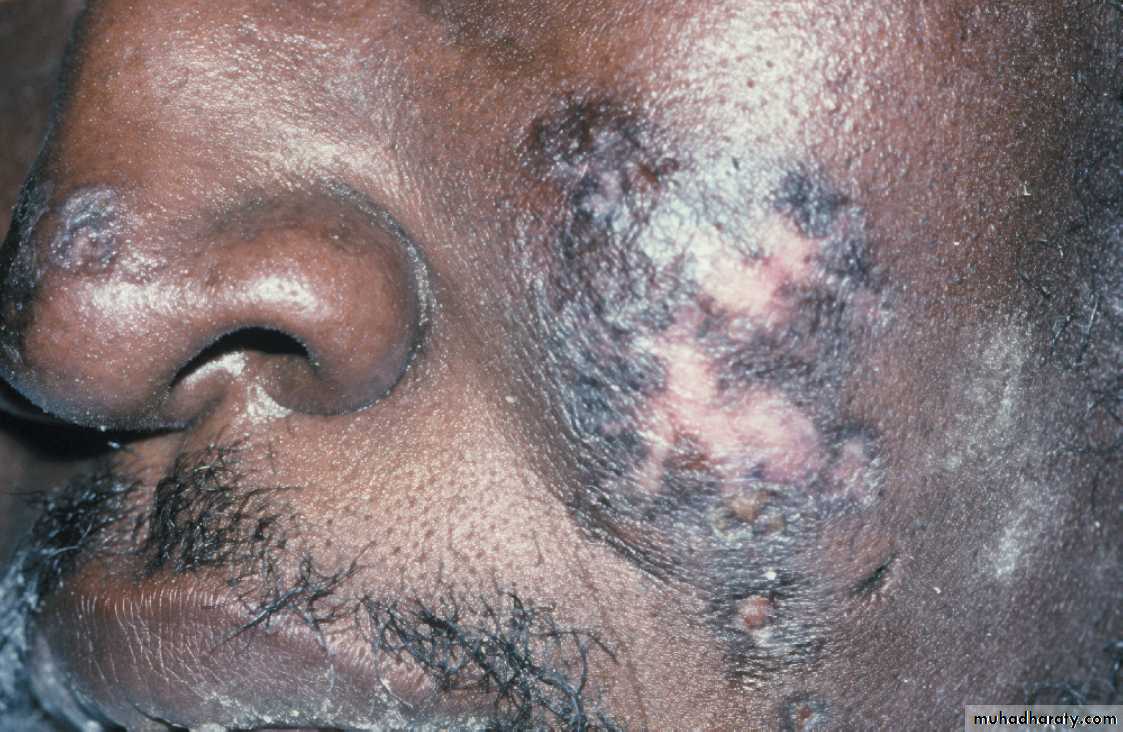
DLE. In dark skin patient. The skin lesions are characterized by scaling, atrophy, and pigmentation disturbances, which are most evident on sun-exposed skin•
Skin lesions of LE
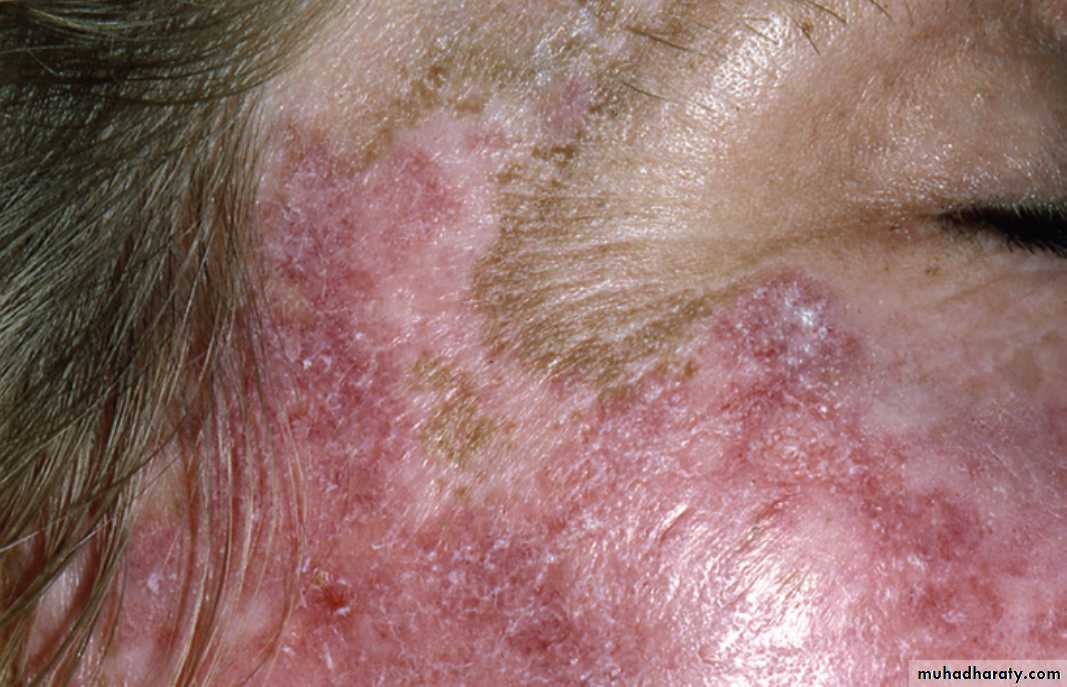
LE in white skin (Caucasian) patient. Red, scaly plaques with areas of regression and post-inflammatory melanosis (pigmentation) involving sun exposed skin.•
Skin lesions of LE
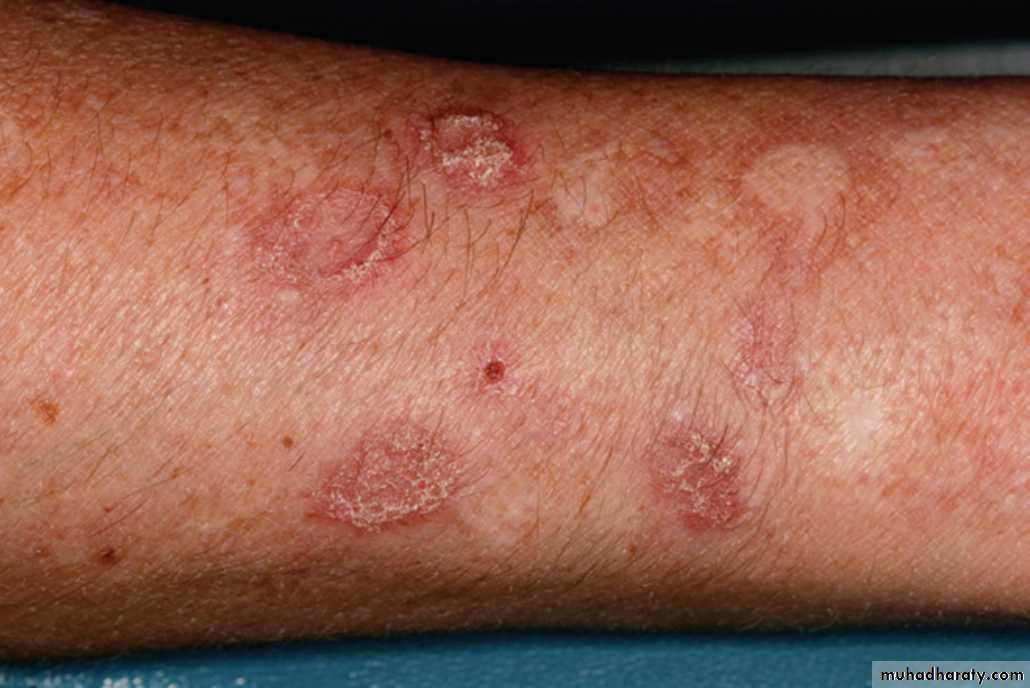
Scaly, erythematous round (“discoid”) plaques of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus.•
Skin lesions of LE
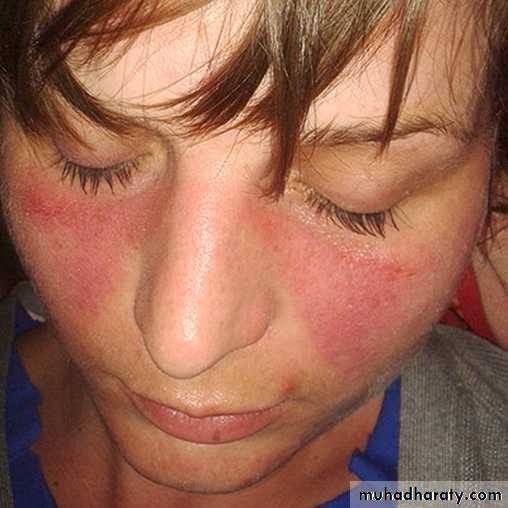
