Cerebrum -1-
• Forebrain
• External features• SurfaceS :
• 1. Superolateral surface• 2. Medial surface
• 3. Inferior surface
• Sulci :
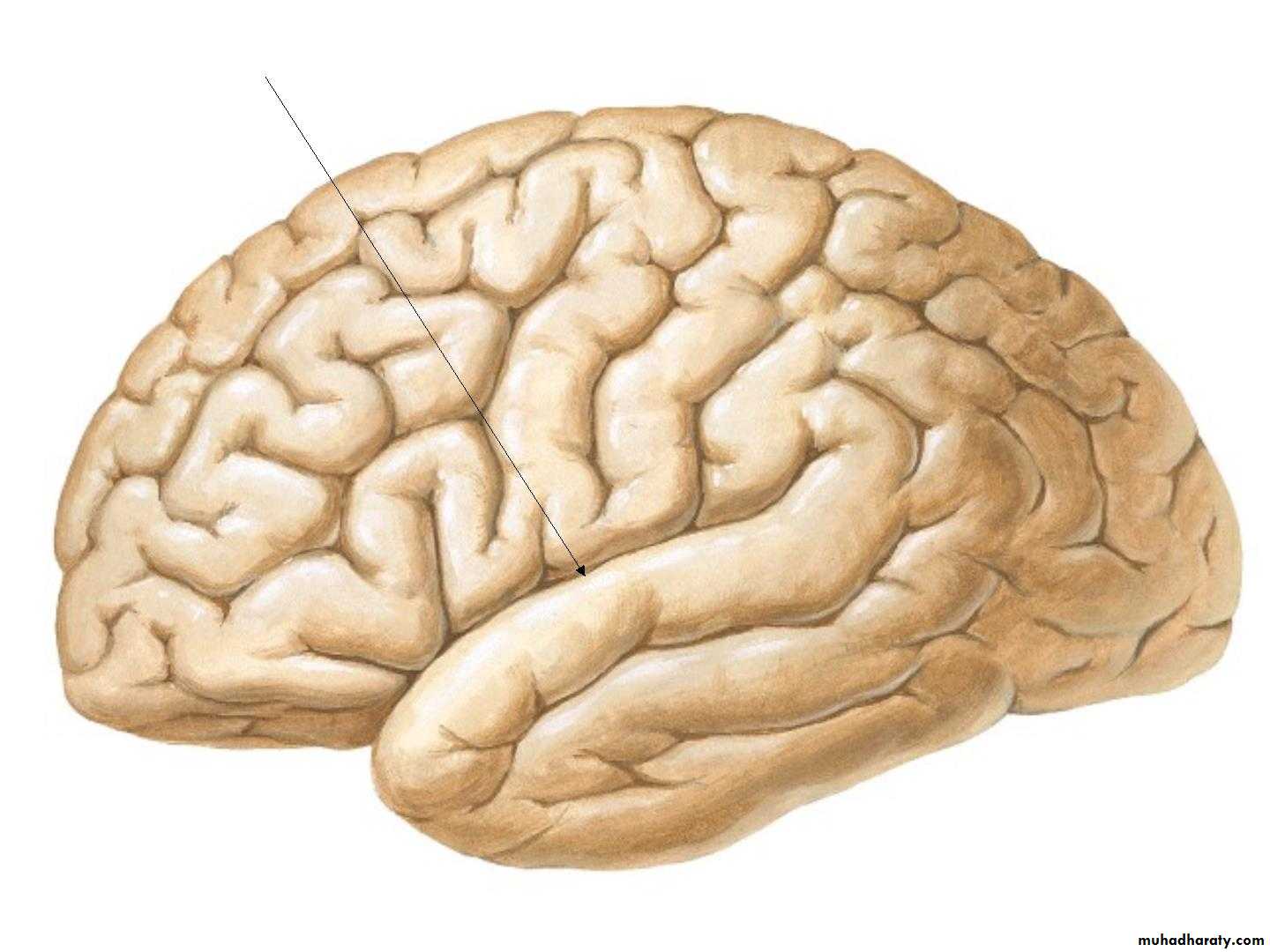
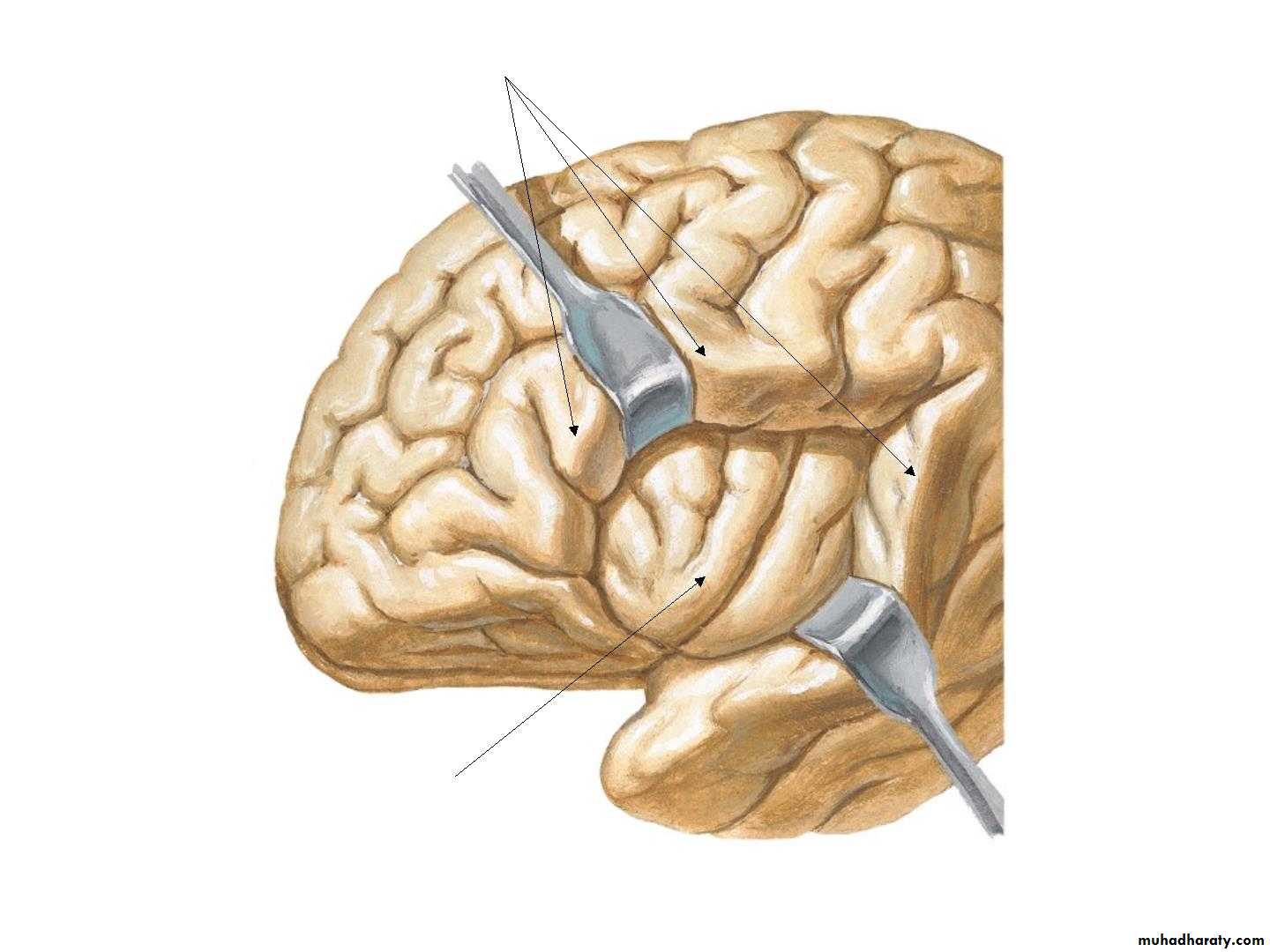
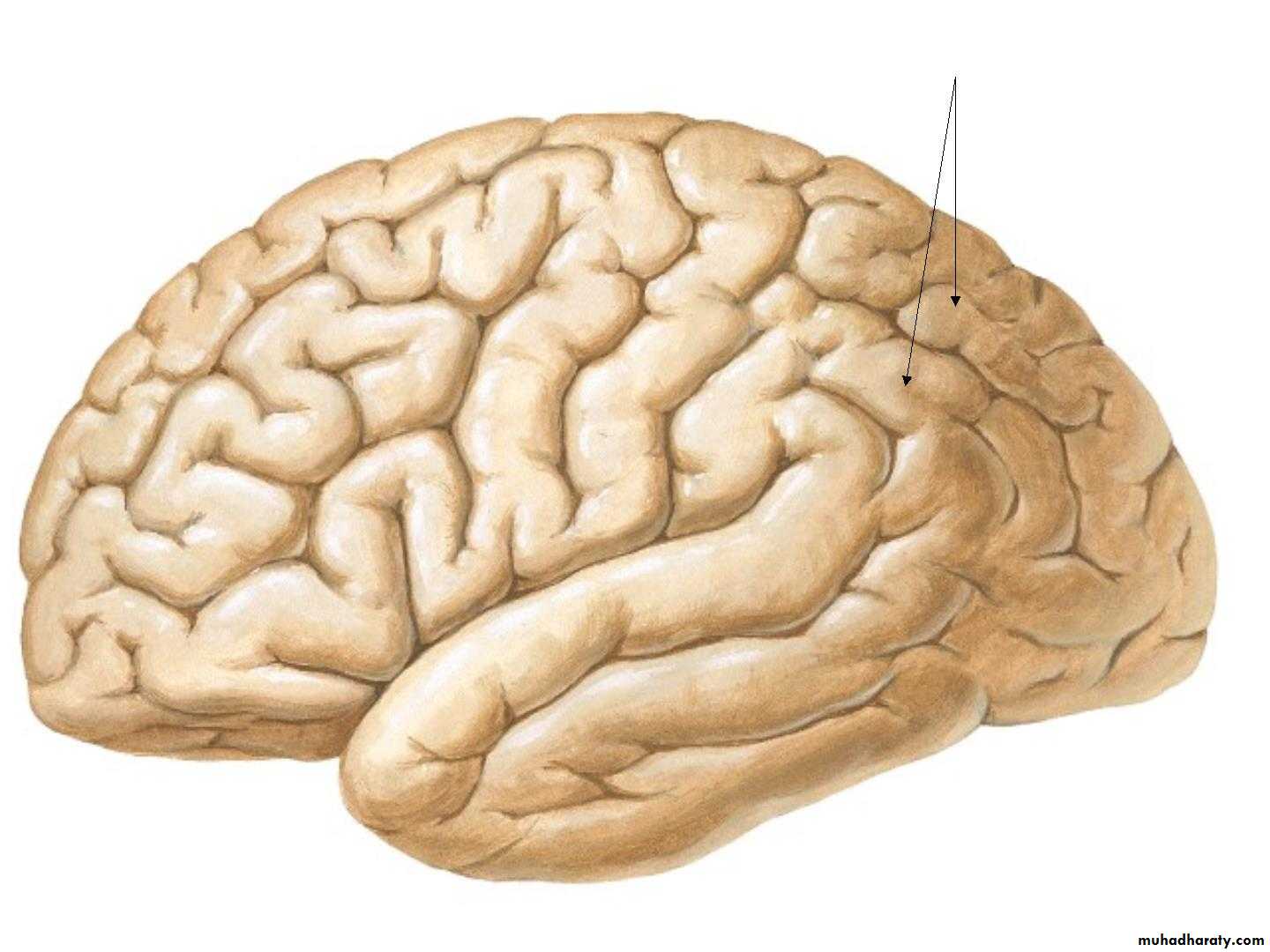
• 1. Central sulcus,• 2. Lateral sulcus,
• 3. Parieto-occipital sulcus,
Main Sulci
Three principal sulciCentral sulcus
Lateral sulcus
Parietooccipital sulcus
Central sulcus
Lateral sulcusParietooccipital sulcus
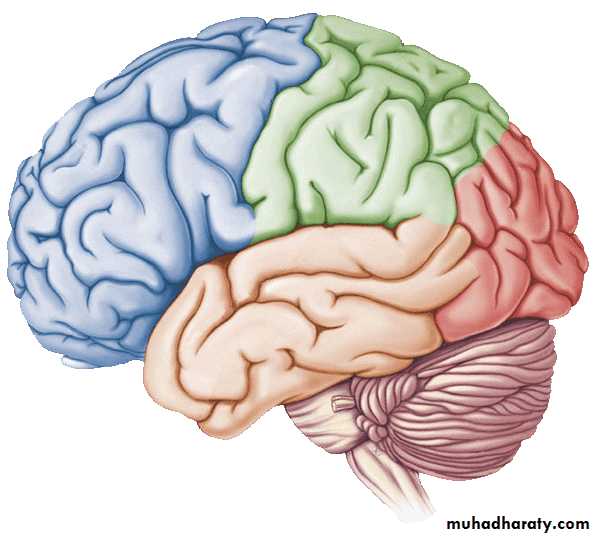
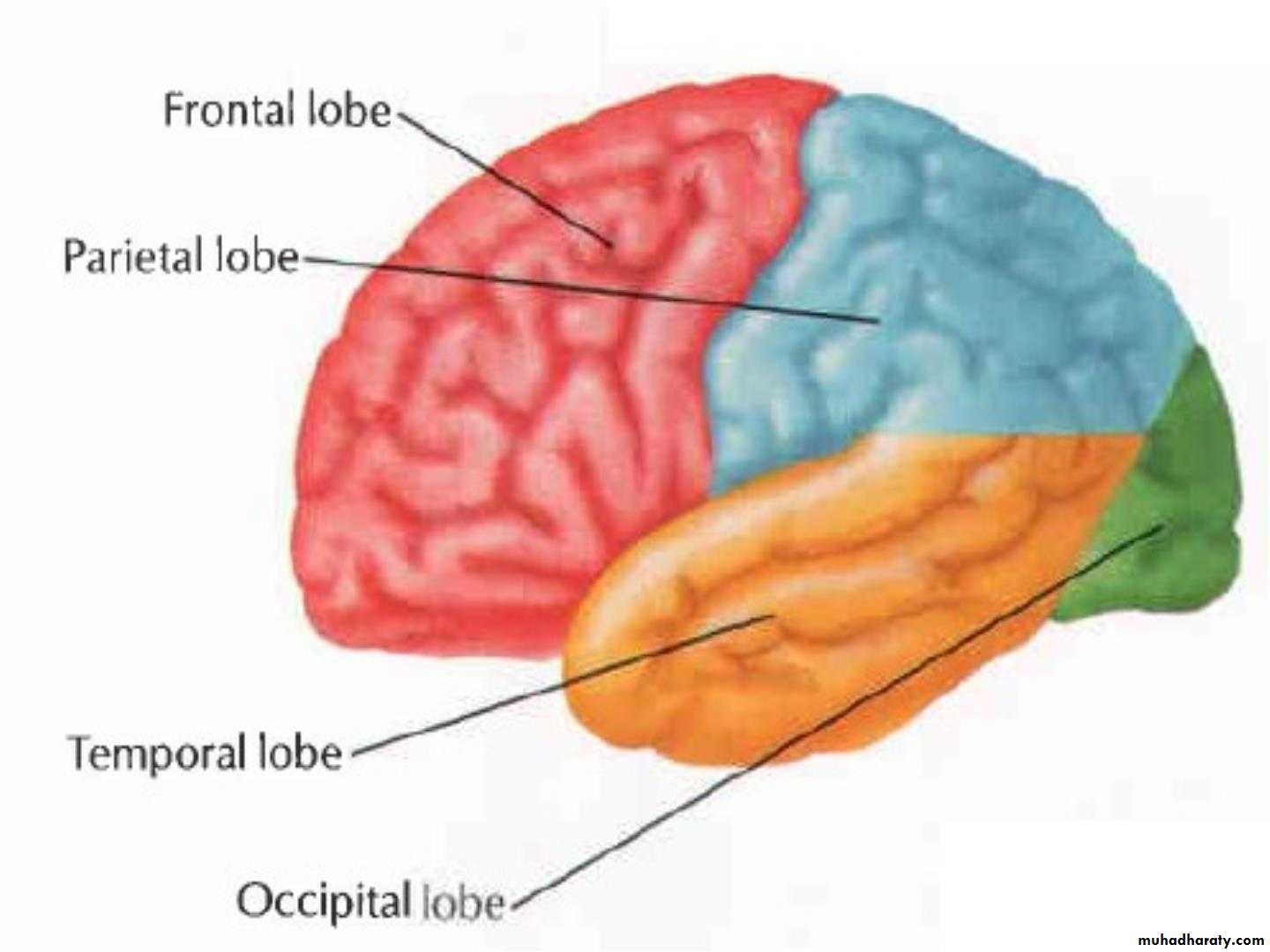
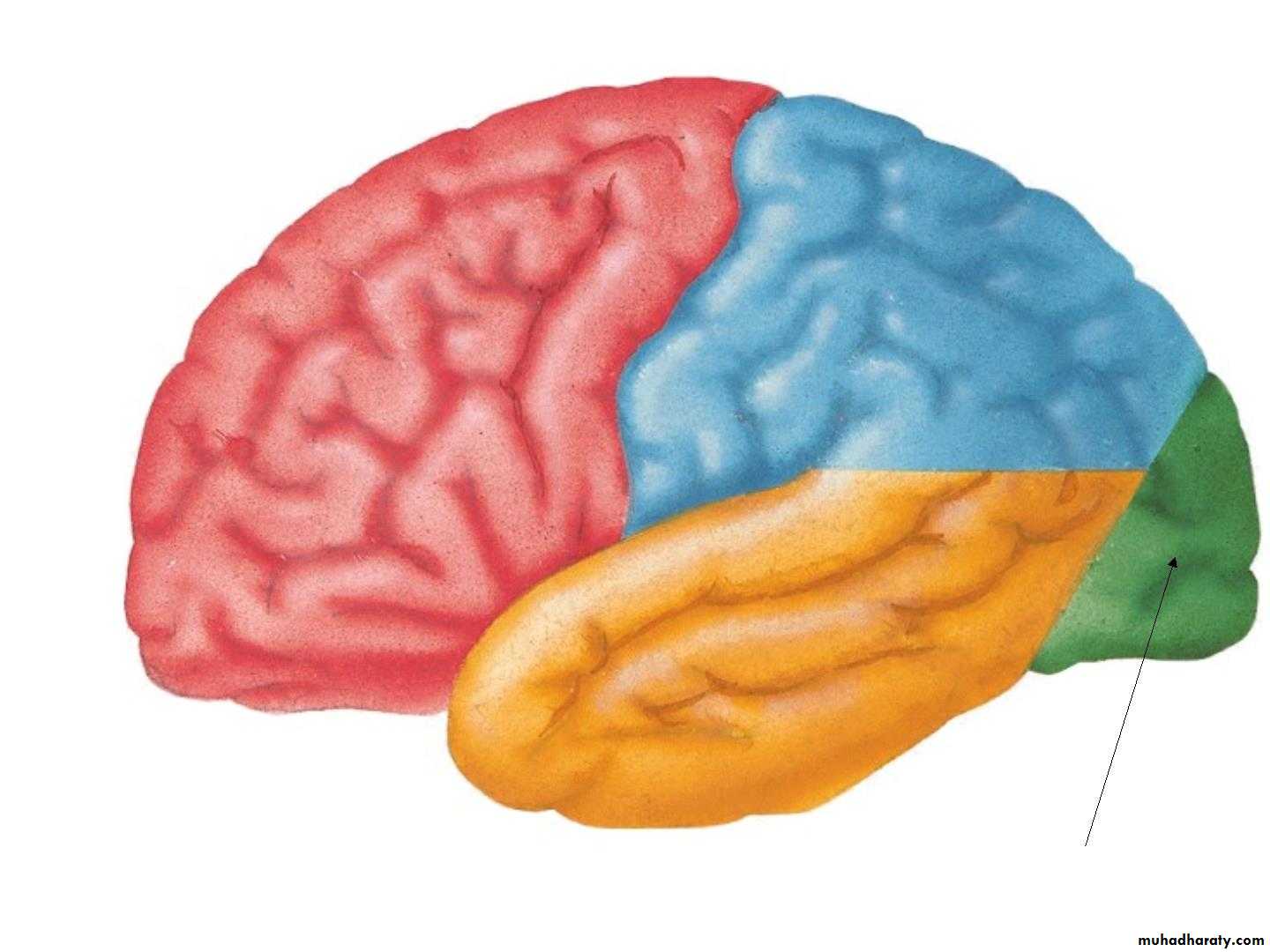
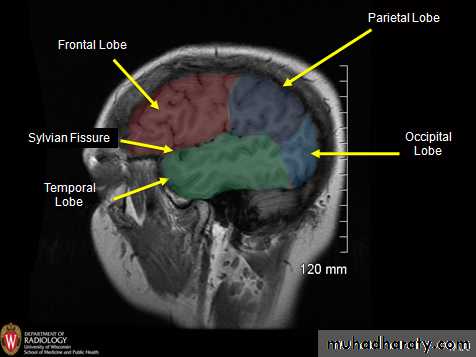
• lobeS :
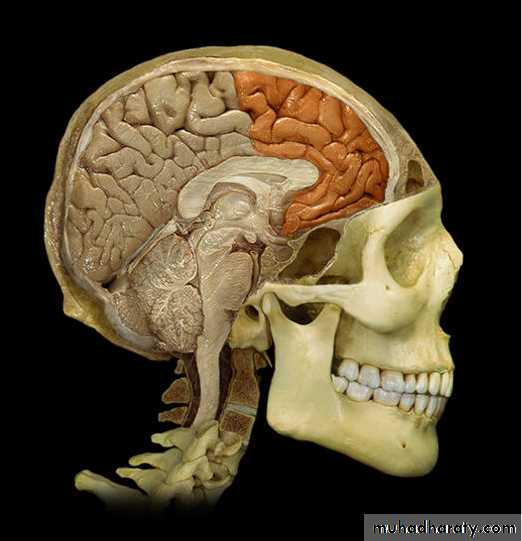
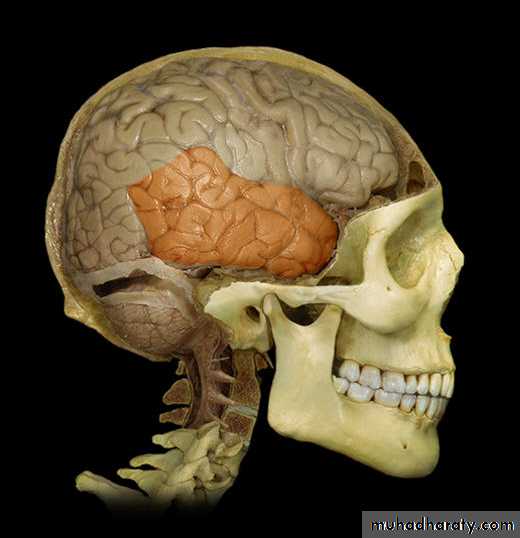
• 1. Frontal lobe (in front of the central sulcus• and above the lateral sulcus),
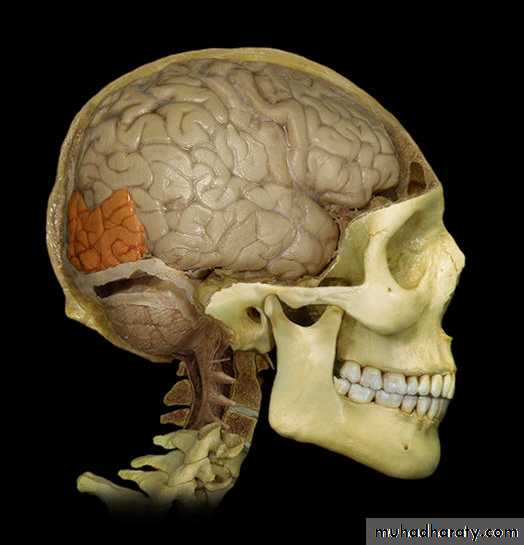
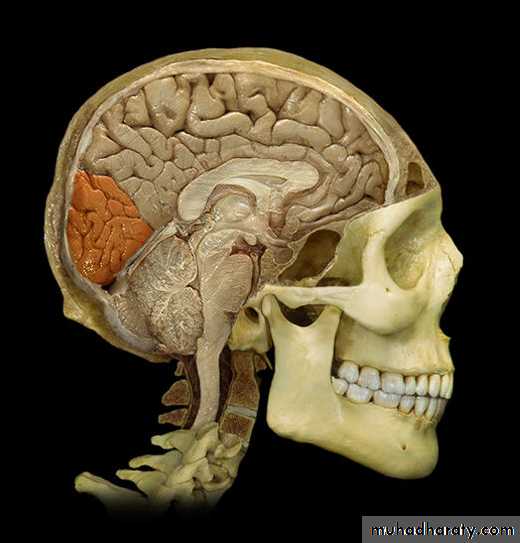
• 2. Temporal lobe(below the lateral sulcus),
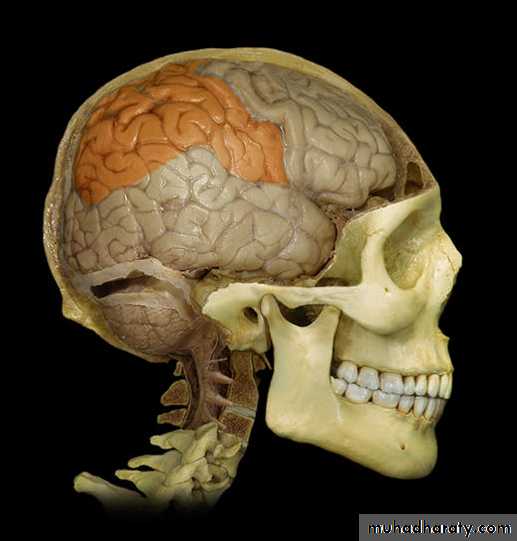
• 3. Parietal lobe (behind the central sulcus and
• above the lateral sulcus),
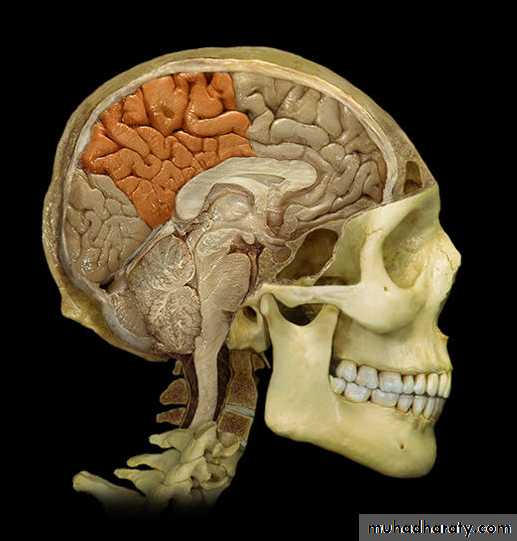
• 4. Occipital lobes (behind the parieto-occipital
• sulcus).