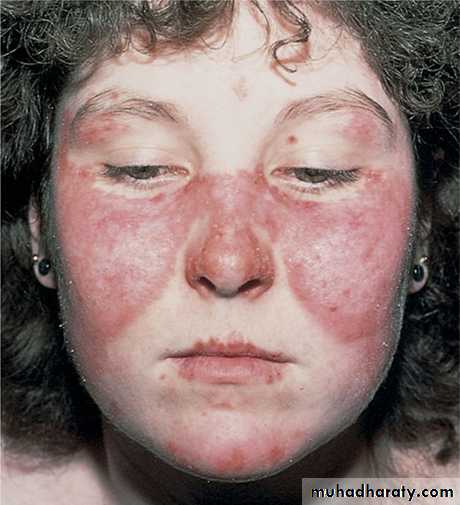
The characteristic skin lesion of Discoid LE & SLE is what is known as the Butterfly or Malar rash which is an erythematous skin macule or patch distributed over the malar & nose regions across the bridge of the nose•
Skin lesions of LE
SLE, The erythematous patches seen in the malar regions•
Skin lesions of LE
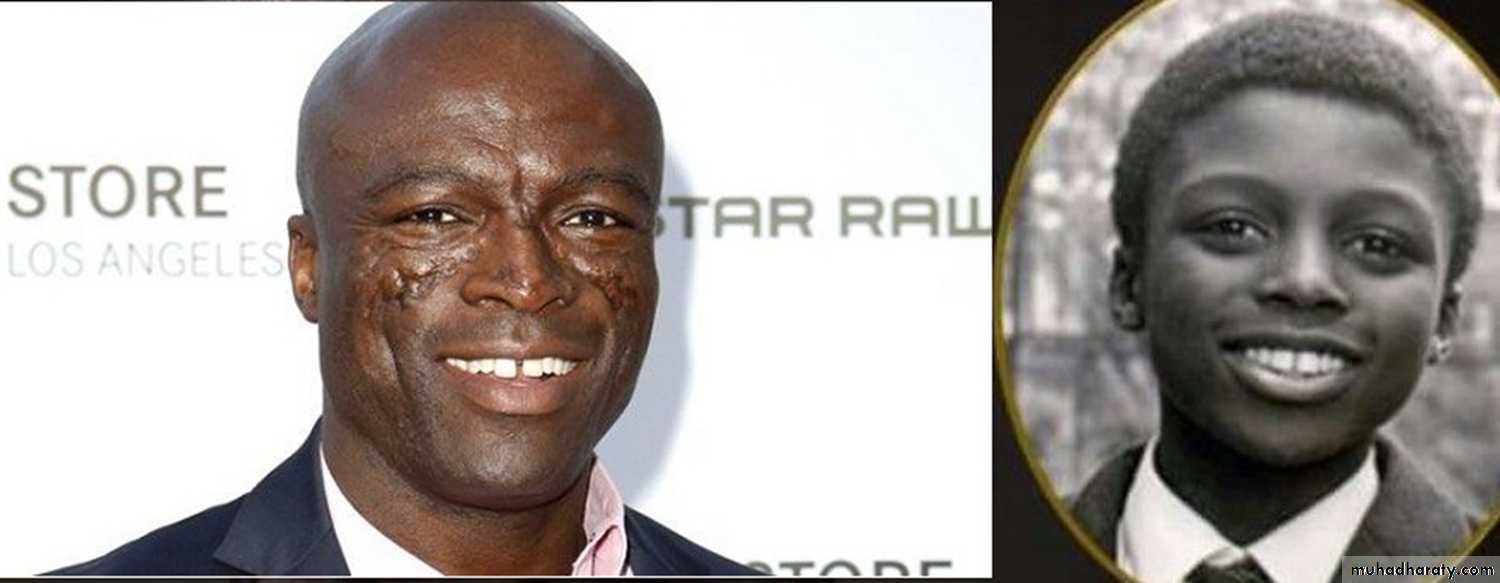
A celebrity with DLE butterfly lesion healed with scarring (British Singer-song writer Seal)•
Oral lesions of LE
Oral involvement is reported in 20-50 % of cases of DLE & 20-30% of cases in SLEThe oral lesions appear prior to or following the skin lesions