• 5. Insula
Lobes of Cerebral Hemisphere
Five lobes
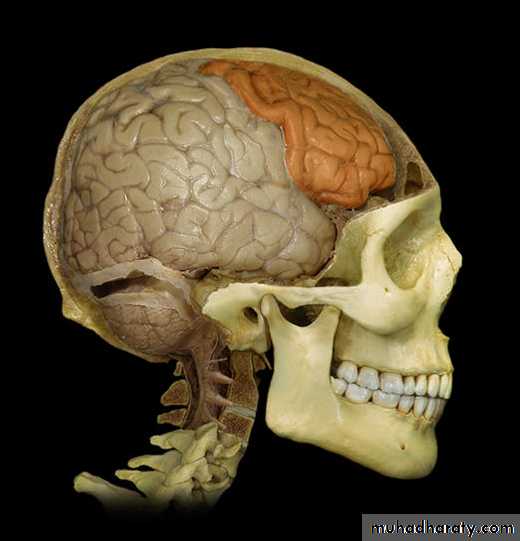
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobe
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobe
Insular lobe
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobeOccipital lobe
Temporal lobe
Insular lobe
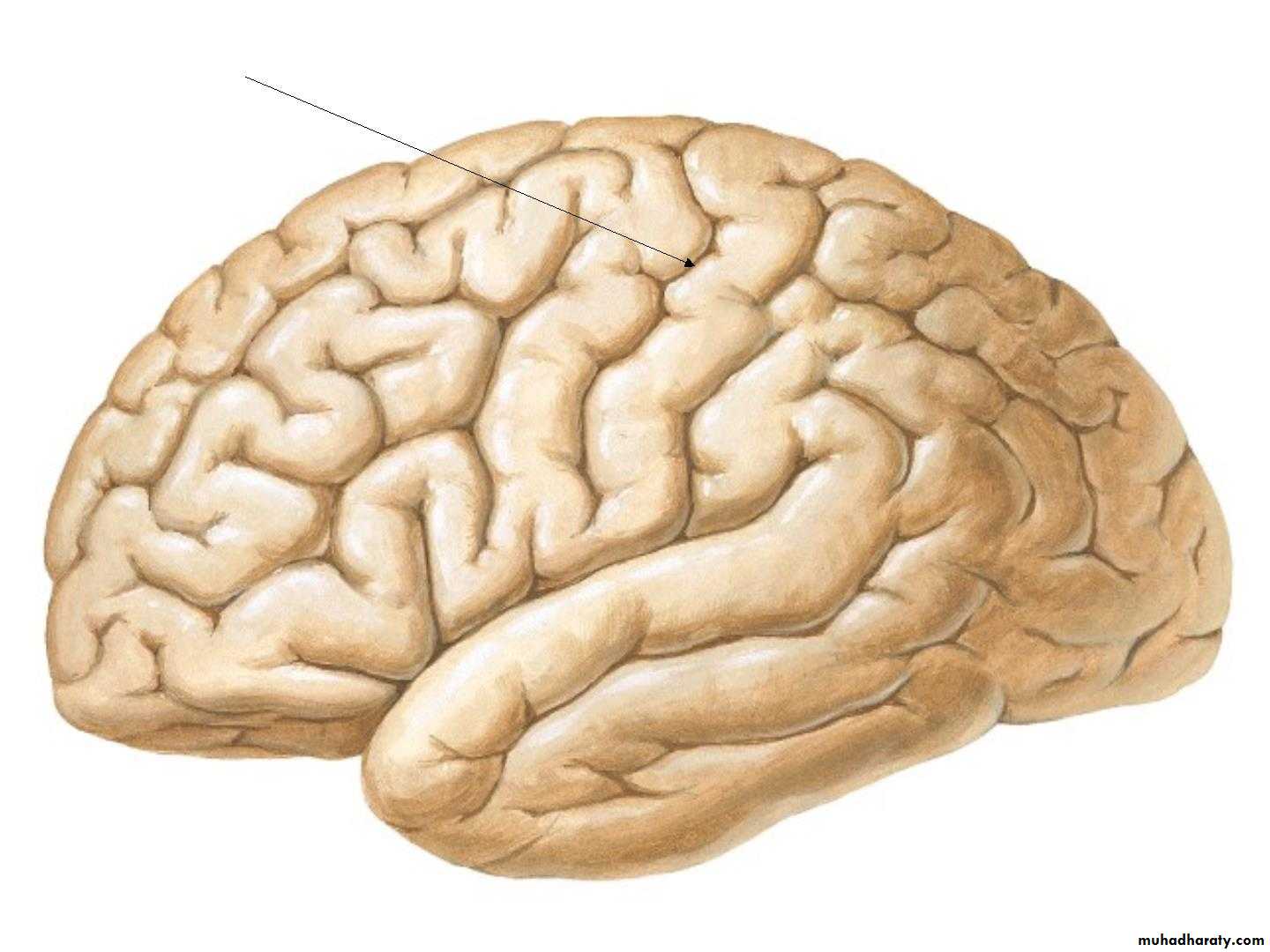
• Superolateral surface
• 1. Lateral sulcus:
• 2. Opercula:
• Insula• Central Sulcus
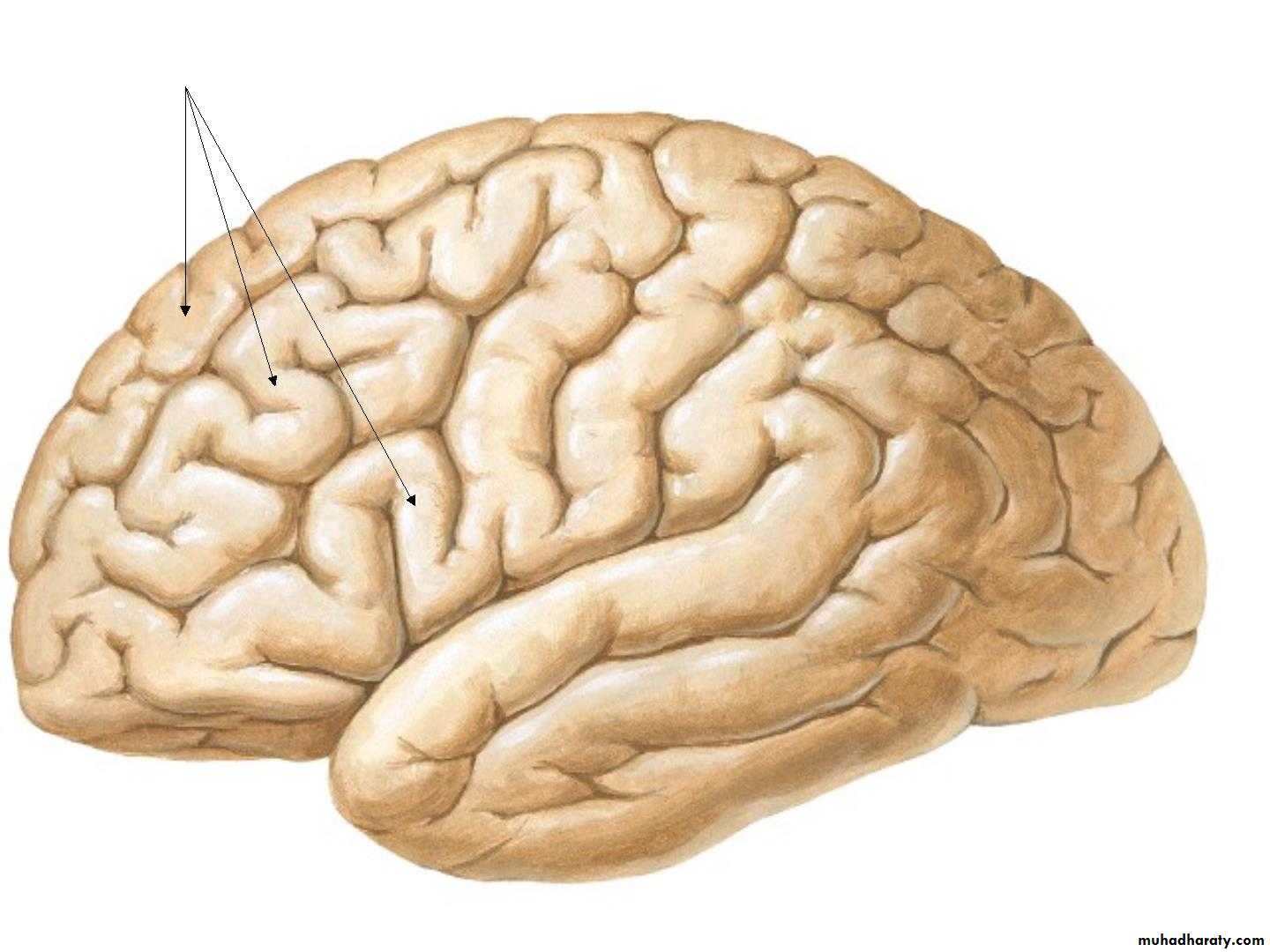
• 4. Frontal gyri:
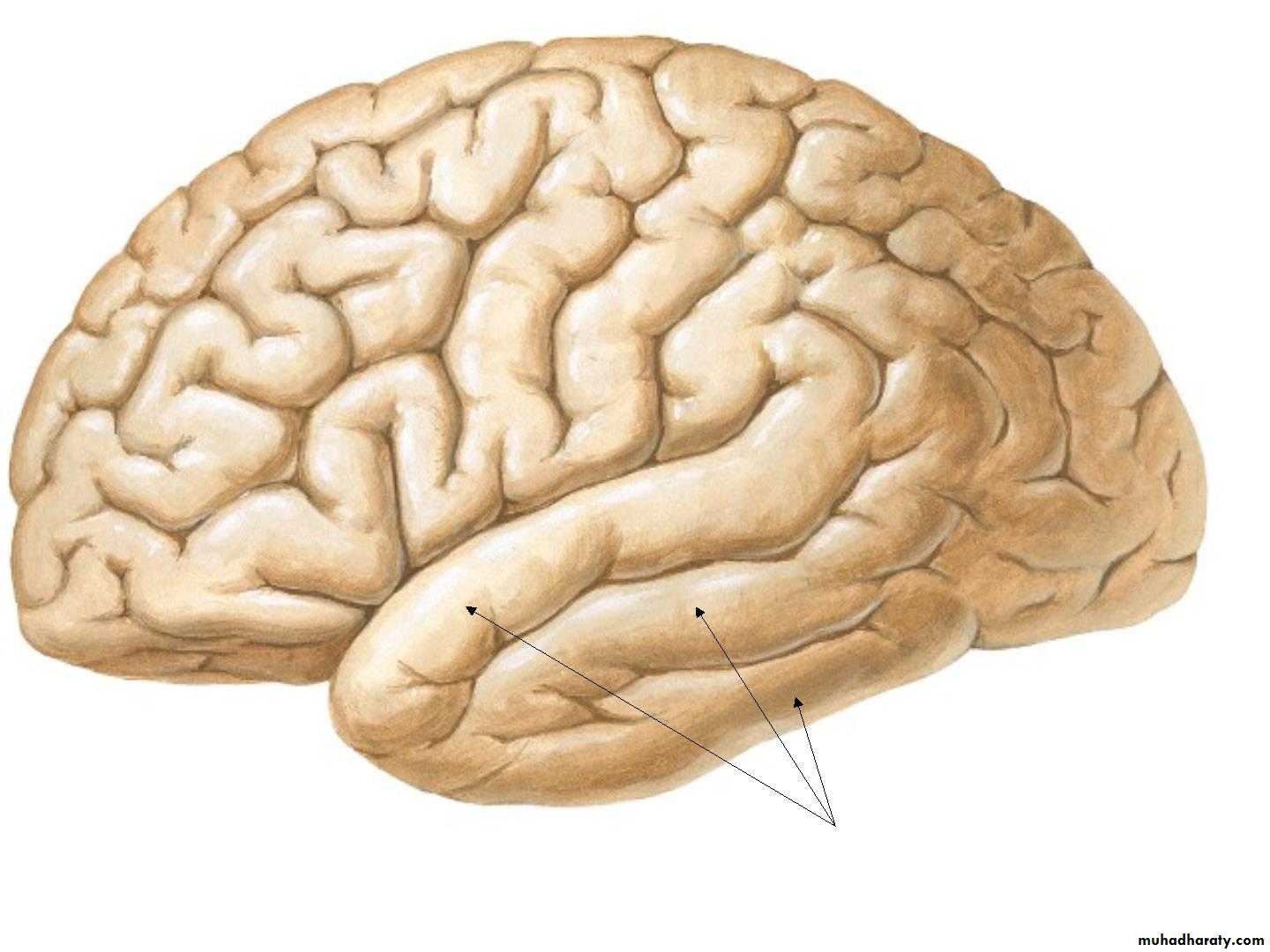
• 5. Temporal Gyrus:
• 5. Parietal lobe :
• 6. Occipital lobe:
Cerebrum14-17
14-17