The oral lesions begin as erythematous areas
Superficial painful ulcerations may occur with crusting and bleeding
The margins are not sharply demarcated but frequently show a narrow zone of keratinization with fine white striae radiate out from the margins
Sometimes the erythematous, atrophic center of the lesion may show a fine stippling of white dots
DD Atrophic & Erosive LP
Oral lesions of LE
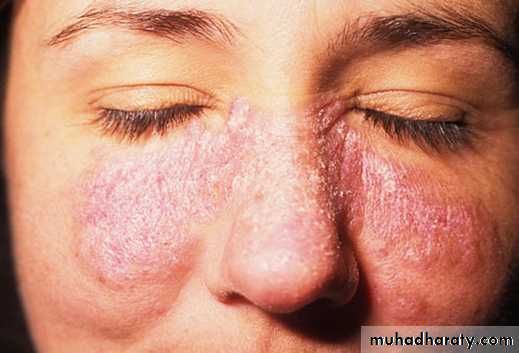
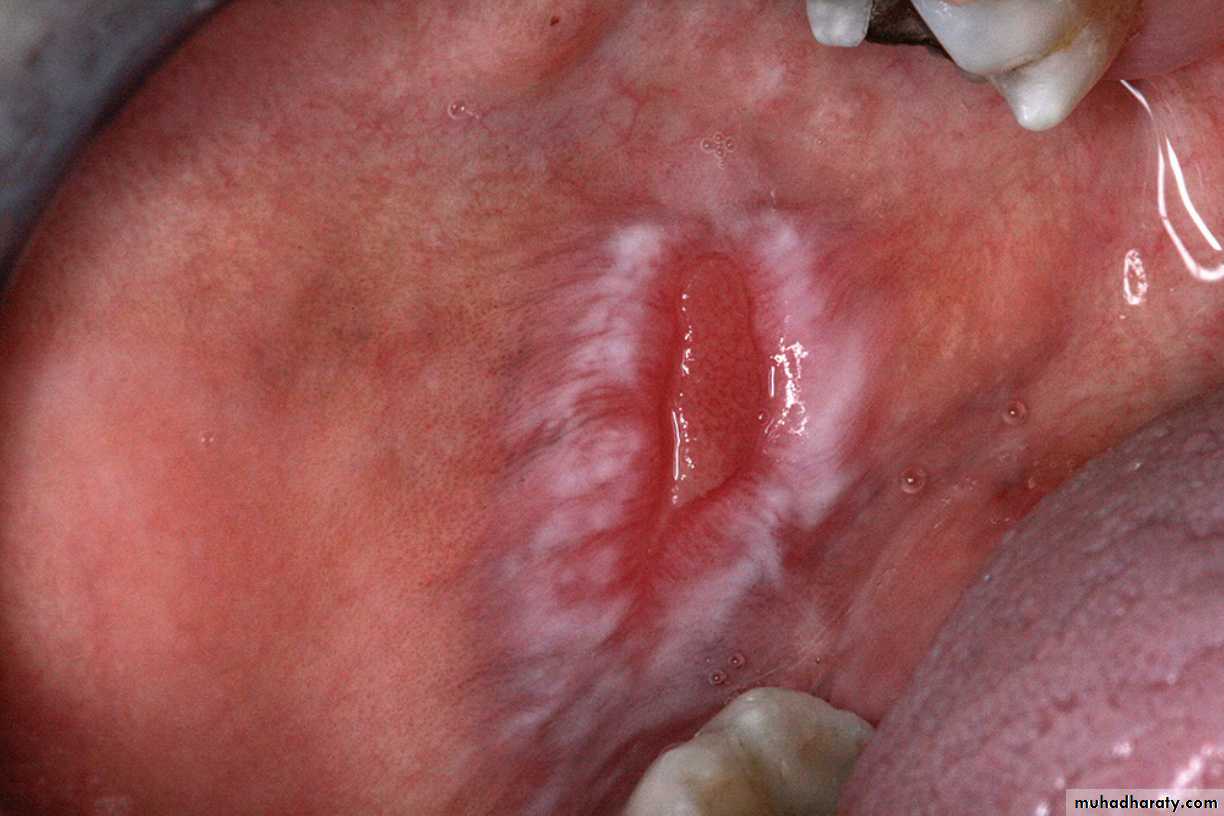
SLE. This ulceration of the buccal mucosa exhibits fine radiating white striae at its periphery, clinically appearing similar to erosive lichen planus
•
Oral lesions of LE
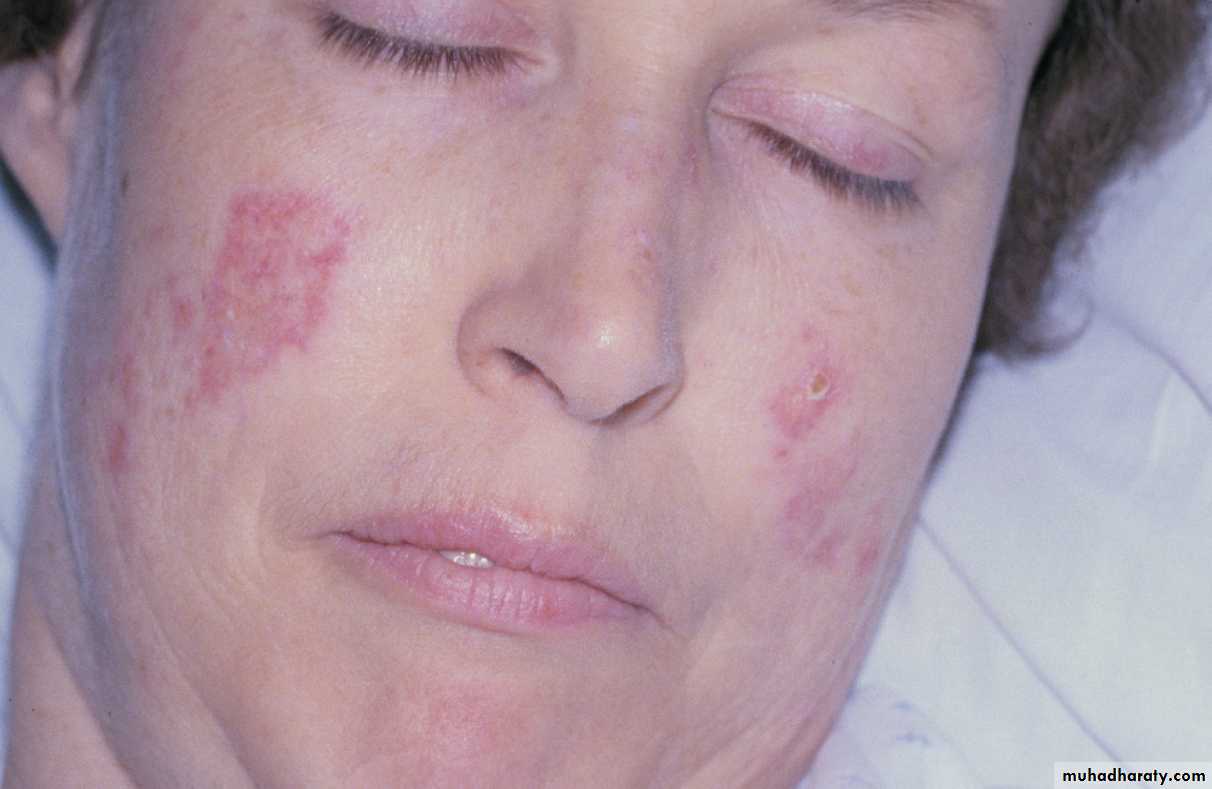
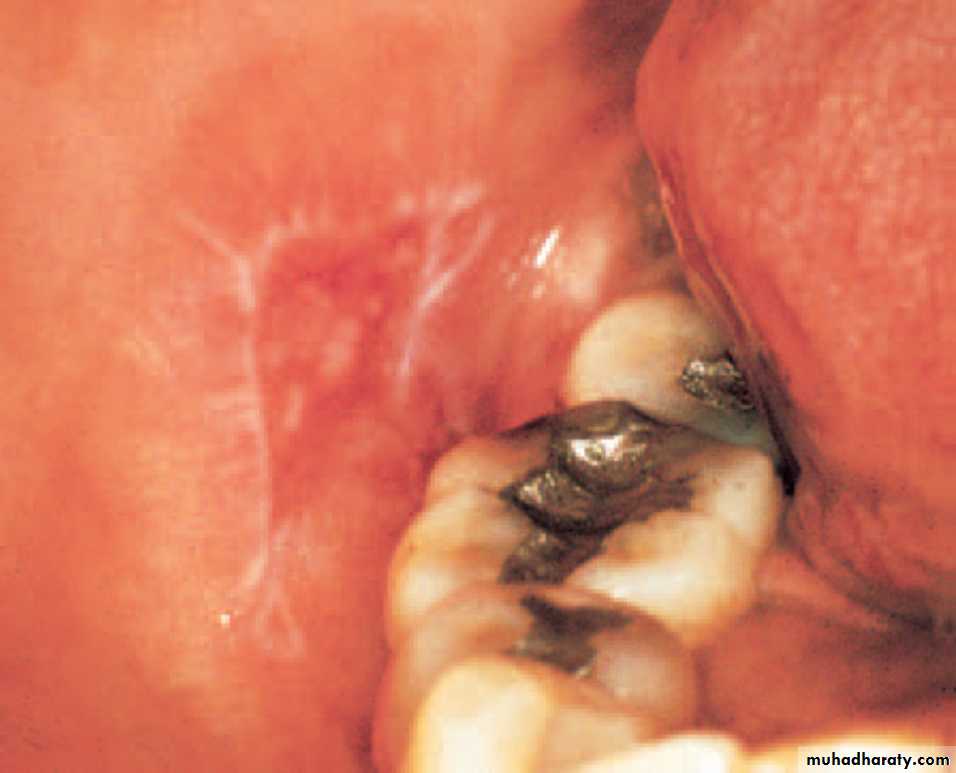
Atrophic lesion with radiating striae, on the buccal mucosa. Such a lesion as here, LE. The clinical presentation is often very similar to LP, therefore, should be investigated for both LP & LE•
Oral lesions of LE
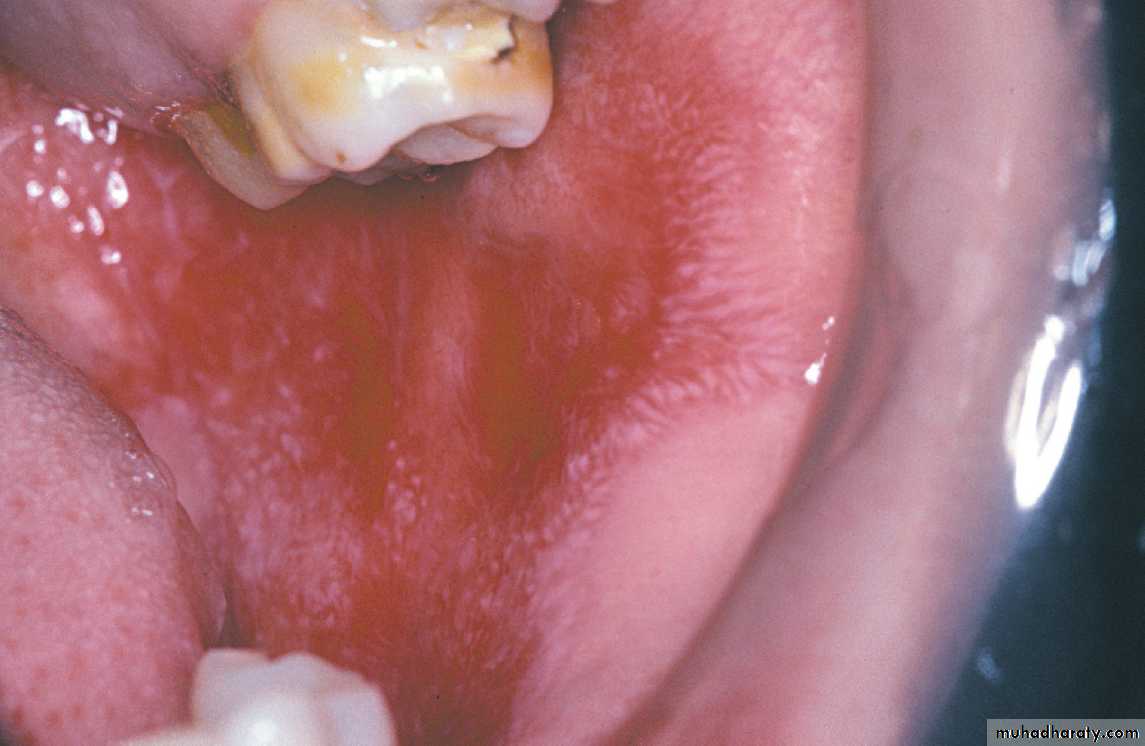
DLE. Radiating keratotic striae surrounding an erythematous zones of the buccal mucosa. These features are similar to those of erosive lichen planus•
Oral lesions of LE
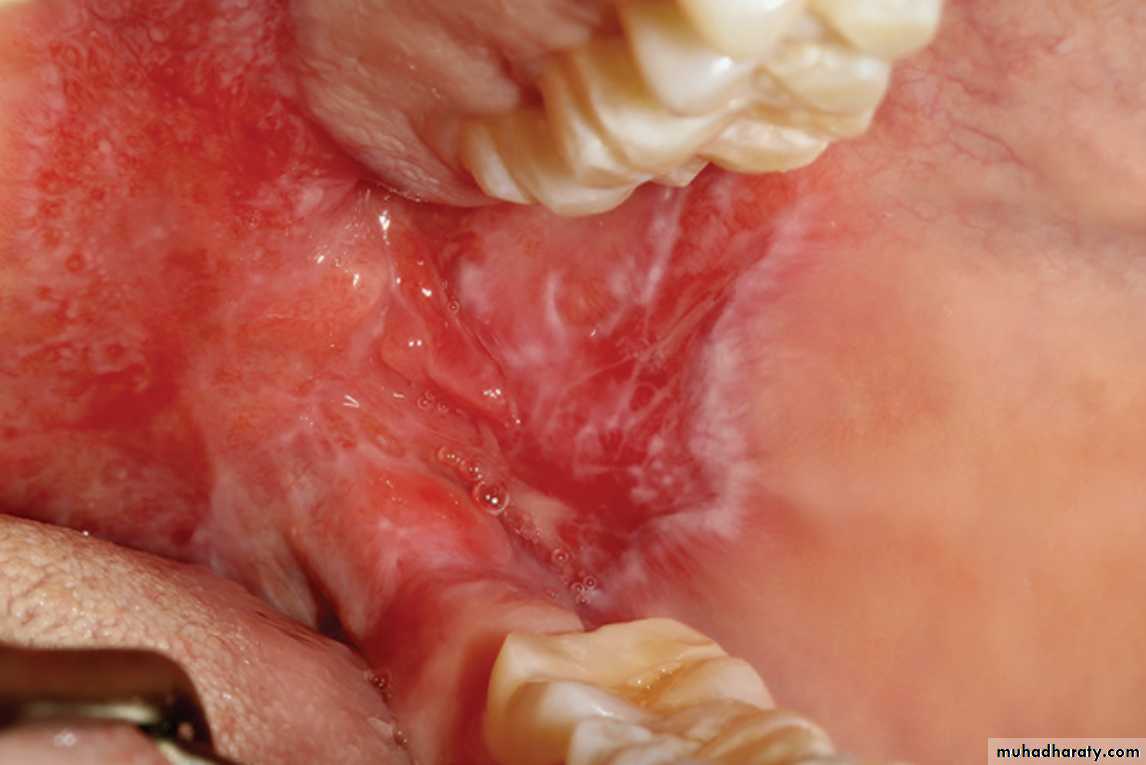