Cerebrum-Frontal LobeCerebrum-Parietal Lobe
14-19
Cerebrum-Occipital Lobe
14-20
Cerebrum-Temporal Lobe14-21
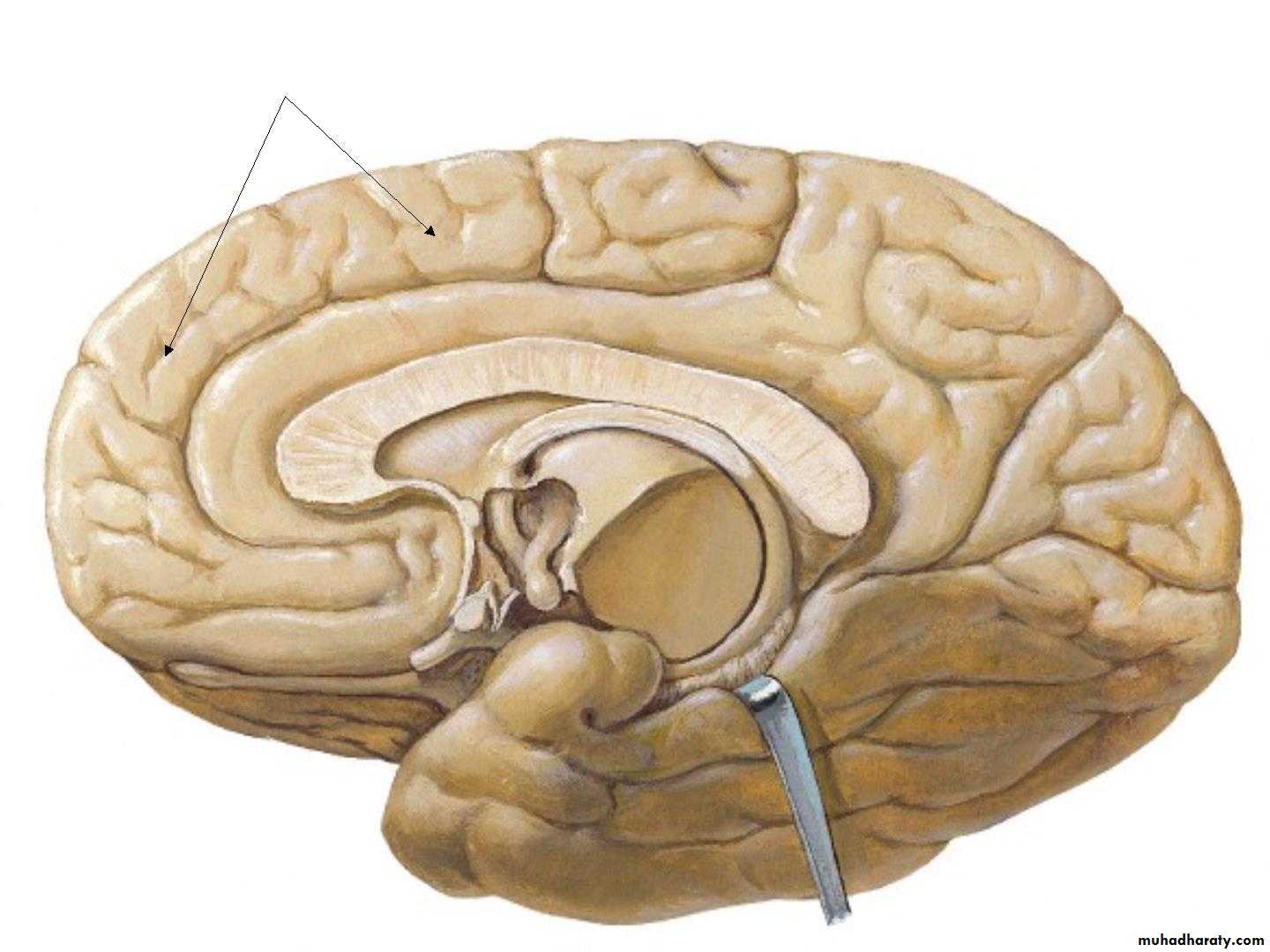
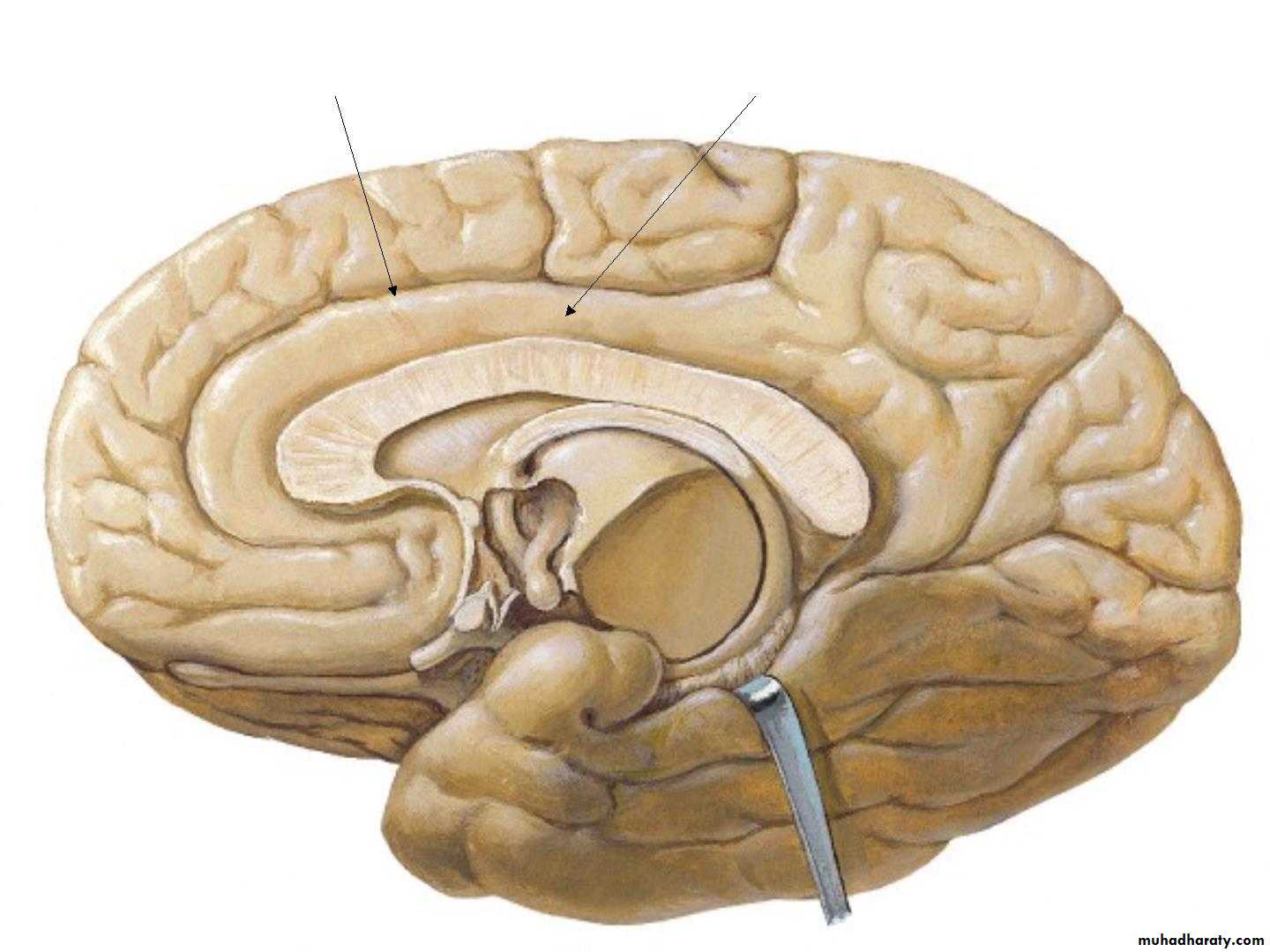
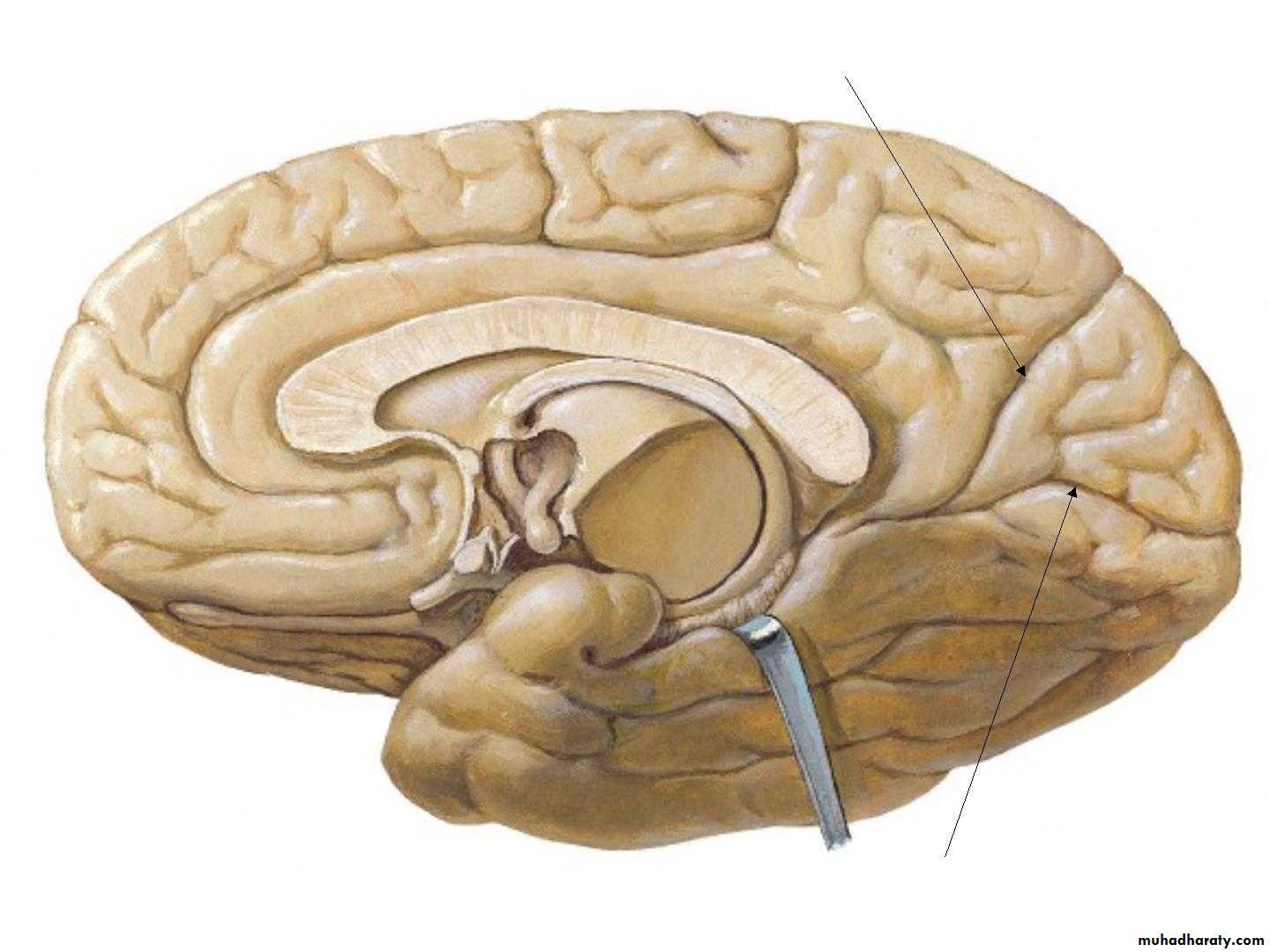
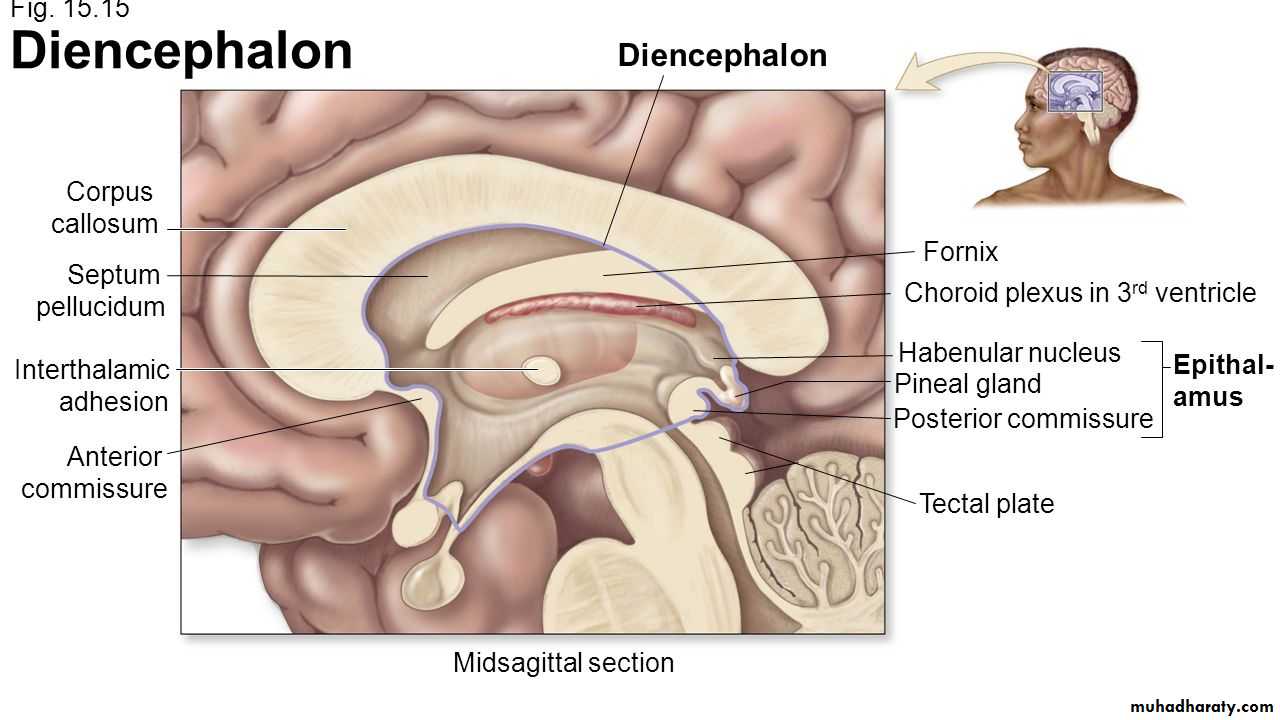
• 2. Medial surface:
• 1. Corpus callosum
• 2. The medial frontal gyrus
• 3. Cingulate sulcus & Cingulate gyrus
• 4. parieto-occipital sulcus
• Paracentral
• lobule
• Precuneus
• Cuneus
• Lingual
• 5. Calcrine sulcus
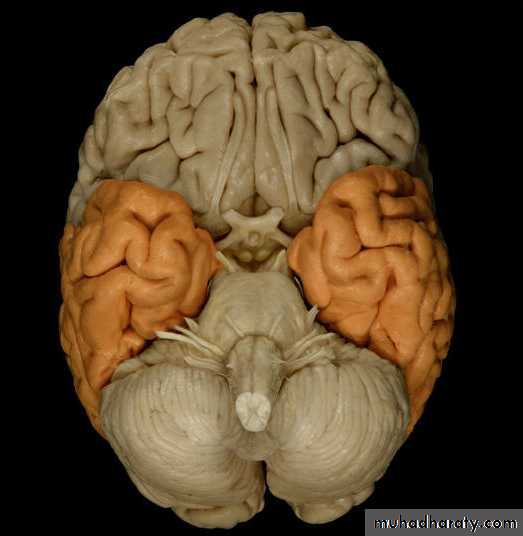
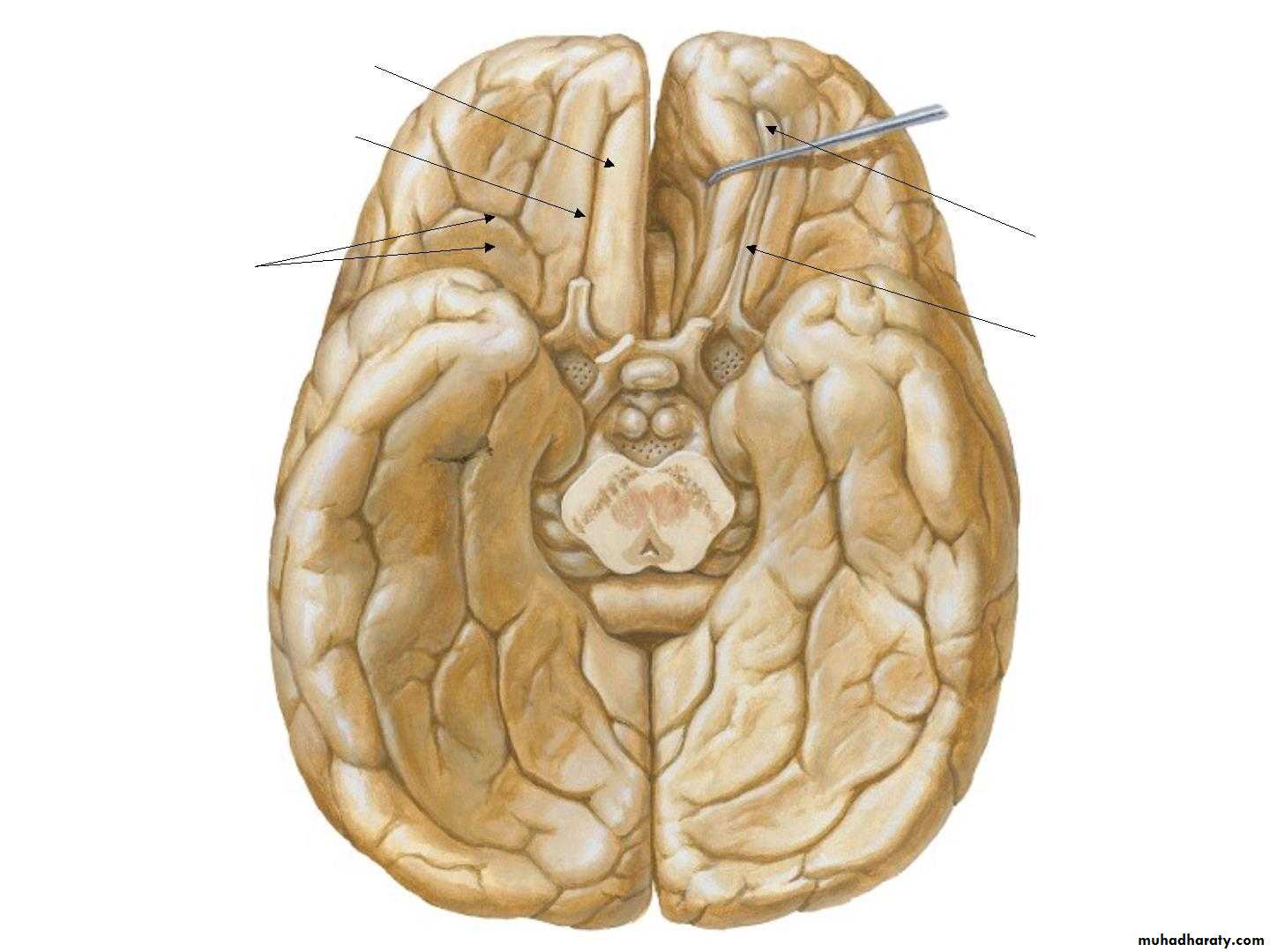
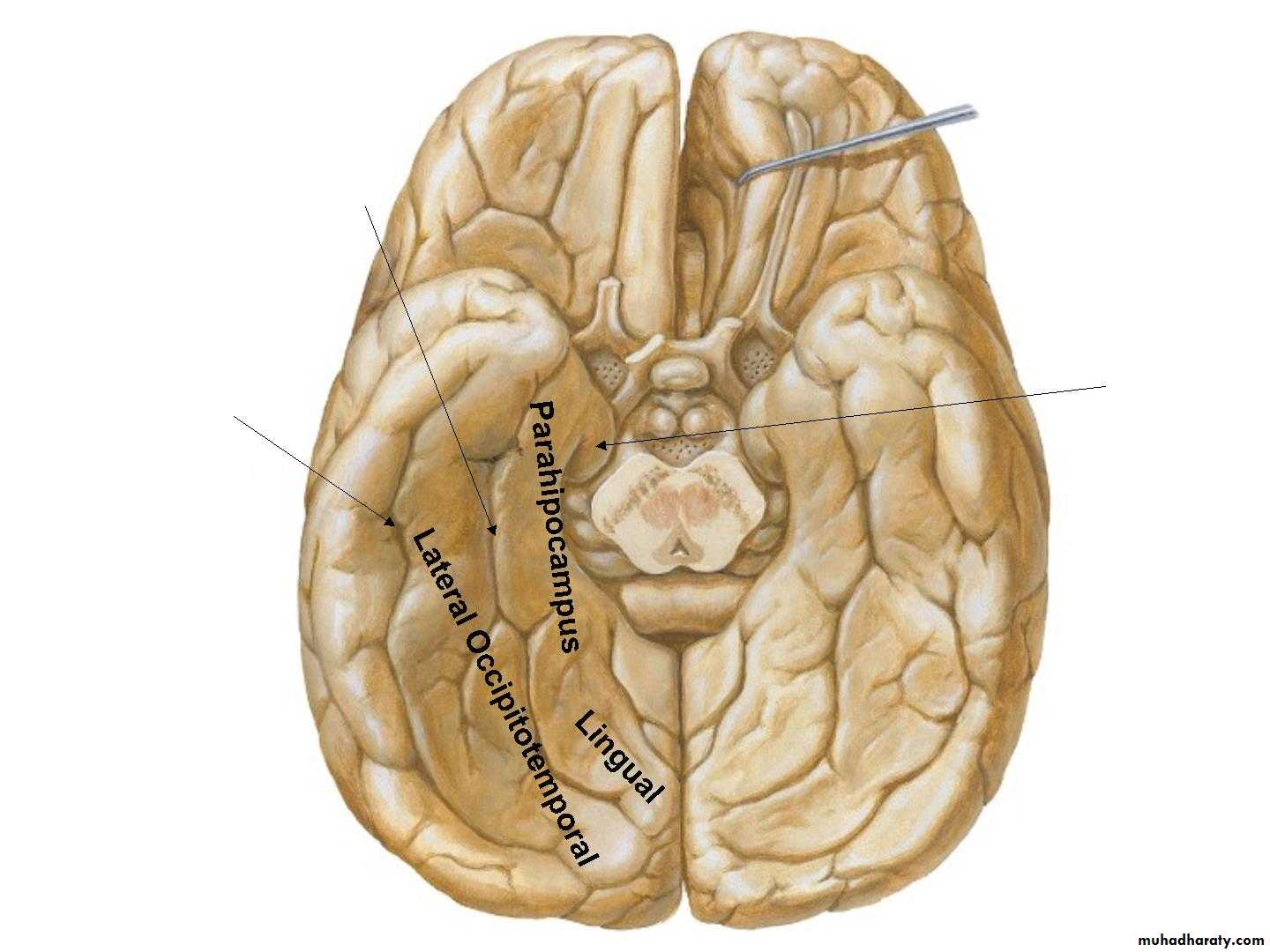
• 3. Inferior surface
• Gyrus rectus
• Olfactory sulcus• Olfactory
• bulb
• Olfactory
• tract ,
• Orbital gyri
• & Sulci
• Collateral sulcus
• Uncus• Occipitotemporal
• sulcus
• INTERNAL FEATURES
• White Matter of the
• Cerebral Hemispheres• •
• •• The white matter is composed of myelinated
• nerve fibers supported by neuroglia.
• The nerve fibers may be classified into three
• groups according to their connections:
• (1) Commissural fibers,
• (2) Association fibers,
• (3) Projection fibers.
• 1. Commissure Fibers:
• •• connect corresponding regions of the two
• hemispheres.
• •
• They are as follows:
• Corpus callosum,
• Anterior commissure,
• Posterior commissure,
• Fornix,
• Habenular commissure.