LE. Oral mucosal lesions often appear similar to those of lichen planus, showing areas of erythema in conjunction with white plaques and striae affecting the buccal mucosa
•
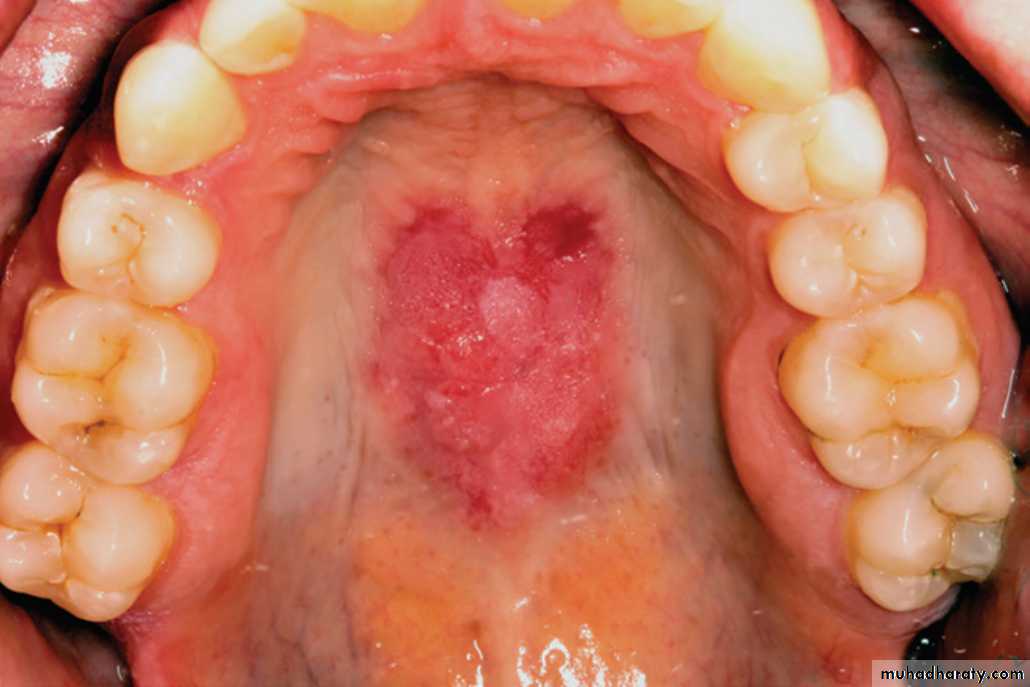
Oral lesions of LE
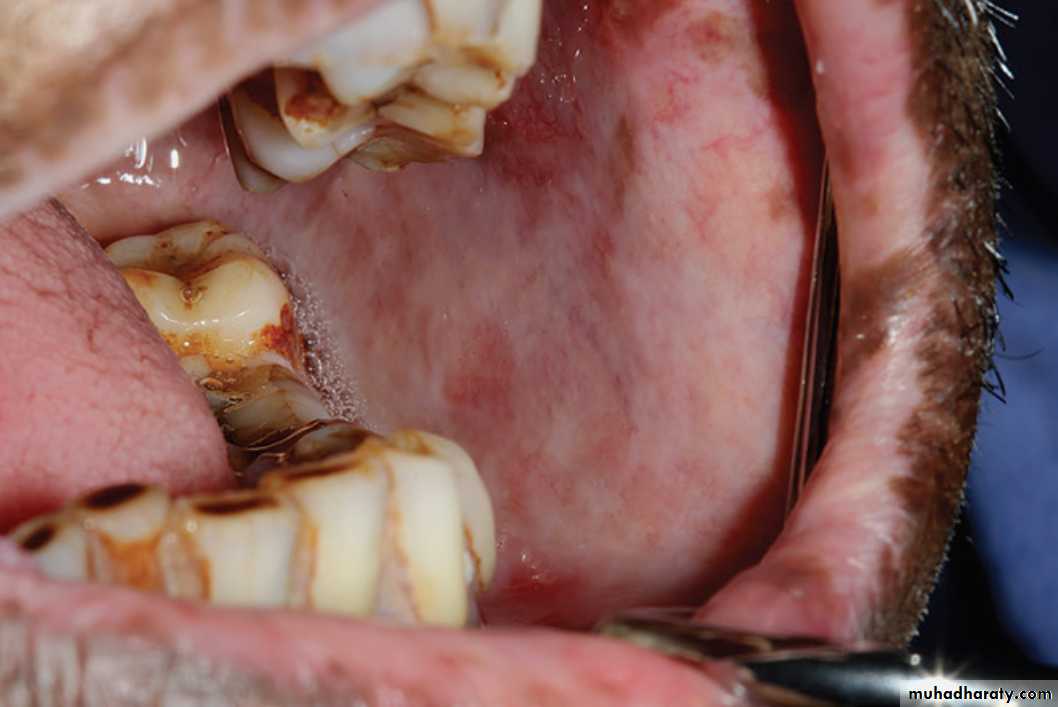
LE. Lesion showing a mixed red and white plaque involving the mid-posterior hard palate.•
Diagnosis of LE
• History & clinical examination• Histopathology
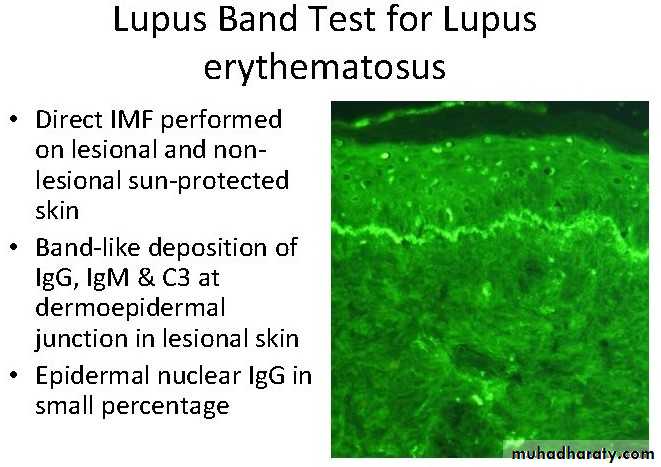
• Direct IF reveals deposition of antibodies at BM
• zone {granular deposition of IgM, IgG, IgA, and C3 (lupus band test)}
• Laboratory findings
• Antinuclear antibodies is positive (Specific)
• Rh factor is positive
• Anemia
• Leukopenia
• Thrombocytopenia
• ESR is increased
• False positive serological test for syphilis
Diagnosis of LE
•
Treatment of LE
• Drug of choice is corticosteroid• To obtain relief of symptoms, potent topical steroids such as clobetasol propionate gel
• 0.05%, betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%, or fluticasone propionate spray 50 μg
• aqueous solution are usually required
• The treatment may begin with applications two to three times a day followed by a
• tapering during the next six to nine weeks. The overall objective is to use a minimum of
• steroids to obtain relief
• Immunosuppressive drugs. Along with antifungals/antivirals to prevent/treat
• opportunistic fungal/viral infections
• Antimalarial drugs:
• Chloroquine 250mg tab twice daily
• Hydroxy chloroquine 200mg tab twice
• Keratolytic agents: Retinoids (Retin A®) & Isotretinoin
• Laser therapy
Intra oral skin grafts
• Pieces of skin grafted into the oral mucosa usually to:
• Line a surgically deepened buccal sulcus
• Repair an oro-antral fistula
• Repair extensive traumatic oral wound
• Such grafted tissue has been mistakenly identified as a white lesion
• The grayish white appearances depends on imbibition of fluid by the thick stratum corneum
• Normal keratinized oral mucosa does not exhibit this phenomenon
Intra oral skin grafts
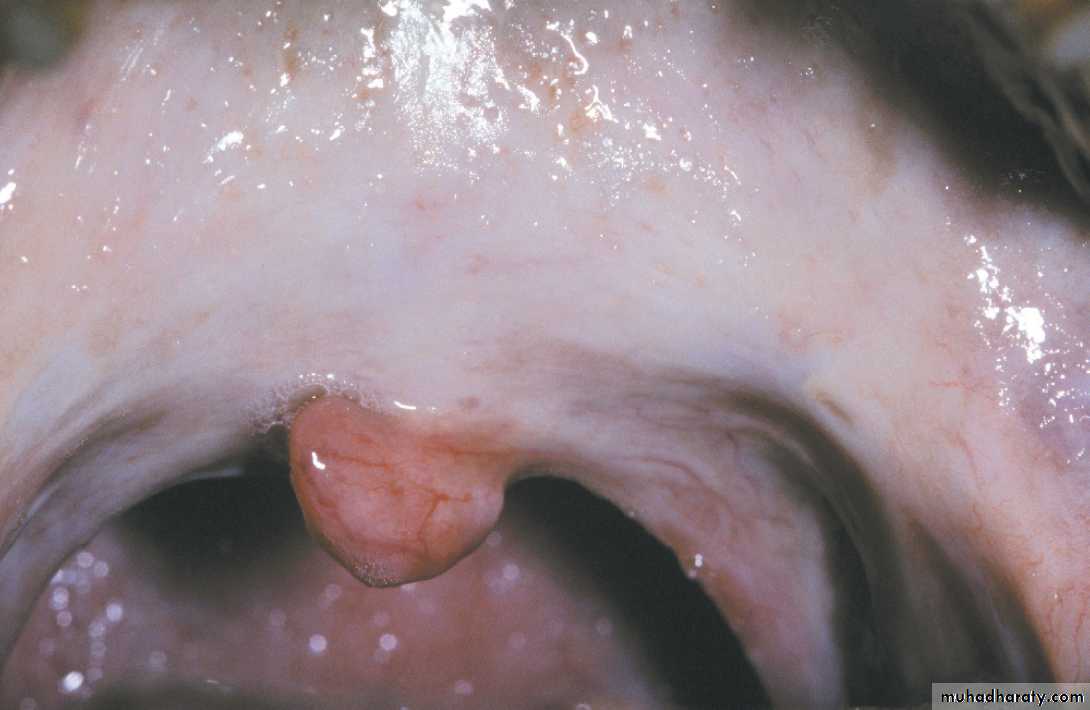
Intra oral skin graft. A skin graft placed on the right posterior hard palate appears as a scar-like, pale patch•
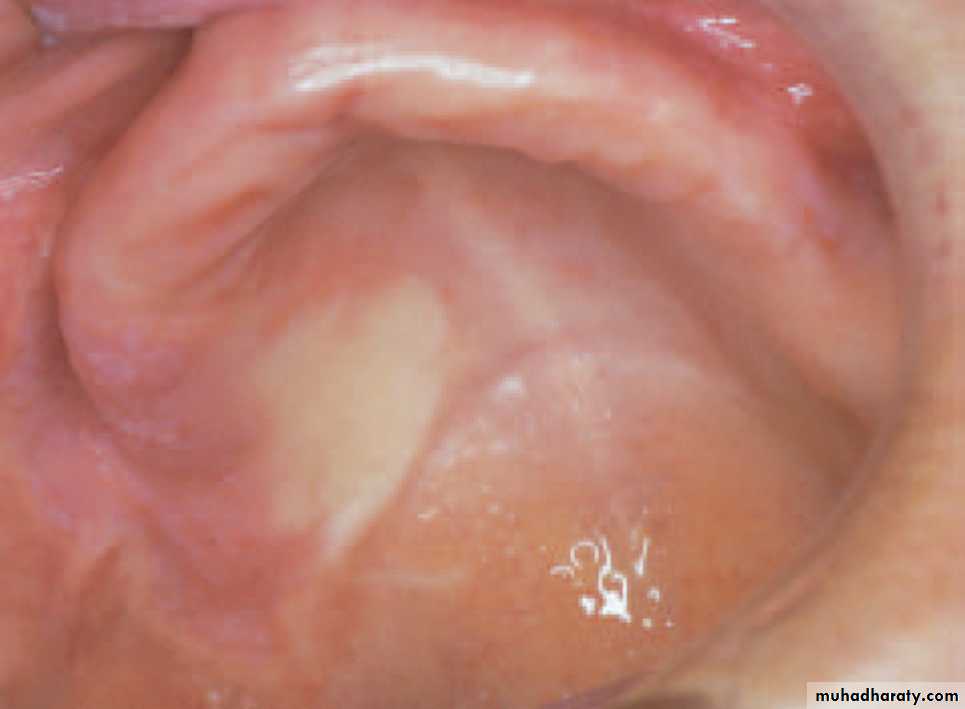
Intra oral skin grafts
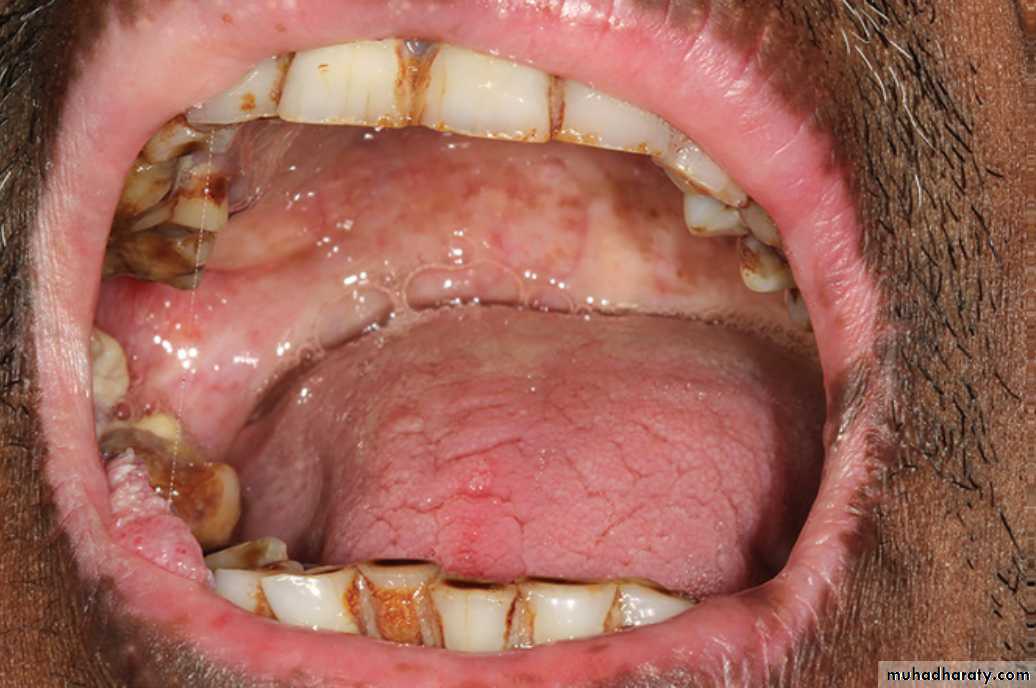
Intra oral skin graft placed on the left buccal mucosa appears as a white patch•
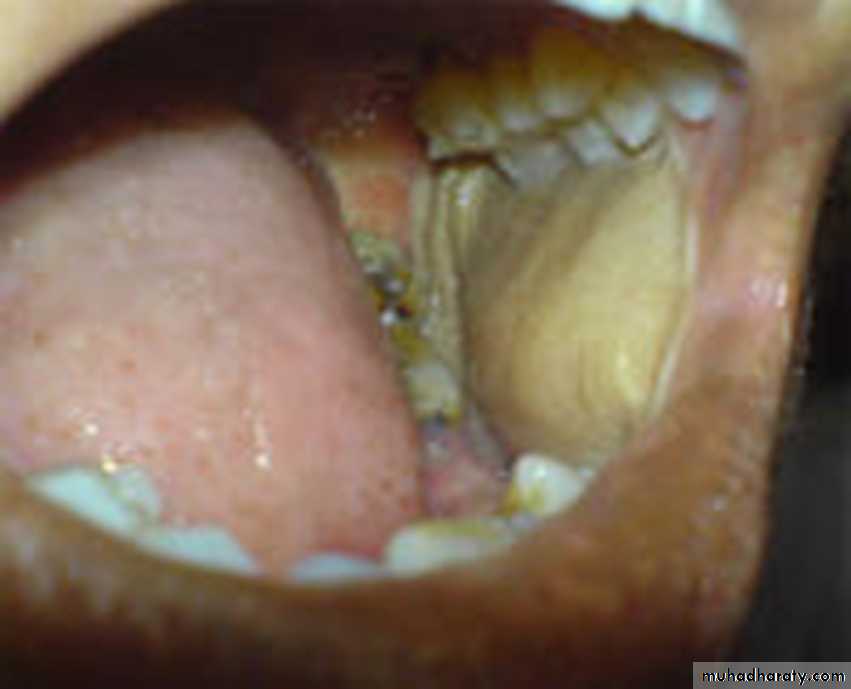
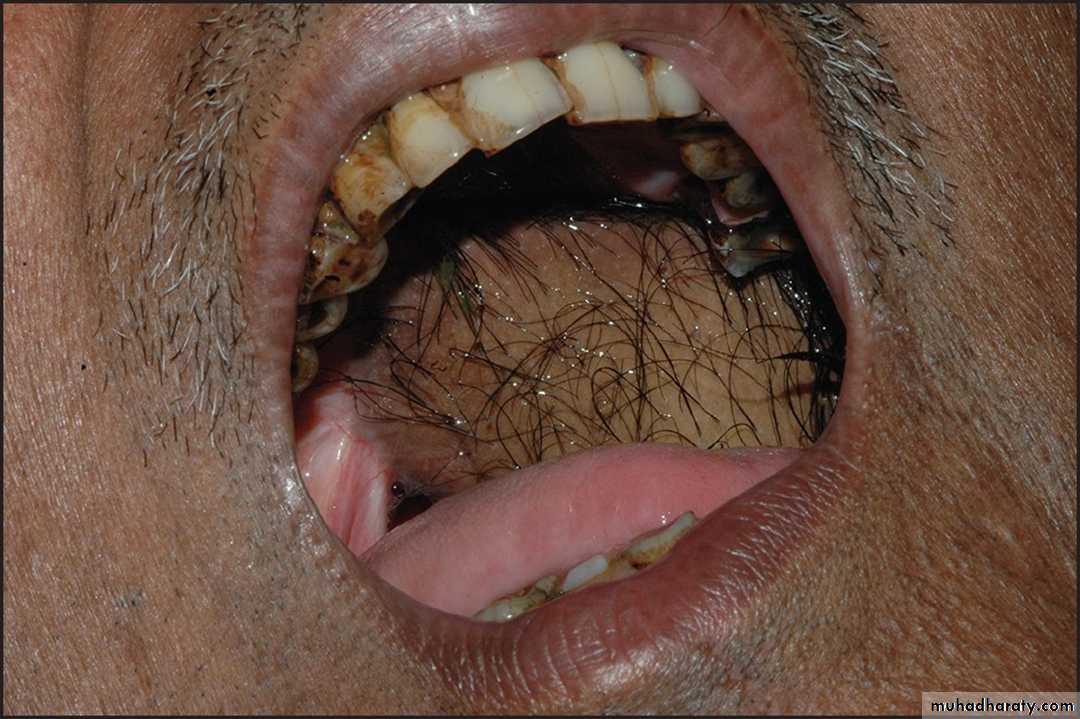
Intra oral skin grafts
Intra oral kin graft, with intra oral hair growth (Hair follicles occasionally survive transplantation to the mouth)•
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021