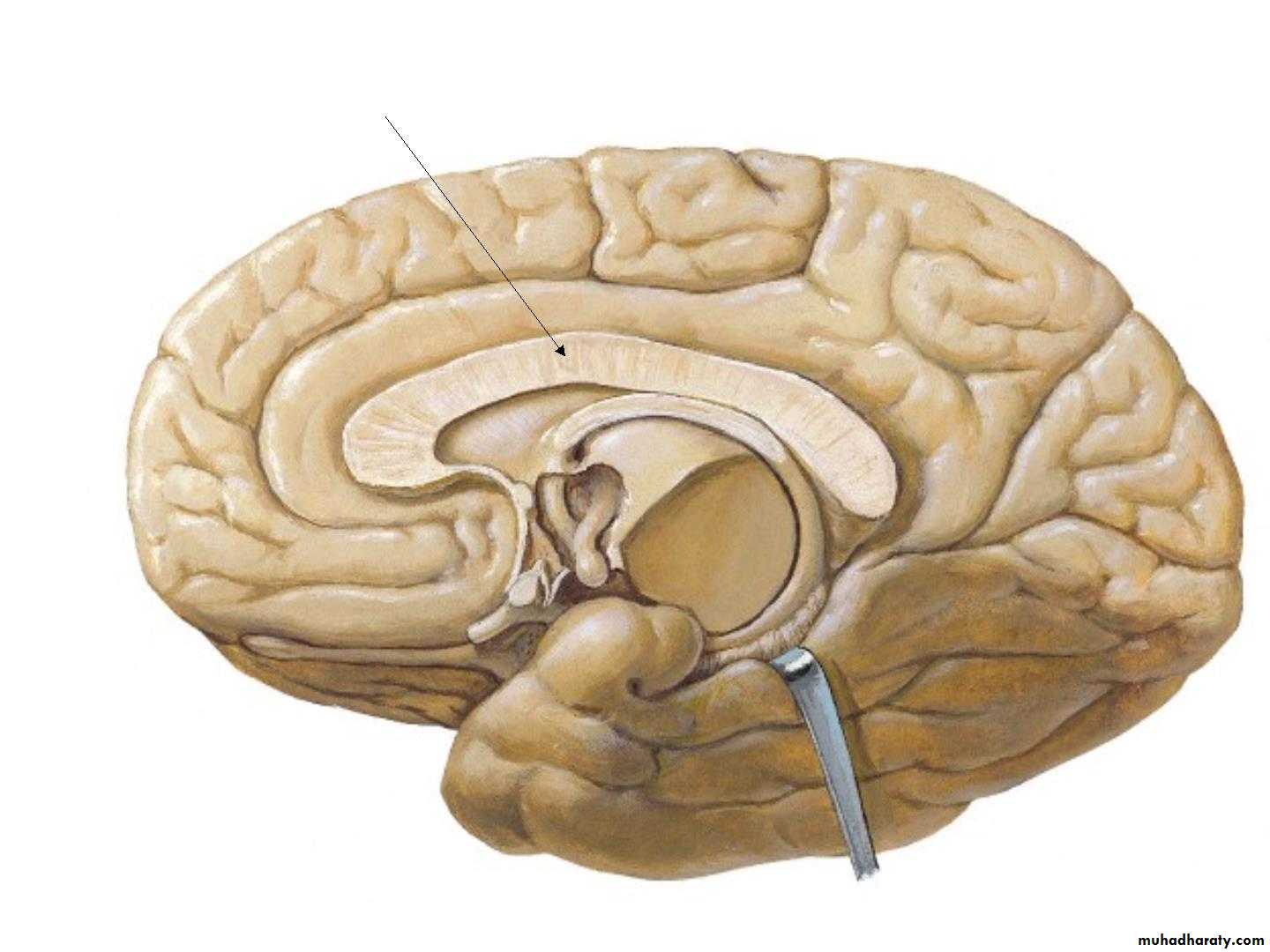
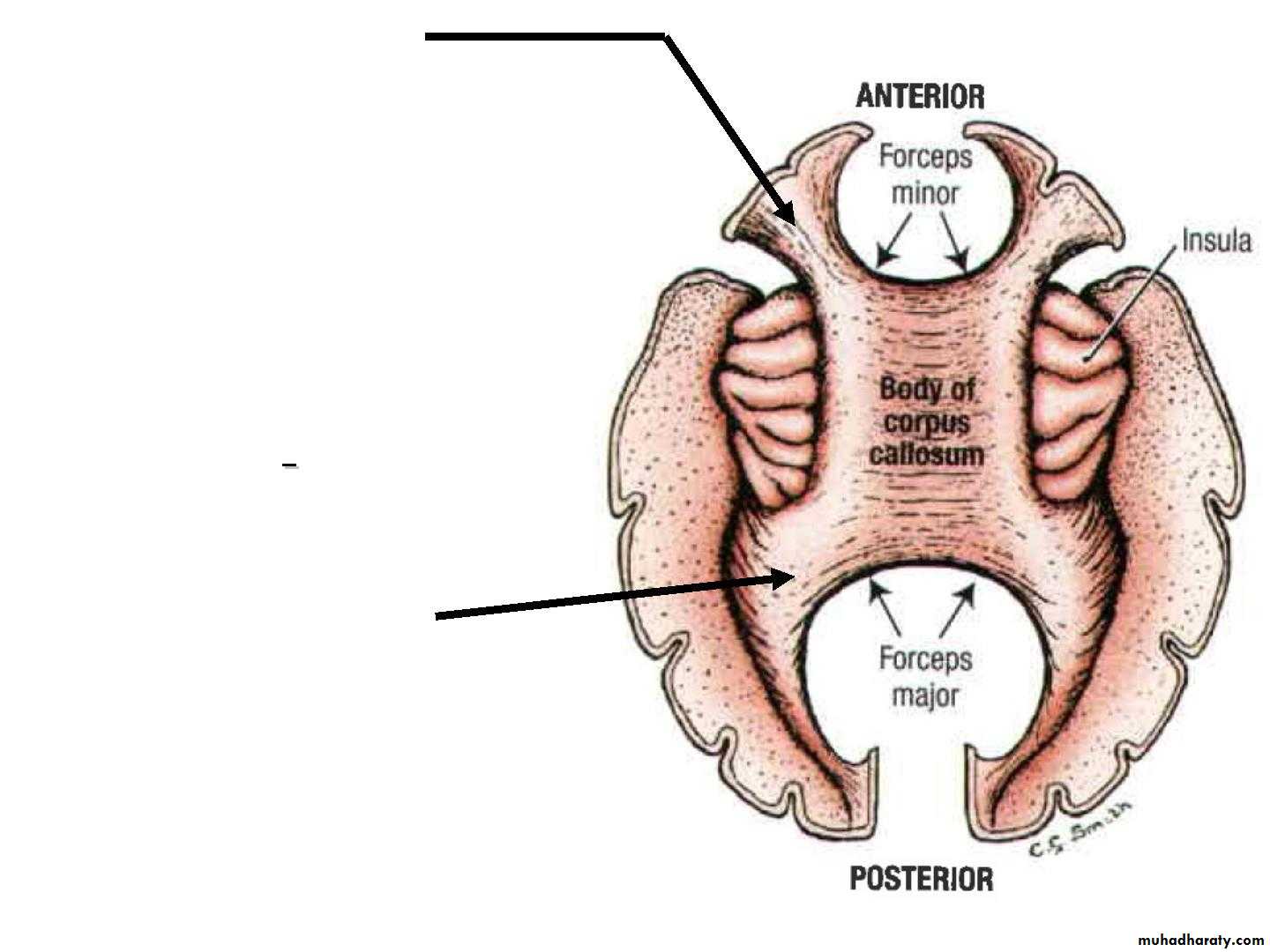
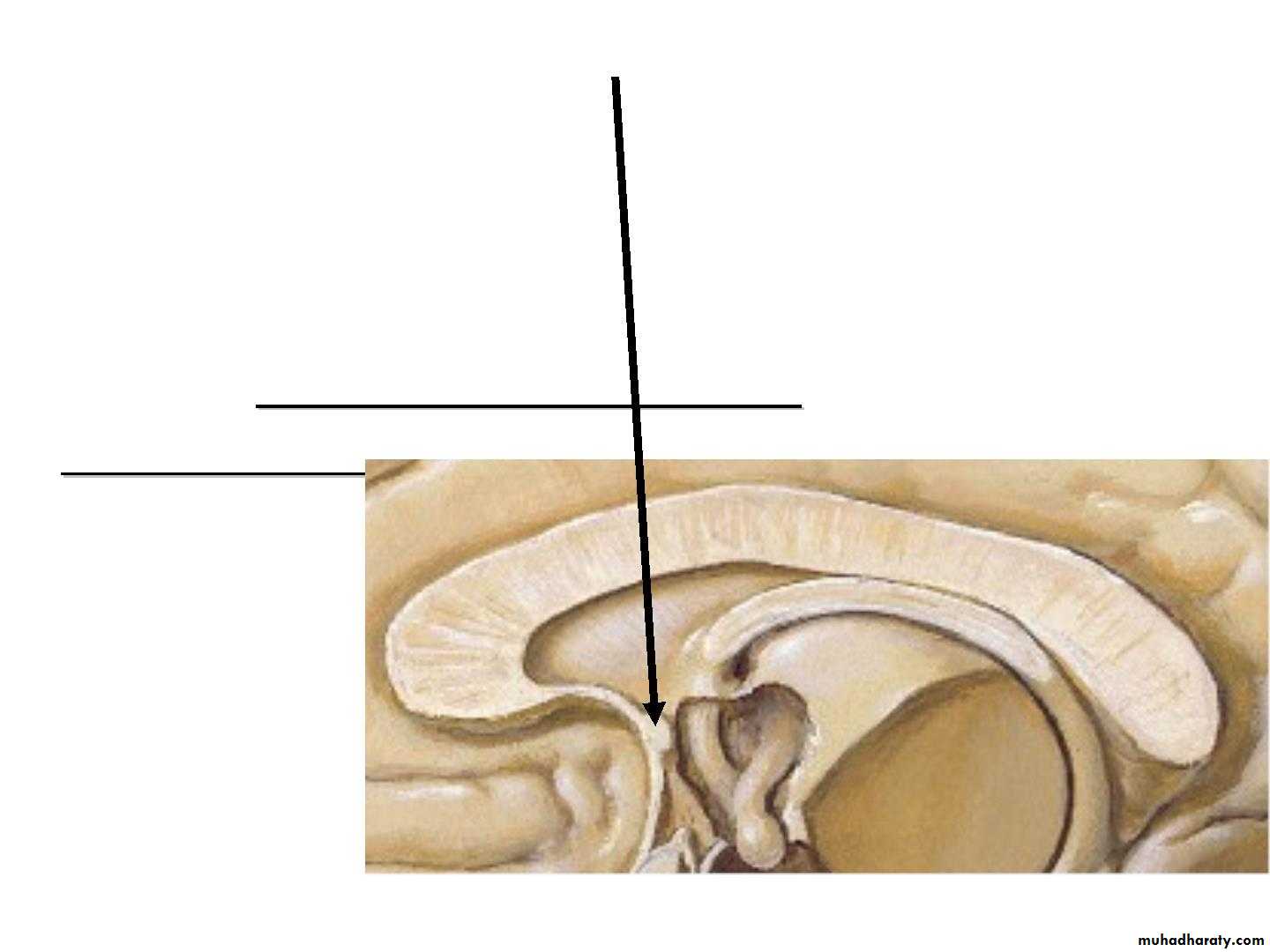
• A. Corpus callosum:
• •• the largest commissure of
• the brain,
• • connects the two cerebral
• hemispheres.
• •
• It lies at the bottom of the
• longitudinal fissure.
• • it is divided into :
• 1. Rostrum :
is a thin part of anterior end of corpus callosum which is prolonged posteriorly to be continuous with upper
end of the lamina terminalis.
• 2. Genu :
is the curved anterior end of the corpus callosum that bends inferiorly in front of the septum pellucidum.• 3. Body :
• Arches posteriorly and ends as
4. splenium
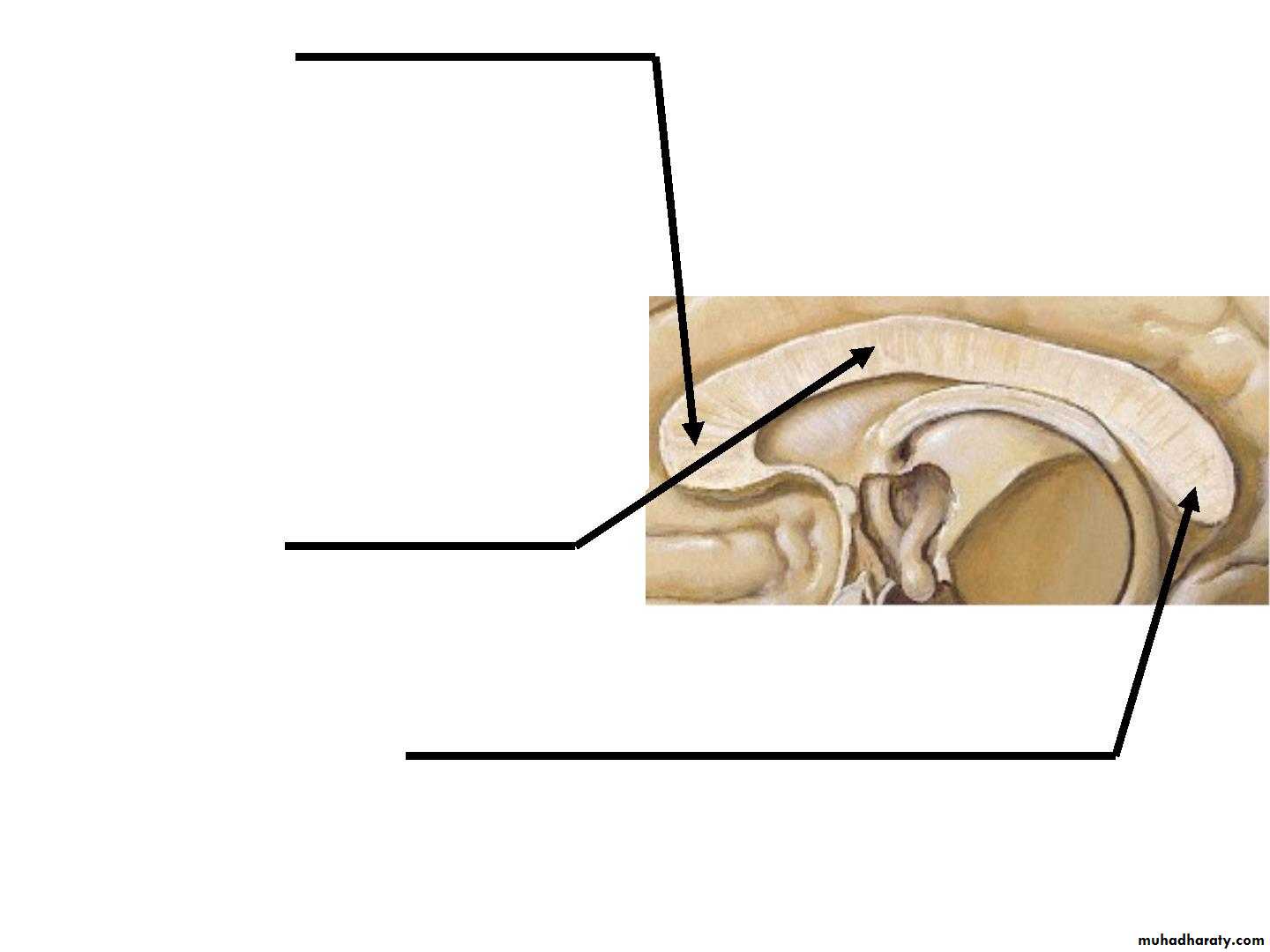
• • Forceps minor :
the fibers directed• laterally of the genu curve
• forward into the frontal
• lobes
• • Radiation of Corpus
• Callosum
• The fibers of the body
• extend laterally.
• • Forceps major :
Traced laterally, the fibers in the splenium arch backward
• into the occipital lobe
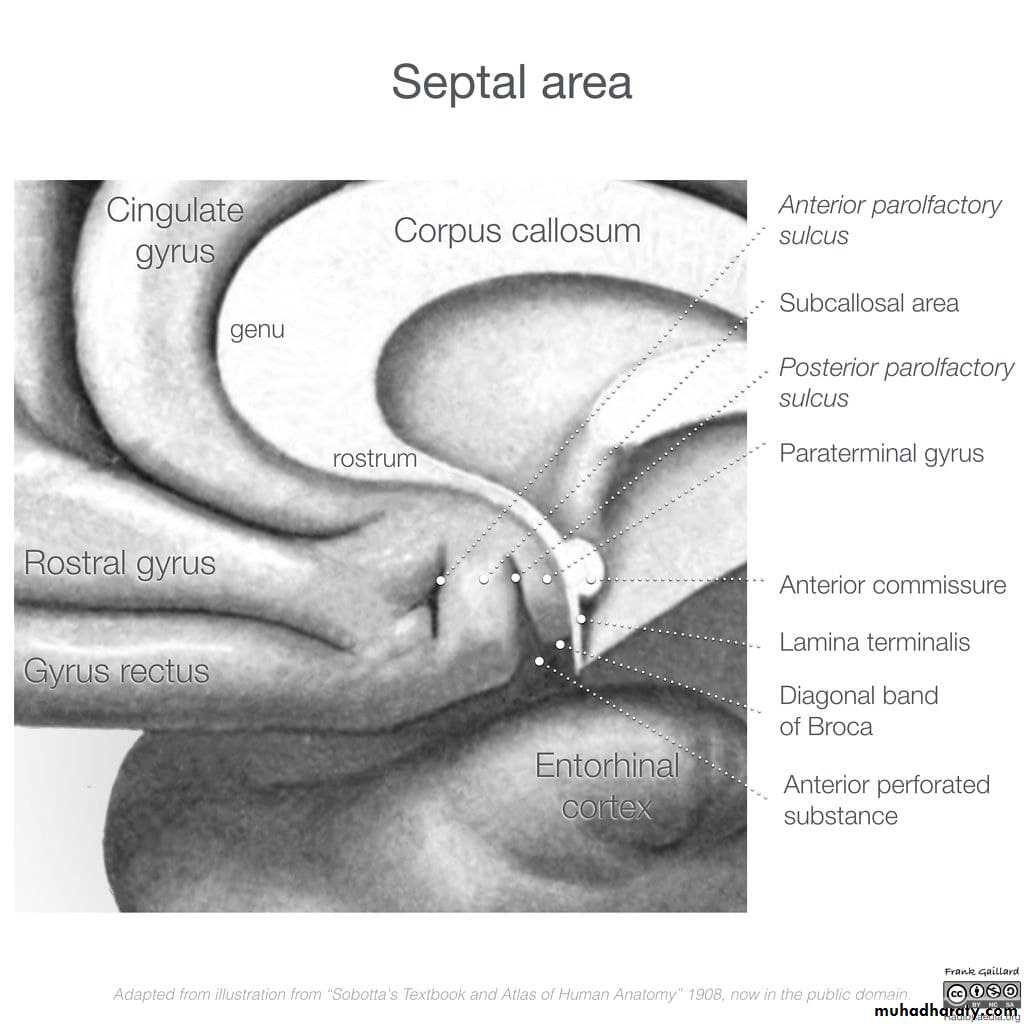
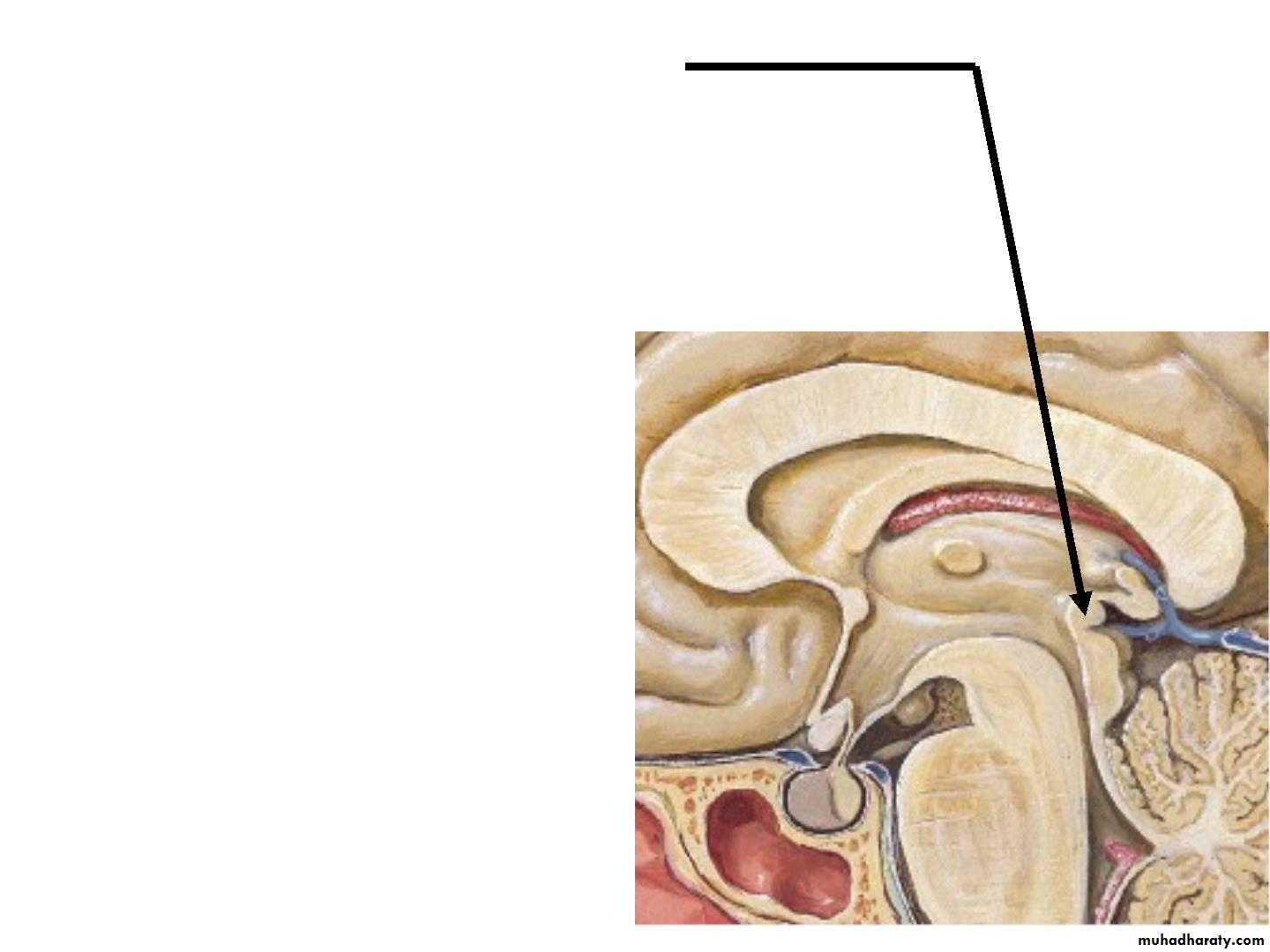
• B. The anterior commissure :
• is a small bundle of nerve fibers that crosses the midline in the lamina terminalis.• C.Posterior Commissure :
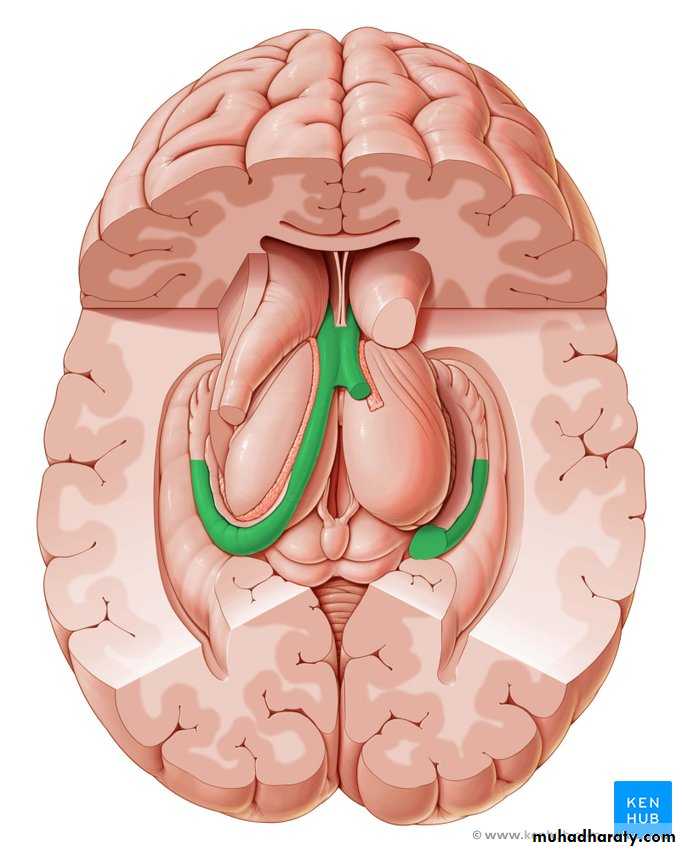
Is a bundle of nerve fibers that crosses the midline immediately above the opening of the cerebral aqueduct into the third ventricle.• Fornix
• 2. Association Fibers :
• • Association fibers are nerve fibers that• essentially connect various cortical regions
• within the same hemisphere and may be
• divided into :
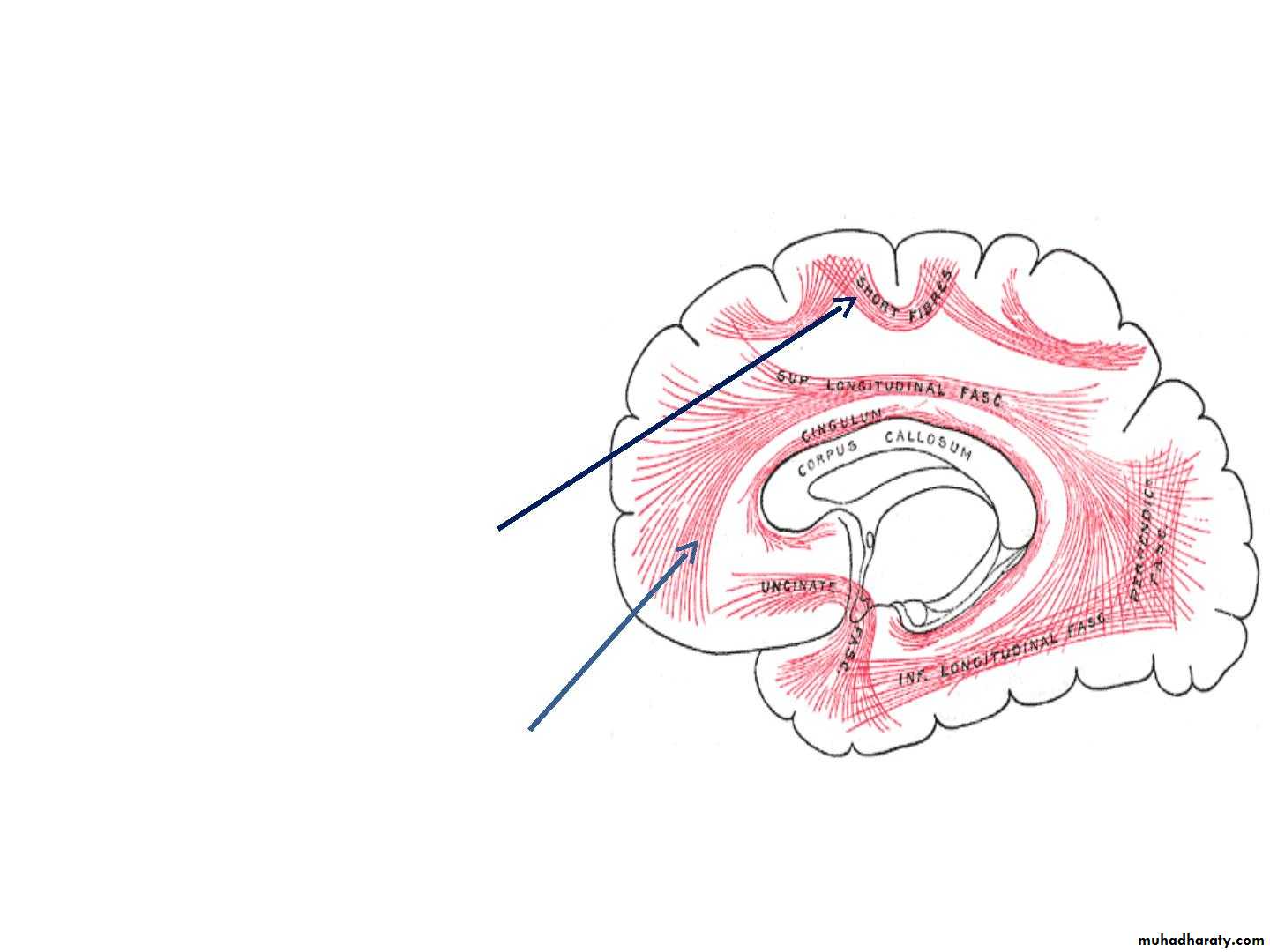
• A. The shorT associaTion fibers
• B. The long associaTion fibers :
• White matter of cerebrum
• Consists of myelinated nerve• fibres which are categorized
• on the basis of their course
• and connections
• B. Association fibres
• • It links different cortical areas
• of the same hemisphere
• • Two types
• v. Short association fibres
• They are entirely intracotical
• Some merely pass from one
• wall of the sulcus to other.
• viii.Long association fibres
• They are present in bundles
• Example: uncinate
• fasciculus,cingulum,superior
• longitudinal fasciculus,etc
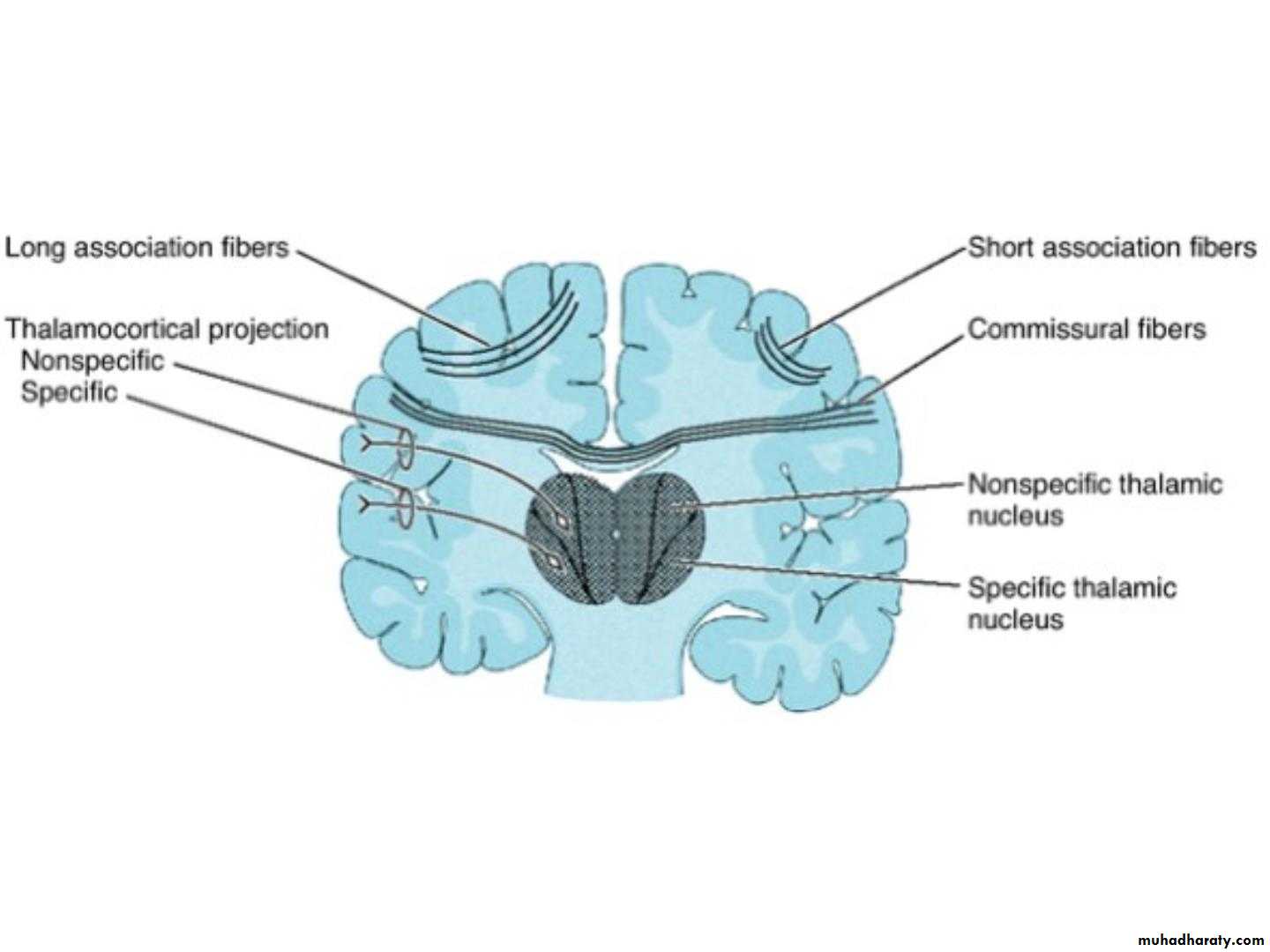
• C. Projection fibres
• • Projection fibres connect• cerebral cortex with lower
• levels in the brain and
• spinal cord.
• • Consists of both
• coticofugal and
• corticopetal fibres
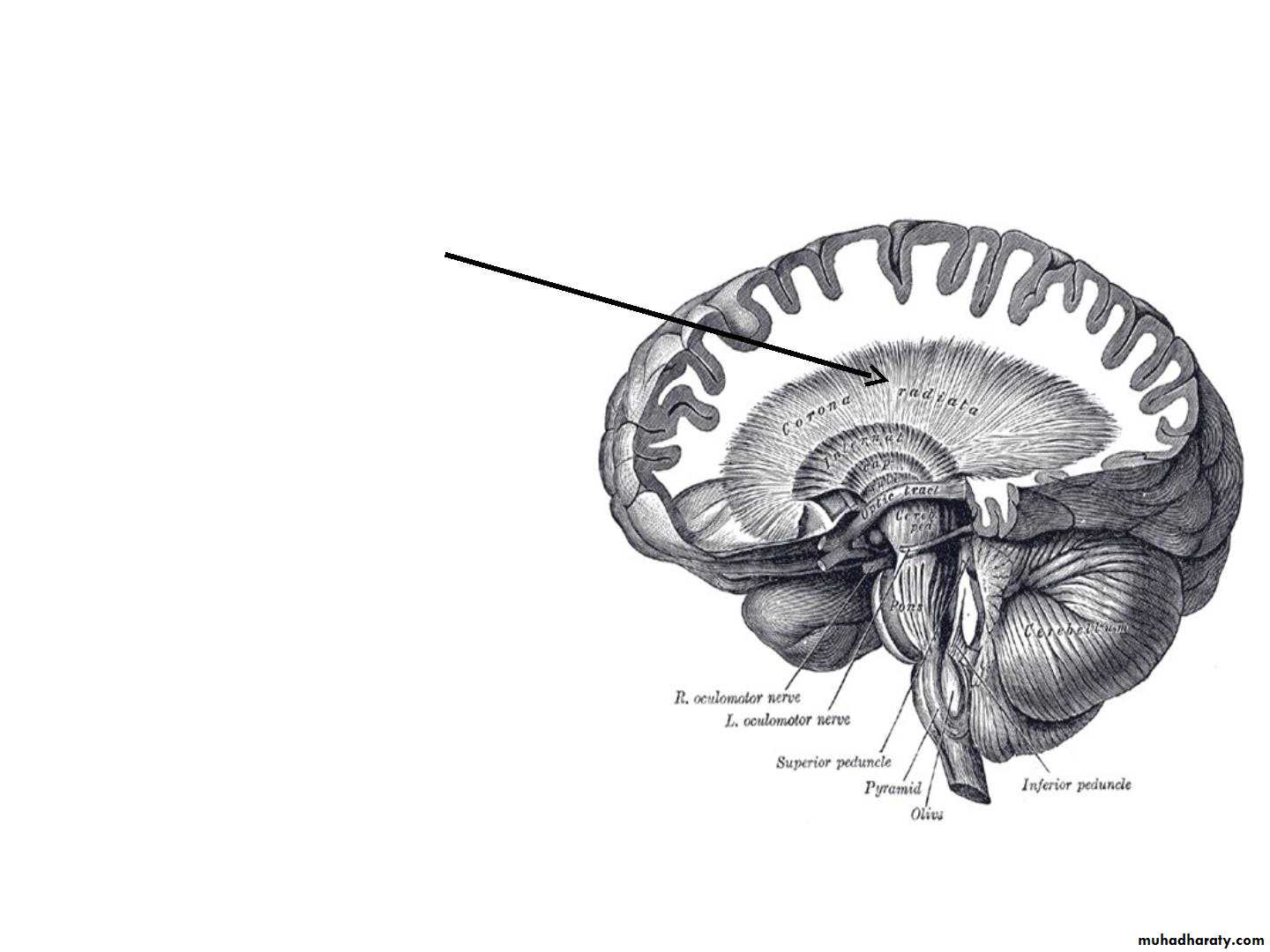
• • Corticofugal fibres
• converge from all
• directions to form corona
• radiata.Corona radiata
• continous with the
• internal capsule.
It is a thick lamina of white matter made up of projection
fibers which pass to and from the cerebral cortex.It is continuous superiorly with the corona radiata, and
inferiorly with pedunculi of midbrain.
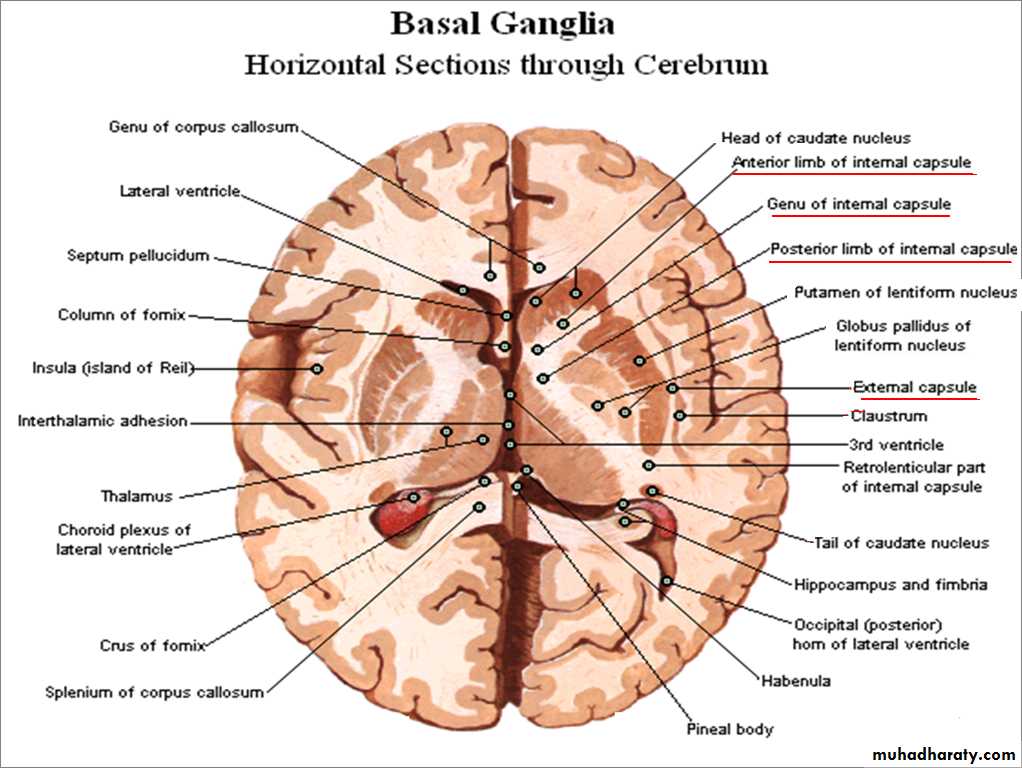
Parts of Internal Capsule:
Anterior limb.
Genu.
Posterior limb.
Internal Capsule